People often mistake growths on the skin for harmless and treat them with traditional methods. This mistake can have dangerous consequences - abnormal proliferation of epithelial tissue aggravates the spread of papillomavirus throughout the body, and some of its strains provoke cell mutation with the formation of various types of cancer.
More than 80% of the world's population are carriers of the human papillomavirus, regardless of age and race.
With a sharp decrease in immunity, a previously dormant disease makes itself felt by the appearance of a large number of genital warts on the skin.
How is the human papillomavirus transmitted? The microorganism enters the human body through mucous membranes or skin. In a benign course of the disease, it does not manifest itself in any way: the epithelium retains its shape unchanged.
If the virus integrates into the genome of the cell, then doctors diagnose a malignant form of the pathology, which is considered to be a precancerous condition.
The more scratches, abrasions and other minor damage there are on the skin, the easier it is for the papillomavirus to penetrate any cellular system. Here are some factors that increase the likelihood of infection several times:
- The body’s antiviral defense cannot cope with the load when immunity is sharply reduced. A person may have this condition due to a common sore throat or cold;
- the virus begins to actively multiply in cells during intestinal or vaginal dysbiosis - these diseases are accompanied by the death of beneficial microflora;
- genital papillomas are easy to become infected if the body already has sexually transmitted diseases: gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, syphilis and others;
- relapse of any chronic disease will become a favorable condition for transmission of the human papillomavirus;
- Stressful situations and depression reduce a person’s antiviral defense, so a pathogenic microorganism can easily penetrate inside the cell.
The risk of contracting the papilloma virus increases in smokers and women taking combined contraceptive medications.
Methods of infection
As mentioned above, there are only three main methods of infection - through sexual contact, through blood, and through household contact.
Penetrating through the protective barrier of the skin, mucous membranes, and circulatory system, HPV has an extremely negative effect on the patient’s health.
Typically, a person experiences:
- Constant weakness.
- Feeling of nausea, heaviness in the hypochondrium.
- Pain syndrome.
- Problems with the urinary and reproductive systems (difficulty urinating, the appearance of sharp paroxysmal pain in the perineum).
- Burning sensation in the groin area.
- Dizziness due to frequent rise in body temperature.
- General decrease in the body's protective functions (frequent colds, long recovery period after illness).
- Skin itching, which is accompanied by the appearance of papilloma.
In order to recognize the presence of a viral infection and consult a doctor in time, it is necessary to take into account the prerequisites for the occurrence of this disease. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the material: papilloma ICD 10.
When the infection appears
The period of time after infection until the clinical picture appears is called the incubation period. The virus reveals itself after several weeks, months or even years. The length of this period depends on the person’s health after infection occurs. A strong immune system prevents the virus from developing, so the disease may never manifest itself.
If the body is no longer able to fight, growths will appear on the skin and mucous membranes caused by the activation of HPV.
Prerequisites for infection
The most common prerequisites for the occurrence of HPV include:
- Weakened immunity.
- The presence of other chronic diseases that undermine the body's resistance to all kinds of external attacks.
- We are talking about hepatitis, human immune deficiency (HIV), cardiovascular diseases, genetic developmental abnormalities, and rare hereditary forms of the disease.
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse.
- Unprotected sexual contact.
- Infection from a loved one in everyday life: when using dishes, bed linen, towels, when kissing, hugging.
- Use of public places of culture and recreation.
- Visiting beauty salons.
- Sharing personal products: combs, manicure accessories.
Important!
Timely vaccination will protect against the most aggressive types of the virus.
Transmission routes
The papilloma virus is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, transplacentally (transplanted from contaminated surfaces), using cerebrospinal fluid (blood, saliva, sweat).
Therefore, if there is a sick person in the family, it is necessary to constantly treat all surfaces with a special antiseptic, follow strict rules regarding personal contacts and monitor the condition of the skin (even microcracks can become the initial area of damage).
Is it possible to become infected with HPV through everyday contact?
Human papillomavirus infection is easily transmitted through shared objects, as well as through saliva. This should not be forgotten if there is a sick person in the house.
Distribution mechanism:
- When kissing, hugging. With saliva and sweat, PVI passes from one person to another. This is possible due to the fact that the virus moves freely through the mucous membranes and is present in saliva and cerebrospinal fluid.
- When using personal hygiene items belonging to the patient.
- When shaking hands. Microtraumas of the skin can be excellent conductors of infection.
- When using shared utensils.
- When transferring things or objects from an infected person to a healthy person (this type of infection is very resistant to the influence of environmental factors).
Can you get HPV through sexual contact?
Since mucous membranes, skin and their derivatives (secretions, blood vessels, saliva) are carriers of genetic material, you can become infected with human papillomavirus through sexual contact; as well as when using public baths and saunas.
Transmission mechanism:
- Directly during sexual intercourse (this especially applies to oral and anal sex).
- When using shared showers, baths, saunas. Without proper antiseptic and antibacterial treatment, such places are breeding grounds for all kinds of infections.
- When using underwear and partner's clothing (especially for women who like to wear men's shirts, T-shirts, shorts, family pants).
Is the virus transmitted from mother to child?
Transmission of infection from mother to child is called “vertical transplantation”. This type of transmission of the papilloma virus is one of the most dangerous, as it injures the child’s body and his intellect.
After undergoing HPV, especially in the early stages (1 trimmeter), doctors insist on an abortion for medical reasons.
Autoinfection
Self-infection is only possible if untreated hygiene products are used. For example: razors, toothbrushes, nail scissors and similar items.
With this form of transmission of the papilloma virus, the patient does not feel discomfort for a long time and leads a normal lifestyle. And when the first symptoms of the disease appear (which are very similar to banal overwork), he ignores them without consulting a doctor.
Human papillomavirus: answering the most important questions
Not all details about the disease can be asked at a doctor’s appointment. But the less a person understands about his diagnosis, the more mistakes he can make during treatment and contacts with others. We answer the most frequently asked questions about HPV and separate fact from fiction.
Many people diagnosed with HPV are concerned about how the infection may affect their lives. But the doctor does not always have time to answer all the questions, and on the Internet you can read all sorts of horror stories.
The purpose of this article is to truthfully answer the most important questions about HPV.
HPV treatment and disease prognosis
Most questions about the papilloma virus are related to its treatment and the risks of complications. But these moments are different for each individual person. Therefore, they can only be fully clarified together with a doctor.
We will clarify points that are common to all, which can be clarified without an in-person consultation with a doctor.
Is the disease completely cured?
Unfortunately, at this stage of medical development, it is impossible to completely cure HPV. But there is no need to worry about this, because the virus does not spoil the life of every “owner”. Conventionally, all people infected with HPV can be divided into 3 groups.
The first ones can be called the luckiest. Their body manages to get rid of the virus on its own. This usually happens within a period of six months to three years. However, some former patients do not even suspect that they have suffered an infection. This group includes about 90% of those infected.
In the second group of infected people, the virus lives in the body much longer. Sometimes - all my life. But at the same time it does not appear at all or appears rarely and weakly. Another thing is that such a patient can be infectious to others - even if he himself has no external signs of the disease. This group includes 6-7% of HPV carriers.
And only the third group of people with papillomavirus have obvious external signs of HPV and experience discomfort from it. In rare cases, manifestations of HPV can cause severe discomfort and impair quality of life. This includes about 2-5% of all people with HPV.
What determines which group a person falls into? On the quality of his immunity. The weaker the patient’s immune system, the more “brazen” HPV behaves. You can read more about when and under what conditions papillomas appear in a separate article.
I have HPV - will I die of cancer?
Not at all necessary! Despite the fact that HPV is partly associated with cancer, it does not cause them in all carriers.
Today, science knows about 600 types of virus (data vary because scientists themselves have not yet agreed). It has been established that most of the types of HPV are not dangerous in terms of cancer: they either do not cause cancer at all, or do so in exceptional cases.
No more than ten types of virus pose the threat of malignant tumors. Moreover, in 90% of all cancer cases due to HPV, two of these ten are “to blame” - HPV16 and HPV18 types. But the probability of becoming infected with just these two types out of 600 is not so great.
Even if a person is infected with HPV16 or 18, there is no need to panic. It takes the virus a long time—many years—for changes to occur in the body’s cells that will turn them into precancerous ones. Sometimes it simply does not have time to change the body, because the immune system defeats it. If changes in the cells have occurred, then a lot of time will pass from their onset to the development of a cancerous tumor - 10-15 years or more.
Thus, the risk of developing cancer with HPV is very low. But given that life is at stake in the fight against infection, all people with dangerous types of the virus need to be checked by a doctor and tested - preferably once every six months.
Is it possible to find out when and from whom the infection occurred?
This cannot be established definitely. If a person is diagnosed with a virus, then he could become infected with it at any time, anywhere and under any circumstances.
Of all the known varieties of the virus, about 40 are transmitted through sexual and household contacts, and about 10 are not transmitted through sexual contact. The rest are still under research.
When exactly the virus entered the body, and especially from whom, it is impossible to find out. Moreover, the presence of an infection in a partner does not in any way indicate that he was the source of infection.
Is it possible to plan a pregnancy with HPV?
In most cases, women quietly become pregnant, carry a child and give birth, without even knowing that they are infected with the papilloma virus.
But what if a woman already knows that she has HPV? Is it worth planning a pregnancy in this case?
So far, scientists have not found any evidence that the papilloma virus affects pregnancy. But research in this area continues. There is reason to believe that in rare cases the virus can cross the placenta to the fetus. However, cases in which HPV has had a bad effect on the development of the fetus have not yet been registered.
If a woman has genital warts in her genital tract, then during childbirth the child can become infected with types HPV8 and HPV11. These strains do not cause cancer, but the child may subsequently develop respiratory papillomatosis - warts in the respiratory tract. However, this happens quite rarely.
The main thing a woman with HPV can do when planning a pregnancy is to remove warts if they are in the genital tract. This needs to be decided individually with your doctor.
What types of HPV are the most dangerous?
The most dangerous types of Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) include types 16 and 18. They have strains that provoke the appearance of malignant neoplasms - cancerous tumors that, as they grow, can give metastases.
The most common manifestation of the impact of the virus strain is the occurrence of diseases such as: cervical cancer, infertility, pulmonary and bronchial changes, acute lack of immunoglobulins.
Note! Cervical cancer can only occur due to the most aggressive form of the virus. Most papillomas are not dangerous.
Types of skin growths due to human papillomavirus infection
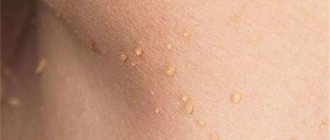
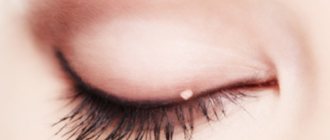
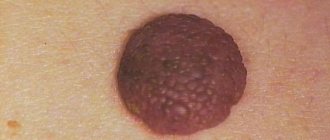
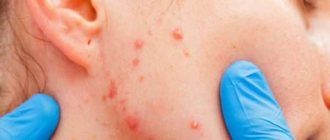
The clinical manifestation of HPV is the formation of growths on the skin. Depending on the location and external characteristics, these are:
- warts (hardened growths mainly on the face, hands and feet);
- papillomas (softer skin growths on the skin and mucous membranes);
- flat and genital condylomas (a type of papillomas in the anogenital area).
You need to pay close attention to such symptoms of infection. All growths are contagious because they are a source of infection.
Diagnostics
A number of the most complex hardware techniques help to detect the presence of the Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) in the body.
- Colposcopy. A colposcope is a medical device that allows you to accurately determine changes in the mucous membranes of the genitourinary system: detect inflammation, damage and the spread of viruses, fungal bacteria. Its use to determine the presence of HPV in the body is used to definitively confirm the diagnosis. This device is capable of: under 30x magnification, find the source of inflammation, determine its nature, take a scraping directly in the affected area.
- PCR examination. This laboratory method represents a differential diagnosis of this type of disease. PCR makes it difficult to determine the type of virus, but also the route of infection. To carry out this analysis, the collection of biomaterial is required: blood, urine, sperm.
- Digene test. A modern diagnostic technique based on separating a small area of the affected skin for study. Using this approach, medical specialists can say 100% what type of virus is present in the body, what its concentration is, whether it is in a reactive form, and what antiviral drugs are sensitive to.
- Cytology. It is the study of a problem at the cellular level. To do this, the top layer of papilloma is removed and a separate section of the mucous membrane is taken. Using a super-powerful microscope and a basic set of reagents, laboratory assistants study the behavior of the virus, its effect on the body (they make a prognosis), and the degree of damage to the internal systems of the body.
- Histological diagnosis. The purpose of this technique is to study morphological changes in tissues. The material for the study is taken using a biopsy.
How exactly is papilloma transmitted through a kiss?
Answering the question whether papilloma is transmitted through a kiss, it must be said that at this time only the virus that causes its appearance can enter the body. This occurs when infected saliva is released into a person's mouth. When the partners’ lips and tongues come into close contact, it lands on “clean” surfaces, and the virus contained in the biological fluid infects healthy cells.
If there is a papilloma in the oral cavity, then its contact with the mucous membranes of another person contributes to the migration of the virus in the body of an uninfected partner. But this path is only possible with active friction of the growth against healthy surfaces. In the case of friendly kisses, for example, on the cheek, the likelihood of this is almost completely eliminated.
Treatment
Treatment of Human Papilloma Virus involves strict adherence to sexual abstinence, the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, immunomodulatory drugs, a vitamin complex, and drugs to reduce the effect of the virus on the body.
Healthy people’s access to personal belongings, hygiene products, dishes and bedding should also be limited. If malignant neoplasms caused by a virus appear, corrective treatment or surgery is carried out with a long period of rehabilitation.
Ways to prevent the disease
The main ways to prevent HPV are:
- Compliance with the rules of sanitary provision of living space.
- Use of contraceptives.
- Monitoring your own health from specialized specialists.
- Use personal hygiene products strictly for their intended purpose, without transferring them to third parties.
- No trips to places with an increased risk of infection: baths, saunas, swimming pools, water parks, massage and beauty salons.
- Protecting the skin from interaction with a large number of external factors.
- Protecting your own health by isolating yourself from people who are sick with any infectious viral diseases or skin diseases.
It is simply impossible to cope with a complex viral infection on your own. Medical control and timely seeking qualified help from a wide group of specialists will be the very first and most serious step to combat the existing problem.
If such a problem occurs in one of your family members, you should immediately undergo routine diagnostics and follow all doctor’s instructions to avoid the spread of the virus. In addition, we should not forget to take precautions that will help prevent infection.