A fairly common complaint that women go to the doctor with is acne on the labia.
Unfortunately, the term “pimple” is not a medical term and can include a number of very different conditions and manifestations.
In general, rashes on the genitals (pimples near the labia, in the groin and perianal area) are included in a separate group of symptoms.
Classified as genital lesions.
Pimples near the labia can be a sign of over a hundred different diseases.
Not all of which are related to sexually transmitted infections.
In addition, with some diseases, rashes can additionally be observed in the oral cavity and other parts of the body.
Rash elements of different types and manifestations are found with herpes, lice, impetigo, candidiasis, allergies, boils, STDs, etc.
As a result, even seemingly harmless lesions require referral to a specialist.
Regardless of which doctor, dermatovenerologist or gynecologist, will conduct an examination and prescribe the necessary studies and tests to identify the cause.
A correctly established diagnosis is the key to successfully getting rid of the problem.
Classification of rashes on the labia
Before answering the question of why acne appeared on the labia, for a correct assessment of the pathology process, it is important to be able to differentiate the elements that make up the rash.
According to dermatological terminology, primary ones are distinguished, appearing on unchanged skin.
And secondary elements, developing from primary ones.
Actually, in most situations, various types of acne on the labia belong specifically to the primary forms.
They are divided into cavity and cavityless.
Sometimes the transition from primary to secondary forms occurs very quickly.
In such a situation, knowledge of the specifics and patterns of transformation makes it possible to determine the type of previous education.
Primary elements include:
- A spot (artificial, non-inflammatory and inflammatory vascular, pigmented) is a limited change in skin color without cavities or elevations. Vascular formations of an inflammatory nature up to a centimeter in size are called roseola, from one to five centimeters - erythema. Examples include roseola syphilitica, erythematous variants of dermatitis, and toxicoderma. Possible secondary forms are secondary pigment spot, scale.
- A blister is a raised, cavity-free formation, the result of edema with acute inflammation in the papillary skin layer, which quickly appears/disappears. It can form due to urticaria, insect bites, and toxicoderma. Such itchy pimples on the labia are usually pink, less often whitish in the central zone, and may be accompanied by a burning sensation.
- Papules, otherwise known as nodules, are hollow, raised elements that usually pass without a trace. Such formations vary in size, depth, and can be inflammatory or non-inflammatory in nature. They may transform into cracks, scales, secondary pigment spots, lichenification (thickening, pigmentation disorders, deepening of the skin pattern). In some diseases, papules merge to form plaques.
- A tubercle is a hollow, raised, dense element up to a centimeter in size, which usually leads to the formation of scars and cicatricial atrophy. It can also develop into ulcers, growths, scales, and crusts. The formation lies deep in the skin and is observed in cases of tuberculosis, leishmaniasis, leprosy, and tertiary syphilis.
- A node is a hollow, raised element measuring over a centimeter (up to 10 cm). It may end without a trace or with the formation of a scar, ulcer, secondary pigment spot, or crust. Formed in the subcutaneous tissue. A subcutaneous pimple on the labia of inflammatory nature may turn out to be syphilitic gumma, a typical manifestation of tertiary syphilis. Non-inflammatory is formed due to the deposition of metabolic products (“pimple wen” on the labia) or as a result of neoplasms (lymphoma).
- A vesicle, otherwise known as a vesicle, is a cavitary single- or multi-chambered elevated formation, up to 5 mm in diameter, with a tire and a bottom. On the labia with genital herpes, watery pimples with serous contents appear on erythematous skin. Also, blisters on the labia are filled with serous-hemorrhagic contents (blood pimples). When the vesicles are opened, weeping erosions, scales, crusts, and secondary pigment spots may appear, but usually in the end there are no traces left on the skin.
- Bubble, bulla - differs in size from the bubble (its radius exceeds a quarter of a centimeter, and can even reach several centimeters). Resolves without a trace or with scarring. It is also possible to form erosions, scales, crusts, growths and age spots.
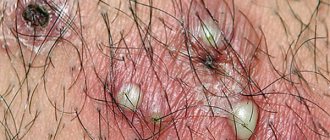
- Pustule, abscess - a cavitary deep or superficial raised formation with purulent contents (a pimple with pus is found on the labia). There are follicular, predominantly staphylococcal in nature, and non-follicular (superficial - phlyctena, deep - ecthyma), usually streptococcal. They can develop into crusts, erosions, spots, scars, ulcers, and growths. Follicular pustules form in the hair follicle, appearing on the labia as characteristic yellow pimples.
Secondary elements:
- scale – loosened horn cells in the form of a layer
- crust – drying contents of primary formations
- crack - a violation of the integrity of the skin that occurs due to a decrease in elastic properties
- abrasion - mechanical damage to the surface layer of skin
- erosion - a defect within the surface layer that appears when formations with a cavity are opened
- ulcer – deep skin defect
- scar - the formation of new connective tissue during the healing of skin defects
- cicatricial atrophy - cicatricial transformation without previous skin damage
- lichenification – thickening, dryness, compaction, staining, deepening of the skin pattern
- vegetation - growth of a skin area in an area of prolonged inflammation
- hyper- and hypopigmentation – weakening/increasing coloration of a skin area
How to treat blood pimples in intimate places at home
If you detect unpleasant inflammatory elements, do not panic. The pathological process is often caused by pathogenic microorganisms. To prevent the spread of infection, wash the affected area several times a day with antibacterial soap. Do not squeeze or pop a pimple. When you remove acne yourself, bacteria can spread to the nearby area, which will increase inflammation.
Most rashes go away on their own within 1-2 weeks.
To reduce the severity of unpleasant symptoms and speed up the recovery process, a number of measures are taken:
- Eliminating the irritant . Pathogens penetrate through skin lesions when the natural pH is disrupted. They stop waxing for a while. Use hypoallergenic personal hygiene products. Avoid the use of oils, they help retain bacteria in the follicles.
- Warm compresses. Clean gauze or cotton cloth is moistened in warm water and applied to the affected area for 5-7 minutes. To eliminate bacteria and accelerate the therapeutic effect, the tissue is moistened in a weak solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate).
- Use of antimicrobial ointments, broad-spectrum solutions. Levomikol, Tomicide, Roxithromycin inhibit the growth of pyogenic bacteria and prevent the spread of infection.
- Use of NSAIDs: Ibuprofen, Nisylit. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
Avoid visiting swimming pools and baths until complete recovery. Water and heat are ideal conditions for the growth of bacteria.
Causes of acne on the labia
There are several groups of diseases, the manifestation of which is acne on the labia (in adult women, in girls, in girls).
They can be triggered by infectious agents (bacteria, viruses, fungi), allergic reactions, autoimmune problems, tumor conditions.
Contribute to the appearance of a pimple on the labia:
- failure to comply with hygiene rules
- injury when shaving intimate areas, using irritants
- poor quality linen
- stress conditions, hypothermia, overheating
- decrease in the body’s defenses due to chronic pathology, pregnancy, due to taking certain medications, etc.
Preventive measures
Even if a problem such as rashes on the genitals is left behind, this does not mean that under the influence of the same reasons it will not return again. Women should draw certain conclusions, especially when the rash appears as a result of a disease, and try to eliminate this factor.
Regardless of the reasons for the appearance of acne, representatives of the fair sex should adhere to simple rules:
- Carefully observe intimate hygiene and use special products and baby soap for these purposes.
- Use comfortable underwear made from natural materials, selected according to size. It is not recommended to use thong panties as an everyday wardrobe item.
- Panty liners should be changed at least every 4 hours. To prevent the development of an allergic reaction, it is advisable to buy unscented hygiene products.
- If sores appear after shaving, you must use a depilatory cream designed for sensitive skin.
- You should follow all the doctor’s recommendations and do not stop therapy at the first signs of improvement.
- Before and after using the toilet in public places, it is strongly recommended to wash your hands with antibacterial soap.
- The ability of the immune system to resist infections is directly related to a healthy lifestyle. Therefore, it is worth monitoring the condition of your body and regularly undergoing preventive examinations at a medical institution.
With age, the risk of developing changes in the internal organs of the pelvis increases significantly and this is often manifested by a rash on the mucous membranes of the genital organs. For this reason, you should definitely visit a gynecologist at least twice a year and strictly follow his recommendations.
Blisters on the labia
Blisters appear at the sites of insect bites (fleas, lice, etc.).
They are characterized by itchy rashes, the severity of which depends on the type of insect and the sensitivity of the bitten person.
Scratching the elements can lead to infection.
Spontaneous urticaria appears as itchy, sometimes burning, blisters.
The state is called:
- taking certain medications
- eating certain foods
- concomitant diseases (chronic gastrointestinal pathologies, diabetes, leukemia, etc.)
- pathological pregnancy, menopause, etc.
The elements first have a pale pink color, which becomes white as the swelling increases.
Usually such blisters disappear within 24 hours.
Diagnosis and treatment
First, a smear is given to analyze the infection, a conclusion is made from the blood whether there is inflammation in the body, and according to indications, a pelvic ultrasound is performed to eliminate the risk of any neoplasms. If you have conditions such as fever, pain in the lower abdomen or pain when urinating, immediately make an appointment with a specialist.
Depending on the appearance of the rash, treatment methods are selected individually. Before visiting a doctor, it is better if you treat the affected area yourself with an antiseptic (alcohol, brilliant green, iodine, chlorhexidine) and start taking multivitamins to increase immune resistance. For local therapy the following will be prescribed:
- cream for children, chamomile or powder with zinc;
- soda or herbal baths, which should be taken on a daily basis.
The systematic approach consists of applying:
- Vitamins and immunostimulating drugs.
- Drugs that fight allergies.
- Antifungal ointments.
- Preparations based on acyclovir.
- Tablets that normalize the activity of the central nervous system (Vitamin B, mint, valerian).
- Antibiotics of the penicillin group if the infection has entered the circulatory system.
- Surgical method. It is used to eliminate fatty cysts, papillomas, and dubious rashes that grow abnormally.
Papules on the labia
Papules occur when:
- molluscum contagiosum
- secondary syphilis (characteristic is the absence of tangible symptoms - pain, itching, i.e. if a pimple hurts on the labia, this suggests another problem)
- Fox-Fordyce disease
- psoriasis
- folliculitis
- scabies
- lichen planus
- trichomycosis, etc.
Infection with molluscum contagiosum in adults occurs through sexual contact.
That is why the main place of localization of formations (unlike molluscum contagiosum in children) is the genitals and the areas around them.
In women, such a “pimple” is more often found on the labia majora, in the perianal area, and on the pubis.
The causative agent of the pathology is molluscum contagiosum virus type 2.
The incubation period varies from a couple of weeks to six months.
A typical element in women is a flesh-colored or pink rounded dense pimple on the labia, with a characteristic depression in the center of the nodule.
If an infected person accidentally or intentionally squeezes out a pimple of this kind, for example, on the labia, a white cheesy mass is released.
In some cases (often in HIV-infected people), a complication develops - the addition of a bacterial infection.
As a result, a “painful” pimple with pus and redness forms on the labia.
With relapse of secondary syphilis, papular syphilide often occurs.
These are densely elastic nodules in the genital area, anus, as well as on the palms and soles.
As a rule, such formations on the labia look like red pimples that are prone to cracking and peeling.
It is important to differentiate the disease from papular pseudosyphilis.
Then, due to hygienic violations, many pimples of a pale pink color, densely elastic consistency, similar to syphilides, form on the labia.
With Fox-Fordyce disease, women complain of severe itching, pimples on the labia, in the armpits, near the nipples, and on the pubis.
Such pimples on the outer labia are formed due to blockage of the ducts of the apocrine glands.
Quite often the condition worsens, the itching intensifies, and pimples on the labia grow before menstruation.
Interestingly, acne on the labia and other manifestations subside during pregnancy.
In postmenopause, regression of the disease can be expected.
In a situation where the labia is swollen, one pimple is located in pairs with another, there are characteristic scabies tracts, itching worsens at night, a diagnosis of scabies is likely.
With this pathology, scabious lymphoplasia can develop due to the body's response to the effects of waste products from mites.
That is, scabies looks like a hard pimple on the labia of considerable size.
A noticeable pinkish-red “blue” pimple with a purple, lilac tint on the labia is found in lichen planus, an autoimmune disease.
A pimple that appears on the labia after shaving is a manifestation of trichomycosis.
It is caused by aerobic corynobacteria in association with pigment-forming bacteria.
These are small pimples on the labia, usually yellow.
Less common, usually in tropical climates, are red and black pimples on the labia.
In the affected areas, sweat acquires a yellow color and a foul odor.
Papular rashes may be normal if:
- micropapillomatosis of the vulva
- seborrheic cysts (Fordyce granules)
- epidermal and pilar cysts
With micropapillomatosis of the vulva, the pimple is localized on the inner side of the labia.
Multiple symmetrical rashes (pinkish-white pimples) on the labia minora, rarely on the labia majora, occur during puberty.
The exact reason for their appearance is unknown.
A small soft pimple of the labia mucosa of a pinkish-flesh color is removed only for cosmetic purposes.
It is important to differentiate the formation from genital warts.
The characteristic distinguishing features are:
- symmetry of location (in condylomas it is chaotic)
- softness (condylomas are dense)
- no blanching in dough with acetic acid
An epidermal cyst is the most common cystic skin lesion.
It occurs when a cavity forms in the skin layer and fills it with horny masses and the production of the sebaceous glands.
Usually this is a single formation in the genital area, chest, face, upper back, neck.
The wall of the formation is thin and breaks easily.
If a pimple of this kind bursts on the labia, the cyst greatly increases in size and hurts.
A small epidermal cyst containing keratin is called a milia.
The formations look like white subcutaneous pimples with a predominant localization on the face.
In some cases, they appear on the labia and limbs.
They develop from the ducts of the sweat and sebaceous glands, hair follicles.
Seborrheic cysts are visible sebaceous glands, very small yellow-white formations.
Non-inflammatory papules with a villous surface, so-called. papulo-verrucous rashes are a sign of:
- anogenital warts
- condylomas lata with secondary syphilis
- bowenoid papulosis, etc.
Genital warts on the labia
Anogenital warts, also called condylomas acuminata, are caused by the human papillomavirus.
They are formations of a characteristic appearance: their lobed structure makes them look like a cauliflower stalk.
Such a pimple forms inside the labia, near the vestibule of the vagina, anus.
There are also varieties with a smooth surface and the color of raw meat (papular warts).
Separately, there is a giant Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma, which can form during pregnancy or in people with reduced immunity.
It is important to differentiate genital warts from broad ones, manifestations of secondary syphilis.
The latter are a dense purple, red dark pimple with a wide base on the labia.
Bowenoid papulosis is a relatively rare disease.
It also occurs when infected during sexual contact with the human papillomavirus (type 16, high cancer risk group).
The main complaint of patients is that a flesh-colored, brown or red pimple has appeared in the pubic area, inguinal folds, perianal area, and on the labia.
Gradually, such papules merge into plaques with a warty surface.
Approximately 3% of cases of the disease result in malignancy.
Disease detection methods
It is not a good idea to use medications before seeing a doctor, as medications can mask the clinical picture. Moreover, if not treated correctly, even a harmless pimple can develop into a serious disease, especially during pregnancy (women should not take many medications during this period or while breastfeeding). No person is able to correctly diagnose without an examination, so women should definitely visit a gynecologist. The doctor will order a general blood test, urine test, and take a smear from the vagina and urethra. Often the patient is offered to undergo an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
If you suspect a sexually transmitted disease, you should contact a venereologist. If spots appear on the legs, stomach, or buttocks, you should consult a dermatologist. The specialist will additionally prescribe scraping from the affected skin or examination under a special lamp. A biopsy is taken from condylomas and various neoplasms to rule out cancer.
Plaques on the labia
If a pimple appears on the labia, its size exceeds 1 cm, and in some cases, the skin in the affected area is thinned and whitened, we can talk about such primary elements as plaques.
Plaque lesions in women are typical for the following pathologies:
- neurodermatitis
- seborrheic keratosis
- lichen planus
- lupus erythematosus
- atopic dermatitis
- vulvitis candidiasis
- psoriasis
- Bowen's disease
- lichen sclerosus, etc.
With a disease such as candidal vulvitis (thrush), pimples on the labia and mucous membranes accompany the main manifestations.
These are curdled moderate/heavy discharge, swelling, redness.
Itching, which intensifies after sexual contact, a hygienic shower, during sleep, irritation, and a burning sensation in the perigenital area are also characteristic.
The problem is caused by the activity of yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida.
Lichen sclerosus - otherwise white spot disease, lichen sclerosus, vulvar kraurosis.
It appears in the form of clearly defined light spots, plaques, papules (“white pimples”) on the labia, in the inguinal folds, and vulva.
The formation of bloody blisters and erosions is possible.
Scarring often leads to fusion of the labia minora.
Bowen's disease is an intraepidermal formation (carcinoma) in the form of a sharply limited plaque with an uneven surface.
Usually detected in old age, it can develop into squamous cell carcinoma.
Pustules on the labia
Usually a pustule, otherwise a purulent pimple on the labia, does not exist for a very long period and may not even be noticed by the patient.
Superficial pustules quickly turn into crusts, while deep ones can form ulcers/erosions.
A group of dermatoses based on purulent inflammation of the skin is called pyoderma.
Pustular lesions are characteristic of:
- folliculitis
- impetigo
- hidradenitis
- syphiloid Sevestra-Jacquet and others.
Impetigo is a small superficial abscess with a convex red border.
The most common causes of the condition are staphylococci (80% of episodes) and streptococci.
A type of streptococcal impetigo in infants is post-erosive syphiloid Sevestra-Jaquet.
A problem arises with poor hygienic care for well-fed children as a result of the irritating effect of urine and feces.
Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicle caused by bacteria, fungi, etc.
Deep folliculitis is called a boil.
Boils are inflamed, swollen pimples on the labia, cone-shaped with a necrotic core.
After the rod is separated, an ulcerative lesion develops in its place.
The recurrent appearance of numerous boils occurs with furunculosis.
A conglomerate of boils is called a carbuncle; it is a dense, up to 10 cm in diameter, node with pus.
Hidradenitis is a purulent inflammatory lesion of the apocrine glands that develops in the genital area, navel, anus, nipples, and axillary area.
In an infant, papulo-erosive streptoderma may appear on the labia, skin of the perineum, buttocks, and thighs - dense bluish-red pimples.
Vesicles on the labia
Blistering formations, similar in appearance to “cold” pimples, on the labia and in the area of the vestibule of the vagina.
They are a sign of a viral infection – genital herpes.
This disease is caused by the herpes simplex virus and is prone to recurrence.
The typical form of the disease is characterized by itching, tingling, burning, and pain that precede the appearance of rashes.
The condition ends with the formation of crusts and areas of hyperpigmentation.
Chickenpox is an extremely contagious acute primary infection caused by a virus.
It is characterized by progressive rashes that appear in successive waves.
The disease is difficult to tolerate in adults and adolescents, newborns, and people with immunodeficiency.
In this case, rashes appear not only on the face and torso, but also in the mouth, on the labia.
They are a mixture of various elements, among which one can simultaneously identify itchy purulent large pimples, blisters, papules, and crusts.
Patients often complain that due to the fact that there are pimples on the mucous membrane and labia, it is painful to write and perform hygiene procedures.
Genital herpes
The disease is caused by two types of viruses:
- Herpes simplex virus 1
- Herpes simplex virus 2
It manifests itself as rashes in the form of bubbles with liquid filling, usually several vesicles (bubbles) located nearby and causing focal inflammation. Before the visible effect appears, severe itching occurs at the site of the lesion; at this time the virus is especially contagious.
Carriers of this virus are 90% of the world's population. The frequency of rashes directly depends on the state of the immune system. The lower the body's defense systems, the more frequent the rashes will be. With a strong immune response, herpes may not manifest itself for years. But at the same time, the person is a carrier of the virus. When conditions are favorable for the virus, visual damage occurs.
There is no cure for this virus. The human body produces antibodies to the virus, and subsequent damage is always easier to tolerate than the first.
Prevention of infection is a general strengthening of the immune system. According to statistics, women suffer from herpes more often, which is associated with a monthly weakening of the immune system caused by physiological characteristics.
Herpes is especially dangerous during pregnancy in the absence of antibodies. That is, if a pregnant woman encounters the virus for the first time, and the body has not developed natural protection. This threatens congenital deformities and pathologies in the fetus. In such cases, the pregnant woman is observed by an infectious disease specialist. Before this, a test is taken for HSV 1 and HSV 2, which determines the presence of antibodies in the body of the expectant mother. If a woman has never had the herpes virus, then during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, when all the vital organs and systems are developing, it is necessary to especially carefully monitor hygiene, since the virus is transmitted through towels and personal hygiene products, such as a razor.
Strengthening the immune system includes the following procedures:
- Frequent walks in the fresh air;
- Eating fresh vegetables and fruits is better than seasonal ones;
- Taking vitamins during the cold season;
- Maintaining a sleep and rest schedule.
Other lesions on the labia
Bulla
A bulla is a huge pimple on the labia, a blister with a diameter of more than 5 mm.
Such formations in most situations are a symptom of serious skin lesions - bullous dermatoses.
For example, bullous pemphigoid is an autoimmune skin disease.
With it, itchy spots and papules first appear, and in their place blisters later develop, gradually turning into erosions.
tubercles
Tuberous dermatoses are rare.
Tend to progress to ulcerative formations with subsequent scarring.
They can be detected in cutaneous tuberculosis, pyogenic granuloma and tertiary forms of syphilis.
Nodes
Nodes are deeply located formations of dense consistency.
They do not exceed five centimeters in diameter and are rarely localized in the genital area.
Diseases manifested by the formation of nodes include:
- lymphangioma is a benign tumor that arises from the lymphatic vessels
- hidradenoma – benign tumor of the sweat gland
- lipoma – benign tumor of adipose tissue
- tertiary syphilis, etc.
A separate problem is pathologies in the area of the Bartholin glands.
They are located symmetrically at the base of the labia majora.
When the lumen of the gland is blocked, secretions accumulate in it and a cyst forms.
If infectious agents penetrate into the lumen, the development of bartholinitis (inflammation of the gland) and abscess (painful node with a purulent cavity) is possible.
When to see a doctor
The pathological process can occur in different ways. The appearance of painful sensations, an increase in the size or number of rashes indicates the progression of the disease. Pyogenic bacteria quickly spread to adjacent tissues and can cause an abscess.
If unpleasant accompanying symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor. He will assess the condition and prescribe adequate therapy.