What is HPV in gynecology
Human papillomavirus in women in gynecology
Often women want to know what HPV is in gynecology and how infection occurs. The pathogen is transmitted through household or sexual contact. Today, scientists know about several hundred varieties of viral diseases. Most of the strains are characterized by good resistance to life in the external environment. It gradually dies at a temperature of 38-39 degrees.
So, what are papillomas in gynecology and how do they develop? Infectious disease manifests itself in different ways:
- Active reproduction in cells dying under the influence of a pathogen. The person suffers from symptoms of papillomatosis.
- The course of the disease is not accompanied by symptoms. The patient learns about the development of the virus by chance, as a result of medical examinations.
The human papillomavirus in gynecology often manifests itself as discomfort during sexual intercourse, itching in the vagina, and the appearance of skin growths on the vagina. Infection does not necessarily lead to the development of symptoms. Before you learn everything about the human papillomavirus (HPV) and its treatment, it is worth understanding the types of viruses and the features of their definition. In medicine, several hundred strains are isolated that cause specific symptoms. Judging by the reviews of many women, when you consult a doctor, the risk of unpleasant consequences decreases.
The pathogen lives in the body of men and women until favorable conditions appear, so it is important to take care in advance to prevent the disease.
How is HPV transmitted?
It is believed that this virus is sexually transmitted and even condoms do not guarantee complete protection against HPV. Gynecologists assure that condoms still reduce the risk of catching this virus. According to research and statistical data from epidemiologists, women are often infected with the papilloma virus in the first 2 years of sexual life.
Many people know that most types of HPV are transmitted sexually. It is much less known that the risk of infection and the severity of the consequences are greater in women than in men.
Moreover, the risk of getting HPV in girls is lower with age, which cannot be said about men. At the moment, scientists have identified almost 150 types of HPV, which are divided into four classes. A number of studies have also been conducted, the result of which was the conclusion that HPV can also be transmitted through household contact. Due to this type of transmission of the virus, a person does not realize that he is already a carrier of HPV.
Types
Human papillomavirus in women in gynecology
The HPV group includes more than 150 types of papillomavirus. Growths occur both in visible areas and in the urethral canal or in the uterus. Commonly encountered pathogens are divided into types according to the risk of transformation into malignant cells:
- Human papillomavirus types 7 and 15, as well as 19-24, cause the development of warts.
- Types 1, 2, 3, 4 cause the appearance of peculiar calluses on the sole.
- Papillomavirus types 6 and 11 have a low level of oncogenicity.
Types 16 and 44 have a high oncogenic risk. The group of these strains is called “HPV a9”.
In women, the virus can cause genital warts and warts on the cervix. Pointed papillomas appear as a result of the proliferation of human papillomavirus infections types 6 and 11.
Treatment of HPV infection
Which doctor treats HPV 16 in women?
Treatment of HPV infection can be carried out by a gynecologist, oncologist, infectious disease specialist, or venereologist.
It is important to understand that accidental detection of the virus in the absence of clinical changes is not an indication for therapy.
Only if highly oncogenic viruses (HPV 16) are detected in women, the doctor decides what to do next.
Is it necessary to undergo diagnostic examinations and examinations more frequently or to prescribe additional studies?
Only a specialist can determine whether it is necessary to treat HPV 16 in women, taking into account the presence/absence of changes induced by the virus.
In a situation with HPV, it is important to trust your health only to highly professional specialists who are familiar with international protocols for managing the infection.
This is especially important when infected with HPV 16, which provokes malignant pathologies in women (reviews on the Internet or from friends will help you decide on an institution and a doctor).
Today, in women, treatment for HPV 16 is based on the removal of atypically changed epithelium.
It should be understood that if women have an infection, there are currently no drugs that destroy the virus itself.
Any international treatment regimen for HPV 16 does not include any antiviral agents.
At the same time, specific treatment for HPV 16 is carried out, in which it is recommended that women take drugs with immunomodulatory and antiviral activity.
It is believed that such drugs mobilize the immune system to fight the virus.
Such products have not been sufficiently tested for effectiveness in clinical trials.
Accordingly, there is no reliable data on the cure rate.
Despite this, many patients note a significant improvement in their well-being after using them.
Immunocorrective therapy for HPV 16 in women includes:
- with human recombinant interferon or its inducers, suppositories (Viferon, Genferon), Isoprinosine, Cycloferon, etc.
- with an immunostimulating effect - Lykopid, Polyoxidonium, etc.
- B vitamins, omega acids and dietary supplements
Often, before prescribing a drug treatment regimen, an analysis of the immune status (immunogram) is recommended.
With determination of indicators of the activity of monocytes, neutrophils, lymphocyte function, levels of immunoglobulins, CD16+, CD8+, CD4+ and others.
Unfortunately, for many drugs, data on the safety of use, complications and relapses after use have not been obtained.
Therefore, it is recommended to refrain from using them for people with:
- autoimmune diseases
- malignant formations (for cervical cancer can be prescribed only after completion of surgical treatment)
- allergic reactions
- bronchial asthma, etc.
As for the generally accepted approach to the management of HPV infection in the international medical community, the following points are positioned here:
- There is no medicine to remove the virus from the body, but the likelihood of self-healing is very high, especially at a young age
- If there are no changes in cellular structures and a virus from a high oncogenic risk group is identified, more frequent and careful monitoring of the patient is carried out
- If changes caused by the activity of the virus are detected, therapy is carried out aimed at eliminating pathological changes
For bowenoid papulosis caused by HPV type 16, tumors are removed using the following methods:
- Mohs excision
- laser therapy
- cryodestruction
- electrocoagulation
- local application of ointments with cytostatics (5-fluorourocil, prospidin, fluorofur)
- intralesional administration of interferon
- oral administration of Neotigazon capsules
Precancerous conditions and the first stages of cervical cancer are highly treatable.
The changed cells are removed using cryotherapy.
For dysplasia, organ-preserving operations are performed: conization of the cervix with a scalpel, electrosurgically, laser with preliminary canal curettage.
For localized forms of the tumor, surgical treatment is carried out, for a widespread process - radiation and chemotherapy.
Taking into account the fact that eliminating the result of virus activity does not remove the infectious agent itself.
The risk of recurrence of pathological changes remains, which, in turn, requires further monitoring of the patient.
In addition, the possibility of HPV reinfection cannot be excluded.
After implementing any treatment option, follow-up tests are recommended.
Since there is a possibility of spontaneous elimination of the virus within 2 years from the moment of infection.
A separate problem is presented by persons with HPV against the background of HIV infection.
It has been proven that the risk of developing cancer in such women is higher, as is the risk of HPV infection itself.
Although primary HPV infection was detected more often, which is associated with the greater prevalence of this virus.
Moreover, the worse the patient’s immune status, the higher the likelihood of her developing HPV-induced cancer.
Therefore, people with HIV status are recommended to undergo HPV testing more frequently.
Treatment is carried out using the same methods as for those uninfected with HIV, with additional specific therapy aimed at suppressing the activity of the immunodeficiency virus.
Sources of infection
Human papillomavirus is often transmitted through sexual intercourse with an infected person. The main condition for the pathogen to enter the partner’s body is unprotected contact.
One of the possible causes of papillomavirus is the transmission of the pathogen from mother to fetus (vertical). The risk of infection with various strains increases with a large number of sexual partners.
One of the reasons for the appearance of an infectious disease lies in infection through an injured growth. If there are easily injured genital papillomas on the body, the likelihood of transmitting the virus to another person increases significantly. If a person has no external manifestations of the disease, he can still infect others.
Another common cause of papillomavirus is infection when using another person’s hygiene products and even shaking hands. The risk of infection is especially high in public saunas and swimming pools. Knowing how papillomavirus is transmitted, you can reduce the risk of infection from carriers.
How is the virus transmitted to children?
HPV is spread through skin-to-skin or blood contact:
- A pregnant mother can pass the infection to her baby through the bloodstream before birth or through the vaginal canal during childbirth. This is called perinatal transmission.
- Children with warts on their hands can transmit the virus through skin-to-skin contact. The spread of the virus to the genital area occurs when touching it with your hands. This route of infection is called autoinoculation.
- A caregiver with warts can transmit the virus through skin contact with the child's hands or genitals. This is called heteroinoculation.
- HPV can be transmitted from a person's skin to the child's genital area through sexual contact - in the event of violence.
- Rarely, HPV can be transmitted through contact with inanimate objects or surfaces. If an adult who has warts uses a towel and then a child uses the same towel, the virus can be passed on to the child. This is called fomite transmission.
HPV is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, even if there are no warts or papillomas on the skin. After infection, the virus remains in the body. A person may be a carrier
Symptoms
Human papillomavirus in women in gynecology
The main signs of HPV in women are the formation of condylomas. They appear 3 months after infection with HPV. Symptoms of the disease boil down to the appearance of tumors that are easily injured and cause discomfort.
One of the symptoms of HPV in women is a precancerous condition of the uterine lining, in which the process of maturation of mucosal cells is disrupted. Today doctors know 3 stages of development of this disease, which have different manifestations.
Symptoms of HPV in gynecology often include growths under the mammary glands. For men, the danger of papillomavirus is lower than for women. Appearing growths rarely provoke cancer in representatives of the stronger sex.
Degeneration of papilloma into a malignant tumor
The transformation of benign tumors into malignant ones can occur in the following cases:
- In case of incorrect self-medication;
— If you remove them yourself mechanically or using chemicals;
— When removing papillomas by a specialist without appropriate qualifications;
— Frequent and long exposure to the sun;
- Chemical or mechanical damage to formations that occurs systematically.
If the doctor is not sufficiently qualified, he may not completely remove the papilloma, leaving tumor cells infected with the virus in the patient’s body. Over time, these unhealthy cells form new growths in much larger numbers, and papillomatosis begins.
Why is it dangerous for women?
Human papillomavirus in women in gynecology
Many women are interested in what the human papillomavirus is and why it is dangerous to health. There are cases when the body heals on its own. However, the virus is dangerous, and the consequences of its activity can be serious.
The virus poses the least danger to young and healthy girls. However, there is still a risk of developing significant complications. With weakened immune defenses, the disease can become chronic.
Some types of HPV in gynecology cause cancer of the external and internal genital organs of women. This complication can occur at any age. Women who smoke are at increased risk.
Also, with the development of the papilloma virus, pointed growths may appear on the labia. This disease causes a lot of inconvenience for sexual life and requires complex treatment. The human papillomavirus appears in women and on the cervix.
Activation of the pathogen can lead to erosive lesions of the vaginal mucosa. During a special examination (colposcopy), the doctor discovers small red wounds. Subsequently, mucosal cells can transform into cancerous ones.
How dangerous is HPV during pregnancy? If there are growths in the vagina or labia during childbirth, the virus can be transmitted to the baby.
Types of papillomas
Infection with the virus often occurs during sexual contact with a carrier. Also, papillomavirus can be transmitted at home (during swimming in a pool, visiting a public bath, or going to the gym). If a woman in labor has a human papillomavirus infection during childbirth, it can be transmitted to the child. During shaving and epilation, warts can be transferred from the affected area to healthy tissue.
The size of papillomas can range from a few millimeters to 1 – 2 centimeters. Most often, the dormant nature of the virus manifests itself when immunity is reduced after treatment of infectious diseases, long-term use of antibiotics, or vitamin deficiency. The first sign of wart rashes is skin rashes of soft, nodular growths. Fungal infections or excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis) contribute to foot infections.
In order to prevent the risk of developing malignant neoplasms, it is very important to distinguish between the types of papillomas. When pathogenic microorganisms enter the body, they rapidly multiply, provoking the process of excessive division of epithelial cells. Each type of neoplasm is characterized by specific features, which can be compared using a photo or description.
Ordinary
When answering the question of what types of papillomas there are, one should immediately say that ordinary nodules or warts are the most common pathology of this type. The development of this type of disease occurs especially often for the following reasons:
- exposure to household chemicals on the skin;
- increased sweating;
- open skin injury;
- dermatitis.
Ordinary papillomas are characterized by a papillary shape, a soft, homogeneous structure of a slightly pigmented shade, close to flesh color.
Filiform acrochords
The neoplasm has a thin stalk with a head that ends it. The nodes have an elongated shape and are most often diagnosed in elderly people. Common locations are the chest, armpits, and neck. Thread-like growths can increase in length, the head has a yellowish or pink tint.
Flat
Flat warts look like small yellow growths that have a flattened shape. Having a dense structure, their root is deeply embedded in the skin. When accidentally touched or pressed, there is pain. Common localization sites are:
- face;
- back of the hands;
- anal area;
- genitals.
This type of neoplasm is difficult to treat. After removing the growths, deep scars remain on the skin.
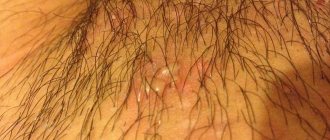
Pointed
Genital warts are localized in the groin and mucous membranes. The neoplasms have a papillary shape and are characterized by rapid growth, leading to the formation of a ridge structure. This type of viral formation tends to cause frequent inflammation and is easily injured, which leads to infection. Genital warts have an increased risk of recurrence even after treatment.
Lewandowski Lutz
A rather rare type of papillomas, most often localized on the hands and feet. Knots that are brown, red, or purple in color have jagged edges. The virus comes in different sizes; the advanced form develops into oncology.
Plantar
Children are most likely to develop plantar warts. The main reasons for their development are reduced immunity, foot injury from uncomfortable shoes, excessive sweating, and disregard for personal hygiene rules. The peculiarity of this type of wart is that they grow inside the skin, forming a rough spot on the surface. Removing the affected areas is difficult; restoration of the normal tissue structure is carried out under a microscope.
Juvenile
This type of wart most often affects a child during birth. Quite often they affect the larynx, which is why in adolescence you can notice a change in voice timbre. Self-detection is difficult; the neoplasm can lead to difficulty breathing, even stopping it completely.
Diagnostic methods
Human papillomavirus in women in gynecology
HPV causes damage not only to the skin and mucous membranes, but also to internal organs. Some types of the virus are highly oncogenic. Therefore, getting rid of the diseases caused by them requires an integrated approach and does not allow self-medication.
Today, gynecologists perform human papillomavirus typing using the following methods:
- examination of the patient;
- colposcopy – the doctor examines the cervix;
- study of smears from the vaginal mucosa;
- cervical biopsy – necessary to obtain accurate information about the pathogen;
- PCR;
- DIGENE test for human papillomavirus HPV.
The last 2 diagnostic methods allow you to get the most accurate results when studying.
During a clinical examination, the doctor discovers warts or genital warts in a woman. Their presence reduces the list of possible diseases. Examination of smears of the vaginal mucosa helps to detect morphological changes in cells that occur under the influence of the papilloma virus. This method is nonspecific and therefore does not allow the identification of viruses that cause cancer. However, the use of this method helps to identify dysplasia associated with the risk of low-oncogenic viruses.
About 70-90% of false negative results occur due to improper sampling. About 30% of errors occur when taking tests by women who undergo cytological screening.
Colposcopy allows you to make the following diagnoses:
- mosaic - the appearance of polygons on a whitish background after treating the mucous membrane with a vinegar solution;
- abnormal transformation zone;
- punctuation - many reddish dots on a white background;
- acetowhite epithelium.
If the result of HPV tests in gynecology is negative, the risk of malignancy is zero.
During a cervical biopsy, tissue is scraped off and examined under a microscope. The purpose of diagnosis is to determine whether there are morphological changes in the cells of the mucosa. If they are found in a woman at an early stage, effective relief from symptoms is possible in the first month.
PCR allows you to determine the type of pathogen. There is foreign DNA or RNA in the patient's tissues. It is she who contacts the reagent that is administered to the patient.
Condylomas acuminata
A skin formation that looks like a “nipple” in appearance. It is considered a benign neoplasm. Although this type can develop into a malignant tumor.
Peculiarities:
- small size (up to 10 mm);
- mounted on a thin “leg”;
- flesh/pink;
- upon palpation they do not cause pain.
Let's celebrate! The infection enters the body through sexual contact. Localization - skin and mucous membranes.
Photo
Genital condyloma looks like this:
Treatment with medications
Human papillomavirus in women in gynecology
To treat papillomas in women, certain groups of drugs for papillomavirus are used:
- means that stimulate the immune system;
- antiviral agents;
- hemopathic drugs;
- cytotoxic substances;
- medications with destructive effects.
Medications with a destructive effect are compositions for external use that contribute to the consistent treatment of pathological growths.
Immunostimulants are used to treat HPV only in the early stages of the disease. They enhance the body's natural defenses. Most often they are prescribed in case of gynecological manifestations of the disease during complex therapy. The purpose of immunostimulants is to activate immune cells and produce antibodies. Common immunostimulants include:
- Allokin-alpha.
- Immunomax.
- Isoprinosine.
They are often used to treat papillomas in gynecology.
Antiviral drugs
No special medications (tablets or injections) have been developed to destroy HPV. The effectiveness of antiviral agents in the fight against papillomas has not been proven. Existing drugs in this category have a wide spectrum of action.
Antiviral drugs for HPV:
- Viferon. It is a popular remedy for human papillomavirus infection, which belongs to the class of natural interferons.
- Altevir. Has a strong antiviral effect.
- Roferon A. Interferon alpha 2-a. Activates the immune system to resist the virus. Has a pronounced effect against infected cells.
To find out how to treat papillomavirus taking into account the characteristics of your body, you should contact a gynecologist.
Treatment regimens
Recently, immunologists often pay attention to the immunomodulator Isoprinosine. The drug is available in the form of tablets and solution for injection. The active substance of the drug is inosine. It penetrates the cell membrane and affects the virus.
Isoprinosine has a wide spectrum of action. It enhances the body's natural defenses. When taken simultaneously with other antiviral medications, the effectiveness of the latter increases.
There are several accepted treatment regimens using Isoprinosine:
- Small pointed growths. The drug is taken orally, 2 tablets three times a day for two weeks.
- Multiple condylomas with individual large growths. In such cases, the dose of the drug should be set by a doctor monitoring the course of the disease.
HPV is actively treated using two-component regimens - a combination of surgical removal of growths and specific antiviral therapy.
Many courses of treatment for HPV include vaginal suppositories Betadine, Genferon and Polyoxidonium. Patients are also prescribed tampons with Manovit No. 10 cream-gel. Among the injectable drugs, Panavir is distinguished.
A short overview of the structure of papillomavirus
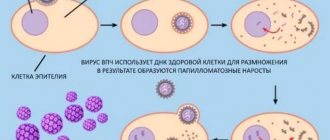
HPV is found in the keratocytes of the cells of the upper stratum corneum of the epidermis in the form of episomes, the essence of which are the genetic elements of bacteria, i.e. DNA. The genome of the form virus is created:
- Early genes that are responsible for HPV genome replication.
- Late genes are responsible for the synthesis of the protein shell.
Papillomaviruses have antigens: species-specific, type-specific. An antigen is any element that the body views as foreign or potentially dangerous, requiring the production of its own antibodies that can produce an immune response.
The formed virus does not have its own cell and waits for conditions to penetrate the body. Once in the environment, it finds the host cell and penetrates it with its DNA, leaving its protein on the surface, which serves as a signal for the immune system to act to destroy it. And if a rash appeared on the skin, then the immune system could not cope, and the papillomavirus was activated.
Removal methods
cervical papilloma
Many patients, when visiting a doctor, want to know how to remove unpleasant growths. There are several methods for removing papillomas in gynecology:
- chemical cauterization of growths;
- surgical cutting;
- cryodestruction – exposure of formations to extremely low temperatures;
- removal of growths using a laser;
- electrocoagulation;
- elimination of tumors using radio wave surgery.
The most basic way to remove papillomas is cauterization with chemicals. As a result of exposure to aggressive substances, the growth dies. After the papilloma is removed, a crust forms in its place and goes away within a few days.
Important! Experts do not recommend tearing off the crust - a scar may form on the skin.
Chemical removal should only be performed by an experienced professional as it can only be done after examining the type of growth. The composition of the products used includes salicylic acid and its analogues. Cantharidin is also used.
Surgical cutting is performed under local anesthesia. After the procedure, a pressure bandage is applied to the cut area. A more modern method is cutting off the growths with a laser scalpel. It is less traumatic and allows you to stop bleeding at the cut site.
Removal with liquid nitrogen – cryodestruction. No anesthesia is required before the procedure. Electrocoagulation is based on cauterization of tissue using high-frequency current.
The cost of operations depends on the number of tumors, their type and stage of development.
Conservative ways to cure skin from papillomas
Warts removed by surgery may appear again if the cause of their formation is not addressed.
Typically, new rashes on the body occur in a third of patients who have had papillomas removed with a laser or other method, which is why it is so important to destroy the papillomavirus in the body. In order not to encounter an unpleasant skin disease again, you need to strengthen your immune system.
In order not to encounter an unpleasant skin disease again, you need to strengthen your immune system.
Indeed, in most women and children, papillomas appear precisely because of the inability of their body to resist infections and viruses.
Immunity will increase if you strictly follow the following medical instructions:
- take vitamins (");
- improve your diet by including vegetables and fruits;
- do therapeutic exercises and hardening procedures;
- drink a general tonic drink (ginseng infusion);
- undergo treatment with immunomodulatory drugs.
By following these recommendations, you can get rid of flat papillomas forever without resorting to radical measures. Young people should especially take note of them.
In combination with drugs that strengthen the immune system, you need to take antiviral drugs.
Treatment of skin for warts on the face and body with antiviral and immunomodulating drugs should be supplemented with external agents.
They will speed up the skin restoration process. For this purpose, it is customary to use ointments that soften the epidermis of the formations, exfoliate their dead cells and stimulate tissue regeneration.
Typically, women's choice falls on salicylic, oxolinic or interferon ointment.
Photo:
These ointments are characterized by an antiviral effect. Skin treatment with any of them will allow you to qualitatively remove growths on the face and body without damaging the healthy epidermis.
But it is better to combine these ointments, since the simultaneous use of ointments will speed up the healing of virus-affected skin areas.
First, the papillomas need to be treated with salicylic ointment, let it absorb, and after 10 minutes apply oxolinic ointment. A combination of salicylic and interferon ointments is considered equally effective.
First, the dermatologist advises treating the growths with pharmaceutical preparations “Cryopharma”, “Solcoderm” or “Kolomak”.
If there is no effect, the specialist sends the patient for surgery to remove papillomas. Strengthening your immune system will help prevent the recurrence of warts.
Diet and vitamins for infected people
Human papillomavirus in women in gynecology
The main task of adjusting the diet of a person with an active papillomavirus is to increase immunity. Basic principles of eating healthy food:
- you need to give your body enough fluid;
- food should be enriched with natural proteins;
- food should contain many microelements and vitamins;
- It is important to monitor your fat intake in moderation.
It is better to drink a lemon drink before your morning meal. To prepare it, take the juice of half a lemon and a glass of boiled water. This solution can improve digestion, cleanse the liver and intestines. In addition, citrus fruits contain ascorbic acid, which increases the body's defenses.
You should consume at least 2 liters of liquid per day, included in soups and drinks. The liquid is able to remove toxins from the body.
The diet should include a lot of fruits and vegetables. It is better to eat fruits that are grown in natural conditions. Juices should be consumed freshly squeezed. Vegetable soups are best consumed undercooked.
You can strengthen your immune system with protein foods - meat, eggs, fish, milk. They are especially useful in winter, when the body receives a minimum of vitamins. It is better to choose lean meat.
Fatty foods should be limited because they contain free radicals. It is important to limit the consumption of refined carbohydrates (sweets and baked goods). You should eat foods containing natural carbohydrates (cereals, cereals).
Among the vitamins useful in the fight against papillomas are:
- A – found in carrots, eggs, liver, dried apricots;
- C – currants, citrus fruits;
- E – salads, cabbage.
- B – buckwheat, mushrooms.
A diet for papillomas involves giving up alcohol. Most medications are usually incompatible with alcohol, which negatively affects the immune system.
Coffee and strong tea should also be avoided during treatment. It is better to drink more herbal tea.
How to get rid of warts on the face
Before starting treatment for flat papillomas, it is necessary to undergo a medical examination to confirm the diagnosis. It cannot be ruled out that the virus may be oncogenic, so consultation with a venereologist is necessary here.
To treat flat papillomas, you can use a conservative method, which consists of using various pharmaceuticals and special ointments. With this treatment, you should not allow the ointment or cream to come into contact with areas of the skin that have not been affected by the disease.
Conservative treatment
The most popular means of conservative treatment of flat papillomas are:
- Super clean. This solution should be applied to papillomas using a cotton swab. If the formations on the body are small, then one lubrication is enough. In order to eliminate large papillomas, they must be lubricated for several days. The solution should be applied to the formations in several layers, which are removed after drying. The procedure is repeated until the papillomas on the body disappear completely.
- Cryopharma performs the function of freezing tumors on the skin. In order to get rid of flat papillomas, one time is usually enough. For ease of application, the solution comes with 12 special disposable applicators, so you should calculate the amount of the drug depending on the number of papillomas on the body.
- A solution of salicylic acid and simple cream. To prepare the product, take a proportion of 1:10. The solution is applied to the papillomas using a cotton swab until the formation softens. This method of treatment differs in its duration. Papillomas on the body will begin to disappear only in the third week of treatment.
- Plasters for papillomas. Single papillomas can be removed using salidop, which can be purchased at almost any pharmacy. This patch contains sulfur and salicylic acid, which can dry and soften skin formations on the body. Before sticking the patch on the papilloma, it must be steamed. The patch is removed only after 24 hours.
Removal
When papilloma appears on the fingers or on the neck, they usually do not cause much concern.
Therefore, papilloma on the mucous membrane requires immediate treatment, and complex therapy is used to maximally exclude remission of papillomatosis.
Papillomas on the mucous membranes appear in the form of growing epithelial tissue, which is caused by the human papillomavirus - HPV.
- It affects up to 90% of the entire population, but may not become active until the end of a person’s life due to his strong immunity.
- The virus is resistant to many conditions, which is why it spreads so quickly and easily.
- The incubation period of this disease can vary in each case differently - from a week to ten years.
Therefore, it is impossible to predict exactly when and under what conditions the infection occurred.
It is easier to become infected with HPV through the fluids that the human body secretes.
Therefore, they are more likely to become infected when:
- shake hands;
- eat from common dishes;
- engage in oral sex;
- sexual intercourse is not protected by a condom;
- go without shoes in swimming pools, public baths, water parks;
- use someone else's towel, razor, toothbrush, etc.;
- An infant born from an infected mother will be 100% infected with HPV.
Once in the body, the virus does not immediately manifest itself, so papillomas will appear on the skin and mucous membranes after:
- there will be a sharp decrease in human immune defense;
- There will be a deficiency of nutrients in the body.
Warts on the face cause great discomfort to their owner, since these unaesthetic growths are visible to strangers.
They can significantly affect a person's appearance and also affect their self-esteem.
Therefore, people try to get rid of such papillomas as quickly as possible.
In their structure, such growths have the appearance of overgrown epithelium.
Warts are benign growths, but this does not mean that they do not need to be removed. These growths are prone to proliferation, especially when injured.
Therefore, if warts on the face are left untreated, there is a high risk of papillomas spreading on the body: they can appear on the arms, legs and even genitals.
This is due to insufficient immune protection during these periods of life.
Why do they appear?
Warts appear as a result of activation of the human papillomavirus, which enters the skin through micro-wounds.
Prevention and safety measures
About 80% of people on the planet are infected with the papilloma virus. The pathogen is activated only when immunity decreases. As a result, papillomas and warts of various strains appear on the skin.
Preventive measures to prevent the appearance of growths:
- streamlining sexual life;
- compliance with hygiene rules;
- maintaining normal immune function;
- limiting contact with patients.
These measures reduce the risk of infection with papillomavirus and its activation.
If you discover neoplasms on your skin, you should immediately consult a doctor who will prescribe effective treatment. You should not use other people’s shoes and things, as well as other people’s hygiene products.
Do facial skin types affect the appearance of papilloma?
Dermatologists have noticed that all types of facial skin are susceptible to the appearance of papillomas, regardless of the level of oiliness, moisture, or dryness.
This is explained by the fact that infection with the virus occurs through sexual contact and direct contact during the appearance of such growths.
And these specific warts or genital warts appear against the background of overwork and stress.
If you do not expose yourself to these factors and monitor the health of the skin of your face and entire body, the appearance of papillomas can be avoided throughout your life.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=MxdVUauCgv8
The article was written based on materials from the sites: cosmetology-info.ru, caringmother.ru.