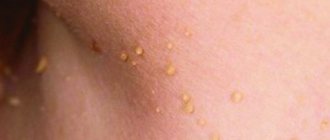
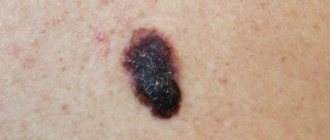
Both moles and warts are benign skin growths, but they have pronounced differences : both externally and in terms of development mechanisms, tendency to malignancy, etc.
A mole (nevus) is a benign pigmented skin growth consisting of melanocytes (cells that produce melanin - a brown pigment).
A wart (papilloma) is a benign skin neoplasm associated with excessive growth of epithelial layers due to penetration of the human papillomavirus into the spiny cells of the epidermis.
In some cases, it can be difficult to distinguish warts from moles by appearance alone, since often, especially old papillomas, can be very similar to moles, and vice versa.
Note! To be absolutely sure of the nature of the growths causing concern, you should undergo a medical examination by a dermatologist.
What is a mole
Moles are distinctive features of our appearance
Moles are distinctive features of our appearance, therefore, when a person disappears, it becomes easier to find someone with a birthmark or a feature such as a small black mole on the face or arm. But what is each mole on our body? This is a benign tumor, it can also be malignant, but in rare cases, which, nevertheless, should not be written off. But in essence, moles are our skin cells that have accumulated pigment and become darker due to exposure to ultraviolet radiation. The color of a mole can be light or flesh-colored, pink or red, or brownish and even black.
Pink and red nevi should be approached a little differently, because... These are vascular moles that are formed not by melanin, but by small blood vessels. Hence the color of such moles, varying from light pink to dark scarlet.
Not every mole becomes malignant, so don't assume that all moles on the body are dangerous. In order not to worry about the health of moles, you should regularly visit a dermatologist or oncologist, who can carefully and competently identify any changes that have begun. Moles appear for several reasons:
- An unexpected sharp surge or decline in hormones, especially in women and adolescents;
- Ultraviolet radiation, which can come from both the sun and solarium;
- Hereditary factor. Genetics can explain a lot, including the appearance of many moles on the body.
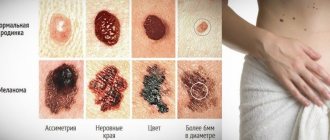
But what could be a sign of a nevus changing in a negative direction, its degeneration into melanoma?
- Pain, itching and burning in and around the mole,
- The appearance of a light or dark halo around the nevus,
- Bleeding and redness of the mole,
- Discharge of fluid from the birthmark,
- Injury to a mole, both partial and complete.
Symptoms
Papilloma developing from a mole is quite difficult to notice immediately. First of all, an alarming signal is a change in the shape of a mole, as well as its growth.
On this topic
In addition, the following signs will indicate transformation:
- blurred boundaries;
- pain during touch;
- change in shade;
- bleeding;
- characteristic discharge from a mole.
It is worth noting that papillomatosis is distinguished by its rapid development, despite the fact that the first symptoms of manifestation may go unnoticed.
What is a wart
A wart is a benign growth on the skin (malignant can also occur, but is extremely rare) in the form of a papilla or nodule
Many people confuse new growths on the body and do not understand whether a mole or a wart appears on the skin. What can you say about warts? These are benign neoplasms on the skin (malignant ones can also occur, but extremely rarely) in the form of a papilla or nodule. Warts are often confused with hanging moles. The cause of warts is the human papillomavirus. What can cause a wart to appear:
- Increased sweating of the skin of the extremities,
- Mental trauma,
- Decline of immunity
- Vegetoneurosis,
- Acrocyanosis.
You can also “catch” warts if you come into contact with a person with the human papillomavirus or use the patient’s things.
Attention! Malignant neoplasms are often confused with simple warts, therefore, in order to avoid future problems, it is imperative to consult a dermatologist for advice and determination of treatment.
Warts can be:
- Senile,
- Viral.
Senile warts are benign growths on the skin associated with aging. They appear not only on the body, but also on the face and neck. They look like loose keratinized plaques and can be gray, black or brown in color.
Viral warts are caused by the same virus, such warts differ in:
- Vulgar or ordinary, including plantar. Such warts have a dense structure, covered with keratinized masses, convex, with a bumpy surface. Most often, such warts appear on the hands; they are completely painless. Plantar warts appear on the soles of the feet in areas where shoes press hard. Often found in people with excessive sweating of the soles of their feet. Unlike vulgar growths, plantar warts are very painful;
- Condylomas acuminata or simply condylomas. These warts are caused by poor or absent body hygiene and most often appear in the groin area, intergluteal fold, and also on the genitals. They look like soft nodules or papillae on a “pedicle” and are pink in color.
- Flat or youthful. From the name it is clear that such warts appear in adolescents and children, which is caused by irritation of young skin. They usually appear on the face or the back of the hands. The shape resembles nodules, both round and flat and irregular.
Diagnostics
If a papilloma formation is detected on a mole, you must seek help from a specialist. First of all, the doctor will collect the necessary information regarding the patient’s medical history, the time when the growth of an additional tumor was noticed, and what symptoms accompany the process.
After this, a visual inspection of the affected area is carried out, which allows you to determine the size and color of the growth.
If this data is insufficient, an additional diagnostic examination is carried out, including several methods:
- biopsy - necessary to take a fragment of the affected tissue;
- histology – a histological examination of a previously taken sample of material is carried out to determine the nature of the neoplasm and the mole itself on which it appeared, which makes it possible to determine the degree of malignancy of the pathological process;
- PCR diagnostics to detect urogenital infection.
Also, if necessary, a laboratory blood test can be performed, which will also show some deviations from the norm in the presence of the disease.
Characteristics of skin neoplasms
| NEW FORMATION | CHARACTERISTICS OF NEW FORMATIONS | LOCALIZATION OF NEW FORMATIONS | COURSE OF THE DISEASE | CAUSES OF NEW FORMATIONS |
Warts | Common warts are small thickenings of the skin with a rough surface. They can be protruding, with a rough surface and a color close to the color of the skin, they can be tiny or reach the size of a small bean. Plantar warts are flat in shape and are often mistaken for calluses. | Most often - on the palms, shoulders and knees. They often take root on the feet. | Appear in childhood and adolescence. Often warts die off on their own, without any treatment. Their single copies do not pose a danger. But, if they linger on your skin, it is better to consult a doctor. | Human papillomavirus. There are about 100 varieties of it. The appearance of warts signals a weakened immune system. The virus enters the skin through a cut or scrape. He especially loves a humid environment, therefore. When in a public bath or swimming pool, never use someone else’s towel or washcloth. |
Condylomas | Genital warts consist of “lobules” and are supported by a thin stalk. The size of one condyloma is no more than a few millimeters. The number can be anything from one to tens and hundreds. | Genital organs, armpits and corners of the mouth. Genital warts can completely cover the genitals. The perineum and anus are their typical habitats. | Condylomas do not go away on their own, but if accidentally or intentionally damaged, a bleeding and poorly healing ulcer forms in their place. | Genital warts are caused by certain types of human papillomavirus. Infection occurs through sexual contact, including during oral sex - in this case the larynx is affected. Condylomas caused by oncogenic types of the virus are especially dangerous. |
Papillomas | Benign tumor. It looks like a wart up to 1-2 cm in size, but has a looser structure and contains blood vessels. The papilloma grows upward outward, and its papillae are scattered in different directions and look like cauliflower. | Skin surface and mucous membranes. When there are a lot of papillomas, this condition is called papillomatosis. | As a rule, papillomas are harmless. In some cases, after removal of papilloma, relapses are possible. In rare cases, they can develop into cancer. | Some papillomas (on the genitals, mouth, nose, vocal cords) are of viral origin. Others are congenital or result from chronic inflammation of the skin or mucous membranes. |
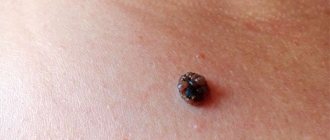
Moles | They can be round or oval in shape, light or dark in color, but always brown. Like warts, moles may be raised, but they feel harder to the touch. | Any part of the body. | People are not born with moles; 80-90% of them appear before the age of 25. At the age of 40, moles begin to gradually disappear and by the age of 80 they are practically gone. As a rule, moles are not dangerous, but sometimes they can degenerate and become malignant. | The result of excessive proliferation of skin pigment cells - melanocytes. |
Keratomas | The first sign of a keratoma is a grayish or coffee-colored spot with slight peeling on the surface. Gradually, this spot thickens and becomes covered with a dense crust. | As a rule, on open areas of the skin. | Appear after 40-50 years. Sometimes they have painful consequences: the crusts can crumble and come off. If the keratoma is large or subject to constant trauma, it may degenerate into squamous cell carcinoma. | Age-related changes that are a reaction of mature skin to ultraviolet radiation. |
What does papilloma look like: photos of HPV in women and men
Human papilloma is a benign tumor that grows on the surface of the skin and has an elongated shape. It consists of connective tissue material and vessels covered with a thin layer of epithelium.
Papillomas can be congenital, acquired during an inflammatory process, or viral (on the genitals).
By the way, I am for natural preparations for the treatment of papillomas, for example, Papillux drops.
Causes of papillomas in humans
Papillomas are easily transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person, and this happens:
- By household means through hygiene and household items. As a result, papillomas appear on the neck, face, chest, and in the armpit.
- Sexually through direct contact. Papillomas in the intimate area occur in men near the head of the penis, and in women on the labia and vagina. Such papillomas are usually called genital warts. It should be remembered that in this case, even the barrier method of contraception does not provide confidence in the impossibility of infection.
In addition, severe stress, any infectious disease, smoking, or alcohol abuse can serve as an impetus for the awakening of the disease. The risk of acquiring papilloma increases with frequent changes of partners, and a condom in this case does not help, because contact with the affected skin or mucous membrane is enough.
The risk of infection is quite high when visiting a bathhouse, sauna, or swimming pool, when the skin is as open as possible. During childbirth, a child can become infected from a sick mother.
Photos of papillomas on different parts of the body
Papillomas on the tongue
Under the tongue in the form of shoots
There is a large scattering of papillomas on the body
But they appear especially often on the neck
Often papillomas appear right in front of the eyelashes
Sometimes there are several of them on the eye
The mucous membrane is a favorite place for papillomas. Therefore, they are most often found on the lip.
HPV is also not uncommon on the penis
This is what an old papilloma looks like on the body
But if the immune system is weakened, papillomas grow in abundance in one place
They can also take on bizarre shapes and colors, but they are all caused by the human papillomavirus
Symptoms of papillomas
When infected, the virus is embedded in the human body and may not manifest itself for a long time, the duration of which will completely depend on the immune system. If it is strong enough, then the papilloma will appear only if it weakens and will subsequently begin to grow without treatment.
In any case, papilloma will make itself felt with the following manifestations:
- Burning sensation, pain during sexual intercourse, strange unpleasant discharge from the vagina.
- Condylomas in the genital area have a pointed shape at the initial stage; with subsequent growth, it becomes similar to cauliflower and turns into a multilayer formation - condyloma. Their sizes range from a few millimeters to a couple of centimeters.
- Warty formations. Depending on the immune system, they may appear and disappear on their own. They have the same shape as condylomas, and the color blends with the skin tone.
Prevention of papillomas
As described earlier, in people with strong immune systems, HPV may not manifest itself. Therefore, it is important to maintain it by taking various vitamin supplements, leading a healthy life, avoiding dampness and protecting cut sites (through which the virus penetrates best).
For any manifestation of papilloma, you should immediately contact a dermatologist, who will conduct an examination and subsequently prescribe individual treatment. If the process is neglected, this is fraught with consequences, and a benign tumor can turn into a malignant form.
Fundamental differences between a mole and a wart
Well, if many people confuse neoplasms, it is worth understanding how to distinguish a mole from a wart. Only a dermatologist can help with this 100%. But you can try to understand on your own how a wart differs from a mole and here’s what you’ll need:
- Warts are mostly covered with horny masses, therefore they are unpleasant to the touch and harsh, but moles, on the contrary, can only be soft and smooth
According to the form. Take a good look at the place where the tumor appears, you can even use a magnifying glass. A wart always looks like a growth on the skin, even if it has a flatter shape. The mole looks more like an artificial spot;
- To the touch . Feel the new growth, don’t be afraid. Warts are mostly covered with horny masses, therefore they are unpleasant to the touch and harsh, but moles, on the contrary, can only be soft and smooth;
- In many cases, you can also distinguish a mole from a wart by color Moles usually have a dark color due to pigment in the cells of the epidermis (brown, black), but warts are most often light-colored (flesh-colored, white, pink, may have a grayish or yellowish tint);
- In count. There are always more moles on the body than warts, which you can verify if you examine the whole body carefully and take the time to count the tumors.
Here's another difference between a wart and a mole - these are methods of treating neoplasms:
- Moles can only be cured by removing the nevus;
- Warts can be treated with both medication and surgery.
However, it is worth understanding that most often warts are easier to remove, because... The effectiveness of treatment is not ideal, it reaches only 75-80 percent.
Removal methods.
Removal of moles and warts
- Cost: 2,000 rub.
More details
Mole removal can be carried out using a laser, radio wave coagulation or electrical coagulation. These manipulations are performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. The choice of treatment method is determined by the doctor in each specific case. In my opinion, the most effective and painless method is radio wave coagulation. We use this technique in most cases, although in some cases we use excision with conventional surgical instruments followed by suturing. When using radio wave coagulation, tissue damage during material collection will be minimal, blood loss is reduced, and the rehabilitation period is shortened, while, for example, with the laser method, the healing process is extended over a fairly long period. Repeated formations do not appear after removal, but if precautions are not followed by the patient himself, infection may occur.
How to distinguish a wart from other skin formations that may appear on the sole of the foot
| wart | dry callus | molluscum contagiosum | splinter |
| It has a dense, hard coating without a papillary pattern. The hallmark of a wart is the small black dots on the surface, which are tiny blood vessels that feed the wart. It is characterized by painful sensations and is located in the forefoot, toes and heel. Moreover, due to constant external pressure, the wart thickens and grows inward, which can lead to damage to the subcutaneous tissue. | It has a dense coating that preserves the papillary pattern. The callus is distinguished by the absence of black dots. Squeezing a dry callus in a transverse direction does not cause pain, but pressing a dry callus in a perpendicular direction can be painful due to the large pressure on the underlying tissue. A typical dry callus always occurs in the area where the bones or joints of the foot experience the greatest stress. | Skin formations ranging in size from 1–2 mm upon appearance to 5–8 mm appear on the feet, usually in children (in adults, molluscum contagiosum affects the genitals). This painless skin abnormality with no change in skin color is similar in appearance to a regular wart, but its main difference from a wart is the presence of a “crater” or depression in the center. In addition, when pressed, a white liquid with a curd consistency is released from this “crater”. | Characterized by a more acute onset. As in the case of a dry callus, in the absence of inflammation, squeezing it is painless. During the inflammatory process, redness and watery or purulent discharge occur on the skin in the area of the splinter. |
Most patients with warts located on the feet or on closed areas of the body, if there is no pain, prefer not to pay attention to it or self-medicate. However, if the diagnosis is not entirely clear, it is necessary to urgently consult a dermatologist or oncologist to rule out skin cancer.
Nevi
Synonyms for the name are mole, birthmark. In essence, all these neoplasms are pigmented nevi (naevus). These are accumulations of nevocytes - skin cells containing a lot of melanin (the pigment responsible for the color of the integument, hair and iris of the eyes).
It is believed that such elements are formed in the fetus in the womb. Some of them appear immediately after birth (4–10%), others during puberty (up to 90%), and others throughout life under the influence of environmental factors. 75% of Caucasians have moles.
Among the causes of malformations of the skin of the unborn baby, there are unfavorable factors to which the woman’s body was exposed during pregnancy:
- hormonal changes - sharp jumps in estrogen and progesterone;
- genitourinary system infections, sexually transmitted diseases;
- intoxication with poisons, alcohol;
- genetic disorders.
There are about a hundred varieties of pigmented nevi. They are located in the superficial epithelium, at the border of the epidermis and dermis or directly in the dermis.
Moles can be flat or raised above the integument, ranging in size from 1 mm to several tens of centimeters. If the spot occupies most of the skin, then it is called giant. Hairs may grow on the surface. Other neoplasms are also classified as nevi:
- hemangiomas - red vascular tumors;
- nevi of the sebaceous glands - do not contain melanin and are localized mainly on the head;
- anemic spots - light areas with a cluster of underdeveloped blood vessels.
The most dangerous type is dysplastic (atypical) nevi, found in 5% of people on the planet. They are initially prone to degeneration into a malignant tumor, and therefore require constant monitoring. This is a transitional form between a regular mole and melanoma or a precancerous condition.
The following symptoms of malignancy of any nevus should alert you:
- change in size, shade;
- bleeding;
- itching, pain, feeling of tension, tingling;
- transformation of a smooth surface into a rough one, the appearance of tubercles, cracks and foreign inclusions;
- changing the shape and smoothing the contours of the spot;
- peeling of the skin.
Diagnosis is carried out through visual examination, a magnifying glass or fluorescent microscope, laboratory tests, and a computer. In case of danger, the nevus is surgically removed along with part of the healthy integument and fatty tissue.
How to remove warts
It is known that in order to get rid of warts, they need to be removed or “removed”. However, “removing” warts with so-called traditional medicines (remedies for warts, ointments and even “spells for warts”) very rarely help. What to do to remove warts? Consult a doctor...
What will the doctor say? It turns out that not all warts can and should be removed. When treating warts, the main approach is to ensure that the treatment does not cause more harm than the wart itself. For these reasons, you should contact a dermatologist to remove a wart in the following cases:
- if a wart bothers you and you feel it (for example, plantar warts),
- if the wart is painful, bleeding, or has changed its shape or color
- if the wart has reached a large size
- if the wart is located in a prominent place and is noticeable to others
- if the number of warts increases
General precautions for growths
The appearance of a formation on the skin is a reason to contact a specialist. After examination and diagnosis, the doctor will offer treatment options. Papillomas, warts, and other vegetations are removed using special devices at the medical center.
General recommendations for nevi and papillomas:
- examination by a dermatologist;
- do not try to get rid of formations using homemade ointments or traditional medicine;
- If it is benign in nature, do not injure the growth with various objects or clothing. According to indications, it is removed in a medical facility;
- It is recommended to get rid of papillomas if a benign tumor is frequently injured;
- do not use aggressive or toxic substances for removal;
- If the formation turns black and begins to itch, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Treatment of warts and papillomas
Treatment of warts should only be done under the supervision of a doctor, since improper treatment can lead to the wart developing into a malignant tumor.
The only radical treatment for warts is their removal. Today, there are quite a few methods for removing warts. They are chosen depending on the location and type of wart.
Some of these methods have complications. Thus, laser removal of warts can cause scarring. Improper use of the Surgitron device for removing simple warts and papillomas can also lead to scars, including disfiguring keloid scars. Therefore, gentle methods of wart removal - cryotherapy and electrocoagulation - remain important today.
Prevention
To avoid possible risks, you need to be careful about your skin. First of all, this applies to people who have fair skin, blue eyes and a lot of freckles on their body. It is this category that is more susceptible to cancer processes.
To avoid the growth of moles and the formation of papillomas on them, it is not recommended to spend a lot of time under the sun. Equally important is proper nutrition and healthy lifestyle.
Moles and papilloma individually are not dangerous to human health. However, if a papilloma growth is formed from the nevus itself, then in this case you need to be extremely careful, and it is better to consult a doctor, since such a condition may signal a possible process of malignancy.
Melanoma in a child
Cancer is no less common in children than in adults. A type of skin cancer, melanoma in children has long been rare, but the trend is changing. The number of cases and deaths has increased. Because childhood melanoma develops very quickly, it is vital for parents to know the symptoms, risk factors and treatments for the disease.
Skin cancer in children develops rapidly and can result in death.
Features of the disease in children
Moles or nevi turn into malignant formations. The occurrence of melanoma on clean skin is much less common. Melanocyte cells, which produce skin pigment, turn into cancer cells. The exact reasons for this phenomenon have not been established for either adults or adolescents. In childhood, gender does not matter for the disease, although among adults women are much more likely to get sick. In adolescents, formations on the mucous membranes are extremely rare, most often on the skin.
Return to contents
At what age does it appear?
Children aged 4-5 years and 11-15 years are at risk by age. The percentage of cases outside these boundaries is less than one. Moreover, before the age of 10, the disease manifests itself in 5% of cases, and in the period from 10 to 20 years, this percentage increases to 15. Among the total number of cases of the disease, melanoma most often manifests itself after puberty - from 15 to 20 years and is 73% .
Melanoma in children can develop in utero and after birth. Return to contents
Types of disease
Causes and risk factors
Children who have large moles from birth are at risk. Such formations most often degenerate and need to be constantly monitored. Under no circumstances should such stains be injured or exposed to other influences. Avoid exposing such moles to direct sunlight. Children, especially those under 3 years of age, should avoid exposure to active sun and use barrier protection if they do have to be exposed to radiation.
Melanoma in children can develop due to radiation, chemical burns, and damage to moles.
Doctors identify the following risk factors:
- Heredity. Children whose parents or other close relatives have had skin cancer are at much higher risk than their peers.
- Fair-skinned and fair-haired babies and albino children are less tolerant of the effects of solar radiation on their skin, which means they are at risk.
- A large number of common moles on the body is a risk factor and should force parents to closely monitor any changes in the skin.
- Exposure of the mother to harmful chemicals while pregnant can have unpleasant consequences.
Return to contents
Symptoms of the disease
- Parents should be alert to any change in the appearance of the mole. If it bleeds, changes structure and color, or itches, you should immediately consult a doctor. A common mole or nevus is symmetrical in both horizontal and vertical directions. When it degenerates into melanoma, this symmetry is broken, the shape of the formation becomes irregular, and bumps and growths may appear on the surface.
- An indirect sign can be the appearance of papillomas near the formation and enlargement of the lymph nodes near the mole in the child. You should listen to complaints about an enlarged knot in the groin or under the armpit.
- In the later stages, symptoms of intoxication of the body appear.
Melanoma in children manifests itself with bleeding, pain, and ulcers at the site of moles.
However, all the signs of melanoma are not necessary for children; often the disease develops asymptomatically or is disguised as a benign formation. Moreover, in children, much more often than in adults, melanoma is immediately malignant and begins to produce metastases. The consequences of the formation of metastases can be irreparable. They primarily affect liver cells, which interferes with the normal functioning of blood cells. The growth and development of the patient slows down, and with further use of chemotherapy and radiation therapy, anemia and a decrease in the protective functions of the body are possible.
Return to contents
Methods for diagnosing melanomas in children
There are several methods for diagnosing the disease:
- Thermography, when a special scanner detects the temperature difference between malignant and healthy tissue.
- Histological examination, when cells taken from the formation are analyzed. For analysis, as a rule, the growth is removed.
- In particularly difficult cases, a radiophosphorus test makes it possible to determine a cancerous or precancerous formation by analyzing inflammatory phenomena.
- Cytological examination of the cells of the formation and tissues around it will also help make the correct diagnosis.
To confirm or refute melanoma, you can undergo several types of diagnostics.
Signs of melanoma will include:
- lymphocyte activity in the area of formation;
- changes in melanocyte cells that produce skin pigment;
- increase in the number of pigment cells.
Return to contents
Features of treatment and prognosis
The first step in treating any type of melanoma in children, as in adults, is to remove the growth. At the initial stage of the disease, in the absence of metastases, removal may be the main method of control. If melanoma in children is in advanced stages, and metastases are already present in other organs, then the same treatment methods are used as in adults. Immunotherapy helps maintain the body's strength, while radiation and chemotherapy help fight the disease.