How to treat papillomas on the tongue
At the moment, humanity is not able to get rid of HPV. Medicines have not yet been developed that completely destroy the virus, but papillomas on the oral mucosa as a symptom can be eliminated. Although a person will forever remain a carrier of the infection, its development can be blocked by various methods. But the first thing you have to do is visit a dentist to cure all existing diseases of the teeth and gums.
Medicines
Drug treatment of oral papilloma begins with the purchase of bactericidal toothpaste. This is the easiest way to prevent bacterial infection of damaged papillomas. In case of extensive inflammatory reactions and the addition of a severe bacterial infection, more powerful antiseptics are used: Rotocan, Iodinol, Eludril. Additionally, the doctor prescribes antibiotics Nolitsin, Siflox.
After secondary infection is prevented, treatment of papillomas can begin. Chemical methods of burning out formations in the mouth are not used. The risk of extensive damage to the delicate surrounding tissues and mucous membranes is too high. Therefore, the impact should be directed at the virus as the source of the problem. It is produced in 2 directions:
- Immunomodulatory therapy. Polyoxidonium, Immunomax, Lykopid are used to directly enhance the body's defenses. Ascorutin and vitamin complexes additionally increase resistance to the pathogenic influence of infection.
- Use of antiviral agents. Amiksin, Viferon and drugs of the interferon group effectively stop the development of the disease, preventing the appearance of tumors.
Only a doctor knows how to get rid of papillomas by determining the HPV strain and types of secondary oral infections based on diagnostic results. Therefore, independent treatment will be ineffective and will complicate further treatment of the formations.
Radical methods
It is strictly forbidden to remove growths yourself. This can trigger the degeneration of papilloma into a malignant cancer tumor or lead to tissue infection by bacteria. Therefore, only a specialist should treat HPV manifestations on the tongue and other areas in the mouth.
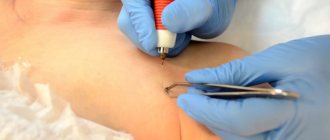
The most popular method today is to remove the formation using a laser.
There are several radical methods for removing papillomas:
- Surgical. The most traumatic and dangerous method. Currently, scalpel excision is used only for very large tumors. After this, wound surfaces remain on the skin and mucous membranes, requiring additional treatment.
- Cryodestruction. Practically not used in the mouth. The use of liquid nitrogen is quite dangerous due to the location of papillomas. Cold also increases the risk of cells degenerating into cancer.
- Electro- and radiocoagulation. Common methods for removing papillomas on the gums and cheeks. Electricity or radio waves are used to excise the lesions. They can later be examined to determine the presence of cancer cells.
- Laser therapy. A powerful light beam burns out warts in a targeted and painless manner. It is considered the safest and most effective method of radical treatment.
Is it possible to help with folk remedies?
Before treating oral papillomas with herbs, you should consult your doctor. Not all strains of HPV can be cured with folk remedies. It is also necessary to clarify whether the herbs will interact with the medications used, or whether there are allergies to them. If everything is in order, then you can use:
Celandine. The herb is considered the oldest medicine for any dermatological problems. To prepare a healing mixture, you need to combine olive oil with chopped stems and leaves in a 1:1 ratio. After infusing for a month, it is enough to apply the oil 3-4 times a day until the growth disappears. Chicken protein. You should only use the mucus that covers the inside of the shell. Several times a day, papilloma on the gum or tongue is smeared with egg
It is important that the protein dries, only then will it work. Therefore, you can use cotton wool or a sponge to protect the area from saliva. Castor oil
The product removes papillomas, disinfects and accelerates tissue regeneration. For treatment, it is enough to buy a bottle at the pharmacy and apply the medicine with cotton wool to the wart three times a day. Therapy continues for up to a month. It all depends on the size of the affected area.
Even after the formations disappear, it is important to find out from the doctor what to do to prevent them from appearing again. Considering that HPV will remain in the body, there is always a risk that benign tumors will return
Folk remedies
Papillomas on the lower and upper parts of the tongue can be treated with folk remedies at home. However, they can only be used as part of the main therapy and after consultation with a doctor. Only in this case will it be possible to achieve an effective result and avoid adverse consequences.
Medicinal herbs help against HPV: lemon balm, rosehip, plantain, chamomile, etc. Infusions and decoctions from these plants strengthen the immune system. You can also consume 100 ml of red potato juice daily.
You can remove formations at home using celandine juice. They need to lubricate the growths. The remedy brings results if the tumors are small. Repeat the procedure three times a day. Duration of therapy is one month.
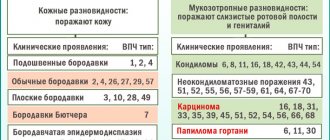
Types and manifestations of pathology
How to treat papillomas on the tongue depends on many circumstances. Affects the choice of methods and the type of tumor formed. Papilloma on the tongue can be of two types:
- Flat. This type of neoplasia rises very slightly above the surface of the skin. It is characterized by fairly large sizes and light color. Usually such a growth is single.
- Thread-like. Its size is somewhat smaller than that of the previous type of papillomas, however, they grow in height. Their color is almost the same as that of the mucous membrane of the tongue. Most often, thread-like formations appear in groups.
There is also a classification of growths according to their location. They can be located under the tongue or on its surface, on the palate, the inside of the cheek, etc. These features also influence the choice of treatment methods, since the further the neoplasia is located on the tongue, the more difficult it is to remove it.
Papillitis of the tongue, unlike other varieties of this disease, is often manifested by severe painful sensations. The pain increases significantly during eating, when food particles touch the papilloma that has formed on the tongue. In addition, other unpleasant symptoms are observed, which depend on where the tumor is located.
Most often, patients who have a pathology such as papillomatosis name the following unpleasant symptoms that occur to them:
- hard breath;
- difficulty swallowing;
- nausea;
- sensation of a foreign object in the mouth.
These unpleasant sensations cause anxiety in patients, so it is very important to answer the question of which doctor to go to with this problem. It is best to visit a therapist and ask him which doctor to see. Pathologies of the oral cavity are dealt with by a periodontist or dentist, respectively, and for papillomas on the tongue, treatment is carried out by this specialist.
In addition, such growths can spread to the respiratory tract, for example, to the walls of the larynx, which can cause serious breathing problems. The likelihood of papilloma on the tongue degenerating into a malignant tumor is very low, but it cannot be ruled out, so high-quality treatment of the disease is necessary.
Diagnostics
If papillomas occur on the root or side of the tongue, you need to consult a dermatologist or ENT specialist. The doctor performs a visual examination and studies the structure of the tumor. The tumor has a lumpy or fine-grained surface.
In pediatric patients, papillomas are easier to distinguish from other diseases. They occupy large areas of the skin. They are often covered with a white coating. In elderly patients, HPV can easily be confused with cancer. Their only difference is that the cancerous tumor is more compacted than the papilloma.
This is followed by a polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It helps identify the pathogen. A biopsy is also prescribed, after which the biological material is sent for histological examination to determine oncogenicity.
HPV also needs to be differentiated from:
- cancer;
- cysts;
- ulcers (calluses);
- stomatitis.
Only after all the diagnostic measures have been carried out can the doctor make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate and effective treatment.
How to treat papilloma in the mouth, on the tongue, the doctor determines
Drug treatment
Many people, faced with a disease, do not know where to turn. Which doctor should you see if you notice warts?
To understand the principle of treatment, you need to find out the cause of the growths. Therapy for adults and children involves an integrated approach to minimize the possibility of relapse. Papillomas under the tongue, on its base and in other parts of the oral cavity are removed according to the following scheme:
- If you have infectious diseases, you need to get rid of them before treating papillomas. Local medications and oral medications are used.
- Immunomodulators and vitamin complexes are prescribed. Sports and proper nutrition are recommended.
- The papillomas are treated, after which interferon is injected into them. In parallel, the patient takes antiviral drugs that affect HPV.
Medicines
Papillomas are prone to growth and injury. Thread-like formations interfere with talking, eating, and easily break off and bleed, causing discomfort.
It is impossible to completely get rid of HPV, but getting remission for several years is possible.
Treatment of papillomas in the mouth is complex. The main method is surgical removal of growths. The medicinal component is aimed at increasing the body’s immunity, antiviral effect, etc.
First of all, it is necessary to eliminate microbes from the mouth and remove infectious foci. To do this, the oral cavity is sanitized:
- dentist treats holes in teeth,
- tidies up gums
- removes plaque,
- removes tartar,
- localizes inflammatory processes.
The patient must follow the rules of oral care, using toothpaste, brush, dental floss, and special rinses. After normal hygiene procedures, the mouth should be lubricated with a special ointment with an antiviral effect.
Removal of papillomas
Before removing the growths, laboratory tests are ordered to determine the type of tumor. Histological examination of a tissue sample determines the presence of viral agents in the material; cytological analysis of smears determines whether the tissue has become malignant.
Growths are only a symptom of papillomatosis. One of the steps of recovery is the removal of papillomas, but the virus will not disappear and will continue to develop in the body.
If growths are detected in the oral cavity, especially on the root of the tongue, you should consult one of the doctors, such as a dermatologist, oncologist, otolaryngologist, or dentist. It is not possible to completely get rid of the virus, but you can put it to sleep for a long time and prevent it from multiplying.
To treat the papilloma virus, a set of procedures is used:
- sanitation of the oral cavity;
- antiviral therapy;
- strengthening the immune system.
The oral cavity should be treated daily during hygiene procedures. It is advisable to change your toothbrush and thoroughly clean it after each use.
The affected areas are lubricated with ointments and gels prescribed by the attending physician. It is advisable to maintain proper nutrition during treatment.
To increase immunity, the doctor prescribes immunomodulatory drugs.
Both the first and second methods are painless, and at the same time there is rapid tissue healing. The surgical method and cauterization with chemicals are not used in the oral cavity due to high humidity and sensitivity.
A person notices changes in the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, inflammation and growths almost immediately. Discomfort intensifies when exposed to hot food or friction with dentures.
This could be a papilloma in the mouth - a tumor-like formation on the mucous membrane
It is important to mitigate as much as possible the conditions that predispose to malignant degeneration of the inflamed and overgrown epithelium
Oral papilloma - benign or malignant tumor?
The proliferation of epithelial tissue in the oral mucosa is caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Its particles are present in the bodies of 9 out of 10 adults on the planet. Some people have no idea about this and do not feel any changes at all. Others have to struggle with the unpleasant manifestations of papillomatosis for many years.
Possible malignancy or malignant degeneration is indicated by bleeding, pain, and thickening of the “leg” of the papilloma.
Benign tumors of the tongue
Benign tumors of the tongue, in comparison with other tumors of the oral cavity, are a fairly rare disease in dentistry. According to their origin, they are divided into epithelial (derived from epithelial cells of the tongue mucosa) and non-epithelial. Common features of benign tumors of the tongue are slow, non-invasive growth and lack of metastasis. However, malignant degeneration of the tumor can occur at any time. This process is facilitated by constant trauma to the tongue tumor in the oral cavity when talking or chewing food.
In children, tumors of the tongue are usually congenital and are the result of dysembryogenesis. Congenital tumors of the tongue are often combined with developmental anomalies of the jaw bones and tongue.
Which specialist should I go to, who deals with HPV removal, a surgeon or a dermatologist?
As mentioned above, you should initially consult a therapist or dermatologist. Further, you may need to consult with specialized specialists, depending on the location of the formation.
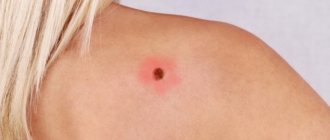
Most often, papillomas appear in places of constant moisture - in the inguinal folds, in the axillary region, on the genitals, and even on the mucous membrane of the growth cavity.
Growth on the neck, on the skin
On the neck, papillomas look like papillary growths that look like cauliflower leaves. The neck is a favorite place for papillomas, and they are injured in this area quite often (friction of a collar, scarf, and so on).
At the initial stage, the growth on the neck may not differ in color from the general color of the skin, but later it may acquire a pink or brown tint.
Papillomas on the neck are treated by a dermatologist; if he determines that the pathology is caused by an oncogenic strain, he will refer the patient to an oncologist; if it is necessary to remove the tumor, the help of a surgeon will be required.
Papilloma on the face
Papillomas on the face can appear in various places. If the tumor is located on the eyelid, you need to contact an ophthalmologist, who, after all the necessary tests, will excise the tumor. Growths located in close proximity to the organs of vision are removed using a laser, liquid nitrogen or a scalpel.
HPV in intimate places on the body in an adult
When the papilloma virus affects the male genital organs, formations can be located on the penis, around the head and on the scrotum.
In women, papillomas are localized on the labia majora and minora, on the vaginal mucosa, on the clitoris and on the cervix. In addition, in people of any sex, papillomas can appear in the anus, urethra and groin area.
Papillomas on the genitals can be:
- thread-like;
- flat - small bumps that can cause an unpleasant itching sensation.
Reference! Most often, genital warts are diagnosed, which are also called genital warts.
Genital warts should be treated by a gynecologist or urologist, depending on your gender.
In the oral cavity, papilloma can be recognized by the following signs:
- the size of the neoplasm is approximately 1 cm;
- the surface of the growth is rough;
- papilloma is attached to the mucous membrane with a thin stalk or wide bottom;
- the color of the neoplasm is light or pinkish;
- the growth does not cause pain when pressed.
In the mouth, on the tongue
If papilloma is detected in the oral cavity, it is necessary to make an appointment with a dentist, who, if necessary, will refer the patient to an oncologist or surgeon.
So, the area of responsibility of a dermatologist includes skin diseases. You should contact this specialist if you have papilloma on the face, neck, armpits, palms, feet, stomach or back. If papillomas are located in the oral cavity and on the genitals, this doctor does not prescribe treatment, but only conducts a superficial examination.
A gynecologist treats genital warts on the intimate organs of women; growths on the genital organs in men are treated by a urologist or andrologist.
If you have papillomas in the anal area, you need to contact a proctologist; in addition to a visual examination of the anus, he will conduct a colposcopy to get more information about the prevalence of the virus.
If the growths are localized on the inside of the cheeks, on the tongue or under it, you need to go to the dentist; if there are papillomas on the uvula and larynx, you need to consult an otolaryngologist.
An ophthalmologist can prescribe the correct therapy for papillomas located on the eyelids. The patient is referred to a surgeon after determining the benign quality of the tumors for their removal.
The help of an oncologist is required if a highly oncogenic papillomavirus is detected in the patient’s body.
Treatment and prognosis of benign tumors of the tongue
Considering the constant chemical (under the influence of saliva) and mechanical trauma to tongue tumors, which can lead to their malignancy, preference is given to radical treatment tactics - removal of the tumor within healthy tissue. The decision to remove the struma of the tongue is carried out jointly with an endocrinologist after examining the level of thyroid hormones.
Removal of a tongue tumor, depending on its type and size, can be performed using the radio wave method. by surgical excision. electrocoagulation. laser removal. cryodestruction. For vascular tumors of the tongue, sclerotherapy can be used.
Benign tumors of the tongue, when removed in a timely manner before malignant transformation occurs, have a favorable prognosis. However, some of them, especially hemangiomas and lymphangiomas, tend to recur.
Source: https://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_stomatology/tongue-tumor
Who to contact
Having decided to remove the papilloma, you first need to visit a dermatologist who will conduct an initial diagnosis and tell you to remove or treat the tumor with medication.
Growth on the neck, which doctor treats it
Infection with human papillomavirus infection does not mean an immediate manifestation of pathology. The appearance of new growths on the skin is the result of the activity of the virus in the body; how quickly it manifests itself depends on many factors, among which the following stand out:
- colds with complications;
- psycho-emotional tension, stress;
- long-term use of hormonal medications;
- abuse of solariums;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- frequent wearing of ties, clothes with collars, jewelry.
In most cases, papillomas appear in places of constant moisture, for example, under the armpit, inguinal folds, elbows, even mucous membranes of the oral cavity, tongue, and intimate areas. When a growth appears, through reproduction in the epithelium of the virus, in the upper layer of the skin, connective tissue begins to grow.
Often papillomas appear on the neck, looking like papillary growths that can be compared to cauliflower leaves. By the way, it is the neck area that is the favorite place for the appearance of papillomavirus neoplasms; here they are most often injured under the influence of collars and scarves. If at the beginning the shade of growths on the neck is no different from the skin, then over time they acquire a darker, pink-brown shade. Each growth has a different structure and has individual vessels that feed it. At the slightest damage, ulcers may leak from it, it may become deformed and turn black.
If papillomas appear on the body or open areas of the skin, you should consult a dermatologist, who, if necessary, will refer the patient to a surgeon to remove the tumor.
Papilloma on the eyelid
If a neoplasm appears on the eyelid, you must contact an ophthalmologist, who, after examining the papilloma and determining the cause of its formation, will perform an excision. Removal of growths close to the organ of vision is carried out using a scalpel with an anesthetic, laser or liquid nitrogen.
Doctor for the treatment of papillomas in the oral cavity
If growths appear in the mouth, papillomas will need to be removed. Which doctor should I contact? By the way, in medicine this pathology is known as papillomatosis of the tongue.
In the language of papillomas there are:
- pointed (located under the tongue);
- flat (appear on top of the tongue and on the sides).
New growths on the tongue look like a small nipple with a pointed or leaf-shaped shape. The flat forms of the growths have the appearance of a wart, with a pinkish tint. The growths on the tongue are completely painless, as long as they are not injured.
Diagnosis of papillomas in the mouth involves a visual examination of the patient and polymerase chain reaction analysis. Using diagnostics, the doctor will determine the type of virus and the extent of damage to the body. If the doctor suspects the degeneration of a neoplasm into a cancerous tumor, a histological examination of the biomaterial is prescribed.
Caution - papillomas in the intimate area
If papillomatous formations appear on any part of the body, you should contact only specialists. Of course, you can try to remove the growth in a beauty salon, but no one there can guarantee you 100% removal of the papilloma.
Only doctors of narrow specialties will be able to not only remove the surface of the tumor, but also its root. In addition, they will send biological material for examination to determine the type of papilloma.
In addition to the fact that growths can appear on any part of the body, very often they form in intimate places where there is constant humidity. If this happens, seek medical attention immediately. Which doctor removes papillomas in the intimate areas?
After examining the patient, examining the site of the lesion, and the diagnostic results, the growths are removed using the Surgitron apparatus using radio wave excision. This method promotes the destruction of papillomas cells, their evaporation, complete sterilization of the body from the virus, without the possibility of re-formation of the growth. This method is also used to remove papillomas on the eyelid and body.
Prevention
To protect your body from getting and developing HPV, you need to be very careful about your own health.
It is worth strengthening your immune system and saying goodbye to bad habits.
Moreover, doctors recommend supporting the immune system with complex vitamins during the cold season. Limit stressful situations as much as possible.
As for sexual life, to protect against HPV it is necessary to use condoms (barrier methods of contraception) during sexual intercourse. Women and men are encouraged to take preventive screenings seriously and visit doctors' offices.
Growth on the neck
On the neck, papillomas look like papillary growths that look like cauliflower leaves. The neck is a favorite place for papillomas, and they are injured in this area quite often (friction of a collar, scarf, and so on).
At the initial stage, the growth on the neck may not differ in color from the general color of the skin, but later it may acquire a pink or brown tint.
Papillomas on the neck are treated by a dermatologist; if he determines that the pathology is caused by an oncogenic strain, he will refer the patient to an oncologist; if it is necessary to remove the tumor, the help of a surgeon will be required.
Papilloma on the face
Papillomas on the face can appear in various places. If the tumor is located on the eyelid, you need to contact an ophthalmologist, who, after all the necessary tests, will excise the tumor.
Growths located in close proximity to the organs of vision are removed using a laser, liquid nitrogen or a scalpel.
HPV in intimate places
When the papilloma virus affects the male genital organs, formations can be located on the penis, around the head and on the scrotum.
In women, papillomas are localized on the labia majora and minora, on the vaginal mucosa, on the clitoris and on the cervix. In addition, in people of any sex, papillomas can appear in the anus, urethra and groin area.
Papillomas on the genitals can be:
- thread-like;
- flat - small bumps that can cause an unpleasant itching sensation.
Reference! Most often, genital warts are diagnosed, which are also called genital warts.
Genital warts should be treated by a gynecologist or urologist, depending on your gender.
In the oral cavity, papilloma can be recognized by the following signs:
- the size of the neoplasm is approximately 1 cm;
- the surface of the growth is rough;
- papilloma is attached to the mucous membrane with a thin stalk or wide bottom;
- the color of the neoplasm is light or pinkish;
- the growth does not cause pain when pressed.
In the mouth, on the tongue
If papilloma is detected in the oral cavity, it is necessary to make an appointment with a dentist, who, if necessary, will refer the patient to an oncologist or surgeon.
So, the area of responsibility of a dermatologist includes skin diseases. You should contact this specialist if you have papilloma on the face, neck, armpits, palms, feet, stomach or back.
If papillomas are located in the oral cavity and on the genitals, this doctor does not prescribe treatment, but only conducts a superficial examination.
A gynecologist treats genital warts on the intimate organs of women; growths on the genital organs in men are treated by a urologist or andrologist.
If you have papillomas in the anal area, you need to contact a proctologist; in addition to a visual examination of the anus, he will conduct a colposcopy to get more information about the prevalence of the virus.
If the growths are localized on the inside of the cheeks, on the tongue or under it, you need to go to the dentist; if there are papillomas on the uvula and larynx, you need to consult an otolaryngologist.
An ophthalmologist can prescribe the correct therapy for papillomas located on the eyelids. The patient is referred to a surgeon after determining the benign quality of the tumors for their removal.
The help of an oncologist is required if a highly oncogenic papillomavirus is detected in the patient’s body.
How to diagnose papillomatosis?
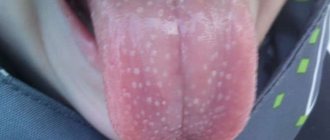
Pathological formations that appear on the tongue cause anxiety in a person, and the first thing he tries to do is find out what it could be. Papillomas are quite easy to diagnose even by sight. They come in two types and look different. Symptoms other than the presence and appearance of a wart are not needed to diagnose the disease.
| Type of papilloma | Characteristic |
| Pointed papillomas | They are pinkish in color and look like papillae. The stalk on which they are attached to the tongue can be very large, which increases the likelihood of injury and even complete tearing off of the wart. This new growth resembles cauliflower in appearance. |
| Flat papillomas | Flat elements that slightly rise above the level of the mucosa and are very different in color from the surrounding tissues. Often they exist for a long time without treatment, since they do not cause discomfort or pain to a person. |
A characteristic feature of papillomas is the appearance of bleeding ulcerations at the site of the torn wart. Such injuries negatively affect the wart cells and over time they can begin to degenerate into cancerous ones.
There are two types of oral papillomatosis:
- Reactive - warts arise due to constant and frequent exposure to irritants (thermal, viral, chemical or mechanical irritation of the mucous membrane).
- Neoplastic - warts are present in large numbers in the form of nodular neoplasms, can be collected in groups, or are located throughout the oral cavity.
Neoplastic papillomatosis of the oral cavity is quite rare. More often, single genital warts can be seen on the tongue.
Treatment nuances
The danger of tongue papillomas is that they can go unnoticed for a long period of time.
Such growths can be from 2 mm to 2 cm. If such formations are detected on the tongue, you should immediately contact a specialist. Self-medication can lead to serious complications.
Important! The specific treatment method is selected depending on the type of papilloma.
An important part of treatment is taking antiviral drugs. They allow you to restore normal functioning of the immune system.
Without timely treatment, there is a risk of papilloma degenerating into a benign or malignant formation.
Places of HPV formation
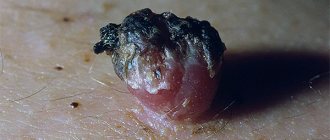
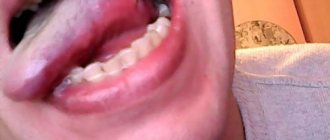
Papilloma on the tongue is a white or light pink neoplasm. Its size varies from 0.5 to 2 cm. As the patient's condition worsens, such a growth changes its color. It comes in brown or dark red color.
The growth on the tongue can be in the form of a drop on a stalk or a flat formation that has clear contours. The exact type of formation depends on the type of human papillomavirus infection present in the body. Cauterization is not used for treatment.
Under the tongue
Papilloma under the tongue does not form immediately. If diagnosed in a timely manner, the doctor can notice the developing disease at an early stage.
The virus that contributes to the formation of this type of growth can simply remain in the body for a long time, waiting for a favorable moment.
The tumor under the tongue is attached with a thin stalk. Such papillary papillomas provoke severe discomfort when swallowing. Papillomas under the tongue can be:
- flat;
- pointed.
To see them, just look in the mirror and lift your tongue up. Such formations can be very easily injured, as they can cling to the teeth or mucous membrane. The damaged neoplasm grows into a large lesion.
On the root
A wart on the root of the tongue causes severe discomfort and pain. This type of localization of growths is very rare.
As the papilloma increases in size, it can cause breathing problems. If the formation compresses the tongue, then a gag reflex may occur when swallowing food.
On the tip
Papillomas on the tip of the tongue are often injured and grow quickly. As a result, a large accumulation of formations is formed, which in appearance is similar to a cockscomb.
Neoplasms in children
The HPV virus may not manifest itself for a long time. Its activation occurs against the background of decreased immunity, which is accompanied by the appearance of neoplasms on the skin and mucous membranes. When the immune defense is normalized, the virus enters an inactive phase, but may reappear during the next episode of immunodeficiency, for example, during infectious diseases.
It often happens that before pregnancy a woman did not know that she was infected with the virus. This can be explained very simply - if there are no papillomas on the skin, then the virus is suppressed by one’s own immunity. During pregnancy, the body is weakened, which in some cases can result in the appearance of papillomas on the skin. In this case, there is a risk of infection of the child when passing through the birth canal.
Papilloma on a child’s tongue can appear at any age, but most often growths are discovered after upper respiratory tract infections, stomatitis or tonsillitis. Such tumors in children are immediately removed. Otherwise, the child’s body will not be able to cope with the virus, which will lead to the appearance of multiple tumors on the skin. Laser removal of papillomas on the tongue and antiviral therapy are usually practiced.
In children, papillomas grow especially quickly, so they need to be removed immediately
Causes of HPV
To the question whether there can be papillomas in the mouth, we will answer positively. Patients complain of the presence of bleeding growths on the mucous membrane, which are often injured.
Condylomas in the oral cavity are soft, mobile, pink or whitish. Sometimes the surface of the formations becomes rough.
A single papilloma on the oral mucosa, the symptoms of which are listed, is rare. More often, warts, as evidence of a virus in the body, grow together on the mucous membranes.
We hasten to reassure you that the process is benign and can be treated. How does HPV (human papillomavirus) get to the mucous membrane? This happens in several cases:
- using someone else's toothbrush or towel;
- insufficient processing of utensils when shared with a person infected with the virus;
- kissing a carrier of the virus (if he has papillomas in the mouth);
- oral sex without protection.
The child will get sick during birth, provided that the mother is a carrier of the virus. Then growths appear on the lips, in the eye area, and mucous membranes. You can become infected, but the virus may not manifest itself right away. When the level of natural defense is high, the latent period can last several years. In other cases, growths on the mucous membrane appear after a few months. It must be treated immediately.
Papilloma virus in the mouth, which doctor to go to and where to go
If you are faced with a problem such as papilloma in the mouth, which doctor should you contact, this is the question that worries you first. Treating formations in the mouth and tongue is the responsibility of an otolaryngologist or dentist.
Self-medication is prohibited. It is forbidden to pull out growths, cut off, cut with scissors and scratch with nails.
This way you can get the exact opposite result: the wart will form again, will be larger in diameter and will grow. Doctors today know how to properly treat condylomas.
The essence of the problem
Papilloma on the tongue, external genitalia, mucous membranes and skin is the result of the activity of the human papillomavirus (HPV). It is transmitted primarily through sexual contact, through unprotected sexual contact. There is a risk of transmission of the virus through oral contact, including during kissing. Often, against the background of a weakened immune system, you can become infected with the virus at home - through hygiene items, dishes, or even by shaking hands if the skin on the palms is damaged and there are open wounds. Infection of the child occurs during passage through the birth canal if the woman is infected.
The statistics are inexorable: every third inhabitant of the planet is infected with papillomavirus. Moreover, the disease is not always dangerous; in most cases, apart from aesthetic discomfort, the presence of papillomas on the body does not threaten anything. The mucous membranes are another matter - papilloma on the tongue simply interferes with chewing food and causes speech defects.
The papilloma virus is present in the body of every third person, but with strong immunity it may not manifest itself
It is a soft neoplasm of the papillary structure. The color ranges from pale pink to crimson, sometimes there are white growths. Sizes can vary from a few millimeters to 2 centimeters.
The peculiarity of papillomas is that they grow after each injury. That is, if you injure a small growth, after a while it will increase. Often, after damage to the skin, another papilloma appears, and after a while they form a small island, similar to a cauliflower inflorescence.