Causes and factors that provoke the development of age spots in children
Pathological skin pigmentation can result from exposure to exogenous (external) and endogenous (internal) factors. Today, doctors have identified several dozen reasons why a child may develop a pigment spot. These include:
- genetic predisposition. Some features of melanin metabolism can be inherited, which leads to the appearance of excessive pigmentation in a child. According to statistics, if parents have pigment spots, then with a probability of more than 60% they will appear in their children.
- hypovitaminosis and insufficient intake of minerals from food. As a rule, hypovitaminosis is observed in the winter-spring period; sometimes a lack of vitamins may occur if the child is bottle-fed.
- immunodeficiencies (congenital and acquired). With pathologies of the immune system, melanocytes can be destroyed under the influence of their own antibodies - this leads to the appearance of areas of depigmentation.
- chronic diseases of internal organs. Severe intoxication, diseases of the digestive, cardiovascular, endocrine and nervous systems can lead to disruption of melanin synthesis.
- intrauterine pathologies of the circulatory system;
- hormonal imbalances during the mother's pregnancy, bad habits, allergic reactions and sexually transmitted diseases - all this affects the development of the child and can lead to hyperpigmentation or a lack of melanin in the future;
- prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation. If the skin is exposed to such radiation for a long time, the body synthesizes a large amount of melanin as a compensatory reaction.
- mechanical, physical and chemical irritants acting on the skin from the outside. In newborns, the skin is especially sensitive to chemical compounds contained in household chemicals, as well as cosmetic care products. Excessive pressure on the skin, friction, and exposure to low or high temperatures can also cause pigment spots to appear.
Each of the above factors can play a decisive role in the development of age spots. The risk group includes children suffering from congenital defects, premature newborns and infants with other skin diseases. If a child has pigment spots, it is necessary to contact a pediatrician who will examine the skin and draw a conclusion about what type of pathological pigmentation this formation belongs to.
Possible reasons
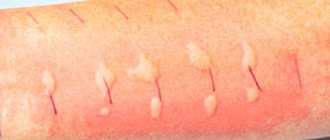
It is quite difficult to determine on your own what caused the red spots to appear on your hands. Of course, they often arise as a reaction to temperature changes. This is due to the peculiarities of the vascular system of each person. So, when overheated, the capillaries expand, and red spots are visualized on the hands. The same reaction can occur with hypothermia. In this case, the cause may be damage to small vessels that burst during prolonged contact with cold. If this happens, your fingers may even slightly lose sensitivity.
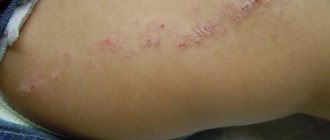
If a red spot appears on your arm, this may be a local inflammatory reaction. It is better to look for the cause of its occurrence together with a specialist. It is important not to miss the first symptoms of lichen, dermatitis or eczema, which can also manifest as redness in areas of the skin. The necessary examinations and treatment should only be prescribed by a specialist.
If the red spots that appear on your hands are itchy, then the cause of their occurrence may be an allergy. In this case, it is important to find out what exactly caused it and try to minimize contact with irritating substances.
The main types of age spots
There are several types of pigment spots in a child, each of them looks different and has its own characteristics of course and therapy. The main types of pathological pigmentation are:
- nevi (moles). These are small round formations with smooth edges, which can be either dark or light. Nevi appear either during fetal development or in the first few years of life. It often happens that such formations are not observed in infants, but by the age of 3 several small moles appear in 95% of children.
- ephelides (freckles). These are small areas of hyperpigmentation that appear in the spring (when the skin is exposed to UV radiation). Most often they are localized on the face, neck, shoulders and back. They may decrease on their own during the cold season and go away with age.
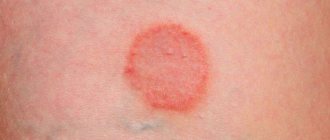
- hemangiomas. This is a red spot that can be localized on any part of the body. Its appearance is due to the fact that in a certain place the vessels grow too much.
- Mongolian spots. Observed in children of the Mongoloid race, they look like small hemorrhages and disappear on their own after a few years.
- medial spots of newborns. These are small spots that are located on the back of the head or neck. They are pale pink in color, but may turn red during physical or mental stress (for example, during physical activity or while crying, breastfeeding). They disappear without a trace after 6-24 months.
- telangiectasia. This is a persistent and constant expansion of subcutaneous vessels (capillaries, arterioles, venules). It occurs as a result of difficult labor and is often observed in premature babies.
- warty neoplasms. They are usually gray or light brown in color, are very rare and, if the skin is extensively affected, require surgical intervention.
- Setton's nevus. This is a large nevus, around which hypopigmentation is observed (like vitiligo).
All age spots should be constantly under the close attention of parents and doctors. If a mole or nevus quickly enlarges, the edges become uneven and asymmetrical - this is a reason for an urgent visit to a medical institution. Consulting a doctor will help determine the type of pigment spot, carry out a differential diagnosis with other skin lesions (for example, infectious or allergic origin), and also take the necessary treatment measures, if necessary.
Features of newborn pigmentation
The color of a child's skin depends on age, time spent in the sun, and race.
The individual traits of the baby delight the parents. They try to capture the baby in photos from the first days of life. But the appearance of dark or colorless spots on the upper layer of the dermis begins to bother mom and dad.
The skin pigment, melanin, determines skin tone, hair color and eye iris. This substance helps protect the epidermis from the harmful effects of ultraviolet rays.
Birthmarks appear frequently in newborns, and parents don't always know whether to worry about them. In any case, it is better to check with a doctor. Pigmentation on a baby’s body changes for two reasons:
- increase in the amount of pigment (hypermelanosis);
- decrease in the amount of pigment (hypomelanosis).
More often the skin becomes pigmented on the back, face, legs or arms. This phenomenon does not affect physical comfort, but is more of an aesthetic nature. By the age of 7, this deficiency often goes away on its own. Moles prevent a baby from living and developing peacefully when they are located on the eye, mouth, or ear. Nevi are flat and convex, porous, covered with hairs. Sometimes such a defect requires surgical intervention.
Age spots in children: main complaints and symptoms
The main complaint that parents make when contacting a pediatrician is pigmentation disorders (excessive pigmentation or depigmentation - white spots on the skin). In most cases, this condition does not bother the child or disturb his condition, however, this does not mean that it is not necessary to monitor the development and progression of the pigment spot.
Nevi, moles and other conditions with symptoms of pathological pigmentation are localized, usually on the face, neck or torso - these are the areas of the body that are most susceptible to adverse environmental factors (including insolation with UV rays). Pigment spots often appear on the arm or leg. The color of these areas of the skin may vary: pink, bright red, brown, and black pigment spots are observed. Often, the color and size of the area with impaired pigmentation is one of the main diagnostic signs.
Some types of pigmentation disorders (such as freckles or medial newborn spots) appear in clusters. In most cases, age spots are round or oval in shape with smooth edges. With some types of hyperpigmentation, dryness and flaking of the skin near the pigment spot may occur.
Treatment methods
| Treatment options | Characteristics of the technique |
| Surgical removal | The method is radical, but accessible and effective. The operation is performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia for large nevus sizes. The method is used to get rid of pigmentation when it degenerates into a malignant formation. |
| Laser therapy | Laser excision is a safe, bloodless and painless method that gives excellent results. The laser acts directly on the mole without affecting nearby tissues. Healing of the removal site occurs quickly, leaving no scars on the skin. |
| Cryotherapy | Removal by freezing with liquid nitrogen is used for warty formations and small nevi. |
| Electrocoagulation | Removal occurs with high frequency currents and is indicated for small congenital moles. |
| Drug treatment | Treatment with drugs is indicated for hemangiomas, vitiligo and some other types of pigmentation. |
It is not always necessary to treat pigmentation on a child’s body. Moles that do not pose a threat to health, freckles, Mongolian and medial spots do not require treatment.
Diagnosis of age spots: what examinations are necessary in this case?
If signs of illness are detected, you should immediately consult a doctor. The pediatrician can refer the child to a consultation with a dermatologist, as well as other specialized specialists - this is necessary in order to exclude all possible concomitant pathologies of internal organs.
At the initial appointment, the dermatologist conducts a questioning and collects an anamnesis - during these procedures, he finds out how long ago the pigment spot appeared, how it developed, and whether there are any other disorders in the general condition of the child. The dermatologist also collects allergy and family history (this is necessary to exclude possible genetic diseases, as well as other skin diseases). After this, the doctor conducts an examination: assesses the size, location, shape, color, symmetry of the formation, and the nature of its edges. If necessary, dermatoscopy is performed.
If it is not possible to accurately differentiate a pigment spot from infectious or allergic skin diseases, a specialist can take scrapings from the skin and do a biopsy. Sometimes it is also necessary to conduct laboratory tests such as a complete blood count and urine test (these tests will help the doctor determine the child's health status).
Spots on the arms and legs of a child
In general, red rashes in children occur for the same reasons as in adults. However, the child’s body is more sensitive to various factors, which is why the frequency of such manifestations increases.
The most common cause is a reaction to food. This phenomenon is especially common in children aged 1-3 years. During this period, new types of food are actively introduced into the diet, which previously did not enter the child’s body. This can provoke an intense reaction, accompanied by rashes.
How to get rid of age spots in a child?
In 90% of cases, after consulting a specialist, parents do not need to take any radical measures. If the spot is evenly colored, has smooth, clear edges, is symmetrical, and does not exceed 5-7 mm in diameter, then you just need to observe this formation.
Parents are advised to monitor the condition of the spot monthly and also measure it - if it suddenly begins to increase, they should contact the clinic. Pediatricians also advise covering the area of hyperpigmentation with clothing while walking (especially in spring and summer). Under no circumstances should you cover a mole with a band-aid - this can aggravate its condition and speed up its growth. You also need to explain to the child that the mole cannot be touched, but if damage occurs, you need to urgently consult a doctor. Also, constant itching, burning and discomfort in the area of hyperpigmentation should be a signal to contact a specialist.
Surgery
It is possible to remove or lighten a stain using traditional and folk methods only after consulting a doctor. Surgical treatment can be done either with a laser or by radical excision. As a rule, with a small lesion, the doctor selects an individual course of laser therapy. During this procedure, the rays of the device act on the skin, making the pigment lighter. When excising a birthmark, all affected layers of skin are locally removed, and the material obtained during the operation is sent for histological examination. Based on its results, one can judge whether the neoplasm is benign or malignant.
Application of whitening creams
Almost all creams for age spots contain components that cannot be used before the age of 12-14 years, so their use is not recommended. In adolescence, the use of whitening creams based on milk proteins, niacinamide and betaine is allowed.
Most modern whitening creams not only lighten age spots, but also intensively moisturize the skin, normalize melanin production, and protect the epidermis from exposure to ultraviolet radiation. It is necessary to apply medicinal cosmetics in courses, between which it is necessary to take breaks. Whitening creams should be selected by a specialist on an individual basis.
Traditional methods of treatment
The advantage of unconventional methods of therapy is, first of all, that they can be used to treat age spots in childhood. They are also quite cheap, and sometimes all the ingredients can be found in the refrigerator. The following are recognized as the most effective traditional medicine:
- cucumber mask. To prepare it, you need to grate a cucumber and apply the resulting pulp to the area of hyperpigmentation for 15-25 minutes, 2-3 times a day.
- mask with lemon juice and yeast. It is necessary to mix the ingredients in a 1:1 ratio and apply to the affected areas of the skin for 15 minutes. After this, you need to wash the child with cool water. Judging by the reviews, the effect can be noticed after the first procedure, and no more than 5 applications are required for complete cure.
- lotion with parsley and milk. To prepare this remedy, you need to take a bunch of parsley and pour a glass of water into it, let it brew for 30 minutes, then add 100-150 ml of milk to the infusion. You can wipe the skin with the resulting lotion several times a day (some experts advise freezing the product and wiping the affected areas with ice cubes).
- potato and egg yolk mask. You need to boil 1-2 potatoes, mash them and add 1 egg yolk, let the mixture cool. The resulting paste must be applied to areas with hyperpigmentation 2-4 times a week.
Despite the fact that some folk remedies have been used for several millennia, individual hypersensitivity reactions cannot be ruled out. Therefore, before using any method of alternative medicine, you must consult your doctor. More effective traditional medicine recipes in this article.
Treatment of red spots
Therapy is carried out using conservative methods. The main method of treatment is taking medications aimed at eliminating the causes of the disorder and relieving their symptoms. In some cases, the rash and accompanying symptoms are grounds for hospitalization (for example, with measles and scarlet fever). Otherwise, therapy is allowed on an outpatient basis.
The mistake many patients make is trying to self-treat. Therapy should be carried out only under the supervision of doctors. Otherwise, the patient's condition may worsen.
Use of medications
Medicines are selected taking into account the diagnosis and the individual characteristics of the patient. The duration of treatment depends on the disease and the degree of sensitivity to the drugs.
The drugs used, depending on the disease:
- Allergy. Treated with antihistamines. These drugs interfere with the secretion of histamine, a substance that causes a reaction to the allergen. As a result, the symptoms gradually, and sometimes instantly, disappear. A prerequisite for successful therapy is cessation of contact with the allergen.
- Infectious diseases. Treated with antiviral, anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating agents. Symptomatic drugs play a supporting role: antipyretics, painkillers, antitussives.
- Insect bites. Local treatment of affected skin areas is provided. Wound healing agents are used to promote tissue restoration in the bite area. Antiseptics are also used to prevent the development of bacterial inflammation.
- Lichen. Complex antifungal therapy is provided. The affected areas of the skin are treated with ointments, gels and creams, the action of which is aimed at suppressing pathogenic fungi. It is also possible to take medications orally. It is forbidden to apply brilliant green, iodine, alcohol solutions and tinctures to stains.
- Nervous disorders. Therapy is prescribed depending on the causes and intensity of the disorder. Patients may be prescribed sedatives, antidepressants, and medications with glycine to improve the functioning of the nervous system. Adequate rest and sleep and avoidance of stress are recommended.
What does Dr. Komarovsky say: are age spots dangerous?
The famous pediatrician, Dr. Komarovsky, has repeatedly touched upon the topic of moles, vitiligo and other pigmentation disorders in childhood in his speeches. The doctor says that areas of hyperpigmentation need to be treated with special caution - because cancer cells can develop in them. But this is not a reason to immediately remove moles if they appear. Komarovsky says that the best way to prevent skin cancer (melanoma) is to constantly monitor the condition of nevi. A well-known doctor insists on a monthly examination of the skin, and moles in hard-to-reach places (in the groin folds, armpits, on the scalp) should not be ignored. In order to remember the main signs that it is time to see a doctor, the doctor suggests examining each mole according to the algorithm. This is an abbreviation that stands for:
- asymmetry (should not be observed);
- the edges of the mole (should be clear and even);
- color (the mole should be uniform);
- size (“safe” nevi in diameter do not exceed 6-7 mm);
- dynamics (rapid progression and growth should not be observed).
If a child has a tendency to develop age spots, you need to keep a notebook in which you write down all the data about each mole every month. If you do this regularly and carry out proper examination, you can detect skin cancer in the early stages.
Pigment spots in children are a cosmetic defect, but, in most cases, it does not cause any inconvenience. Often, in order to avoid the progression of tumors and the appearance of complications, it is enough to monitor their condition, undergo timely examinations by a pediatrician, and also protect the skin from the sun and other irritating environmental factors.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Sw0g5JDVlLE
Preventive measures
There are many reasons for the formation of age spots and it is not always possible to prevent their appearance. It is impossible to influence the hereditary factor, the individual structure of the child’s internal organs and vital systems.
But parents should monitor the baby’s health and limit his exposure to the sun. If age spots have already appeared, you need to show them to a doctor to understand the cause and prevent the consequences.
If parents notice a change in skin color or the appearance of tumors, there is no need to panic. Birthmarks often go away on their own, leaving no mark on the child’s skin. But it's worth watching them.
Spots on elbows
It is worth noting that the appearance of redness does not always indicate problems. For example, often spots on your elbows can be due to the fact that you have been leaning on them for a long time. But if they itch, then you should pay attention to them. In this area, discomforting redness may occur due to malfunctions of the thyroid gland. Often the same reaction is caused by excessive slagging in the body. But in most cases, redness will not be the only symptom; problem areas will not only itch, but also peel off.
Dermatological manifestations
There are several types of red spots that are independent of diseases and infections. They often last a lifetime and cause no trouble. However, it is necessary to consult a pediatrician if you notice even slight redness in your opinion.
Dark spots
These are spots that appear due to genetics, as well as a malfunction of skin cells. Most often they remain for life, but they can disappear from the skin over time. Pigmented red spots in a child can be regular round or irregular in shape. If a large amount of pigmentation has formed on the body, then you should not postpone going to the doctor.
Red birthmarks
They often occur in babies in the facial area - on the forehead, wings of the nose, back of the head or lips. Such marks appear due to the expansion of capillaries during the birth of a child. There is a pattern that symmetrical spots disappear from the skin in the first year of life, but single spots can remain forever.
Hemangiomas
These are specific spots that protrude slightly above the surface of the skin. They are formed from small blood vessels located critically next to each other. They are often mistaken for red birthmarks on a child, but hemangiomas have a significant difference - they do not grow with the body.
As a rule, in the first few months of life, the spot increases or does not change size, and then begins to disappear. Usually such spots are completely harmless, but if inflammation occurs, the hemangioma will have to be removed surgically or with cryotherapy.
Treatment
After a correct diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment in which the red spots are eliminated, itching, pain and peeling go away. The most popular means for local counteraction to the causes of the disease are ointments and creams. The drugs have a variety of effects:
- Fenistil gel – anesthetizes, heals;
- Solcoseryl – accelerates cell regeneration;
- Elidel – relieves itching, eliminates inflammation;
- Advantan – reduces redness, swelling;
- Elokom - dries.