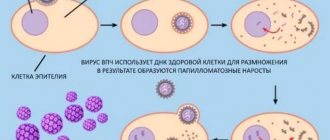
Today in gynecology, papillomas on the cervix are quite common.
This pathology consists of numerous growths in the form of warts, which are located on the epithelium of the cervix. Their appearance is triggered by the human papillomavirus (HPV), which can enter the human body in several ways. This virus is in a passive state, but when a person’s immunity decreases, it is activated, causing the development of a serious disease of the genital organs, which can trigger the appearance of an oncological tumor.
Papillomas on the cervix: what is it?
Cervical papillomatosis is a serious disease caused by HPV, which is characterized by large-scale proliferation of uterine tissue. The disease is considered dangerous, since in half of the cases it can cause the formation of malignant neoplasms. According to ICD-10, this disease is coded D26 and B97.7, which includes benign uterine tumors and papillomaviruses.
Note! The presence of the virus in the human body for a long period of time, as well as damage to the reproductive organs, can cause cervical cancer, which often leads to death within two years.
Cervical papilloma
Today, medicine knows about one hundred strains of HPV. Strains of the virus such as 16 and 18 are considered to be particularly dangerous; they can provoke the development of a cancerous tumor. Viral infection of the cervix often leads to the spread of inflammation to those structures that are nearby.
Papilloma on the cervix may not show symptoms for a long time, without causing discomfort. After HPV activation, it begins to actively multiply in the epithelium of the cervix, disrupting its structure and provoking the appearance of growths in the form of papillae.
Treatment and removal from the cervix
Papilloma on the cervix requires complex treatment. Therapy includes methods of influencing the infection, restoring the body's immune defense and directly removing growths. This scheme allows you to speed up the recovery process and prevent the likelihood of relapse. Taking antiviral drugs works to neutralize the strain’s ability to reproduce.
A weakened immune system is not able to cope with the pathogen on its own; immunostimulants come to the rescue, helping to restore protective functions. Against this background, the body suppresses the infection “stunned” by the drugs. Removing the growths removes the predominant accumulation of pathogen cells.
Treatment for cervical HPV at home is dangerous and impractical. The growths are in a hard-to-reach place. Selection of the necessary drugs is possible only on the basis of a diagnostic study. Folk remedies are not able to guarantee the required effect, but can cause aggravation of the condition. Treatment procedures to eliminate the virus and its symptomatic manifestations must be carried out exclusively in a medical facility.
Antiviral agents
Antiviral drugs inhibit the ability of the infectious agent to reproduce and prevent the growth of formations.
Immunomodulators that are effective for treating HPV include:
- Natural interferons: Interferon, Leukinferon.
- Recombinant interferons: Viferon, Genferon, Kipferon, Reaferon.
- Cell wall peptidoglycan fragments: Lycopid.
- Synthetic immunomodulators of different groups: Isoprinosine.
- Peptide immunomodulators: Allokin-Alpha.
- Interferon inducers: Cycloferon.
The listed drugs have a complex effect on the infectious agent. The doctor prescribes medications for HPV based on the information received about the condition of the patient’s body.
Chemical degradation and cytotoxic effects
The growths can be removed by means of chemical destruction and cytotoxic action. This category includes special suppositories, ointments, gels and solutions.
Epigen intimate is a drug based on glyceric acid. Has a mild chemical effect. Apply by injection. Approved for use by children aged 1 year and older.
Condilin is a remedy for removing condylomas. Apply to the formation, avoiding contact with healthy areas. Cauterization is carried out twice a day for 3 days.
Solkovagin is a solution for the treatment of benign tumors of the cervix. When applying, avoid contact of the drug with healthy skin. The treatment can only be carried out by a doctor.
When treating internal organs, potent chemical agents used to eliminate warts on the skin are contraindicated. It is permissible to purchase medications at a pharmacy only after agreement with the doctor.
Laser therapy
This is the most common form of getting rid of growths on the cervix. Thanks to a special device that generates a laser beam, you can get rid of papillomas of any size. The laser burns out formations with high precision, eliminating the possibility of relapse. The main advantage of the method is its coagulative effect: the coagulation of proteins in the tissue prevents bleeding and the likelihood of the spread of infection. The disadvantage of the procedure is that it is not possible to conduct a histological analysis of the condyloma.
Physical methods
Cryodestruction is the use of liquid nitrogen to freeze formations. Under the influence of cold, the growths are destroyed and die. It takes 2 weeks to completely get rid of warts.
Electrocoagulation involves the use of high temperatures to cut out growths. The method is bloodless and requires the use of anesthesia.
Radio wave method . Under the influence of high-frequency waves, layer-by-layer burning of papillomas occurs. The most gentle procedure. It is distinguished by its bloodlessness and lack of direct contact. Treating growths with this method does not hurt.
Surgery . A method that allows you to cut off growths with a scalpel. It is used quite rarely, especially in nulliparous women. The procedure is invasive, entails bleeding and long-term rehabilitation. Makes it possible to obtain samples for further analysis.
Types of uterine papillomas
In medicine, the following types of cervical papilloma are distinguished:
- Pointed papillomas on the cervix, which are characterized by the proliferation of connective tissue and epithelium that form on the surface of the cervix. They are presented in the form of small folds into which vessels and connective tissue grow, so they have a thin or wide base, and resemble cauliflower in appearance;
Pointed papillomas of the cervix
- Squamous cell papillomas rise above the surface of the epithelium; as they develop, they contribute to the deformation of the uterus. In appearance, such a formation resembles a wart;
Squamous papillomas
- Inverted papillomas on the cervix have the ability to grow deep into the tissue, destroying the organ. This type of disease is classified as precancerous conditions.
Inverted papilloma
Methods for treating human papillomavirus in women
There are many ways to combat papillomas on the cervix, including the use of medications and surgery. Let's look at each method in more detail.
Antiviral agents
In the early stages of papillomatosis development, it is enough to take antiviral drugs. The following medications have proven themselves well in the fight against the disease: Interferon, Ingaron, Zovirax, Gevaxone, Viferon. During the period of drug therapy, immunomodulating drugs are also prescribed to increase the body's defenses.
HPV removal
There are several ways to remove growths on the cervix. The choice of a particular one depends on the degree of damage to the organ, as well as on the financial capabilities of the woman.
Chemical methods
Destructors are used to chemically remove tumors. They contribute to the death of pathological cells, as a result of which they disappear.
Since the lining of the cervix is very sensitive, not every destructor drug is suitable for eliminating papillomas. Usually the following medications are prescribed for this purpose: Solcoderm, Ferezol, trichloroacetic acid.
Important! You cannot remove papillomas using chemical methods on your own. Only the attending physician can treat the cervix with the selected drug.
Surgical intervention
This is a classic method, which involves excision of the pathological formation using a scalpel. The operation is performed under anesthesia. After surgery, a woman requires a long period of rehabilitation.
This method is significantly inferior to modern methods of removing papillomas, but it is the only one that can remove malignant cells, therefore it is used for advanced forms of papillomatosis on the cervix.
Cryodestruction
The essence of the method is to freeze pathological tumors. For this, liquid nitrogen is used, after exposure to which the growths are gradually rejected.
After such exposure, the epithelial layer is gradually restored, and healthy cellular structures grow in place of the papilloma.
Important! With the help of cryodestruction, it is not always possible to remove all atypical cells. This risks the woman having a relapse after a certain time.
Laser vaporization
This is the most popular method of removing papillomas on the cervix today, and also the most gentle. Laser treatment of pathological cells is recommended for young girls who are planning to give birth in the future. Laser removal of papillomas is effective even in advanced cases.
Radio wave method
This is a low-traumatic method of removing growths. It is a device that generates radio waves. Upon contact with tissues, they heat cellular and extracellular fluids, resulting in their evaporation and destruction.
Then, after a while, a white scab forms, which disappears after a few days. Removal of growths on the cervix is one of the safe methods; it does not require postoperative hospitalization; the period of complete healing occurs within 2 months.
Electrocoagulation
It is an electrical cauterization of damaged areas. This method is only suitable for women who still do not plan to give birth in the future. The problem is that the current is highly conductive, which can result in scarring on the cervix.
Traditional medicine
Alternative medicine offers many ways to combat papillomas.
Important! If papillomas occur on the cervix, it is strictly not recommended to use folk remedies to remove the growths directly. This can lead to dangerous consequences
Only the use of drugs that help increase immunity is allowed on your own.
- Pine drink. You will need 2 tablespoons of chopped pine needles (this could be pine, cedar, spruce and others), pour 1 glass of boiling water. Place on low heat to simmer for about 20 minutes. Leave to brew for half an hour. Filter the finished broth, drink 1 tablespoon 3 times a day.
- Potato juice. You should take red potato tubers, rinse thoroughly, do not cut off the skin, remove only the dark spots. Grind using a blender or meat grinder. Squeeze the juice out of the resulting pulp using gauze. Take 100 ml 3 times a day an hour before eating.
- Juniper. Every morning you need to eat a handful of juniper berries on an empty stomach, chewing thoroughly.
Reasons for the development of the disease
HPV enters the human body in the following ways:
- Intimate relationships with an infected person, and the virus can end up inside the body as a result of a kiss, since it also lives in saliva;
- Visiting swimming pools, baths, saunas, beauty salons or solariums, where the virus can enter through household means;
- Transmission of infection to a child from a mother in whose uterus the papillomavirus is localized during childbirth.
Once in the human body, the virus can remain in it for a long time in a passive state. When immunity decreases, it is activated, triggering the development of pointed and then squamous cell papilloma of the cervix.
Note! A condom may not always protect against HPV infection. The virus can travel through pores in the latex from which the condom is made.
One of the reasons for decreased immunity is bad habits, so women who abuse smoking, alcohol and drugs are at risk.
With a stable and strong immune system, the papillomavirus in women can disappear on its own within several years. But this is observed only in the absence of chronic diseases in the field of gynecology. The reasons for the development of cervical papilloma may be as follows:
Uterine erosion
Immune system disorder;- Constant stress and depression;
- Infectious diseases in acute form;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Having an STD;
- Erosion of the uterus;
- HIV infection.
Reasons for appearance
Papillomatous condylomas, which appear inside the vagina, arise as a result of the development of human papillomavirus (HPV) in the body. This virus contains its genetic code in a DNA helix, which it inserts into the DNA of target cells, causing them to develop in a different way. Their new shape, size and all vital parameters are completely controlled by the virus.
According to the international system ICD-10, which classifies diseases, human papillomavirus corresponds to codes D10-D36.
This large group of viruses contains many strains, each of which has its own digital code instead of names. These strains cause different symptoms, determine the course of the disease and the possibility of complications.
Some strains, after a long presence in the body, provoke the onset of an oncological process, so experts divided them according to their level of oncogenicity into three main groups:
- non-oncogenic strains (almost never cause the development of a malignant process);
- strains of low oncogenicity (sometimes provoke the degeneration of benign tumors into malignant ones);
- highly oncogenic strains (often cause the transformation of papillomatous warts into cancerous tumors).
The strains that cause cancer in humans make up a small group of the total number of strains that cause papillomatous infection, but they are quite widespread and highly contagious, and are also more difficult to treat. Women with a predisposition to cancer should pay special attention to the development of warts. In people who do not have such a predisposition, even highly oncogenic strains do not cause cancer.
Routes of infection with HPV
- Sexual path . Most often, the infection enters the body through sexual intercourse. The pathogen enters the body during vaginal, oral or anal sex. The presence of any cracks, microtraumas or scratches on the epithelium facilitates the easy passage of the virus through the integumentary tissue. Using condoms during sex does not provide a person with complete safety, but it reduces the likelihood of illness several times.
- Household way . The infecting agent is found in all human physiological fluids, so a woman can become infected through close contact with a sick person or his things: wet towels, dishes, bedding and underwear. Since the virus is present in urine, saliva and semen, the disease can be acquired when visiting public toilets, saunas, swimming pools and other public places.
- Transmission during pregnancy . The fetus can become infected from the mother during the prenatal period. Often the baby gets the disease during childbirth, when it moves along the birth canal and comes into contact with papillomatous warts in the vagina through thin skin.
After infection, a characteristic clinical picture with the formation of warts or condylomas does not always appear. It has been proven that most women are carriers of HPV, but a small percentage of them develop symptoms.
Factors contributing to infection
- Onset of sexual activity before age 17.
- Neglect of barrier contraception (condoms).
- Other sexually transmitted infections.
- Injuries to the vaginal epithelium.
- Vaginal dysbiosis.
- Endometriosis.
- Any long-term illness.
- Pregnancy and lactation period.
- Excess weight.
- Hypovitaminosis (in particular, group B).
- Immunosuppressive therapy.
- Disorders of the thyroid gland.
If the rules of intimate hygiene are neglected, the risk of infection increases significantly, especially in women.
After infection, the progress of the disease directly depends on the woman’s immune status: if the body’s resistance is high, the virus can be inactivated by phagocytes or remain suppressed.
Symptoms
Diagnosing the disease is difficult because it often does not show symptoms.
At a late stage of pathology development, the following signs may be observed:
- Pain during intimacy;
- The appearance of bleeding and unpleasant odor from the vagina;
- Enlarged inguinal lymph nodes;
- Pain in the lower abdomen;
- Itching and burning in the vagina;
- Menstrual irregularities;
- Loss of appetite, weight loss;
- Swelling of the legs.
Typically, women pay attention to such symptoms and come to a medical facility to undergo an examination by a gynecologist, who identifies the cause of the development of the pathology.
The gynecologist identifies the manifestation of the following signs in the female body:
Tuberosity of the cervix
Formation of warts on the cervix, while the color of the mucous membrane is not changed;- The tuberosity of the surface of the cervix indicates the presence of single or multiple pointed papillomas;
- Presence of erosion;
- Areas of dysplasia.
The last two points may indicate a precancerous condition and therefore require immediate treatment.
Symptoms
With cervical papillomas, symptoms may be absent for a long time, since the immune system suppresses the development of the virus that provokes the disease. Gradually, genital warts may appear in the vagina.
We recommend reading Intramural uterine leiomyoma - types, indications for surgery, treatment
After a certain time, they may disappear, remain unchanged, or begin to grow. There are also options for other manifestations of the virus:
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- periodic occurrence of pain in the lower abdomen;
- unpleasant odor of discharge;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- bloody discharge after sex;
- the appearance of copious discharge;
- the presence of itching in the genital area.
Clinical symptoms largely depend on the type of tumor. If a woman experiences an acute development of an infectious process, this is typical for acute papilloma. The chronic course of the disease can be seen with a flat form.
During the examination, the gynecologist may detect warty formations in the cervical area, which often disappear on their own and return after a while. On palpation, you can feel the tuberous epithelium, especially with pointed formations.
Papillomas and pregnancy
If papillomas were discovered during pregnancy planning, they must be treated without fail to prevent deformation of the uterus and the growth of formations during the period of gestation, as this can cause a complicated birth.
If the disease manifests itself during pregnancy, there is a risk of miscarriage. Infection of the fetus occurs in 80% of cases, while HPV often affects the respiratory and genitourinary systems of the child.
Note! Often, the papillomavirus, which was diagnosed during a woman’s pregnancy, disappears on its own after labor.
Features of the disease during pregnancy
Symptoms of the virus may bother pregnant women. Experts have repeatedly noted that in women, activation of the disease often occurs during pregnancy. This phenomenon is associated with a sharp deterioration in the immune system. Changes in hormonal levels also bring adjustments to this process.
Dormant virus often becomes active during pregnancy
Expectant mothers worry that the resulting papillomas can become a threat to the development and life of the unborn baby. In fact, these fears are in vain if the growths appear outside the reproductive system. In this case, the tumors do not harm the child. But they bring severe discomfort to the woman. As a rule, after childbirth, the growths go away on their own.
The situation is different with papillomas on the cervix and vagina. They can become a serious problem for a woman. These growths contain a large amount of active virus. There is a chance that it will be passed on to the child during his birth.
Sometimes the fragile body of a newborn child manages to suppress the influence of infection. In this case, painful growths will not appear on his body. Only occasionally do doctors diagnose the entry of papillomavirus into the respiratory tract of babies. With this course of the disease, neoplasms begin to appear in the larynx. This makes the process of air entering the lungs much more difficult. Asphyxiation attacks are a consequence of a pathological process.
Only a doctor who monitors the pregnancy of a woman infected with the papilloma virus can decide whether she needs treatment or not. To find out, he must examine the patient and familiarize himself with the results of the diagnostic procedures she has undergone. As a rule, therapy is not carried out in the first half of pregnancy. Treatment at this stage can lead to fetal poisoning with aggressive substances that are part of medications.
If the virus requires immediate treatment, then the pregnant woman is prescribed surgical removal of papillomas on the cervix.
If doctors fail to diagnose papillomas in a timely manner, they can grow to enormous sizes. Then the neoplasms will interfere with the normal course of labor. In case of this violation, women in labor are prescribed a caesarean section.
In advanced cases, a caesarean section may be required
Diagnostic measures
Cervical papilloma requires a comprehensive diagnosis, which necessarily includes tests to identify the type of infectious agent, on the basis of which treatment tactics are developed.
The examination begins with a gynecological examination of the cervical epithelium using multiple magnification. During the examination, the doctor takes a smear, which is then sent for cytological examination.
The results of this analysis can be presented in several forms:
- The first and second forms indicate the absence of a violation of the tissue structure;
- The third form requires further research;
- The fourth and fifth forms indicate the presence of signs of a malignant neoplasm.
Cytological analysis
Note! The gynecologist prescribes colposcopy and biopsy followed by histological analysis. This is usually done in case of uterine dysplasia and when a third class is detected according to the results of cystoscopy.
Lugol's solution
One of the diagnostic methods is a test using acetic acid. In this case, the gynecologist exposes the cervix and treats it with acetic acid and Lugol's solution. In the presence of papillomavirus, the epithelium of the cervix will be unevenly colored.
PCR is also prescribed to identify the type of pathogen and ultrasound of the pelvic organs. When carrying out PCR, it is necessary to take samples of at least fifteen strains of the virus. This study helps to identify forms of the virus that can disappear on their own.
The doctor differentiates cervical papilloma from diseases such as leiomyoma, endometriosis, and erosion.
Diagnostics
When a patient first contacts a gynecologist, he conducts an examination on a gynecological chair, during which he determines the presence, shape, extent of the lesion and the condition of the papillomas. Colposcopy is immediately performed using magnification, which allows you to examine the affected area in detail. Before examination, the vagina and cervical canal must be treated with a weak solution of acetic acid, which makes the surface of the warts more contrasting.
At the second stage of diagnosis, the following tests may be prescribed:
- PCR test . To do this, take a scraping from the affected area and determine the DNA of the virus in it. This technique makes it possible to identify the pathogen during carriage.
- Digen test . This type of analysis is a modified version of the previous one. It allows you to accurately determine the strain of the virus, which makes it possible to assess oncogenicity and further prognosis of the development of the disease.
- Serological analysis . To do this, a blood sample is taken and antibodies to the papillomavirus are determined in it.
- Vaginal and cervical smears . The selected material is used for oncocytology under a microscope. This method makes it possible to detect cancer cells in biological material.
- Tissue biopsy for histology and cytology . Samples are stained with microbiological dyes and atypical cells are identified.
If HPV is suspected, all patients are required to undergo tests to determine HIV infection and RW (syphilis).
Learn more about human papillomavirus and cervical cancer in this video.
Drug therapy
Zovirax
Treatment of the disease should be comprehensive, aimed, first of all, at increasing human immunity. The patient is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits, take vitamin and mineral complexes, and immunomodulators. Therapy is carried out under the supervision of the attending physician.
Drug therapy involves taking cytotoxins, interferons, and antiviral agents. Ingaron, Interferon, Zovirax and others have proven themselves well. These drugs are not prescribed during pregnancy. It is also recommended to take vitamins and minerals.
Note! Because human HPV can manifest itself in a variety of ways, including spontaneous resolution, therapeutic interventions are usually aimed at eliminating the manifestations of the virus.
Surgical therapy
As a surgical treatment, the doctor performs destruction, in which surgical removal of papillomas is performed in one of several ways:
- Cold therapy
Moxibustion; - Laser therapy;
- Cold therapy;
- Electrosurgery;
- Chemical destruction. This method of therapy can be used during pregnancy.
Surgical removal of tumors does not provide a 100% guarantee of complete recovery, since there is always a risk of relapse. The infection can be in a passive state in the body; with a significant decrease in immunity, it will appear again.
Doctors recommend following preventive measures after treatment to prevent recurrence of the disease.
Video: removal of cervical papillomas
Methods for diagnosing the disease
The disease can be identified using:
- Gynecological examination. The specialist visually determines the presence of genital papillomas on the cervical mucosa.
- Cytological examination of a smear. Detects the presence of papilloma virus in the body and the possibility of cancer.
- Colposcopy of the cervix. This is done using a specialized microscope.
- PCR method. Allows you to determine the type of virus.
- Immunofluorescence analysis.
ethnoscience
One of the effective folk remedies for HPV is a collection of herbs such as plantain, horsetail, nettle and lemon balm, rose hips and dandelion root. They are mixed in equal parts, and then three spoons of the mixture are poured with one liter of boiling water and left for about three hours. After this, the decoction is taken four times a day before meals.
This herbal collection can be alternated with a decoction of thyme or oregano. Two spoons of one of these herbs are poured with half a liter of boiling water and left for two hours. Take half a glass of decoction three times a day before meals. It is recommended to use the product for at least two weeks.
Treatment
Treatment of papillomas on the cervix for each patient is chosen purely individually. What kind of therapeutic actions will be carried out depends on the location of the papilloma, its type, the state of immunity, the patient’s age and test results. If HPV with high oncogenic activity is diagnosed, the doctor prescribes complex effective therapy, after which they begin surgical removal of the papilloma and treatment of sexually transmitted infections.
Drug treatment
Patients are prescribed therapy with antiviral drugs, the action of which is aimed at suppressing the proliferation of the human papillomavirus.
These drugs are most often used in the treatment of pathology:
- Panavir;
- Bonaftone ointment;
- Ridoxol ointment.
Women also need to take sedatives and vitamin complexes.
To remove formations, special solutions are used:
- Solcoderm;
- Collomak;
- Condillin;
- Feresol;
- Celandine oil.
To prevent recurrence of the virus, an intramuscular vaccination is given.
Surgical removal of formations
Surgery is prescribed in cases where medication methods have been unsuccessful.
The process of removing papilloma on the cervix can be carried out using the following methods:
- laser vaporization;
- chemical coagulation;
- radio wave exposure;
- cryodestruction;
- diathermocoagulation.
All actions to remove papilloma in the uterus are performed only under anesthesia, including methods of destruction. After eliminating the disease, there remains a small chance of relapse, so in order to prevent it, you must strictly follow all the doctor’s prescriptions.
Therapy with folk remedies
If a woman has a good immune system, her body can independently resist the virus and prevent it from becoming more active.
Treatment with folk remedies is based on increasing immunity. To do this, you can use decoctions of the following herbs:
- nettle;
- horsetail;
- dandelion roots;
- plantain leaves;
- Melissa.
These ingredients must be mixed in equal doses and 1.5 tbsp. add a spoonful to half a liter of hot water, then boil for about ten minutes. The decoction should sit for several hours. You need to drink two tablespoons three times a day. To improve the taste, you can sweeten the broth with sugar or honey. The use of essential oils is also very beneficial. To use you just need to add a bath of them. The procedure can be performed several times a week.
If the doctor prescribes only monitoring for papilloma, then drug treatment can be replaced with folk remedies. But such remedies should be used only after consultation with a doctor. Treatment at home may be ineffective and harm your health.
Forecast
The prognosis of the disease will be favorable if the pathology was diagnosed at an early stage of development, has a small affected area, and treatment was started in a timely manner.
The virus can be suppressed provided that the patient follows all the prescriptions and recommendations of the attending physician and the rules of personal hygiene. An unfavorable prognosis occurs when a woman has unprotected sexual intercourse during treatment, does not use complex therapy, or does not comply with the gynecologist’s instructions.
Note! Left untreated, uterine cancer can develop, often resulting in death.
Video about possible complications
Causes of the disease
There is a widespread belief that papillomas can only be contracted through sexual contact, but is this true? Indeed, unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected partner entails infection with this virus. However, this is not the only reason for infection
Please note the list below
- The papilloma virus can spread from partner to partner, even if the couple uses a condom. Sometimes, in order to get on the mucous membrane, even a kiss from a sick person is enough for him.
- Infection can even occur through household means. For example, when visiting a sauna, swimming pool, solarium and beach. Try not to use other people's towels and washcloths.
- Papillomavirus is transmitted from mother to child through the birth canal.
- Decreased immunity creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of kandilomas. Immunity may decrease for the following reasons:
- Stress;
- Alcoholism;
- Tobacco smoking;
- Sick stomach.
All varieties of papillomavirus are quite persistent in environmental conditions. Therefore, try to avoid using other people’s personal belongings and hygiene products. Without personal contact with an infected person, you can become infected with this infection through household means.
Prevention
For the purpose of prevention, women are recommended to undergo periodic examinations by a gynecologist, have one regular sexual partner, and undergo vaccination.
Sexual activity should not begin at an early age, but from the age of eighteen; during this period, the uterine tissues fully mature, and the epithelium has local immunity, which can protect against the manifestation of the virus. It is unacceptable to perform numerous abortions and curettages in order to avoid injury to the walls of the uterus. A woman should lead an active healthy lifestyle, constantly increasing the body's defenses.
Note! Vaccination is carried out against several strains of the virus at once, which can cause cancer. Vaccination is used only for the purpose of prevention.
Prevention against HPV
Recommendations for HPV prevention:
- Timely treatment of any diseases that can reduce immunity.
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Having a reliable sexual partner.
- Avoiding stress and hypothermia.
- Complete rest.
- Taking vitamins.
- Vaccination.
Important! Today there are two vaccines that can protect against the two most dangerous types of HPV.
Photo 2: Vaccination is recommended for girls aged 9 to 13 years who have not yet begun sexual activity. Both types of vaccines are highly effective if given before exposure to the virus. Source: flickr (Pan American Health Organization).
The vaccine does not kill papilloma viruses and does not treat related diseases , such as cancer. It only helps create immunity against infection.