Every year, more and more people suffer from allergies, regardless of age, including newborn babies. One of the most unpleasant manifestations includes allergic rashes behind the ears and on the ears themselves.
Any allergy is a response of the human immune system to the introduction of a foreign protein. This disease is quite serious and it is simply impossible to completely cure it with the help of ordinary ointments and lotions. To do this, it is necessary to identify the essence of the problem and conduct a series of diagnostic examinations.
In addition, allergic symptoms can cause discomfort for a small child who is not able to cope with the unbearable itching on his own, so he begins to be capricious and show restlessness. That is why allergies require a serious approach, similar to other diseases.
Factors provocateurs
Provocateurs of allergic reactions in the ears are most often chemicals and medications used in everyday life.
These include:
- antibiotics;
- bleaching agents;
- cosmetics for face and body care;
- powders containing phosphates;
- detergents;
- benzocaine and benzophenones;
- substances containing a sulfonamide group;
- para-aminobenzoic acid esters, etc.
Important! The use of almost any inexpensive household chemical can lead to an allergic rash on the ears.
Causes of the disease
Eczema is a dermatological disease, and its development is based on dysfunction of the nervous system.
In addition, the causes of a rash on the ears of a child may be hidden in disorders of the endocrine glands, increased sensitivity of the body to the effects of various irritants and genetic abnormalities.
Most often, ear allergies develop in those children who have a tendency to exudative-catarrhal diathesis.
The following reasons can cause redness behind the ear:
- Diseases of the endocrine system. Most often, a rash on the ears appears as a result of disruption of the normal functioning of the gonads, adrenal glands and pituitary gland. In addition, hypothyroidism and diabetes mellitus, which often cause malfunctions of the immune system, can be provoking factors.
- The impact of external factors on the auricle. Ear dermatitis can be caused by constant mechanical friction, severe hypothermia, and skin interaction with chemicals and cosmetics.
- Decrease in the body's defenses. Often, ear rashes in children and adults develop as a result of disruptions in the functioning of the immune system due to insufficient intake of vitamins and chronic stress. Ear dermatitis can appear when taking cytotoxic drugs for too long, undergoing radiation treatment and cancer.
- The presence of foci of chronic infection in the body. Untreated carious teeth, otitis media and tonsillitis can serve as a source of pathogenic microorganisms. Pathogens can enter the skin of the auricle by contact or lymphogenous route, which causes dermatitis.
Often, allergies behind the ears are diagnosed in young children, and among the main causes are exudative diathesis, tuberculosis and rickets. In addition, the development of pathology is possible due to various physical damage to the skin and the penetration of infectious agents into the resulting wounds.
“Sudocrem”
The drug has a complex composition. The main functioning element is zinc oxide. The cream softens the skin, relieves irritation, dries and anesthetizes the affected areas of the skin. The medicine helps restore the dermis, disinfects, protects against pathogenic microorganisms and fungi.
The cream is gently rubbed in until a thin film remains on the skin. It is allowed to be used up to 3-5 times a day. Contraindications for use are considered to be personal intolerance to the ingredients of Sudocrem and purulent skin infections. In case of personal intolerance, irritation, a slight rash and redness of the skin are possible.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with the Cause of a small rash on the shoulders of an adult
Stages of the disease
There are the following stages of ear allergies in adults, which are accompanied by the appearance of certain symptoms:
- Crust stage. This stage of the disease is characterized by drying of the resulting secretion and the formation of yellow crusts. If timely effective therapy is not carried out, the person’s condition worsens significantly, the epidermis is destroyed, the auricle itches and the likelihood of infection spreading is high.
- Wet stage. This stage is characterized as a period of exacerbation and the opening of previously formed blisters occurs. A pathogenic fluid is released from them, which causes severe irritation and wetness of the skin behind the ears.
- The appearance of rashes. Blisters appear on the patient's skin, inside of which fluid accumulates. With this pathological condition, the ears are very itchy, but this should not be done.
- Erythematous condition. This stage of the disease is characterized by slight redness of the skin and its thickening.
It is important to diagnose ear dermatitis as early as possible and begin treatment. This is due to the fact that ear allergies can become chronic. In this case, characteristic symptoms occur in the patient with some frequency, and relapses are replaced by short remissions.
Dermatitis in the ear area in an adult
Causes of the disease
There are a number of reasons that can cause the body to react to the ears.
The most common of them are:
- animal fur: dogs, cats, rabbits and others;
- pollen of flowering plants;
- ticks and other insects;
- cigarette smoke;
- mold spores;
- hypothermia or, conversely, prolonged exposure to the sun;
- allergies to certain foods;
- bacteria and fungi;
- house dust;
- weakened immune system;
- stressful situations and much more.
Among other things, ear allergies can be caused by damage to the body by microbes and parasites in the intestines, as well as by uncontrolled use of various medications.
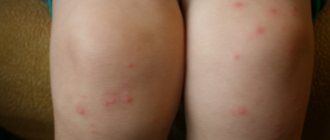
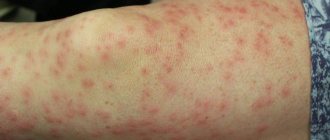
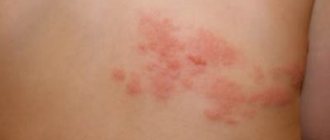
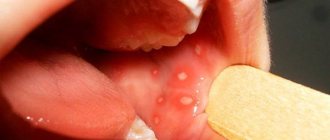
Characteristic forms of rash behind the ears
- A very itchy, profuse rash of small red spots may indicate lupus erythematosus and sexually transmitted diseases.
- A rash that is very painful when touched indicates damage to the body by amyloidosis, sarcoidosis, or severe viral infections.
- A colorless or translucent rash is a sign of keratosis; a whitish rash is observed with lichen and vitiligo.
- Watery, weeping rashes are characteristic of dermatitis, streptococcal and parasitic infections.
- Dense pimples and acne are observed during puberty, hormonal imbalance, and abuse of fatty foods.
- Small pink pimples in children indicate heat rash.
- A pustular rash can be the result of microbes getting under the skin.
Seborrhea is often the cause of a rash behind the ears in adults.
If a rash is detected on the ears, you must first consult a dermatologist who will make a diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. If metabolic disorders in the body are recognized as the cause of the rash, it is necessary to change the diet, introduce foods rich in protein into the diet, and eliminate sweets, salty foods and fatty foods. To determine the microorganism that caused the skin inflammation and the spread of the rash, swabs are taken from the earlobes.
After determining the origin of the pathogenic flora, a course of antimicrobial or antifungal therapy is prescribed. Autoimmune diseases are treated with hormones and immunosuppressants. Physiotherapy is used successfully in the treatment of rashes behind the ears of various etiologies.
Rash on ears itches
The rash that appears on the ears often itches. Typically, itching is observed with allergic rashes, poor hygiene and some infectious pathologies. However, in some cases, the cause of the rash lies deeper - in problems with internal organs. Thus, itchy rashes on the ears and neck may indicate a lack of oxygen due to pathology of the respiratory organs, in particular the lungs. Therefore, a rash on the ears, especially if it itches, is a reason to consult a specialist.
Poor hygiene can also cause itching and rashes on the ears and other parts of the body. In addition to regular washing, bedding should be changed periodically. If this is done too rarely, pathogenic microorganisms begin to actively multiply in the folds of the laundry. They, in turn, can cause the formation of rash elements.
In addition to reasons such as infections and allergies, a rash on the ears of a child in the first month of life may be associated with hormonal changes in his body after birth. Such rashes appear on the skin of the face, neck, and can also occur on the ears. This rash does not pose any danger and does not require special treatment. Attention should only be paid to maintaining hygiene and preventing secondary infection.
A rash on the ears and other parts of the body later in life indicates the presence of diseases or other problems in the child’s body. Therefore, when it appears, you should immediately call a doctor.
In adults, ear rashes appear for the same reasons as in children. In most cases, rashes are associated with an individual reaction to some factor, hygiene errors and allergies. A rash on the ears may appear in response to eating certain foods, wearing jewelry, or using cosmetics and detergents. In this case, firstly, you need to establish what exactly caused the reaction and remove this factor.
In addition to allergies, a rash on the ears in an adult can occur due to various diseases, such as measles, dermatitis, eczema and others. Only a qualified doctor can determine the correct diagnosis.
Symptoms
The main symptom indicating an allergic reaction to the ears is otitis media, which may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- allergic rhinitis - rhinitis;
- effusion in the middle ear - accumulation of fluid;
- rashes and the ears themselves are swollen;
- swelling of the mucous membrane in the area of the tympanic cavity;
- weeping eczema in the area of the external auditory canal;
- leakage of fluid from the external auditory canal.
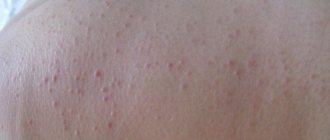
Photo: Redness of the ears
In addition to the above symptoms, the patient during the onset or exacerbation of allergies may be accompanied by:
- insomnia or, conversely, excessive sleepiness;
- sweating;
- irritability;
- weakness;
- decreased performance and inability to concentrate.
In advanced cases, mucus and pus begin to secrete from the external auditory canal.
Itchy
During an exacerbation of allergies, the patient may experience itching of the ears. With allergies, the ears itch, and at the same time painful sensations may occur.
Itching in the ears can occur periodically or continue constantly, leading the patient to nervous stress.
Photo: Dry ear
Lays
In addition, the patient may experience hearing problems. According to people who have experienced this disease, many of them had an unpleasant feeling as if their ears were blocked.
The sensation is especially acute when there is a sudden change in pressure.
Swelling
Upon examination, swelling inside the ear can be diagnosed, which is asymptomatic.
Otitis
Allergies aggravated by otitis media, in case of infection, are accompanied by acute shooting pains. However, most often allergic otitis media is asymptomatic.
Allergic otitis media can be either middle or external. It is most often caused by either food allergies or bacteria.
With late diagnosis and treatment, the patient may be at risk of complete or partial hearing loss.
In addition, autophony may occur when the patient hears his own voice too loudly.
Itching behind the ears: popular causes
13.06.2018
If you have been itching behind your ears for a long time, it is not recommended to ignore this condition. It may indicate the development of serious pathologies that require immediate treatment.
To avoid the development of complications, if itching occurs in this area, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Symptom manifestation
When it just itches behind the ear, a person may not pay attention to it if there is no severe itching. Typically, concern arises if the condition causes discomfort for a long time and other signs of developing pathology appear.
Typically discomfort is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- swelling of the soft tissues near the auricle;
- peeling of the epidermis;
- spread of itching to other areas of the skin;
- the appearance of rashes, after which a crust may remain on the epidermis;
- headache;
- general deterioration of health;
- increase in body temperature;
- tearfulness;
- rhinitis.
The epidermis behind the ears can itch in both adults and children. Most often, this condition occurs in women and children.
In women, this is usually associated with the regular use of cosmetology products and household chemicals that cause allergies and irritation.
Itchy skin behind a child's ear most often indicates irritation. Any such condition that does not go away for a long time is a reason to visit a doctor.
Probable diseases
Itching behind the ears is a symptom of some diseases. To determine exactly why this condition occurs, it is recommended that you make an appointment with your doctor.
The causes of itching behind the ears in adults coincide with the causes of this condition in children. It may be a symptom of the following pathologies:
- Allergic reaction. This condition usually occurs due to an allergy to hair detergents or styling products, jewelry, or dust;
- Otitis externa is a pathology of the ears caused by inflammation. This disease can also cause discomfort;
- Seborrheic dermatitis is an inflammatory disease of the epidermis. The main symptoms are itchy ears and head, itching is accompanied by flaking, dandruff appears;
- Psoriasis is a skin disease that causes rashes. During an exacerbation, the rash is accompanied by itching and peeling. The rash is localized throughout the body, and also appears in the area behind the ears and on the scalp;
- Atopic dermatitis is a disease of the epidermis in which red spots appear on the back of the head, which can become wet and itchy. The rash spreads throughout the body;
- Fungus. If this is the cause of the itching, then the ears themselves will also itch.
Independently determining the cause that led to this condition is not always accurate. For a more reliable diagnosis, it is recommended to consult a professional. You can find out about the causes of itchy ears in a child in this article.
Treatment options
Treatment of itching behind the ears is carried out based on the cause of this condition. If the discomfort is caused by an allergy, the patient is prescribed antihistamines for oral and external use.
When itching behind the ears occurs due to a fungus, the doctor prescribes antifungal drugs to the patient.
If the area behind the ears not only itches, but also gets wet, a specialist will also tell you how to treat it. In this case, complex therapy is prescribed. The treatment system includes:
- following a diet that is based on avoiding eating sweet, spicy, salty and starchy foods;
- taking antihistamines;
- ointments, gels and creams with anti-inflammatory properties;
- drying agents;
- the use of multivitamin complexes to increase the body's defenses.
For weeping rashes behind the ears that cause itching, water procedures are prohibited. You are not allowed to visit the swimming pool, sauna or bathhouse, or take a bath. Showering is allowed, but in such a way as to avoid getting water on the rash.
Traditional medicine will help speed up the healing process. For internal use and external use, it is recommended to use decoctions of chamomile, nettle, horsetail and blackcurrant leaves.
If itching occurs behind the ears, it is recommended to consult a doctor if this condition persists for several days. This will help to diagnose the pathology in a timely manner and begin therapy, which will reduce the risk of complications.
Itching behind the ears: popular causes Link to main publication
Source: //syponline.ru/cheshetsya-za-ushami
Mechanism of development of allergic otitis
Otitis media occurs in dogs most often due to allergic reactions in the ear. External agents, allergens, enter the body and quickly spread; the body secretes lymphocytes to fight them.
Symptoms of otitis media appear when the body uses histamines to help, which in turn improves vascular permeability. As a result of these processes, plaques and nodes appear in the area of the outer ear. Inflammation with otitis media in dogs most often occurs on both ears at the same time.
Typically, allergic agents cause itching in the ear area of dogs. The pet scratches the area of irritation until there are open wounds, other pathogens get there and other infections are added to otitis media of allergic etiology.
Causes of the rash
There are diseases when a rash may appear on the skin or mucous membranes:
• infectious diseases;
• allergic;
• vascular and blood diseases.
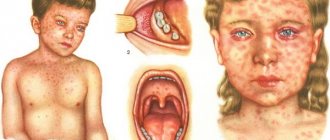
Most often, a rash appears during infectious diseases (measles, rubella, chickenpox, scarlet fever, herpes, infectious mononucleosis, erythema infectiosum, etc.). In addition to skin reactions, there are also other symptoms: fever, lack of appetite, chills, sore throat, headache, runny nose, cough or diarrhea.
Ear allergies in a child
In infants, breast milk can trigger an allergic reaction behind the ears. It's all about the allergens it contains.
The blame for this lies primarily with the mother, who, despite feeding, eats foods that contain allergens. The same applies to complementary foods.
The causes of allergic reactions in older children are not much different from the causes in adults.
Photo: Manifestation of diathesis
Prevention
To prevent cracks behind the ears in a child and the possible consequences of this symptom, follow these rules:
- pay attention to any allergic manifestations after your child consumes a new product;
- walk in hot weather for no more than 1 hour in the shade;
- carry out timely wet cleaning of the room and ventilation;
- strengthen the child's immune system;
- carry out careful hygiene in the area behind the ears;
- select anti-allergenic detergents and hygiene products;
- moisturize the skin with special baby creams;
- carry out timely treatment of the parotid area in the presence of scratches, cuts and other microtraumas;
- During pregnancy and lactation, monitor your diet and do not overuse allergenic foods.
Allergic reactions and various skin dermatitis are not uncommon in childhood, so you need to carefully monitor your baby's skin. If you know that your child is predisposed to allergies, then try to take all preventive measures to avoid dangerous complications.
Diagnostic methods
Seborrhea in the ears is accompanied by the appearance of pronounced symptoms, so diagnosing it is not difficult.
If the first signs of the disease occur, you should consult an otolaryngologist or dermatovenerologist, who will examine the patient. The diagnosis is made based on medical history, patient complaints and a specific clinical picture.
Particular attention is paid to the presence of endocrine diseases, the state of the immune system, working conditions and a tendency to allergic rashes.
Diagnosis of eczema on the ears includes the following examination methods:
- visual inspection;
- dermatoscopy;
- otoscopy.
In addition, allergy tests are carried out to determine substances to which a person is hypersensitive. If it is not possible to differentiate eczematous dermatitis from other pathologies of the epidermis, a skin biopsy is performed.
Diagnostics
In addition, it is much more difficult for an adult to identify the allergen to which such a reaction occurred. Most often, to determine the allergen, it is necessary to undergo a special provocative test using skin tests, smears, and a blood test. Recovery is possible only after contact with the allergen has been identified and excluded.
Otherwise, the patient is at risk of the allergy becoming chronic, which, in turn, is fraught with other, much more serious problems.
To identify hearing impairment, it is necessary to conduct a series of studies, based on the results of which doctors prescribe treatment for complications that arise.
Treatment
After all the research, the doctor prescribes medication for ear allergies.
Swabs from the auricle make it possible to determine the flora located there, as well as to choose the most appropriate antibiotic for the patient to combat pathogenic bacteria.
Using this method, fungal infections of the skin inside the ear are also detected.
In no case should treatment of an allergic reaction inside the ear be delayed, as this will most likely lead to the spread of inflammation and infection to other areas, which is fraught with much more serious consequences.
Read how to prevent allergies to seeds. Can a child be allergic to cheese? How to identify it and how to treat it? Read here.
In addition to the antibiotic, the patient must be prescribed an antihistamine, this could be: diazolin, suprastin, fenkarol, lorano and others.
To boost immunity, immunomodulators are prescribed. In addition, you can take vitamin complexes. Rashes on the auricle and behind the ear are treated with special ointments and solutions.
The doctor may also decide to prescribe sedatives to normalize sleep, relieve stress, and make it easier to bear the itching that occurs.
At the same time, doctors may recommend a special diet, which not only excludes the consumption of allergy-causing foods, but also introduces a number of restrictions, for example, on:
- alcoholic drinks;
- tea and coffee;
- spices;
- smoked meats;
- dairy products.
In advanced stages of the disease, the patient may require surgical intervention. So, in particular, if the effusion in the middle ear does not go away within several months, the doctor may prescribe an operation to pump out the fluid.
Otherwise, the patient may:
- the eardrum atrophies;
- facial paralysis occurs;
- develop a tumor formation - cholesteatoma;
- retention cysts may form, which can also be called tumor formations.
Ear drops
For local treatment of otitis, ear drops are prescribed, which not only prevent the development of infection, but also relieve swelling.
Associated symptoms
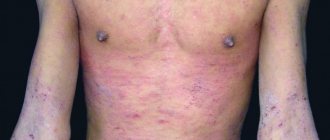
A rash behind the ear can be the result of many causes. Although different infections that cause it may present with different symptoms, there are some similar ones:
- Itchy bumps
- Bumpy rash
- Swollen lymph node behind the ear
- Headache
- Redness
- Peeling of the skin.
In many cases, the symptoms listed above go away on their own without treatment. If you do not experience relief from using any medications within one week, you should definitely consult a dermatologist to determine the cause of the problem.
Description of the disease
Scrofula is a common popular name for a childhood disease similar to the manifestations of diathesis. It affects children of preschool and primary school age; it practically never occurs in adults.
The disease received this name due to the similarity of the crusts behind the ears (the main symptom of the skin disease) with gold. The crusts are pale yellow. It can be assumed that scrofula is the ancient name for allergic dermatitis.
Interesting fact: in the old days it was believed that a king could cure scrofula by touching his hand and chanting: “The King will touch you, the Lord will heal you.” The latest data on this method of treatment date back to 1825.
Important: Scrofula is a non-infectious skin disease. The disease affects children under 10 years of age and practically never occurs in adults.
Scrofula in children behind the ears
Signs of illness
- The very first sign of scrofula is the formation of diaper rash behind the ears, as well as on the scalp. Subsequently, the redness takes on a different form: yellowish crusts
- The affected areas are very itchy. The child may repeatedly scratch the sore areas with his hand or move his head on the pillow to relieve the itching.
- The location of scrofula is behind the ears and on the head. If the disease is not treated, the rash may spread to the face
In addition to yellowish crusts and itching, the following symptoms of scrofula may be observed:
- Bloating
- Indigestion
- Discharge from the nose and ears
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck
- Joint pain and swelling
- Redness of the eyes
These can be food products, pharmaceuticals, bacteria and other elements. In this case, characteristic lesions of the mucous and skin layers, lymph nodes are observed.
Scrofula can develop in children as a continuation of exudative diathesis; scrofula in adults in this case is the result of the spread of harmful agents from other foci - for example, from the lung area.
However, most often the pathology in the younger generation develops precisely because of diathesis, and scrofula behind the ears is accompanied by the appearance of golden crusts.
At the same time, doctors find it difficult to give an exact definition in terms of what specifically provokes the development of pathology in childhood, but presumably the impetus can be given by:
- The baby's stay in unsanitary conditions, prolonged refusal to take baths.
- Conceiving children under the influence of alcoholic beverages or drugs.
- The pathology is inherited when the parents of the affected children were previously diagnosed with scrofula disease.
- Children born to an older couple are also at risk, and the parents have a history of tuberculosis, malignant neoplasms, and syphilis.
- Lack of vitamins in the child’s diet and lack of a balanced diet.
- Sweets consumed by the baby unlimitedly.
- In cases where the causative agent of the disease enters the body of a woman carrying a child, the fetus may become infected.
- Artificial feeding - medical statistics state that a high percentage of children who were diagnosed with scrofula grew up on special formulas without receiving mother's milk.
Types of disease
In dermatology, there is a classification of eczema based on the type of lesion.
During the period of illness, a person is not contagious, so his isolation from others is not required. The following types of pathology are distinguished:
- The abortive type is characterized by the formation of multiple spots, which are accompanied by itching and peeling. They can be oval or round in shape, and when severe irritation occurs, the spots begin to become wet. Often, rashes of this type appear in patients during periods of tonsillitis or respiratory diseases. In children, the abortive type of eczema is especially pronounced and is accompanied by severe itching and exudation.
- The true form of ear eczema is characterized by the formation of microvesicles on it, which quickly open and multiple erosions form in their place. The skin becomes wet behind the ears and causes severe discomfort. Gradually, some bubbles do not burst, but dry out, which causes the formation of a kind of crust and bubbles.
- The professional form is diagnosed if the organ of hearing interacts with various chemicals that negatively affect the surface of the skin. Most often, such ear allergies are observed in those people who work in industrial production.
- The microbial form occurs if the patient constantly scratches the rash on the skin and thereby introduces infection into the wounds. The consequence of this phenomenon is the re-development of a chronic inflammatory process. It is for this reason that if the ears are peeling and swollen, then it is necessary not to scratch the skin and monitor the hygiene of the ear cavity.
In childhood, the disease is most often accompanied by the appearance of signs of true and seborrheic eczema, which appear in various combinations.
Folk remedies
Along with traditional medicine, traditional methods can also be used to treat ear allergies.
Decoctions are used as an external remedy. The most effective of which is a decoction of lentil straw.
To do this, pour half a kilogram of straw with 3 liters of water and put it on the fire to boil. The broth should boil for 10 minutes. After which it is filtered and allowed to cool.
Then cotton pads soaked in the broth are applied to the affected areas of the skin on the ears and behind them. If the disease has entered deep into the ear canal, then you can make small tampons, which are also moistened in the broth, squeezed out and placed shallowly in the ear canal for half an hour.
If you are allergic to flower dust, it is recommended that after each return from the street, rinse your mouth and throat with water with the addition of a few drops of valerian or motherwort.
Allergies can be treated with calendula infusion.
To prepare it, pour 1 teaspoon of calendula flowers with 500 milliliters of boiling water, after which it is left to infuse for at least 3 hours. It is better to do this in the evening and let the infusion stand until the morning. After which the infusion is carefully filtered. You need to take 1 tablespoon 3 times a day.
It is worth noting that it is necessary to resort to traditional medicine only in combination with traditional methods of treating allergies, and not in any way replacing it.
In addition, beware of self-medication. All procedures must be prescribed by a qualified specialist based on test results and his or her experience.
Prevention
Despite the fact that the predisposition to allergies is genetic, this does not mean that fighting it is useless. Prevention of allergic reactions is as important as the treatment itself.
To prevent allergic reactions in children, the expectant mother must adhere to a diet.
The same applies to breastfeeding. The development of allergic reactions in the future is also influenced by the duration of breastfeeding.
The longer a young mother breastfeeds her baby, the less likely he is to have allergic reactions in the future.
Adults should reconsider the household chemicals in the house and switch to less dangerous substances, for example, phosphate-free powders, shampoos and other detergents.
In addition, it is necessary to get rid of cosmetics containing harmful substances: creams, shower gels, decorative cosmetics.
Lifestyle is no less important for prevention.
Find out what are the symptoms of atopic type allergies. Don’t know how to treat pimples if you are allergic to solariums? Find the answer here.
See photos of folic acid allergies here. Doctors recommend:
- adhere to a proper healthy diet;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- take care of your health;
- seek help from specialists in a timely manner.
Preventive measures not only reduce the likelihood of allergic reactions, but also help the body resist exacerbations that occur as a result of the onset of the disease.
When talking about ear allergies, you need to understand that this seemingly mild disease can lead to very serious and even irreparable consequences if you do not pay proper attention to it. At the first symptoms, be sure to contact a qualified specialist who will prescribe the necessary tests, and then treatment.
Why does it itch behind the ear?
Itching is a signal from the body that forces you to pay attention to a particular organ. It is difficult to ignore this unpleasant sensation, especially if the scalp, for example, the parotid area, is itchy. Why does it itch behind the ears? This feeling is based on irritation of nerve endings under the influence of various mediators, primarily histamine.
articles
- Possible reasons
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
Allergy sufferers are well aware of this phenomenon, since histamine plays an important role in the development of an allergic reaction. But not only allergies cause itching - it can occur as a result of infection, insect bites, contact with irritating chemicals, etc.
Itching is characterized by an irresistible desire to rub or scratch the irritated area. Scratching can damage the outer layer of skin. Damage to the skin only increases itching and leads to secondary problems, such as infection, purulent inflammation, scarring, etc.
This is why it is very important to treat itching behind the ears while the integrity of the epidermis is not compromised.
Possible reasons
Why do people itch behind their ears? The reasons for this phenomenon are very diverse. Thus, itching of the parotid area of the skin occurs under the following conditions:
- seborrheic dermatitis - inflammation of the skin associated with hyperactivity of opportunistic fungal microflora of the skin; accompanied by peeling, itching, and dandruff;
- allergic reaction to dust mites, jewelry, cosmetics (for example, if a woman itches behind her ears after dyeing her hair, the possibility of an allergy to the dye should be considered);
- psoriasis is a multifactorial disease; its main symptom is a rash covered with dense keratinized skin scales; in many cases, psoriasis primarily affects the area behind the ears and the scalp;
- with otomycosis - a fungal infection of the outer ear - itching behind the ears, in the auricles and in the ear canal is disturbing;
- with atopic dermatitis, the skin behind the ears itches, becomes wet, and turns red; At the same time, other areas of the body where the skin is thin and dry are usually affected.
It is not always easy to independently determine why your ears itch behind your ears - it all depends on the severity of the accompanying symptoms. To identify the true cause of the disease, an examination and consultation with a dermatologist will be required. In some cases, tests are necessary to clarify the diagnosis.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a fungal disease that affects areas of the skin rich in sebaceous glands. If a person suffers from itching specifically in the parotid area, the possibility of this disease should first be considered.
Seborrheic dermatitis develops as a result of an increase in the number of fungi of the genus Malassezia in the skin microflora. It is known that this disease affects people suffering from hypersecretion of the sebaceous glands (the fungus feeds on the lipids that make up the sebum).
Malassezia is considered an opportunistic fungus, meaning it is present on the skin of most healthy people. When immune defense is reduced (for example, due to hormonal imbalance, sudden climate change, treatment with antibacterial drugs, etc.), the amount of fungal microflora increases significantly.
As a result, the following violations develop:
- peeling skin behind the ears;
- dandruff;
- itching;
- oily skin and hair;
- the appearance of a rash (“irritation”) as a result of inflammation of the sebaceous glands;
- decreased skin resistance to infectious and chemical irritants.
Some symptoms are caused by the influence of fungal waste products on the skin, others by a decrease in the number of beneficial bacteria (since fungi and bacteria constantly compete for the surface of the epithelium as a habitat).
Seborrheic dermatitis primarily affects the scalp - the scalp, the upper part of the forehead and the area behind the ears. In rare cases, inflammation spreads to the groin and armpits.
The affected areas of the skin behind the ears often crack and bleed. The situation is aggravated by the patient scratching the skin (this increases the risk of secondary infection). The fungus that causes seborrheic dermatitis can also affect the ear canals, in which case otitis externa occurs.
If left untreated, seborrheic dermatitis develops into seborrheic eczema.
Diagnostics
Itching behind the ear - what could it be? It is not always possible to independently determine the exact cause of the disease.
A patient who is concerned about itching and flaking of the skin behind the ears should consult a dermatologist. Such symptoms often turn out to be harbingers of serious systemic pathologies - there is no need to waste time.
Some diseases can be diagnosed based on an in-person examination (for example, with psoriasis, the rash looks typical, and an experienced doctor is unlikely to confuse it with something else). For others, additional research will be required. Thus, the diagnosis of otomycosis is based on the results of bacteriological culture of a smear from the affected surface.
Diagnosis of seborrheic dermatitis, in addition to culture of skin microflora, includes the following studies:
- blood chemistry;
- blood test for hormones (testosterone, cortisol, thyroid hormones);
- in some cases - ultrasound of the thyroid gland;
- collecting anamnesis - the patient’s complaints, his feelings, history of the development of symptoms, family history.
If the presence of an allergic factor is suspected, the patient is asked to take a blood test for immunoglobulins E (markers of an allergic reaction).
Treatment
There is no universal remedy that can cure itching behind the ears of any etiology. However, there are drugs that can improve the well-being of patients, regardless of what is causing the itching.
For example, many topical preparations with cooling and moisturizing components can temporarily relieve discomfort.
Ointments containing anesthetic components also relieve itching (as they reduce the sensitivity of nerve endings).
If the itching behind the ears is constant and very severe, the doctor may prescribe sedatives (sedatives, usually in the form of tablets). Antihistamines are also effective (they are usually prescribed for allergies).
Their action is based on blocking the production of histamine, a neurotransmitter of inflammation. Thanks to this, the main symptoms of inflammation are suppressed - itching, pain, swelling, redness, etc. Antihistamines are also the drugs of choice for itching behind the ears caused by allergic dermatitis.
In addition to taking antihistamines, the patient should limit contact with allergens.
It is important to understand that symptom relief is not a cure. To get rid of annoying itching behind the ears forever, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the disease.
Treatment should be based on what causes the unpleasant symptoms. This is why it is so important to make a correct diagnosis. When the main cause of the disease is eliminated, the unpleasant symptoms will go away on their own.
Thus, the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis, like many other superficial mycoses, includes drugs containing antimycotic substances - selenium disulfide, lithium succinate and ketoconazole.
If the skin is peeling, but there are no inflamed areas, you should moisturize it with cream. During treatment, you should use only those cosmetics (cream, shampoo, shower gel, etc.) approved by the doctor.
Tsiklauri Oksana
Sources: medscape.com, health.harvard.edu, medicalnewstoday.com.
Source: //globalmedclub.ru/simptomy/pochesyvanie/zud-za-ushami.html
Preventive actions
You should also remember that you need to monitor the condition of your ears. This will make it easy for you to notice if your child has irritation or a red spot near his ear. The greatest attention should be paid to the condition of the ears of newborns, since babies are more susceptible to various diseases than others. If your young child's ears become red, try not to scratch them.
To protect the outer ear from redness, children should:
- arrange daily water treatments;
- Do not forget to give children hats to protect their ears from cold and sun rays.
If your child complains that his ears are itchy and you notice that the areas around his ears are red, contact a specialist right away.
Scrofula in children: causes, symptoms and treatment
Scrofula is another disease during which the child experiences redness behind the ears. This area itches very much with this disease. In the initial stages, diaper rash appears behind the ears, which after some time become covered with yellowish crusts. The wounds are very itchy, and children often scratch them, which makes it even worse for themselves. The affected areas spread further - to the scalp, and sometimes to the face.
There are several main reasons why children suffer from scrofula:
- insufficient hygiene;
- allergies, atopic dermatitis;
- tuberculosis.
Treatment of this disease must be comprehensive. It comes down to eliminating local manifestations - redness and itching, but it is imperative to act on the body in a comprehensive manner - eliminating the allergen if scrofula appears due to an unbalanced diet of the child or constant contact with aggressive substances. Sweets, citrus fruits, and overly spicy and salty foods should be removed from your baby’s menu. It is important to wash children's clothes and bedding with hypoallergenic products, and best of all, with laundry soap. Drug therapy comes down to the use of special ointments and creams. While the wounds are wet, they need to be dried with zinc-containing preparations, and the skin, on the contrary, will have to be moisturized to prevent the appearance of cracks.