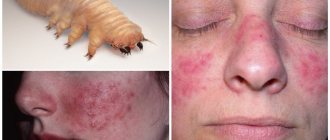
Scraping for demodex is one of the types of tests that are taken when there are signs of damage by the subcutaneous mite of the genus Demodex (which is an opportunistic microorganism). Two species parasitize humans: folliculorum and brevis.
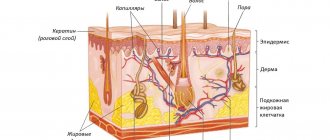
The first lives, mates, and reproduces in hair follicles, the second - in the sebaceous glands associated with them. Demodex feeds on fat and epithelial cells. This tick mainly affects women and older people with increased sebum secretion.
Infection of one person from another occurs mainly through direct contact.
Symptoms of the disease
Demodicosis manifests itself depending on the location of the scabies mite.
Symptoms specific to the eyes:
- Rapid eye fatigue.
- Angioedema is manifested by swelling around the eyes, similar to an allergic reaction.
- Hyperemia of the skin in the area of the eyelid margin.
- Severe peeling of the skin around the eyes, especially in the area where the eyelashes grow.
- Severe loss of eyelashes, which mostly fall out without roots. If the eyelashes fall along with the roots, this may indicate alopecia areata or telogen effluvium.
Manifestations characterizing demodicosis of the skin:
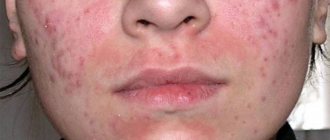
- Red spots, mainly in the face area.
- Increased secretion of sebaceous fat.
- Presence of follicles and pimples on the skin.
- Paleness of the skin.
- The appearance of areas of peeling on the face.
- Itchy skin.
- If demodicosis is prolonged and no therapeutic measures have been taken, then hair loss on the head begins.
Methods of infection
Infection with demodicosis can occur in two ways:
- directly from person to person in case of close bodily contact with a carrier of the disease (kisses, hugs);
- indirectly - through a shared towel, items for applying cosmetics, bed linen, feather pillows, wearing shared clothing.
There is a debate in science about the possibility of transmission of ticks from animals to humans, but thanks to scientific research it has been proven that the species that parasitizes the body of an animal is safe for humans.
Transmission occurs not only from an unhealthy person, but also from a healthy person who is a carrier. This parasite can exist on the human body and not manifest itself in any way; it is activated only when there are external and internal conditions associated with the weakening of the body:
- allergies;
- weakened immune system;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diabetes mellitus;
- stressful situations;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- liver pathologies.
Ticks exhibit peak activity in the heat, so exacerbation often occurs in the spring and summer. The likelihood of being affected by demodicosis increases with age; approximately 2/3 of those suffering from this disease are elderly. Scientists attribute this fact to the fact that with age the body secretes more sebum.
Demodex's favorite habitat is eyelashes. The ducts of the meibomian and sebaceous glands open between the eyelashes - this is their epicenter, it is comfortable for mites to live and reproduce in them. One follicle can contain up to 25 mites; they move at a speed of 8-16 mm/hour.
An ophthalmologist or dermatologist can prescribe a test to identify mites. Initially, the doctor examines the roots of the eyelashes for the presence of cylindrical dandruff, indicating the possible existence of parasites, and invites the patient to take an eyelash test for demodex. The test can be done in a private clinic without a doctor’s referral.
How to get tested for demodicosis
This disease is caused by subcutaneous mites that live in the sebaceous glands and hair follicles. They can remain in the human body for a long time without manifesting themselves. But if the work of the sebaceous glands is activated and against the background of a decrease in the immune system, symptoms of demodex occur, which are characterized by increased itching in the head, face and the appearance of rashes.
To make sure that the disease was caused by a tick from the genus Demodex, you need to get tested. This is human biological material that is tested in laboratory conditions. But the study should be carried out only when symptoms of demodicosis are present.
It is known that with this pathology the internal organs are not affected, the mite attacks only the upper layers of the epidermis, therefore scraping for demodex is carried out from the affected areas of the body.
An adult tick is oblong in shape and can only be seen under a microscope.
In small quantities these microorganisms are safe. Moreover, they regulate the acid-base and hormonal balance of epidermal cells. But if for some reason mites grow, they begin to multiply in the subcutaneous layer, causing symptoms of demodicosis disease.
What is it and why is it needed?
Scraping for demodex is a procedure for selecting biological material for the purpose of studying its microflora. When the mite multiplies in the subcutaneous layers, it leads to itchy skin.
Analysis is necessary in order to distinguish demodicosis from other similar pathologies.
When the result of skin scraping for demodex is ready, the doctor will be able to confirm or deny the presence of the disease, after which treatment will be prescribed, which involves the use of drugs that affect the nervous system of the scabies mite and prevent its further division.
How is the test for subcutaneous mites carried out?
Demodecosis has different localizations:
- Subcutaneous epithelial layer of the body, head and face.
- Tissues and circumference of the eyelids.
Therefore, the order in which the biological fragment is scraped will also depend on which segment of the skin material is susceptible to infection.
If there is a suspicion of demodicosis of the epithelial tissues of the eyelids, then a dermatologist takes an eyelash from the eyelid for analysis, which in this disease is easily separated from it. Then the eyelash is placed in a special solution, which serves as a kind of preservative. If demodex is present in the tissues of the eyelids, then parasites and their eggs will be found on the eyelash follicle.
A scraping from the face on demodex or from other skin surfaces of the body is taken as a smear. A specialist laboratory technician uses a cotton swab to remove biological material from the surface most susceptible to disease. Then this cotton swab is placed in a sterile plastic package, where information about the patient undergoing examination is also indicated.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, it means that a family of demodex mites and their eggs were found in the smear.
Treatment
Demodectic mange of the eyelids is treated by an ophthalmologist if the eyes are the only focus of the disease.
To treat demodicosis of the scalp, you should contact a trichologist .
A dermatologist will help you get rid of facial demodicosis . The disease can be treated only after confirmation of the diagnosis.
The main goal of treatment is to destroy demodex , create unfavorable conditions for it, increase immunity, eliminate hormonal disorders, gastrointestinal diseases and other factors that affect its development and reproduction.
Treatment of cutaneous demodicosis
The patient is prescribed products containing metronidazole, zinc, ichthyol and many other components. The duration of therapy is up to two months.
To avoid relapse, it is not recommended to stop using medications early.
Vitamins and antihistamines are prescribed internally . Less commonly, metronidazole. The patient is prescribed a diet.
It is necessary to exclude from the diet:
- alcohol;
- spicy food;
- sweets.
During the period of therapy you should avoid wearing cosmetics. Bed linen and towels must be changed daily. It is better to wipe your face with disposable towels.
Cosmetic procedures are also very effective against demodex. During mesotherapy, special drugs are injected under the skin to eliminate it. Cryomassage can also quickly get rid of ticks.
Treatment of demodicosis of the eyelids
Therapy is long-term , and premature cessation of treatment may contribute to relapse. It is necessary to disinfect bed linen and personal hygiene items.
Clean the skin of the eyelids and eyelashes with calendula tincture using a cotton swab. After cleansing the skin and drying it, apply a medicinal cream prescribed by a doctor (Demalan, Demazol and others). All inflamed areas of the skin are treated.
If there are symptoms of purulent damage to the mucous membrane of the eye, additional antibacterial eye drops (Tobrex, Tsipromed and others) are instilled.
In order to increase the effectiveness, drug therapy is supplemented with eyelid massage, ozone therapy, and the doctor can also prescribe medications to correct the functioning of the immune system and normalize metabolic processes.
A long-term absence of necessary therapy can lead to various infections and complications: acne, rosacea, seborrheic dermatitis and other diseases.
Therapy will be effective only with correct diagnosis . At the first symptoms, you should consult a doctor and do the necessary tests.
Video: About the most important thing: How to protect yourself from demodicosis?
Scraping in vitro
Where will a demodex scraping be most informative - in the laboratory or in other medical institutions?
The most informative analysis will be a scraping in a laboratory. In this case, it will be possible to identify the type of tick that attacked the skin and select the necessary treatment.
Depending on its type, the location of its distribution will be determined:
- Demodex brevis - this type of scabies mite lives in the sebaceous glands, so scrapings are taken from the affected surface.
- Demodex folliculorum is common in hair follicles, so taking 2-3 eyelashes will be enough for analysis.
If you are interested in where to submit a scraping for demodex, it is better to ask your doctor about this. He can refer the patient to a laboratory at a public clinic or to private medical centers. For example, in Moscow you can contact “ON CLINIC”, “Elegy”, “MedicCity”.
Progress
How to take tests for demodex (what type of material and how to take it) is decided by the doctor, depending on the type of manifestations.
The following biomaterial can be taken as a research subject:
- eyelashes, hair from the head or eyebrows along with the follicle;
- epithelium (scraping). Scraping is usually taken from the facial skin in the area of the nose, eyebrows, chin and interlash space;
- contents of the papule (pimple).
As an additional test, a complete blood count is sometimes taken. The goal is to identify additional pathologies: anemia, allergies, parasitic lesions, bacterial infections.
Skin scraping
To detect subcutaneous mites on the face in the presence of acne, ulcers and papules, scraping is done. For the procedure, an eye spoon or scalpel is used, which is passed over the affected surface, collecting epithelial particles.
The process of collecting biomaterial for analysis is painless. The resulting preparation is not highly informative, since there may be no mites on the outside.
An analysis taken from the skin of the face is placed on top of an alkaline glass slide (a few drops of 10% alkali are added), which is then examined under a microscope.
Superficial and skin biopsy
Epithelium can be collected by superficial biopsy. The essence of the procedure:
- glue is dripped onto degreased glass: cyanoacrylate, sulfacrylate or BF-6;
- apply glass to the affected area for 1 minute;
- remove it along with the adhered biomaterial.
Instead of glue, the doctor can use regular tape (test tape), which is applied to the affected area, then removed and pasted onto the glass. An alkaline solution is dripped onto the resulting biomaterial, then examined under a microscope.
Skin biopsy is the removal of part of the epidermis or the contents of the sebaceous glands using a scalpel (excision method) or a puncture needle (punch method). The method is traumatic, but the resulting material is the most informative.
It is kept in 10% neutral formaldehyde for 24 hours and stained with eosin or hematoxylin.
Extrusion
Squeezing is used to extract demodex from the sebaceous gland. Disadvantages of the method: it is traumatic, it is impossible to take analysis from a large area.
When the skin around the sebaceous gland is squeezed, a thread-like white mass (fat) is released from its duct, which is immersed in a special solution for subsequent dissolution. The resulting suspension is then examined under a microscope.
Eyelash analysis
If there are signs of eyelid inflammation, 3-4 eyelashes are carefully pulled out from above and below to test for demodicosis (eyelash test). The doctor holds the area where the hair is taken, preventing damage. The method is traumatic, but it is the only one available for eyelashes, allowing one to study the contents of the follicle.
The resulting material is placed inside a transport medium (glycerin or alkali solution). Directly on the slide, the follicle is squeezed out or kneaded for a more complete view.
The biomaterial can be placed in an Eppendorf tube (Eppendorf tube), a disposable microcentrifuge container of a conical shape that ensures absolute sealing of the contents. The epithelium and eyelashes are placed into it without a transport medium.
Eyelashes for demodex analysis
If it is indicated to take eyelashes for analysis, then you should not be afraid of the pain; the procedure for pulling them out is absolutely painless. Moreover, only 2-3 eyelashes are needed for the study. If demodicosis is present, the affected eyelash bulbs quickly separate from the skin.
In order for the analysis to give a reliable result, it is necessary to follow some rules:
- Do not wet your eyelashes the day before the test.
- Do not apply decorative cosmetics or medications to the eye area.
- When washing your hair, do not allow shampoo to come into contact with your eyes two days before going to the laboratory.
- Stop taking eye drops the day before going to the test. Exceptions are those cases when drug withdrawal may cause negative consequences.
If the symptoms of the disease are pronounced, but demodex was not detected in the tests, then it is worth thinking about the fact that the patient has signs of seborrhea.
Self-analysis
It happens that it is not possible to conduct an analysis for demodicosis in the laboratory. You can also make it at home. To do this, you need to collect several eyelashes during the day, and if scabies has developed on the skin, then stick adhesive tape to the rash, preferably overnight. The next morning she is squeezed between two glasses.
After this, any family member can go to the laboratory with the submitted biological material. After which a microscopic examination is carried out.
Despite these actions, this method of identifying the disease is not so informative. And sometimes the analysis is repeated in a laboratory setting.
Home collection of material
If the patient does not have the opportunity to undergo analysis in a specialized institution, you can collect biological material yourself. Rules for scraping for demodicosis:
If the patient has a rash that is accompanied by itching, then this is the body’s response to damage by Demodex.