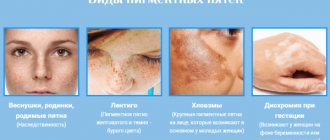
Moles are limited formations on the skin with a brown or black color. Sometimes moles protrude above the surface of the skin, peel off, and hair can grow from them. The scientific name of these formations is nevus. The neoplasms themselves are benign; without traumatic effects, the transition to a malignant form does not occur. If the nevus is located in a visible place and causes aesthetic discomfort, many decide to remove it.
Attention! Never remove a nevus yourself! This is very dangerous - there is a high chance of developing complications in the form of cancer. The operation must be performed by a doctor in a specialized clinic.
If you go to the clinic, you will be offered several methods that differ in technology and cost: surgical and laser removal, cryodestruction (use of liquid nitrogen) and electrocoagulation.
The advantage of the latest technology is that it is much cheaper than laser correction and safer than surgical intervention in the surgical area. The secret is simple - using a direct or high-frequency electric current during the removal process, which causes a tiny burn to the tissue. If the size of the mole is small, you will not even need anesthesia; subjectively, you will only feel a slight burning sensation.
What is mole removal by electrocoagulation?
The most common way to remove nevi is electrocoagulation. It is a surgical intervention used to eliminate various tumors. Through this manipulation, it is possible to eliminate nevi without pain and in the shortest possible time.
Although electrocoagulation is considered a surgical procedure, the process takes place in a completely different way, and the consequences do not cause concern to the patient. Previously, the surgical technique involved removing nevi using a scalpel. Scars appeared frequently, and the procedure itself was painful.
You should not delay visiting a specialist; in particular, this applies to owners of convex nevi. Removing flat moles is not necessary if they do not cause inconvenience.
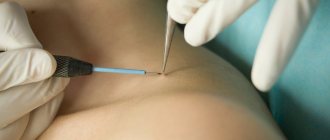
The basis of this method is the use of high-frequency current, which plays the role of an electric knife. Through such discharges, small incisions are made in stages, which remove the mole layer by layer.
The electric field helps create a strong thermal effect, and therefore no bleeding occurs, and the likelihood of infection will be minimal. The device that supplies the generated current is called an electrocoagulator.
Causes of neoplasms
One of the main reasons leading to the appearance of papillomas is HPV (human papillomavirus). In addition, the tumor may be to blame for:
- unprotected sex or indiscriminate change of sexual partners;
- disruptions in the hormonal system;
- pathologies of the digestive system;
- various pathological addictions: smoking, drugs, alcohol abuse;
In addition, an infected mother can pass the virus to her baby during natural childbirth.
It is impossible to cure HPV, it is only possible to drive it into a stage of stable remission with the help of immunomodulators and by changing your usual lifestyle.
To identify the human papillomavirus, it is necessary to donate blood for general and biochemical analysis, a biopsy from the affected area and conduct a PCR test.
Indications
Like other medical procedures, nevus removal should be carried out only for certain indications. The specialist determines the origin of the mole. When symptoms of malignancy are identified, instead of electrocoagulation, a standard surgical operation is necessary.
Typically, a suspicious nevus is excised together with a large area of skin around it to prevent the formation of relapses. When electrocoagulation is carried out due to cosmetic factors (the patient does not like nevi), then this technique is ideal, since it makes it possible to carry out the manipulation quickly, without leaving scars on the skin.
The only exceptions may be large formations in diameter (1 cm or more), which are optimally removed surgically, and the wounds in the treated area are sutured with threads in order to speed up recovery and prevent suppuration.
Often, nevi are removed in the following situations:
- when they are near the neck, where friction and serious injury from clothing occur all the time;
- if they are located in the armpits and there is a risk of damage during shaving;
- when they are located on those parts of the body where chronic injuries through elastic bands, straps and other elements of clothing;
- when nevi are localized on the scalp in the scalp and there is a possibility of injury during cutting or combing.
On this topic
- Moles
All about dangerous moles
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- September 27, 2020
Elimination is carried out only for medical reasons. Electrocoagulation is carried out only in a situation where there are no signs of malignancy of the growth, in order to avoid metastasis. When there is a suspicion of oncological degeneration of a nevus, surgical methods are used to remove it.
It is forbidden to eliminate a nevus yourself; complications can be extremely life-threatening, since a nevus can turn from a benign formation into a malignant one.
Reasons for appearance
One of the reasons for its appearance is considered to be genetic predisposition. They can appear in large quantities in a short time during pregnancy and puberty, as hormonal changes occur. Mole removal is contraindicated for pregnant women.
Excessive solar radiation is recognized as the most dangerous stimulator of reproduction and growth. For this reason, owners of a large number of moles should avoid tanning beds and reduce the amount of time they spend in the open sun.
Contraindications
Elimination of nevus using electrocoagulation has a number of contraindications. Manipulation is not recommended for:
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels (heart rhythm disturbances, angina pectoris, high blood pressure);
- personal susceptibility to the procedure. active stage of herpes;
- inflammatory diseases in the place where the nevus is located;
- poor clotting ;
- allergic reaction to anesthetics;
- somatic diseases, in particular during exacerbation;
- malignant growths.
In the presence of malignancy, surgical methods of elimination are used, which make it possible to excise a fairly significant part of the skin near the mole in order to avoid relapses. Electrocoagulation for malignant neoplasms can cause subsequent metastasis.
Degeneration into melanoma
Most moles are harmless, but some indicate a predisposition to malignant transformation, melanoma and skin cancer. Be attentive to pigment spots that have uneven edges and gradually grow. If the size of such a formation has reached a diameter of 6-7 mm, you need to consult a dermatologist or oncologist, since timely removal will prevent the formation of melanoma. The following signs indicate that a mole has become dangerous and is degenerating into melanoma:
- uneven coloring;
- increase in size;
- discoloration or sudden pigmentation;
- redness around the tumor;
- the appearance of bleeding and/or cracks;
- uneven contours or irregular shape;
- loss or change in skin pattern over raised areas;
- itching at the site of formation, inflammation or pain.
Back to Contents
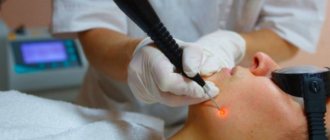
Progress of the procedure
Electrocoagulation is a virtually painless procedure. The entire manipulation, taking into account the size of the mole, lasts approximately 20 minutes.
The patient does not need to prepare for the procedure; the main thing that is needed is consultation with a specialist. During the operation, local anesthesia is used, so there is generally no pain during electrosurgical intervention.
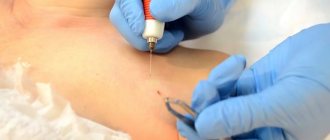
However, upon completion, discomfort or minor pain is possible, but not so intense as to require the use of anesthetics. Next, the problematic nevus is cut off using a metal loop, which is under high-frequency current.
On this topic
- Moles
Everything you need to know about laser mole removal
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- September 25, 2020
At the same time, a small amount of nearby tissue is cauterized using a coagulator, and the vessels are sealed, preventing bleeding. This makes it possible to eliminate such adverse consequences as postoperative shock, swelling, and infection entering the wound.
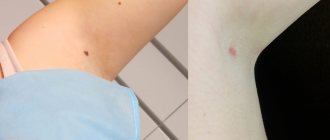
The treated area will be covered with a crust, which will fall off on its own after 3-6 days, and a flat, virtually invisible scar will form in this area. Minor spots after eliminating nevi by electrocoagulation will heal mainly within 5 days, and after 14 days they are practically not noticeable.
The process of eliminating nevi with an electric knife is carried out in specialized institutions, after preliminary dermatoscopy.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
Modern medicine offers several methods that can quickly and painlessly rid a person of a nevus, which is dangerous. One such method is electrocoagulation of moles. A qualified doctor uses high-frequency electric current to remove an unwanted mole. Advantages of nevus removal with a coagulator:
- After surgery, no special wound care is required. The skin restoration process takes a short period of time.
- Due to the effect of electric current, there is no bleeding during mole removal with an electric knife.
- The removed nevus is subject to histological examination, which reveals the presence or absence of cancer cells.
- The operation does not take much time.
- The scar that is visible after removal disappears after two to three weeks.
- The price of the procedure is affordable, so removal of moles by electrocoagulation always has positive reviews.
- The operation is safe and therefore allowed for pregnant women.
- Since there will be no scar on the skin, nevi located on the face, head, and intimate areas can be removed.
- Does not require specific preparation before removing moles with an electron.
- By using a coagulator, the doctor can monitor how deep the high-frequency current is applied to remove the nevus deep in the dermis.
- There is no risk of infection.
In addition to the advantages, there are several disadvantages of the method:
- During excision of the nevus, local anesthesia must be administered.
- The healing period lasts longer than with laser removal.
- The wound needs to be treated several times a day.
- The site of excision of the spot should be protected from ultraviolet radiation, water (the first three days) and mechanical stress.
- Removal of moles with a coagulator covers the area that is located near the nevus. A burn may occur.
After care
Elimination of nevi by electrocoagulation is carried out in the shortest possible time, and the rehabilitation period does not take a large amount of time. At the end of the nevus removal procedure, a protective crust is formed at the excision site. It helps prevent infection from entering the wound and protects against bleeding.
In the postoperative period, you should care for the surface of the wound, treating it with antiseptics. Moreover, the cut area must be protected from extraneous influences (ultraviolet radiation, cosmetics, etc.) and moisture penetration.
You should not remove the crust yourself; after final restoration, it disappears on its own. By following all the rules during the rehabilitation process, it is possible to minimize the formation of pigmentation at the site of removal and other possible consequences.
Why do people choose this method
Many people prefer to choose the electrocoagulation method to get rid of an unwanted or dangerous mole. It is used to remove both large and small nevi. The operation lasts from three to fifteen minutes.
The choice of electrocoagulation is also popular due to its affordable cost and fast recovery period and has many positive reviews. And also the absence of complications after surgery. The condition for this is the conscientious implementation of the doctor’s recommendations regarding wound care. Otherwise, there is an increased risk of developing a scar, which will spoil the appearance if a mole was removed on the face.
Possible consequences
In a situation where the nevus was eliminated on the surface of the face, the patient initially feels pain near the wound and observes slight swelling. Such changes do not require special therapy and can go away on their own.
In certain situations, discomfort can also manifest itself during the process of removing a mole on the body. However, the use of anesthetics is very rarely prescribed.
After 14 days, the protective crust will fall off, and a pink spot of a new layer of epithelial tissue will form in that area, which will turn white over time. Despite the safety of surgery, certain complications are likely to occur:
- Infection. Premature removal of the protective crust from the wound can provoke the penetration of infection into it, which can cause suppuration.
- Scarring. When the infection penetrates deep into the wound during excision of the nevus, purulent contents form under the crust, which leads to its peeling. As a result, suppuration contributes to the appearance of scars at the site of mole removal.
Risk factors
Often a person does not notice the degeneration of a nevus into melanoma. But melanoma is life-threatening, and it is almost impossible to cure it at an advanced stage. Therefore, it is advisable to remove the mole before it becomes malignant. The first symptoms of degeneration:
- change in the shape and size of the spot;
- violation of color uniformity;
- changes in texture, such as wrinkling or peeling;
- painful sensations;
- microbleeding.
Two or more of these signs serve as a reason for medical consultation and removal of the mole. It is worth getting the spot examined as soon as possible, because melanoma quickly spreads to healthy cells. Reasons why nevus degenerates:
- heredity;
- birthmark injuries;
- hormonal imbalance;
- excess ultraviolet rays.