Causes of psoriasis in children
The exact causes of psoriasis in children have not yet been identified. However, it is known that symptoms are provoked by a shortening of the life span of skin cells.
In patients with psoriasis, these cells live several days less than expected. They die before they can be replaced by new ones. As a result, an accumulation of dead scales occurs on the skin, which layer on top of each other and cause inflammation.
The risk group includes children with the following disorders:
- weakened immune function;
- metabolic problems;
- endocrine pathologies;
- diabetes;
- skin injury;
- the presence of parasites in the body;
- problems with the nervous system;
- infections (for example, flu or sore throat);
- liver pathologies.
There is also an opinion that psoriasis occurs more often in children with a genetic predisposition to it.
More often, psoriasis in a child (photo available on the Internet) is diagnosed in winter. This may be due to decreased immunity and the aggressive effects of cold on the skin.
Find out more
Mechanism of disease development
The disease progresses in different ways.
Psoriasis is characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission. There are several factors that trigger the development of the disease. These include:
- temperature changes;
- change in climate zone;
- damage to the skin in any form;
- the presence of a viral or infectious disease;
- poor nutrition;
- influence of external negative factors;
- long-term treatment with medications;
- constant stress and insomnia.
It should be noted that if parents have a predisposition to this disease, it is not at all necessary that it will appear in their children. Each child is individual and his body tolerates this or that load in its own way.
In this regard, one child has enough malnutrition to provoke psoriasis, while another will easily tolerate all the above-mentioned moments and will not suffer from these diseases.
The initial stage of psoriasis in children
The initial psoriatic stage in children is somewhat different from the situation in adults:
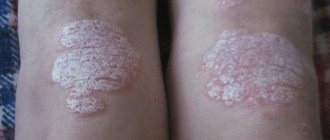
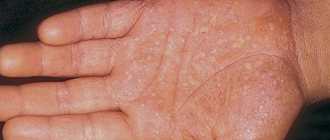
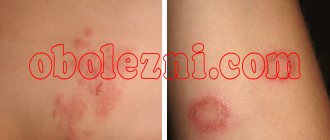
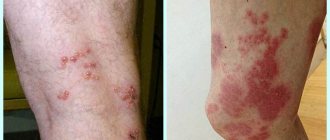
- First, red spots appear on the child's skin. Usually - in fold areas. Less often - on the head, face and genitals. Very rarely - on the feet and palms. The rash is similar to diaper rash, but the main distinguishing feature is peeling. Photos of the initial stage on the Internet will help you become more familiar with these manifestations of psoriasis in a child.
- Over time, scales and crusts form on the formations. Some papules increase in size and merge with each other.
- The child is bothered by intense itching.
Psoriasis in adolescents is often similar in symptoms to pathology in adults. In infants, papules may be smaller.
Since psoriasis in children is common, there are many photos of the initial stage on the Internet.
Medicines that will help your child
It is very important to start treating the psoriasis shown in the photo at the initial stage and continue treatment until the plaques completely disappear. Therapy is usually based on the use of local drugs. Lesions on the child’s body are regularly treated with glucocorticoid-based ointments.
WE RECOMMEND YOU TO WATCH:
Subtypes of childhood psoriasis
Psoriasis has several types. They are distinguished by the nature of symptoms and localization of the rash:
- Diaper subtype. Formed in babies up to one year old. The rash usually appears on the buttocks. It is difficult to diagnose the pathology due to the similarity of symptoms with irritation. Photos of psoriasis in infants clearly demonstrate the situation.
- Plaque-like. Or ordinary. The most common not only in children, but also in adults. Reddish spots are visible on the skin, slightly rising above the general surface. The spots gradually grow in area and become covered with silvery, easily detachable scales. May appear in different areas. However, more often - in the fold areas. It is also often possible to notice psoriasis on a child’s head.
- Teardrop-shaped. The formations are small and drop-shaped. It often develops into plaque psoriasis, but may simply disappear over time. Between the ages of 4 and 5 years, this subtype usually appears due to a streptococcal infection.
- Generalized. Appears quickly and unexpectedly. Affects large areas of skin. The formations are pustular and painful. May cause complications in the form of pathologies of the heart and kidneys.
- Pustular. Appears at the age of 7 years. It rarely happens before this age. The skin swells and becomes covered with blistering formations with liquid inside. Often the disease occurs in conjunction with inflammation of the lymph nodes. Photos will demonstrate these signs of childhood psoriasis more clearly.
- Erythrodermic. It is formed due to improper thermoregulation of the body. The rash affects large areas and is very flaky and itchy. Over time, the skin peels off. This type of psoriasis can cause death. Especially for kids.
- Psoriasis of the flexor surfaces. Formed in fold areas. The formations are smooth and convex. There is no peeling.
- Nail psoriasis. Formed on the nail plates.
- Arthropathic. Affects joints. Muscles lose mobility, joints and fingers swell.
In addition, psoriasis is divided depending on the time of year when it appears. In children - usually in winter and late autumn. Due to different forms of psoriasis, symptoms and treatment in children may differ slightly.
Nail damage
Yes, this pathology can also affect children, especially if the disease is advanced. However, this is quite rare. The nail literally decomposes. And the nail bed will be exposed. The main thing is to notice the symptoms of damage to the nail plate in time. They are:
- on the nail itself you will notice small depressions similar to dots;
- the nail plate itself will begin to become cloudy;
- If you press on the nail bed, the child will feel pain.
Symptoms of psoriasis in children
Symptoms depend on the stage:
- Progressive. Small formations of a reddish hue. They itch and peel. Gradually they grow in volume and spread. Over time, cracks form on the rashes. Minor bleeding is possible. If the course is severe, the child may experience a rise in temperature, enlarged lymph nodes, swelling and thickening of the skin (these symptoms of psoriasis in children are rarely shown in photographs).
- Stationary. The rash stops growing and spreads. The degree of peeling is reduced.
- Regressive. The formations smoothly dissolve. After them, depigmented rims form on the skin surface.
During the period of remission, all symptoms go away. The duration of this time depends on the care taken in caring for the child and his menu. Relapses are often triggered by infectious diseases.
Unlike adults, little patients have almost no terminal film.
Scalp damage
On the scalp, psoriasis appears as red spots that are covered with white plaques. All this constantly itches, causing a lot of inconvenience to the child.
The initial symptoms will be:
- The skin will turn red.
- Afterwards it will soften a little.
- Single rashes with peeling will appear.
- If treatment is not timely, the plaques will begin to merge.
Treatment of psoriasis in children
Since the pathology is chronic, it cannot be completely cured. Therefore, the key goal of therapy is to increase the duration of the remission period, as well as quickly relieve symptomatic manifestations.
Treatment of psoriasis in children includes several areas:
- Drug therapy. Includes both preparations for external application and systemic preparations. The latter are usually in the form of tablets. At first, especially if the flow is fairly mild, they resort only to external compounds. They relieve inflammation and soothe the skin.
- Treatment menu. Proper nutrition for psoriasis is the basis. The child should not be given fried foods, high-fat meat, butter and lard, baked goods, sweets (especially chocolate), fatty dairy products such as cheese and sour cream, strawberry and strawberry fruits, and any citrus fruits. It is also worth limiting salt.
- Physiotherapy. Also more often prescribed to adult children. Usually, for childhood psoriasis, photo-, UV- and laser therapy give good results. Salt baths are used less often.
- Psychotherapy. Suitable for adult children and is designed to relieve internal psycho-emotional stress, which can provoke an attack of rash.
- Natural treatment. Includes short sunbathing.
In case of psoriasis in children, the causes and treatment of the pathology are determined exclusively by the doctor - after analyzing the symptoms and accurately diagnosing the patient’s condition.
Treatment of psoriasis in children with folk remedies
Before using any of the traditional recipes, you should consult your doctor. Especially with psoriasis in newborns (photos of the consequences of improper therapy, unfortunately, are rarely published).
Popular recipes:
- Flax infusion. One tablespoon of seeds is poured into a glass of boiling water. Pour into a thermos and let it brew overnight. Drink 0.3 or 0.5 cups on an empty stomach. The course duration is two weeks.
- Kalanchoe compress. A paste is made from the leaves of the plant. Apply the mixture to the affected area and secure with a plaster. Keep for 30 minutes.
- Celery compress. The root of the plant is thoroughly crushed. The resulting mixture is applied to the affected areas and kept for 2 hours. The procedure is daily.
Traditional methods can serve as prevention and adjuvant during the period of main therapy. Using them separately and without taking medications is ineffective.
Otherwise, symptoms may worsen and immune function may decrease. With some types of psoriasis, serious disturbances in the functioning of internal organs can occur. This is what will happen if psoriasis is not treated.
Treatment of psoriasis in children with medications
Most often, drug therapy includes the following types of drugs:
- Ointments, gels and creams. Designed to relieve symptoms and soothe the skin. The drugs relieve inflammation, reduce swelling, relieve itching and redness. For example, for psoriasis in children on the scalp, theophylline ointment is often prescribed. One product can perform several functions, but more often several formulations are prescribed in combination. Separately, an antibacterial ointment may be prescribed to prevent infection. In severe and advanced cases, hormonal ointments are used. However, they are not recommended for young children.
- Desensitizers and sedatives. Usually come in tablet form. Designed to calm the child and relieve symptoms. Children are often prescribed valerian tincture.
- Antihistamines. Relieves itching and inflammation. For acute attacks, injections are prescribed. In other cases - tablets.
- Tranquilizers. Occasionally prescribed to adult children.
- Vitamins. Needed to strengthen immune function. Indicated products include ascorbic acid, vitamins B12 and B15, as well as vitamins D, A and E.
- Pyrogenic agents. Needed to enhance the body’s protective activity and harmonize the permeability of vascular walls. Indicated for patients over 3 years of age.
- Glucocorticoids. Oral hormonal drugs. Indicated for serious cases.
For psoriasis in children, medication is prescribed by the doctor.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of psoriasis is made by a dermatologist or pediatrician. This happens primarily through external manifestations. It is quite easy to recognize the disease by the characteristic foci of inflammation. Usually, an external examination is enough to make a diagnosis, since the manifestations of dermatological rashes and changes in the skin are typical only for psoriasis.
Diagnosis of psoriasis is made by a dermatologist or pediatrician
In some cases, particularly during the neonatal period, these symptoms are often not enough to make an accurate diagnosis. To do this, a small piece of skin is taken for biopsy, which is examined by a pathologist. Based on the examination of the tissue sample, a conclusion is given about the presence or absence of the disease. In this case, a blood test will not give results, since the course of the disease is only external. Complete damage to the body occurs in some severe forms. In such cases, general exhaustion of the body, dehydration, and water-salt imbalance are observed.
In some cases, joint damage may occur. Then pain is noted in these areas. An examination for psoriatic arthritis is prescribed: x-rays, blood tests.
Hemoscanning
One of the most modern methods of examining a patient for the presence of psoriasis is blood hemoscanning. This method is quite controversial.
Its principle is to visually examine blood using a powerful electron microscope connected to a computer. A drop of the person's blood is placed on a glass slide, and the plasma and enzyme structures are examined using high magnification. In the presence of psoriasis, there are characteristic blood changes that cannot be noticed with other examination methods.
One of the most modern methods of examining a patient for the presence of psoriasis is blood hemoscanning.
This method is quite informative; it can be used to recognize many diseases, including psoriasis in various forms of its manifestation. But it cannot be used as the only diagnostic method; it must be used in conjunction with other, more traditional methods.
Prevention
Particular attention should be paid to prevention in cases where there is a genetic predisposition:
- carefully monitor the cleanliness of the skin;
- monitor the surrounding air and humidity, they should be within normal limits;
- The baby’s clothes are chosen to be loose, made from natural materials;
- The mother of the child, if she is breastfeeding, should carefully monitor the diet, excluding fatty fried foods from it;
- The family environment should be calm and friendly.