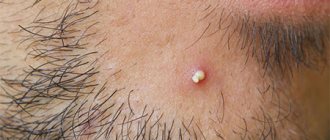
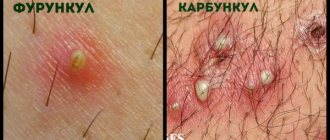
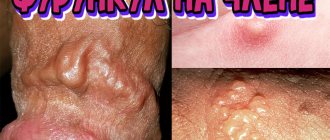
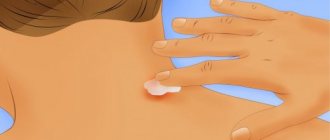
How many days does a boil take to mature - stages of development
Can a boil last a long time? Why does it take so long? The process of ripening of an abscess goes through several stages:
The process of ripening of an abscess goes through several stages
- Infiltration - counted from the moment the infection penetrates the layers of the dermis. Initially it manifests itself as hyperemia with swelling and pain, without definite boundaries. At the site of injury, itching, pain when pressed, and local pulsation are felt. Swelling depends on the number of blood vessels passing through the affected areas. The development time of the stage is about 4 days, with a gradual transition to the secondary stage. During this period, enlarged lymph nodes are detected.
- Maturation is indicated by the appearance of a purulent core. The boundaries of the lesion are clearly marked, the head of the rod is clearly visible. The secondary maturation time is 4 days, then there is a gradual decrease in the level of inflammation. The result of the stage is a mature boil. Pus begins to come out.
- Autopsy - after a week, the formation is opened independently (breakthrough of the boil), with the removal of purulent contents and gradual cleansing of the wound surface. Over time (after it bursts), after the final cleaning of the wound, self-healing of the tissue occurs, with the formation of a scar. Traces of necrotic changes practically do not disappear - the skin becomes hard, with a slight bluish tint.
How long can a boil take to heal? With the normal development of the disease, the entire process (with breakthrough) will take from 10 to 14 days; if you use auxiliary therapy, the cure will take about a week. It all depends on the general condition of the body and the functioning of the immune system.
Complications when a boil occurs can arise from attempts to independently squeeze out the abscess - the process may further spread through the tissues and purulent bacteria enter the bloodstream.
Prohibited methods of influencing a boil
The boil may not go away if you do the following:
- try to pierce, cut or squeeze out a boil yourself;
- apply wet compresses to the boil;
- use only traditional medicine methods for treatment;
- overheat the sore spot in baths, saunas, under the sun;
- stretch the skin around in the hope that it will open on its own.
The danger when squeezing out a boil on your own is the spread of infection. Pressing on the abscess leads to damage to the thrombosed vessels. Blood clots spread through the veins of the head. Inflammation of the meninges, sepsis, or new lesions may develop.
If he doesn't mature
If the maturation of the head of the boil at the first stage lasts for more than four days, you should seek professional help. Postponing a visit to the doctor can result in:
If the boil does not break out, be sure to inform your doctor about it.
- critical temperature levels;
- spread of the inflammatory process;
- abscesses;
- vascular thrombosis;
- meningitis;
- sepsis, etc.
When contacting a medical institution, a diagnosis will be made to determine the causative agent (the root cause), based on the results of which symptomatic treatment will be prescribed. If the boil does not break out, be sure to inform your doctor.
What antibiotics are used to treat furunculosis
Penicillin (ampicillin, bicillin, amoxicillin, ampiox). One of the most effective drugs intended for the treatment of inflammatory processes on the skin.
Cephalosporins (cefuroxime, cephalexin, cepphim, cefazolin). Used to stop the spread of the infectious process.
Macrolides (azithromycin, erythromycin, sumamed, macropen). Used in case of complications:
- temperature rise,
- feverish condition of the patient.
How to speed up maturation
What to do if the boil does not ripen? First you need to make an adjustment:
- nutrition - remove sweet, fried, salty, spicy, smoked foods from the daily diet;
- take vitamins, minerals and dietary supplements (yeast);
- normalize the amount of water consumed - up to 2 liters per day;
- practice body hygiene at least once every 24 hours.
Drug therapy
What if the boil does not ripen? The process of boil maturation can be accelerated by:
- ultraviolet irradiation - prescribed to increase immunity and destroy harmful microorganisms, regenerate damaged cells, improve oxygen supply;
- thermal effect - to accelerate the removal of purulent contents from the wound;
- wiping the skin around the abscess with antiseptic drugs - hydrogen peroxide, boric alcohol, iodine, salicylic acid;
- applying applications containing ointments - "Ichthyol", "Vishnevsky", "Tetracycline", "Erythromycin" - to accelerate the process of ripening of the boil;
- applying dressings with antibiotics - used after the opening of the abscess (after the rod has come out), to stop the spread of the inflammatory process and disinfect dead tissue.
If within 7 days the patient understands that the boil does not want to open (break through), the duration of the process is longer, then he needs to consult a surgeon.
Surgical procedures
If the boil does not go away for a long time, despite conservative treatment, then they resort to the help of a surgeon. The doctor administers local anesthesia and opens the growth with a scalpel. After opening, the wound surface is cleaned of pus, the necrotic core and dead tissue are removed.
If the boil does not go away for a long time, then resort to the help of a surgeon
A drainage is inserted into the wound for five days, after which it is removed (on the 5th day). The surgical field is covered with a bandage with an antiseptic solution, additionally moistened with antibiotic ointment. At the same time, a course of antibiotic therapy, vitamins and immunomodulators is prescribed.
The secondary method is to remove the boil with a laser - to speed up the healing process, the abscess is burned out with a laser, along with the necrotic contents. The entire treatment period takes place in one procedure and takes no more than half an hour. This manipulation is considered the most modern and safe, not leaving ugly scars after healing.
What to do at home
To make the boil open faster, the affected area can be lubricated with folk remedies:
- applying aloe leaves, cabbage, grated beets to the affected surface;
- anoint the affected area with aloe juice;
- treatment with a baked onion - after baking, it should be cut in half and applied to the sore spot, etc.
After how many days can treatment be done with folk remedies? From the very beginning, from the moment redness appears on the skin. When opening a formation, these methods are not recommended. The disease should go away within 7 days.
If a boil develops on the face, then home therapy is not suitable - in order to avoid an unsightly scar, it is better to seek medical help. Boils break through the skin, purulent masses come out, and after healing the tissues become scarred. The face cannot be covered with clothes, and such scars do not decorate anyone.
How does the human factor influence this problem?
If there are many reliable and proven folk methods for treating cheria, they help many people cope with this unpleasant phenomenon. Unfortunately, this does not always happen and the person himself can harm himself using different recipes. Not all folk methods from the Internet are correct, effective and positive, and many even do more harm than good.
Frequent reasons why a boil does not ripen or open are precisely these processes:
- Incorrect use of traditional medicine, failure to comply with proportions and measures
precautions.
- Using some unknown recipes that can have the opposite effect.
- Independent acquisition and use of potent pharmaceutical drugs and antibiotics.
- A person is constantly in the cold and the boil does not have the opportunity to ripen.
A person’s carelessness will be a factor in the fact that he will have to be treated for a very long time, and the process of maturation and breakthrough of the boil will become more painful than is the case in standard cases. If a person buys pharmaceutical drugs without taking into account the usual antiseptics, without the recommendation of the attending physician, he risks his own health and even life.
If the boil does not mature for a long time and does not burst through the fault of the person himself, he may encounter phenomena such as a strong increase in body temperature and an increase in the density of lymphatic fluids.
Preventive actions
To prevent the occurrence of suppuration, a number of rules should be followed:
To prevent the occurrence of suppuration, a number of rules should be followed
- Maintain hygiene standards at all times;
- avoid damaging the leather surface with synthetic or rough clothing;
- use products that reduce sweating;
- Check your blood sugar levels periodically;
- conduct seasonal vitamin therapy;
- normalize the daily routine;
- avoid constant stressful situations;
- cure colds in a timely manner without turning them into chronic forms;
- for any damage to the dermis (scratches, splinters, small cuts), treat with special antiseptic preparations;
- reduce the use of antibacterial soap.
To prevent the development of complications with existing furunculosis, there are separate rules of behavior:
- It is forbidden to heat the site of inflammation using heating pads or hot objects;
- during the acute phase it is necessary to avoid taking baths and visiting saunas;
- Take a shower regularly – at least once a day;
- do not touch the affected area, do not comb;
- If additional foci of formation appear, seek qualified help.
Possible complications
Spontaneous opening of chiria threatens the spread of inflammation to the healthy layers of the epidermis. The bacteria then enters the bloodstream, causing irreversible consequences.
Dangerous furunculosis in the face: forehead, nose, nasolabial triangle. The process of suppuration can affect areas of the brain. The clinical picture must be treated in a hospital. Proper care and health care will help avoid the development of uncomfortable formations.
If removed and healed incorrectly, a scar may remain.
The boil can come out again and again, form an abscess, and lead to sepsis. If stye appears on the eye, it should not be squeezed out. This may cause visual impairment. The article has been verified by the editors
Summarizing
After we have dealt with the main stages of the ripening of boils, it remains to understand what the danger is of opening an immature abscess on your own. Some patients try to squeeze out the annoying pimple to speed up the maturation process.
It is strictly not recommended to do this - having broken through, the pus will fall on the surrounding tissues and into the bloodstream. Self-medication in this case threatens necrosis of surrounding tissues and blood sepsis. Without timely treatment, sepsis will lead to the death of the patient.
How dangerous is treatment at home? A ripening boil can burst both outward and inward. The opened abscess will begin to slowly melt the necrotic core, simultaneously melting the adjacent tissues. What should be done in this case? Urgently seek help from your local clinic.
Standard ripening is when the rod comes out of the opened boil and does not decompose inside the dermis. Specialists should deal with this problem, even if we are talking about boils in the buttock area. A boil can develop in any area except the palms and soles - there are no hair follicles there.
Did you know that Staphylococcus aureus normally lives quietly on the surface of the skin of all people? Only if the skin is damaged and gets into the wound, vigorous activity begins, followed by reproduction and spread.
Reasons for the breakthrough
The harmful microorganism enters the body through skin damage due to poor hygiene and decreased immune defenses.
Weakening of immune defense occurs for the following reasons:
- Chronic diseases, infectious processes.
- Metabolic disorders: diabetes, obesity.
- Dermatological diseases: eczema, scabies, atopic dermatitis, prurigo.
- Long-term use of glucocorticosteroids, drugs whose action is aimed at suppressing the immune system.
- Increased sweating.
A purulent abscess in the area of the auricle and nose occurs due to exposure to mucus and pus from chronic rhinitis, adenoiditis, otitis, and sinusitis.