Red spots on different parts of the body cannot but bother you. Such formations are most often signs of other ailments, including a number of diseases of internal organs. Sometimes a rash is the only symptom of pathological conditions, allowing them to be identified at the earliest stages of development.
Very often, such a symptom is accompanied by itching, peeling, discomfort, and the like. But it happens that red spots on the skin do not itch, peel, hurt or bleed. In a word, they do not disturb the patient in any way other than their presence. Doctors warn that even such a symptom cannot be ignored. What could it be, and how to deal with such spots?
Classification of red spots
Red skin spots that do not itch or flake are classified as follows:
- Vascular formations. They arise as a result of pathological transformations in the blood vessels.
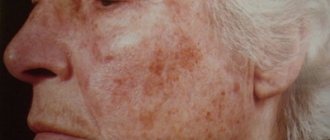
- Dark spots. They appear in the process of increasing or decreasing the synthesis of the skin pigment melanin.
Depending on the causes of development, there are such types of spots on the skin as:
- pathological, which is a symptom of a dermatological disease or diseases of internal organs;
- traumatic or spots that appear after burns or injuries.
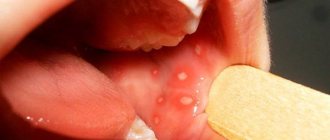
Causes of allergic reactions and their mechanism of action
Skin allergies, red spots itching: treatment, photo
Allergies cause a specific reaction of the body to the ingress of a foreign body with sensitizing properties. The perception of such an agent as hostile gives rise to a chain of processes and the activation of defense mechanisms, sometimes working against one’s own cells. Why is this happening?
A number of factors contribute to the development of allergies:
- living in regions with poor environmental conditions;
- genetic predisposition to allergic reactions;
- exposure to a huge amount of chemicals on the body that poison it;
- chronic intoxication (allergies on the legs and sides of the body);
- long-term use of medications;
- frequent contact with household chemicals (allergies on hands in the form of red spots);
- poor nutrition.
The cause of allergies in a child may be hereditary lactose intolerance, as well as eating large amounts of sugar and baked goods. Therefore, it is very important for a baby to have a balanced diet, excluding foods that have sensitizing properties.
Red spots on the body do not itch or flake: reasons
When such a symptom appears, the patient needs to see a specialist and take measures to get rid of the problem. Naturally, the choice of treatment tactics will depend entirely on the causes of the development of the rash. Doctors warn that such pathological formations on the skin can be caused by a variety of agents. Therefore, you should not engage in self-diagnosis and try to treat red round spots on the body on your own. Such actions most often have disastrous consequences, leading to exacerbations of the underlying disease and its transformation into complicated forms.
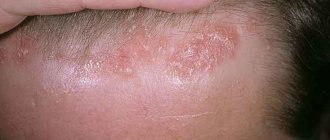
Ringworm
The disease is an infectious disease that is fungal in nature. It is characterized by a vivid clinical picture when a person’s skin is covered with large red round spots. Most often, these formations peel off, but do not itch. Over time, small bubbles with clear liquid may appear along their edges. In the center, each such spot is colored more intensely than along the periphery.
Pityriasis rosea
The pathological condition is also called Giber's disease. It is assumed that the pathology develops under the influence of herpes virus types 7 and 8. This disease is of an infectious-allergic nature and tends to worsen in the warm season. It appears in the form of reddish spots of quite large sizes, which do not itch, but become covered with scales over time. In parallel, the patient complains of muscle pain and general malaise.
Borreliosis
The causative agents of this infectious disease enter the human body after ixodid tick bites. The disease is diagnosed after the patient develops red spots on the body that itch but do not peel off. Against the background of an increase in general body temperature, they increase in size and resemble a target in appearance.
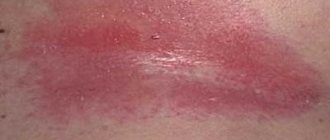
Erysipelas
The disease belongs to the group of ailments that are caused by group A streptococcus. With this pathology, the patient’s body temperature rapidly rises and symptoms of intoxication increase. A bright erythema appears on the skin of a sick person - a source of infection. This formation is very painful, itchy, and pus is released from its surface.
Injuries and burns
Red spots on the skin are common symptoms of injuries and burns of the epidermis. Such formations on the body do not itch or flake. They are accompanied by pain and disappear without a trace over time, unless we are talking about severe burns, after which scars and pigmentation remain on the skin.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
SLE is one of the autoimmune processes in which the body begins to produce antibodies to its own cells. The disease is a systemic pathology, as it affects almost all internal organs and systems. The pathology is inherited and primarily affects the female body.
In the initial stages of the disease, a characteristic red rash appears on the back of the nose and cheeks of a person, shaped like a butterfly. Such spots do not itch, but as they develop they become covered with scales. The rash may be accompanied by joint pain, spontaneous fever, and damage to internal organs.
Vegetovascular dystonia
In medical practice, the pathological condition is also called autonomic dysfunction. This painful process includes disorders of all organs and systems, provoked by changes in nervous regulation. One of the common manifestations of the disease is a rash all over the body in the form of red rashes that do not itch or hurt. Such dry patches on the skin can be caused by problems with thermoregulation, which results in changes in blood flow to the skin.
Neuroses
Dry spots on the skin of red or pink color often occur with neuroses, severe stress, panic, anxiety, phobias and the like. Their usual places of localization are the neck, décolleté, and face. Redness of the skin of neurotic origin is sometimes accompanied by chills or a feeling of heat that spreads throughout the body. In this case, paresthesia (numbness, tingling) and pain may appear in the limbs, and severe discomfort in the area of the projection of the heart.
Hemangioma
This benign formation is an area of abnormal growth of small blood vessels. In most cases, it is small in size, so it does not affect a person’s quality of life in any way. When large in size, the formation may have a bright red color. The person experiences discomfort and tingling in the area of the skin lesion. Hemangiomas, when localized in the facial area, are a serious cosmetic defect. They are also dangerous due to the increased risk of transformation into malignant tumors.
Rosacea
This dermatological disease of the facial skin is also known as rosacea. The disease is hereditary and manifests itself in adolescence, although symptoms of the disease can also be diagnosed in an adult. With rosacea, patients are bothered by red spots on the skin of the face, which may resemble stars in shape.
Hemorrhagic rash
An allergic reaction can manifest itself in several forms:
- urticaria, which is characterized by the appearance of red spots protruding above the surface of the skin and in appearance resembling a nettle burn,
- atopic dermatitis, often accompanied by intense itching and characteristic polymorphic rashes (represented simultaneously by various elements: erythema, vesicles),
- eczema, which can be very itchy (this variant of the disease is manifested by itching, burning, and the appearance of first weeping and then flaky rashes on the swollen surface).
Diagnostics
If a person has a red spot on the skin that does not itch or peel, he should consider visiting a doctor. Non-flaky red spots on a child’s body deserve special attention. Such rashes require immediate diagnosis and all necessary measures aimed at solving the problem through drug correction of the underlying pathological process.
A comprehensive examination, allowing a specialist to determine the exact causes of the development of red spots on the skin, should include the following diagnostic techniques:
- general blood analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- scraping of the skin at the site of the lesion followed by microscopy, allowing to determine the nature of the infectious agents;
- test to identify probable allergens;
- stool analysis for the presence of worms.
Psoriasis
Another disease in which pink spots form on the dermis. The formations have a characteristic convexity, which is a thickening of the layers of the dermis at certain points. A scattering can appear anywhere, and the exacerbation takes a cyclic form. Sometimes the lesions merge and cover huge areas of the body, which leads the patient to despair.
Advice! Even ordinary stress can cause an exacerbation of psoriasis. As a rule, it is nervous shocks that provoke a high intensity of distribution and dynamics of the color of spots from pale pink to scarlet and burgundy.
Red skin spots that do not itch or flake: treatment
Therapy for a pathological condition should be aimed not only at eliminating red spots on the skin, but also at eliminating the underlying disease that caused their development. First of all, a person must change his lifestyle and pay more attention to health. This can be achieved if you follow the simple recommendations of your doctor:
- stop drinking alcohol and smoking;
- do not eat allergenic foods;
- change bed linen and underwear frequently;
- regularly carry out wet cleaning of the room with ventilation.
A detailed diagnosis will allow the doctor to determine the real causes of red spots on the skin.
- If the disorder is bacterial in nature, the patient is advised to take antibiotics. As a rule, they are prescribed in the form of injections, less often in tablet forms. Most often, patients are recommended injections of broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs, for example, Clarithromycin, Ciprofloxacin, Augmentin, and the like. The dosage and duration of taking antibiotics is determined by the attending physician depending on the severity and extent of the pathological process.
- Fungal skin infections are treated with ointments with an antimycotic effect. The patient is recommended to apply antifungal ointment twice daily to the affected areas of the skin. Good results in the treatment of skin fungi and lichen can be achieved through the use of Clotrimazole, Batrafen, Canesten, Keto plus. An exception to the rule is pityriasis rosea, which does not require treatment, since over time it regresses on its own and goes away without a trace.
- For viral lesions, local antiviral drugs, as well as immunomodulators, are prescribed.
- Spots that appear due to psycho-emotional stress can be eliminated by using sedatives. Such patients are prescribed tincture of valerian or motherwort, 10 drops three times a day. It will also not be superfluous to take a vitamin complex or injections of B vitamins, which stabilize the nervous system and eliminate the manifestations of stress.
- If a person has complex autoimmune processes with skin lesions in the form of red spots, he is advised to take hormonal drugs, in particular local drugs. Patients may be prescribed Hydrocortisone or Prednisolone ointments, which should be applied to the rash until it completely disappears. Physiotherapeutic treatment is also recommended for such patients, which has a drying effect and promotes the regeneration of damaged skin areas.
Lichen
If pink spots on your legs, body, or arms begin to itch, peel, or cause a burning sensation, it could be ringworm. There should be no self-medication, only professional help. Ringworm is a contact disease and can affect anyone. Trouble in a large affected area, pain. With ringworm, the hairs break off at the root, leaving bulbs in the skin. The inflammatory process begins very quickly, the skin acquires a purple tint, becomes smooth and very painful on palpation. And the lichen itches terribly, but you can’t comb or exfoliate it.