A nevus or mole is a benign neoplasm, the basis of which is made up of pigment particles of the epithelium - melanocytes. If you notice that a papilloma is growing from a mole, this may be the beginning of the process of malignancy.
READERS RECOMMEND!!!
To treat papillomas, our readers actively use the remedy... Read more
Important!
The danger of nevi is their tendency to degenerate into melanoma.
Melanoma or skin cancer is the most serious cancer. Today there is an increase in melanomas certified by doctors, as well as an increase in the fatal outcome of this disease. There are characteristic features that help distinguish a nevus from melanoma.
What is a mole
Moles or nevi (medical term) differ in shape, color and size.
They can be brown, black, purple and red.
They are located on the surface of the skin or slightly rise above the skin.
After six months of age, the first nevi may already form on the child’s body.
They can appear throughout life with varying intensity.
The formation of nevi is associated with the accumulation of melanocytes in certain areas of the skin surface.
A mole is a benign formation and does not pose a danger, but under the influence of negative factors it can degenerate into a malignant form - melanoma.
The neoplasm carries a mortal danger to humans, as it has the ability to very quickly metastasize throughout the body.
I have a lot of moles. Is it dangerous?
This is a reason to visit a doctor. Over the past 10 years, the incidence of melanoma has increased.
This type of cancer spreads quickly. Sometimes the focus is not found, but is diagnosed by metastases that develop rapidly.
Melanoma is a malignant skin formation. The average person may not be able to distinguish it from an ordinary mole. Because of this, early diagnosis of the disease is difficult.
If you have more than 20-25 moles on your body, make an appointment with a dermatologist. Armed with a dermatoscope, the doctor will check for suspicious nevi.
You can ask for a map of your moles to know exactly when a new one appears or an old one suddenly begins to change.
For self-diagnosis there is an ACCORD system, based on the first letters of dangerous symptoms:
A – asymmetry. Melanoma, unlike a mole, is not symmetrical relative to the center.
K – edges. A mole has smooth edges, while a melanoma has excised edges.
K – bleeding. If a mole bleeds at the slightest injury, bring it to the attention of a specialist.
O – color. The mole is evenly colored, it is monochromatic, melanoma can be multi-colored.
R – size. Formations larger than 5 mm in diameter deserve attention.
D – dynamics. Moles grow slowly. Rapid growth, discoloration, inflammation are signs of melanoma.
Only 30% of melanomas arise at the site of existing moles. Most often this is a newly appeared spot. Therefore, it is important to examine your body and keep an eye out for new moles.
Ultraviolet radiation can affect the degeneration of an existing one. So, if you have a lot of moles, fair skin, blue eyes, tanning is contraindicated for you, and solarium is strictly prohibited.
Reasons for the appearance of a mole
Among the reasons for the formation of nevi are: genetic predisposition, prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the skin, hormonal pathology and other factors.
Most often, the formation of moles on the body is observed during puberty and in women with the onset of pregnancy.
This is explained by an increase in pituitary activity during this period of a person’s life.
Often people tend to consider any formation on the skin as moles, however, this is a big misconception.
Therefore, any neoplasm on the skin must be identified by a specialist.
Laser removal
This is a modern method of excision of formation, which has become widespread.
Its popularity is due to its advantages:
- painlessness;
- low-injury;
- bloodlessness;
- speed of the procedure;
- minimal risk of infection;
- short rehabilitation period;
- no scars.
Thanks to the precision of the laser beam, it is possible to remove growths even in particularly sensitive areas, such as the intimate area, eyelid, etc.
What is papilloma
Papilloma (wart) is a benign formation caused by papillomavirus (HPV).
Growths can appear on various parts of the body, both on the skin and on the mucous membranes, including the surfaces of internal organs.
Favorite places for warts to be localized are the groin and axillary areas, feet, and neck area.
Some types of the virus are highly oncogenic, causing cancer formation.
The tendency to malignancy is more typical for hanging and large papillomas.
Infection with the human papillomavirus can occur not only through sexual contact, but also through household contact.
Papillomas can vary in shape and size, and sometimes remain completely invisible.
HPV is able to penetrate the body through the skin and mucous membranes.
The pathogen immediately begins to reproduce, causing organ damage.
Signs of infection do not appear immediately, so the patient may find out that he has an infection months or even years later.
Controversial cases
There are controversial cases in which even a specialist finds it difficult to establish an accurate diagnosis. Usually in this case, additional examination is carried out.
Papilloma with black dot
When burgundy or black dots appear on a papilloma or wart, patients begin to worry. However, doctors say that if there are no other manifestations such as bleeding, severe pain, or changes in the structure of the growth, there is no need to worry.
Most likely, the vessel inside the formation was damaged. If the dots cover the entire growth and additional signs appear, you should consult a doctor.
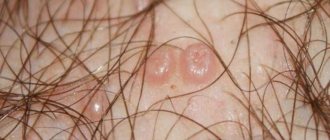
Papilloma grows from a mole
If a patient discovers a sprouted papilloma on his mole, he should immediately consult a doctor. This deviation is due to the fact that the human papillomavirus can even infect areas of melanin accumulation.
Such a growth requires immediate removal with subsequent observation by a doctor.
Papilloma or melanoma
You can distinguish a mole from a papilloma after becoming familiar with the features of these neoplasms. However, patients should also know when to see a doctor, because the growth can develop into melanoma.
Melanoma is a malignant neoplasm of the skin, which most often occurs as a result of the degeneration of cells of a common nevus. Papillomas extremely rarely degenerate into melanomas.
The main signs of malignancy:
- Pain and burning in the area of the tumor.
- Change in color, rapid increase in the size of the mole.
- Change in the outlines of the nevus to indistinct, blurred.
- Bleeding from a neoplasm.
If such signs appear, you should immediately visit a doctor.
Why do papillomas appear?
The main reason for the formation of papillomas is infection of the body with HPV, which most often occurs through casual sexual contact.
Factors that can trigger the growth of warts include:
- decreased immune defense of the body
- alcohol abuse
- presence of chronic, regularly recurring infections
- pathology of the digestive system
- stress conditions and depression
- long-term antibiotic treatment
- visiting the swimming pool, public bath, sauna
The distinctive features of papillomas are:
- rapid appearance of growth
- spread of papillomas due to rapid growth
- increased risk of cancer
- high contagiousness of papillomas
- merging of warts into one large growth
When multiple neoplasms appear on the surface of the skin, this should be the reason for a full diagnosis for HPV infection and urgent treatment.
How to treat human papillomavirus
It is impossible to cure HPV, but you can suppress the virus by raising the body's immune defense to the proper level. Doctors are fighting only the consequences of HPV. General therapy is prescribed, for example, when papillomas are localized in the anogenital area. Immunomodulators and antiviral drugs are the main ways to combat the effects of the virus. External manifestations of HPV - papillomas - can be removed surgically, cosmetically or using traditional medicine.
Human papillomavirus in women - treatment
If a woman is diagnosed with HPV, this may explain many of her health problems.
Thus, the human papillomavirus in women in gynecology is a serious threat to the development of cervical cancer. A vaccine has been developed, which is already used in our country on teenage girls and young women. However, it has not yet been proven that it actually saves from oncology, and the consequences of its action may manifest themselves unknown how and when. According to rumors, the vaccine is simply being tested in our country, and our girls are guinea pigs for foreign pharmacologists. HPV is often the cause of miscarriage, recurrent miscarriage, or infertility. Externally, the human papillomavirus in women has the most common symptoms - neoplasms on the skin, as well as herpes - a cold on the lips so familiar to many, but laboratory tests of a blood sample help to accurately determine the presence of the virus.
Purely aesthetic discomfort is the most common reason why women want to be cured of cosmetic flaws. Which doctor should I contact for papillomas? To a dermatovenerologist or cosmetologist. But if the neoplasm is of a low-quality nature, only an oncologist can provide assistance.
Human papillomavirus in men: treatment
HPV also causes a lot of trouble for men. Perhaps the most serious of them is papillomas in the bladder and ureters.
Pain may occur when going to the toilet, and blood may appear in the urine. At the same time, the formations can affect the epidermis of the penis, which makes sexual contact painful, and visually this is not the most pleasant sight.
A urologist will tell you how to treat papillomas in intimate places, and you should definitely visit them if they are found on the penis. In other cases, a dermatovenerologist will help.
What is the difference between a mole and a papilloma
The main distinguishing feature of neoplasms is the cause of origin.
Papillomas are formed as a result of infection of the body with papillomavirus, and nevi are formed as a result of the accumulation of melanocytes.
To understand what kind of tumor this is, you need to pay attention to the following signs:
- Localization location. Warts form in places where skin friction and sweating most often occur, as well as on mucous membranes. A nevus can form on any part of the skin surface. No factors can influence the location of the mole.
- The edge of a healthy mole is always smooth, the formation has a symmetrical shape.
- The size of the wart is small; if damaged, it can rapidly increase in size. Nevus can have different sizes: from small to very large.
- Presence of pigmentation. The mole can have a color: black, brown, red, purple. Papilloma always has a light pink tint.
- Warts are characterized by a loose structure, while nevi are dense, hard formations. It should be noted that these formations do not always meet these criteria.
- The mole does not contain any vessels. Papilloma is equipped with capillaries.
- Nevi can be inherited, but papillomas cannot.
Main characteristics of papilloma ↑
Papilloma refers to viruses that develop on the skin and mucous membranes. There are household and sexual transmission of the virus, as well as the following types of papillomas:
- Warts. These neoplasms are characterized by surface density and formation in different areas of the skin. The following warts are distinguished: simple, flat, plantar and genital.
- Condylomas are pointed papillomas, the area of development of which is the genitals and anus.
- Senile papillomas are neoplasms in the form of thin threads that are often found on the neck and face.
- Cutaneous horn. Outwardly, such dense keratin neoplasms resemble small horns, which is why they got their interesting name.
There are flat and hanging papillomas, the latter of which are easily distinguished by their thin stalk. In medical practice, there are papillomas of different sizes, which can reach 2 cm in diameter.
Moles and papillomas: what must be removed and when
Experts do not recommend removing moles if they behave calmly and do not cause discomfort to their owner.
If any complications arise from the nevus, and doctors strongly recommend removing it, then it is advisable to do this as soon as possible.
It is strictly not recommended to do this yourself at home.
It is necessary to get rid of unwanted moles only in a medical facility.
Before removing the tumor, the specialist will conduct the necessary examination, after which he will suggest one of the methods for removing the tumor.
Doctors are well versed in which nevus removal methods are the most effective and safe.
As for papillomas, you will also need to consult a doctor.
After an examination and a series of diagnostic tests, the doctor will prescribe removal of growths using the most gentle method and antiviral therapy.
Treatment of papillomas and warts comes down to their removal; the difference is that for each type of tumor, the doctor selects the method that will be most optimal for each specific case.
If it is necessary to send biomaterial for diagnostics, radio wave therapy or surgery will most likely be used.
In order to remove tumors, the following techniques are used:
- Cryodestruction . The technique is based on the use of low temperatures. Liquid nitrogen is used to freeze papillomas, which provokes necrosis of pathological tissues.
- Chemical removal method . Medications containing high concentrations of substances that cause chemical burns are used. The formations dry out and subsequently fall off.
- Electrocoagulation. High frequency current is used for removal. The tumors are burned out.
- Laser therapy. This technique is the most preferable, since after removal of papillomas there are no traces left on the skin. After the procedure, the recovery period is short.
- The radio wave technique is based on the use of radio waves, which promotes excision of the growth.
- Surgical method of removal . A scalpel is used to cut out the affected tissue, after which the material is sent to the laboratory for histological analysis. The technique is indicated for suspected malignancy of the process.
For small papillomas, conservative therapy is carried out using antiviral drugs.
Differences
There are several criteria that will help even a person without specialized education to understand the difference between a mole and a papilloma. But at the same time, it is advisable to show all skin pathologies and neoplasms to a specialist as soon as possible and undergo preventive examinations.
Main Difference
The main difference between papillomas and moles is their source of origin. The former are a manifestation of HPV, and the latter are a collection of pigment cells under the epidermis. Papillomatous formations are always acquired, and nevi are congenital pathologies inherited from parents to children.
Appearance
When a papilloma or mole appears, a dermatologist knows very well how to distinguish these neoplasms from each other. These skin growths externally differ in the following parameters:
- Size. Moles can be quite large, to the point that they can take up half of the face. And growths of viral origin usually do not exceed 1.5 cm.
- Structure. When you feel the nevi, the skin in the lesion remains smooth and has pores. Papillomatous formations have a loose structure or a pronounced increase in skin lines.
- Shape and color. Formations of a viral nature do not have a clear shape, they are asymmetrical, their color is pinkish or flesh-colored. Nevi can have different colors, are always symmetrical and have a circle shape.
Papillomatous neoplasms have vessels, and moles consist only of dermal cells.
Locations
Viral tumors are most often found in the groin, armpits, feet or neck. They are localized in areas of increased friction and severe hyperhidrosis. Moles can be located anywhere. Their appearance is not affected by humidity, temperature or other factors.
Causes and time of appearance
A mole is an individual feature of the body. The spot forms while the baby is in the womb. Babies are born with nevi, which remain with them throughout their lives. Various types of papillomas appear after the introduction of papillomavirus into the body during contact with a carrier of the infection.
These growths have the following distinctive features:
- rapid appearance;
- rapid (in a few weeks) generalization of the process;
- merging of individual growths into one large one.
If multiple growths appear on the skin, then this is a reason for a full examination to identify strains of papillomavirus and provide the correct therapeutic effect.
Should I delete it?
If a mole does not cause cosmetic or physical discomfort, then doctors do not recommend touching the areas of pigmentation. If there are objective reasons for getting rid of nevi, then it is under no circumstances recommended to remove a dangerous mole at home. A dermatologist-oncologist is well versed in the methods of removing moles, and after examining the patient, he will select the most optimal option.
The same is true with papillomas. Only a specialist can determine which papillomatous formations can be removed and by what method. To remove papillomas, there are the following methods:
- Chemical method. The use of special medicinal solutions that dry out the papillomatous formation and it disappears over time.
- Laser method. This method is preferred because after removing the growth, no traces remain and the patient quickly recovers after such manipulation.
- Cryodestructive method. Freezing tumors with liquid nitrogen. The disadvantages of this method are the high probability of relapse.
- Electrocoagulation method. Burning out build-up using high-frequency current.
- Radio wave method. To eliminate the tumor, the affected area of skin is dissected using radio waves.
- Surgical method. This method is used in cases where there is a suspicion that the growth has degenerated into a malignant form. In this case, the formation is cut off with a scalpel.
If the papilloma is small in size, then they try to resort to conservative treatment using specific antiviral agents.
Diagnosis of moles and papilloma
If a neoplasm is detected on the skin or mucous membrane, you should not wait for it to resolve on its own.
This will not happen.
To dispel all doubts regarding the oncogenic activity of the growth, you should immediately go to a specialist, preferably an oncologist-dermatologist.
The doctor will examine the tumor and decide what tests need to be taken.
What is the difference in tests and histology for papillomas and moles?
It all depends on what kind of neoplasm it is.
- 1. If it is a nevus that does not show signs of degeneration, then it will be removed, and the biomaterial will be sent to the laboratory to determine the nature of the neoplasm. If malignancy is present, histological analysis will show a positive result.
- 2. If HPV is suspected, the patient will be examined for the presence of papillomavirus and its type. After removing the growth, a histoanalysis will be performed to determine the presence of cancer cells.
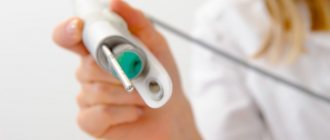
There is no difference in performing dermatoscopy and the initial examination of moles and papillomas.
The use of a dermatoscope is necessary so that the doctor can evaluate the structure of the skin formation and identify possible changes.
How to cure
To date, there is not a single proven treatment for HPV in the world.
The tactics for combating papillomas and condylomas are as follows:
- removal of formation;
- antiviral therapy – to suppress the activity of the virus;
- immunomodulatory therapy – to improve the functioning of the immune system.
To get rid of the growth, various methods are used:
- laser removal;
- cryodestruction;
- radio wave exposure;
- electrocoagulation;
- chemical removal;
- traditional surgery.
The choice of method is made by the doctor depending on the type of formation, its location, size, etc.
Treatment of moles and papillomas
Therapy will depend on the type of tumor.
- 1. After removal of a mole, as a rule, no treatment is required, unless it is malignant. In case of degeneration, the patient will continue to be treated by the oncologist.
- 2. If the PCR analysis confirms the presence of the virus, this means that the neoplasms were provoked by papillomavirus. After they are removed, the patient will be prescribed antiviral therapy. The results of the analysis will also answer the question regarding the possibility of degeneration into an oncological disease.
The use of medications to remove papillomas is possible only with the approval of a doctor.
Since the prognosis of the disease with unauthorized removal of growths can be sad.
Of the products that are sold in the pharmacy chain for the removal of papillomas, the following are very popular: Salicylic acid, Podophyllin, Feresol, Superclean.
If there is no effect, more radical methods are used to remove growths.
When growths degenerate into a malignant neoplasm, the method of surgical excision is used.
In the area of special attention
It's easy to miss melanoma developing from a mole. And pigmented areas of the skin are at risk of epithelial degeneration at the cellular level. The sharp growth of a nevus should be a warning first of all.
Additional evidence of cell transformation into cancer is:
- Blurring boundaries;
- Pain on palpation;
- Color change;
- The appearance of bleeding;
- Leakage of fluid from a mole.
Important!
The appearance of such signs is grounds for immediately visiting a doctor!
Failure to consult a specialist in a timely manner can cause the progression of cancer and the development of metastases.
Cryodestruction
This removal method is only used for skin tags. It consists of a short-term effect on the formation of liquid nitrogen. Pathological tissues are destroyed by flash freezing.
Cryodestruction
The advantages of cryodestruction include easy tolerance by the patient, no need for anesthesia and no risk of scar formation. Disadvantages are difficulty in controlling the depth of impact and a longer rehabilitation period.
Manifestations of HPV in various areas of the skin and mucous membranes
| Type of papilloma | Description of symptoms |
| Simple or vulgar papilloma | Popularly, this variety is often called a “wart.” They are most often located on the back of the hands, on the knees of children. Typically these are dense, knobby growths with a hard surface of horny substance. Warts often reach more than 1 mm in diameter and can merge with each other |
| Papilloma in the mammary ducts | When intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland develops, symptoms are most often associated with fluid discharge from the nipple (clear or mixed with blood). If the papilloma in the milk ducts reaches a size larger than a pea, the mammologist can determine it during an examination |
| Flat papillomas | Flattened growths on a wide base with a smooth or rough surface. They are usually localized on the skin of the face and neck, in the armpits, and under the mammary glands in women. These bumps retain the color of normal skin or become darker shades. Shape: round and oval. Average sizes are 3–5 mm. Flat papillomas often cause discomfort in the form of itching and burning, especially when sweat gets on them |
| Acrochords (thread-like papillomas) | They look like a broken thread, a round or oval papilla on a stalk. Most often they appear in the neck area, on the eyelids, and in the armpits. The consistency is elastic, the color varies from flesh to shades of yellow and brown. Average sizes reach 5–8 mm. They can become inflamed if injured by clothing or a bag strap. |
| Condylomas acuminata | Transmitted through various sexual and household contacts. They occur in the groin area and affect the mucous membranes of the external genitalia, vagina and cervix, and bladder walls. They look like a cockscomb. Color - pearl, pink, flesh. Sizes vary from 1 to 10 mm |
| Laryngeal papillomatosis | If laryngeal papilloma appears, the symptoms of the disease appear in the form of characteristic growths in this part of the respiratory tract. Often with this type of papillomatosis, the vocal cords are affected. Difficulty breathing and speaking |
| Plantar papillomas (spikes) | The “body” of a plantar wart does not grow on the dense surface of the foot or in the periungual space, but goes deep into the soft dermis (inner layer of skin). First, a small bump appears, similar to a callus, but without liquid contents inside. The bubble then turns white or yellow. The rough surface, unlike calluses, is not covered with a skin pattern; dark areas—clogged capillaries—can be visible through it. Spine diameter – from 2 to 12 mm |
| Papillomas in the throat | When papillomas develop in the throat, symptoms are noticeable on the palatine tonsils, uvula, on the walls of the larynx, and the mucous membrane of the initial part of the esophagus. Single growths may not show their presence in the pharynx; multiple growths cause hoarseness, coughing, and attacks of suffocation. The patient complains of frequent sore throats, acute respiratory infections, bronchitis and pneumonia. Symptoms of esophageal papilloma are similar to those that occur with reflux esophagitis - heartburn, belching |
Folk remedies
On the Internet you can find many recipes and techniques for removing papillomas and condylomas. However, you should not self-medicate. Only a doctor can safely and effectively get rid of the problem. Any attempts to bandage the formation with thread, cauterize it with celandine juice and other popular folk methods can provoke complications.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter