Just a few years ago, the human papillomavirus was classified as a group of diseases of infectious etiology, infection with which was associated exclusively with the appearance of warts and growths on the skin.
Today, it has been scientifically proven that HPV infection provokes the emergence of a wider range of problems, which include genital warts on the genitals, the risk of malignant degeneration of tumors, as well as the development of cancer. According to the specifics of clinical manifestations, the characteristics of invasion and the course of infectious diseases, HPV types of low, medium, and high oncogenic risk are distinguished, which are worth discussing in more detail.
Features of the development of oncogenic viruses
HPV (human papillomavirus) are viruses divided into groups and types. A total of 120 of them are known. The types in women (16-56) and in men pose a particular danger to the body, as they can cause serious illness and death. Viruses are transmitted mainly through sexual contact. A person is least likely to become infected through wounds and microcracks.
Types of viruses are also divided into levels of risk of oncogenicity: high, medium and low.
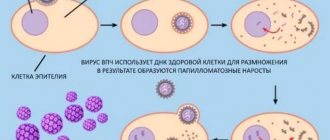
Once in the body, the papillomavirus produces special substances that facilitate penetration through the intercellular substance and further passage into the basal cells of the dermis. There he lingers. As soon as the papillomavirus DNA enters the human cell nucleus, it begins to rebuild. Before entering the nucleus, no changes harmful to the body occur.
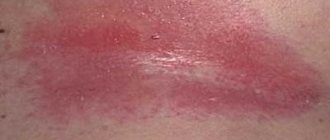
Along with the restructuring process, the cell changes its own DNA and pathogenic growth and reproduction begins. As soon as the processes of change begin, the cells grow and multiply in disorder, which is why neoplasms (condylomas and papillomas) appear on the skin and mucous membranes of the human body, which at first they may be indistinguishable from the natural color of the skin.
Women are most susceptible to the disease; papillomavirus causes diseases associated with the reproductive system, including oncology. The risk of infection is especially high at the beginning of sexual activity. Promiscuous sexual intercourse, neglect of contraceptives - all this can lead to the development of HPV.
Much less often, infections occur through dirty medical devices or during procedures (including cosmetic ones). HPV has an incubation period - usually 15-20 years.
Papillomavirus is divided in most cases into types, including:
- Type 16 – the most dangerous for women; if it enters the body, the risk of genital cancer is the highest;
- Type 18 – also dangerous, causing the appearance of condylomas when it enters a cell;
- Types 31-33 are also oncogenic, more typical when Bowen’s disease occurs and are located in the scaly layer of the epidermis.
- Types 51-56 – medium-high risk of oncology, the disease develops only in an environment favorable for the virus (for example, with reduced immunity).
The latter types are also capable of causing mutations in the female organs, and are the cause of infertility and menstrual irregularities.
What kind of virus is this
Papillomavirus is one of the most common pathogenic microorganisms. Moreover, the virus is widespread both in terms of occurrence in the population (and it is observed in almost 90% of the planet’s inhabitants) and in terms of the number of representatives (27 species and more than 170 types from harmless to oncogenic).
Types of human papillomaviruses differ in the method of transmission (through a handshake, kiss, dirty towels, sexual contact), and in targets (skin or mucous membranes, various parts of the body). If the functions of the immune system are not impaired, it inhibits the activity of the pathogen, and it remains in a latent state, sometimes for decades. But with weakened immunity, the disease manifests itself in the form of skin neoplasms. Different types of papillomavirus can cause vulgar or flat warts, plantar corns or genital warts.
Human papillomamirus was first recorded as a single species in 1971. Since then, knowledge about what types of HPV there are has increased. In 2003, the group was divided into 27 species and 5 genera. In 2010, the classification was revised so that the scientific names of the groups reflect the genus to which they belong. In medical practice, their significance indicates the main clinical manifestations of human papillomavirus infection.
How is HPV transmitted?
The cause of HPV can be not only unprotected sexual intercourse, but also:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- reduced immunity;
- disrupted eating patterns;
- consumption of low quality products.
It is worth noting that with frequent stressful conditions, the risk of suffering from HPV increases significantly.
Consequences and danger
Of course, the most dangerous complication of HPV 59 is cancer. Most often it affects the cervix. For men, the risk is much lower, but the chance of getting a prostate tumor still exists. In addition to this deadly disease, papillomavirus can cause:
- infertility;
- impotence;
- vision problems;
- hearing impairment;
- chronic intestinal disorder.
Remember that HPV of any type affects the entire body, although it affects the reproductive system most of all. If you miss the onset of complications, the treatment will ultimately be much more complex than with early therapy. So try not to be promiscuous, and also maintain good personal hygiene.
You can also learn about several facts about HPV: how you can become infected with it, as well as what tests you need to take.
What danger does papillomavirus pose?
In the absence of proper treatment, as well as constant exposure to adverse factors, can lead to the development of dangerous pathologies:
- restructuring of vaginal cells and uterine canals;
- development of cancerous tumors of the vagina and anus;
- oncology in uterine tissue;
- a warty-looking neoplasm on the external genitalia and anus;
- pathogenic formations in the mouth and larynx;
- growth of papillomas and condylomas on the genitals of men;
- damage to the mucous membrane of the eyes;
- cancer formations in the esophagus and nose;
- malignant formations on the feet.
Skin lesions are also an aesthetic problem. It is important to note that when new formations grow, they can involve nearby tissue in the process.
Thus, papillomas in the nose or larynx impair breathing and voice, and their occurrence on the male genitals leads to disruption of urinary function. The formations also provoke bleeding and bladder diseases.
Symptoms
If a person has papillomas or condylomas in the reproductive system area, he should urgently consult a specialist. When there are no external symptoms, it is possible that the disease is located inside the genital organs, or in the rectum area. The following symptoms will help determine this:
- problematic bowel movement, accompanied by pain and discomfort;
- a deceptive feeling of intestinal fullness;
- excessive flatulence, pain in the gastrointestinal tract;
- altered stool containing blood;
- causeless loss of body weight;
- feeling of weakness, dizziness.
When a doctor diagnoses the presence of genital warts in the rectal area, and the patient complains of any of the symptoms described above, they often talk about infection with HPV type 59.
People who are carriers of the infection or have a hereditary tendency to its occurrence should be attentive to their health and well-being. They must be registered with an oncologist, as well as monitor the status of the virus and undergo regular examinations.
Oncogenic classification of HPV
Oncogenic classification is the division of papilloma virus types into several large groups, indicating the degree of their danger. This is done in order to have a clear idea of which strains of the virus are dangerous for causing serious diseases and which are not.
First group
The first group is also called non-oncogenic. This includes HPV types 1,2,3,4 and 5. These papillomas do not degenerate into a malignant tumor and do not rearrange cells, forming mutations. The only thing that can happen is the formation of papillomas. If they are small and do not cause inconvenience, they are not removed and will not cause harm.
Second group
The second group is a low risk of cancer. It includes types 6, 11, 42-44. Vaccines have been developed against the most common ones (which are 6 and 11). If these strains are detected, the risk of cancer development is low. In order for pathology to begin, several factors are needed to provoke it.
HPV types in women and men.
People who are prone to cancer, have been exposed to radiation, or suffer from immunodeficiency should pay attention to this. Basically, neoplasms do not degenerate into malignant ones.
Third group
The third group is a high risk of oncogenicity. The types belonging to this group are 16, 18, 31-35, 45 and 51-56. These strains always provoke the appearance of cancer, which manifests itself mainly on the genitals.
Human papillomavirus and pregnancy
The formation of papillomas in expectant mothers is not an indication for cesarean section. Infection rarely poses a risk to pregnancy and fetal development. The exceptions are types 6 and 11 - they cause genital and anal condylomas, and during childbirth they come into contact with the skin of the fetus, causing infection. After the incubation period, the newborn may develop respiratory papillomatosis. The cesarean section method is used if there are condylomas in the mother’s body that interfere with the expulsion of the fetus or can cause bleeding in the woman.
Diseases caused by a virus
The human papilloma virus can cause not only oncology and pre-cancer diseases, but also benign diseases of the skin and mucous membranes. But due to the virus entering the body, some other equally dangerous diseases can arise.
When examined and tested, their cause becomes known. When the virus enters the body, it does not manifest itself immediately, being in a latent state. If it continues to remain silent, no treatment is required.
Among women
The HPV type in women (16-18 most often causes serious illnesses) can provoke not only cancerous tumors of the uterus, external genitalia and anus.
The virus can also cause health problems such as:
- cervical dysplasia;
- diseases of the mucous membranes;
- diseases of the mucous membranes of the genital organs;
- erosion of the uterus;
- different types of warts (flat, plantar);
- condylomas.
A patient may be diagnosed with several types of HPV at once; this phenomenon is not uncommon.
In men
Men can also be significantly affected by the development of human papillomavirus, although the incidence is lower. Usually infected are men who are sexually active and often change sexual partners.
In this regard, diseases arise:
- genital warts on the genitals;
- oncology of the genital organs;
- difficulty urinating;
- sexual dysfunction.
If tumors appear, you should immediately seek help from a urologist or venereologist for further removal.
Transfer methods
The most common route of transmission is unprotected sex with HPV carriers . The risk of contracting the virus in the first three years after first sexual intercourse is 46%. That is why those women and girls who can only have one sexual partner are added to groups traditionally at risk, for example, prostitutes. In particular, a high percentage of infections occurs among adolescents. Infection can occur through any type of sexual contact, including anal and oral.
Another method of infection is infection of newborns passing through the birth canal. If the expectant mother is a carrier of HPV, the child has a high chance of catching the virus during natural childbirth. Subsequently, such children may develop laryngeal papillomatosis, a viral disease characterized by the appearance of papillomas in the larynx. Therefore, before planning a pregnancy, a woman needs to treat the infection, if present.
Diagnosis of HPV strains
HPV type in women (16 and others) and in men (it is believed that 31-33 are the most dangerous for the male body) can be diagnosed using different methods. However, diagnosis of certain strains is rarely sought. Most often, people come to the doctor to remove tumors, since they bring discomfort and aesthetic disgust.
Education does not allow one to maintain normal personal hygiene and lead a full sex life.
But when growths appear, you should be examined and tested - further development of the virus seriously threatens the body. It is recommended to carry out diagnostics immediately. People with the HPV virus are referred to a urologist, gynecologist, cosmetologist and venereologist.
Preparing for analysis
Before collecting material to study the presence of HPV, the doctor performs a visual examination of the patient. It is important to distinguish the papilloma virus from other dermatological diseases. The doctor evaluates the nature of the growths, their size, color, frequency of distribution, and will also ask questions from which the diagnosis will become clearer.
It is necessary to distinguish warts from lichen, calluses or syphilis. An enlarged mole can become a neoplasm, and in this case this already indicates possible oncology. The doctor should determine whether the growths on the patient's skin are cancerous. Additionally, a consultation with an oncologist is possible.
If there is a suspicion of HPV, the doctor will prescribe the following tests:
- PCR;
- Digene;
- DAD.
Several other tests may also be performed. Before visiting the hospital for tests, the patient needs to prepare. The further result depends on this (as well as on the quality of research procedures).
The requirements before submitting the material are as follows:
- do not take antibiotics 2 days in advance (or notify your doctor about taking them);
- men should not empty their bladder within an hour and a half;
- exclude sexual contact for 2 days;
- Women should not be tested during menstruation.
Also, you should not conduct research during the period of exacerbation of existing chronic diseases and infections. To take tests such as a Pap test, it is advised not to use medications in the form of suppositories or tampons.
Collection of material for research
After being examined by a doctor and given directions, the patient must undergo several mandatory tests that will help determine his disease, strain and risk level.
There are usually 2-3 mandatory tests:
- PCR. This type of analysis involves scraping from the urethra followed by examination of the material. Helps determine the type of papilloma virus and calculate the number of pathogenic cells. Also, thanks to this analysis, it is possible to identify the approximate timing of infection with the virus.
- Digene. This method (hybrid capture) examines women over 30 years of age. Diagnostics are carried out once every 3 years. The test is very sensitive and helps to accurately determine the degree of HPV infection and determine the genotype. The accuracy of the Digen test is 99%, it is available and can be performed in conjunction with cytological analysis. Does not require complex preparation.
- DAD. Used in gynecology and means scraping from the cervix. The Pap test allows you to determine the presence of malignant neoplasms and changes.
There are some other methods for studying biological material. Thus, HPV in a patient can be detected using ELISA. However, this test cannot determine the type of virus. The method is based on testing blood for the presence of antibodies that are produced as a result of a response to infection. With its help it is possible to determine whether it is a primary infection or a relapse.
Decoding the results
During the analysis, it is determined whether there is a papilloma virus in the human body, and what its concentration is. To evaluate the analysis, a special designation “Lg” is used.
| Meaning | Decoding |
| Lg less than 3 | The virus is present in the body, but it is in low concentration. |
| Lg 3, 4, 5 | The virus is present in the body in quite serious concentrations. |
| Lg more than 5 | The virus is in high concentration in the body. |
The test may fail and the result will be positive (false positive).
This phenomenon occurs due to:
- the patient was not properly prepared for the tests;
- before collecting the material, the person took certain medications;
- the material was collected incorrectly;
- biological material was contaminated.
Laboratory tests are combined into several groups that meet certain criteria for everyone who was analyzed. Some of these groups: women after childbirth, men and women from 25-30 years old and others. This is done in order to obtain normal indicators for a particular population group. If the result is positive, there is no need to worry too much.
According to statistics, 7 out of 10 people are infected with the papilloma virus. Some people live their entire lives without even knowing about their diagnosis. The pathological development of HPV begins with weakened immunity. Therefore, in cases of a non-hazardous type, the doctor prescribes immunostimulating medications.
However, if the results showed HPV type 16, 18, 31-33, 56, this means that the patient requires urgent treatment . This is especially important for women, since these types provoke diseases of the reproductive system.
Identified strains do not always mean oncology (although in most cases the help of an oncologist is necessary), however, it is necessary to especially monitor the condition of the body, undergo examinations and take courses of medications.
Development of HPV 59
If we consider the features of the formation of this type of virus, we can distinguish 4 main stages:
- Latent. At this stage, the virus has already entered the body and has begun to develop, but has not yet manifested itself clinically. It can only be diagnosed in laboratories using DNA tests.
- The appearance of neoplasms (genital warts). After the virus has penetrated the epithelium of the affected areas, the cell's DNA is replaced with HPV DNA. As a result of such a “failure” in the program, neoplasms develop on the mucous membrane of the genital organs, in the groin and anus. Condylomas are small in size, pinkish-brown in color, and usually occur in groups.
- At the stage of dysplasia, changes occur at the cellular level, that is, the structure of the cells changes. Doctors call this condition precancerous. At this stage, it is still possible to begin treatment to avoid cancer.
- Carcinoma. Formation of cancer cells.
HPV treatment depending on type
HPV type (in women 16, 18 and some others can cause pathologies of the genital organs, as well as the bladder) provoke diseases depending on which group they belong to. Each type has its own treatment methods; therapy is especially necessary for the second and third groups.
HPV in these groups does not always mean oncology, but other serious health problems may arise. Even the slightest deterioration in health or the appearance of neoplasms should be a reason to visit the hospital for examination.
14 type
Type 14 (for women and men) belongs to the group with a low oncogenic risk. The danger arises in people with malignancy, and in this case the doctor prohibits self-medication. Otherwise, type 14 causes the formation of warts, which can be removed both at an appointment with a specialist and at home. The doctor also prescribes antiviral drugs (for example, Isoprinosine).
To prevent further growth of formations on the skin, cryotherapy or its analogues are used. Some remove growths using caustic alkaline preparations. Type 14 is not dangerous and provokes cancer in quite rare cases (a combination of factors, severe weakening of the immune system).
16 type
HPV type 16 in women is considered one of the most dangerous. It increases the risk of malignant pathologies several times. Type 16 can cause cervical cancer - this type was found in approximately half of women with this disease.
Actively dividing, pathogenic cells cause the formation of papillomas and genital warts on the mucous membranes and skin. During the development of type 16 virus, cervical dysplasia appears - a sure sign of oncology of the reproductive organs.
18 type
Papillomas and condylomas grow most rarely with type 18 of the virus. However, with this type they also manifest themselves and can grow together into one large growth. Formation on the external genitalia, thighs, and oral mucosa leads to discomfort and other inflammations.
In men, type 18 can cause Bowen's disease (the formation of warts on the penis), which is also a prerequisite for the occurrence of cancer.
Typically, type 18 is not as common as type 16, but its development occurs much faster. Detection of this type means immediate therapy, the prescription of immunomodulators, vitamins and subsequent removal of unpleasant tumors.
31 and 33
Most often, these types of HPV cause diseases such as bowenoid papulosis and cervical neoplasia. Women's disease can be mild or severe.
The latter is already oncology. When combined with other types, women may develop neoplasms (condylomas). Bowenoid papulosis is most characteristic of the male body and occurs against the background of promiscuity.
51, 52 and 56
These strains also belong to the high-risk group and are transmitted mainly through sexual contact. These types provoke the occurrence of genital warts, including around the anus and rectum. In women, these HPV types cause cervical erosion and dysplasia. Types 51, 52 and 56 are the causes of oncology of external and internal diseases of the genital organs.
Why are types 16 and 18 dangerous?
The most dangerous types of HPV are strains numbered 16 and 18. The presence of these types of viral microorganisms in the body in seven out of ten cases leads to the development of cervical cancer in representatives of the fair half of humanity. For men, this type of HPV is also dangerous and can cause cancer of the bladder or colon.
The considerable danger of high-carcinogenic risk HPV 16 and 18 also lies in the absence of clinical manifestations characteristic of most strains. It is impossible to determine infection even with standard medical diagnostic procedures and tests. To identify the above types of HPV, the use of highly targeted research methods, carried out only in a laboratory setting, is required.
Is recovery from HPV possible?
Complete elimination of HPV is possible, but only at a young age. Almost 90% of cases of recovery are registered up to 25-26 years of age. For cure, immune therapy and removal of growths are used. The patient’s own immune system is no less important - if it is strong, there is a high chance of a complete recovery.
Immunomax, approved according to the instructions for the treatment of pathological conditions (condylomas, warts, dysplasia, etc.) caused by the human papillomavirus, is becoming increasingly popular among modern immunomodulatory drugs.
Immunomax
Experts note that the use of the drug Immunomax in the complex therapy of HPV-associated diseases leads to a decrease in the frequency of relapses and clinical recovery from infections.
When a person gets older, his immunity is no longer as strong as before. The virus remains in the body, waiting for the body to weaken, and then be activated (formations appear). A medicine that can destroy the virus has not yet been invented. The patient's recovery depends on himself and on auxiliary treatment.
Although HPV can no longer be eliminated after a certain age, therapy aimed at suppressing the activity of papillomavirus is still necessary.
Principles of treatment of papillomavirus
Modern HPV treatment is aimed at eliminating the consequences of the papillomavirus and is used if the tumors represent a serious cosmetic defect or are caused by a highly oncogenic virus.
To remove papillomas, the method of surgical excision, electrocoagulation, laser therapy, cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen, radio wave therapy, and chemical cauterization is used. If the concentration of the virus in the tissues is high, antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy is prescribed at the same time.
The most reliable protection against papillomavirus is provided by natural immunity. According to research from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, this factor causes the body to heal itself within 2 years in 90% of cases. The immune system suppresses the action of the virus, and it constantly remains in a latent state.
Recipes for folk remedies to suppress activity
Traditional medicine can be used in treatment only after consultation with a specialist. It is impossible to replace full-fledged treatment with her, as this can lead to a worsening of her condition.
If the doctor has authorized the use of home remedies as additional ones, you can use the following 5 main opponents of growths:
- Onion or garlic . Vegetable juice is rubbed into the tumors 2-3 times a day. The course lasts approximately 3 weeks.
- Rowan . Berries cut in half or rowan puree are applied to the warts and then secured with a bandage.
- Potato . Raw potatoes are grated into a paste and applied to the formations. Use this method daily for 1 month.
- Wormwood . Wormwood seeds are poured with alcohol and a tincture is made (3 days). Then it is filtered and taken orally, 4-6 drops per day.
- Eggshell . Egg shells are ground and applied to the growths, covered with sterile cotton wool and fixed. The procedure is carried out once every 2 days. Course – up to 3 weeks.
These products should not be taken by people with an allergic reaction to these products, individual intolerance, or if the neoplasms are not identified (these are not papillomas or condylomas).
Price for tests
The cost of procedures depends on the place of residence and can vary significantly from region to region. Average prices for virus diagnostics are as follows:
- quantitative PCR test with determination of 12 genotypes of the virus – 600-800 rubles;
- identification of individual HPV strains – 250-350 rubles;
- colposcopy – 900-1400 rubles;
- cytology – 700-1200 rubles;
- Digene test for identifying highly oncogenic strains of the virus – 5000-6000 rubles;
- histological examination – 2000-3000 rubles.
The patient should select a diagnostic method together with the attending physician, since each situation requires individual consideration. In addition, it is necessary to re-do the diagnosis after some time to analyze the quality of the treatment provided.
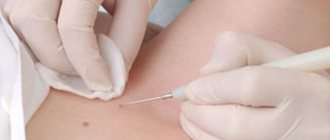
Can a vaccine protect against the virus?
The HPV vaccine exists and it gives the expected results. However, it is worth considering that it only works if the person is no longer infected with the virus. After the vaccine is administered, the body produces special antibodies that prevent HPV from entering cells and developing.
For vaccination, 2 drugs are used: Gardasil and Cervarix.
The vaccine is safe for humans. However, it cannot be used for treatment. The effect of the drugs was tested only on women, since the percentage of cases is much higher. Administration of the drug to men prevents the growth of condylomas.
When and how to vaccinate
The HPV vaccine is administered to girls aged 9-12, 16 and 17 years. Vaccination is mandatory and serves to strengthen immunity. Vaccination includes 3 stages. After 1 re-vaccination is carried out no earlier than 2 months. After 2 - not earlier than 4. If a woman is pregnant during vaccination, stage 3 occurs after childbirth.
HPV and its types that develop in women and men may well be preventable. Such dangerous types as 16 or 31 may not bother you if you use protection during sexual intercourse, conduct examinations and maintain the condition of the immune system.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Basic diagnostic methods
Examination of a woman by a gynecologist
When neoplasms are detected in the intimate area, the cervix is examined first. To do this, its mucous membrane is treated with a solution of acetic acid, followed by an iodine solution. If the drugs are unevenly absorbed and a characteristic mosaic pattern is detected, the presence of papillomavirus is confirmed. Its strain and concentration are not determined by this method.
Cytological examination
To do this, the gynecologist takes a smear from the woman’s cervix or cervical canal during the examination. Laboratory testing determines the presence of cellular changes that should not normally be present. If pathologically altered cells are detected, we can talk about cervical dysplasia.
This analysis is performed using a PAP test, the results of which can be as follows:
- Grade 1: normal cell structure.
- Class 2: minor changes in individual cellular elements were detected. Possible inflammatory process. Additional tests and treatment are prescribed, after which a repeat analysis is carried out after 3 months.
- Class 3: changes in their nuclei were detected in individual cells. The results of the analysis are uncertain. To clarify the data, a histological examination and repeat cytology after 3 months are required.
- Class 4: morphological signs of malignant changes are determined; At this stage, urgent treatment is required.
- Grade 5: typical cancer cells were detected. Cervical dysplasia is confirmed. To determine the extent of tissue damage, histology is prescribed.
Manifestations in men
Symptoms occur in the anogenital area. People often do not notice the developing small growths located on the anus. Education often forms here if a man has anal sex. Another papillomas of strain 59 develop on the penis and scrotum. The higher the activity of the virus, the more growths on the surface of the skin. With HPV 59 in men, condylomas can unite. This formation resembles cauliflower. The disease is manifested by other symptoms: pain during sex, uncharacteristic discharge, decreased libido due to discomfort.
Diagnostic technique
A highly specialized specialist should conduct an external examination. If the presence of HPV in the body is suspected, the doctor can confirm the guesses by the formed papillomas on the mucous membranes or skin in the anogenital area. However, the diagnosis can only be made using the following methods:
- Examination of the cervix using a colposcope. In this case, at multiple magnification, the tissue condition is assessed.
- Cytological examination. The analysis is taken from the mucous membrane during colposcopy. In this case, the infection can be detected by changes in cell structure.
- Blood and urine tests. By changes in the composition of biological fluids, you can find out whether a viral infection is developing in the body.
- Polymerase chain reaction. Thanks to this technique, virus cells are detected. If this DNA of HPV type 59 is present in the body, then it is possible not only to confirm the presence of the virus, but also to determine the strain.
- For viral load, another type of test is recommended - the Digene test. This method allows you to evaluate the quantitative component of HPV.
- Biopsy followed by histology (a test to identify malignant cells).
- AAT - the test is carried out using acetic acid. Atypical cells are detected. In this case, the mucous membranes are treated with a solution (concentration 3-5%). After applying acetic acid, formations with atypical cells become white.
Which doctor should I contact?
It is necessary to choose which doctor to see if there are obvious or hidden signs, taking into account the location of the formations. In particular, the main specialists are:
- dermatologist, dermatovenerologist;
- gynecologist;
- dentist;
- ophthalmologist;
- surgeon;
- oncologist.
Initially, if you have not yet visited any doctor, you should make an appointment with a local therapist or dermatologist. After conducting an examination, they will, if necessary, refer you to other, more specialized specialists.
Prevention
An important condition for prevention is protected sex. But it also does not guarantee that the virus will not be transmitted to a healthy person. HPV is so small that it can penetrate even the pores of a condom. Therefore, it is best to avoid sexual contact with a person who has HPV.
Particular attention should be paid to vaccination. It is given to girls from 10 years old and women up to 30. Injections are carried out in stages. The first vaccination is given when visiting a doctor. The second after 2 months, and the third only after 3-5 months. It is better to protect yourself from HPV than to undergo long-term treatment later. Vaccination provides 99% protection against the penetration of the virus and its reproduction in the body.
What is and features of HPV genotyping
Genotyping in the classical sense is a study that allows us to compare and contrast gene sets of different individuals. If we are talking about viruses, this analysis allows us to identify pathogen strains.
Papillomavirus is a common disease. The main route of transmission is contact, during sexual intercourse, and in the home. More than 170 varieties of the virus have been identified, 40 of which infect humans. The classification of HPV is based on the principle of oncogenicity. There are low, medium and high risk strains.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Genotyping of papillomaviruses is used to determine the type of virus. This allows you to assess the severity of the disease, select treatment tactics for the patient, make a prognosis and give recommendations for preventing relapse of the disease.
In addition, determining the HPV strain during genotyping will help the doctor differentiate the disease - an acute process or a relapse - when the patient returns. This allows you to adjust the course of treatment.
Infection with a new strain, recent infection has a favorable prognosis; within a year there is a high probability of spontaneous recovery and an adequate response to treatment. In the chronic course of the disease, independent suppression of the virus is unlikely and the prognosis is not optimistic. This is an indication for additional examination of the patient, identifying factors contributing to re-infection or activation of the papillomavirus.
HPV during pregnancy
If type 16 or 18 was diagnosed during pregnancy, then with a high probability she will be prescribed a cesarean section. These are quite dangerous species and they can be transmitted to the child during passage through the birth canal. In general, the papilloma virus can become an obstacle to conception, and also increase the risk of pregnancy with complications.
If a woman knows before pregnancy that she has an oncogenic form of the disease, she should consult a doctor and undergo the necessary tests. If test results are normal, pregnancy can be planned. The papillomavirus itself cannot be a complete contraindication to pregnancy. Until now, there has been virtually no evidence that it has a negative effect on the fetus and the course of pregnancy itself. But having such a disease, you need to be more careful about conception, pregnancy and childbirth.