There are a large number of common infectious diseases similar to chickenpox in the world.
First of all, this concerns the clinical manifestations of pathologies: often parents, when a rash appears on the child’s body, assume the presence of chickenpox. However, this sign may indicate more dangerous infectious processes.
Many infectious pathologies are accompanied by the appearance of a skin rash. Often the symptoms of these diseases are very similar, which makes diagnosis very difficult.
Despite this, diseases similar to chickenpox have certain distinctive features. Knowing them, even a non-specialist will be able to distinguish these pathologies in most cases.
Standard symptoms of chickenpox compared to other diseases
Chickenpox goes through several stages with characteristic symptoms:
- The incubation period from exposure to first symptoms is the longest of all infections, ranging from 10 to 21 days.
- The prodromal period from the first symptoms to the onset of rashes lasts from several hours to a day. General deterioration of the condition: fever and chills, headache and weakness, as in all diseases. Following this, red spots appear throughout the body, quickly turning into papules, very similar to other infectious diseases.
- Acute period - high temperature (up to 38.5 ° C and above) at the peak of the rash, there can be 2-3 waves, and each is accompanied by a new rise in temperature, then a decrease for 1-2 days between waves, unlike all other diseases in which the temperature remains consistently high or rises in the evening and at night.
- Itching from a rash is present in almost any disease, its degree depends on the individual sensitivity of the body.
- The rash quickly develops from a spot, first into a papule (bump), then into a single-chamber watery vesicle (vesicle) with a red rim - this is a typical element of a chickenpox rash. Such pimples or blisters form a few hours after the spots appear or the next day. This is how chickenpox is recognized.
- Then the blisters dry out, turn into crusts and disappear without a trace. Recovery occurs when the last scab falls off, after 3-5 days.
- The main difference from other infections is the picture of polymorphism of the chickenpox rash, when due to the waves all elements are visible simultaneously - spots, papules, vesicles and crusts. With any other infection, the rash occurs simultaneously, the picture is homogeneous.
As you can see, there are cases when acne appears like chickenpox, but not chickenpox, and it is necessary to differentiate them.
Many people know what chickenpox looks like; this can be understood by the appearance of characteristic rashes all over the body.
Allergy similar to chickenpox
The main symptoms of allergies are as follows:
- itching;
- burning;
- runny nose;
- headaches;
- tearfulness;
- disturbances in the stomach and intestines, stool upset;
- emotional instability;
- rash.
Typically , allergies have the following characteristics:
- uneven distribution of the rash;
- allergies occur annually to natural manifestations (pollen, flowering) or to food;
- treatment of an allergic reaction is aimed at isolating allergens from the body;
- Allergic manifestations increase every year.
Principles of diagnosing infection
Chickenpox is also diagnosed by external, physical signs during a medical examination. Once your child has red pimples on the body, as well as all other signs of chickenpox that can be distinguished from prickly heat, you need to call a medical facility and consult with a specialist on further actions and treatment. If you feel unwell, complain about headaches, or fatigue, you should see a specialist.
Citizens who are at high risk of infection with the causative virus (a pregnant woman who has not had chickenpox before, people who have a weakened immune system, although they have had chickenpox before) are required to be examined for the presence of immunity developed against it. If they have not encountered the disease before, they are recommended to get vaccinated and increase the likelihood of not getting sick or catching it.
At the early stage of smallpox infection, you can treat yourself, but still do not neglect consulting a doctor.
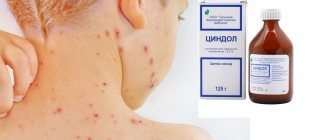
Of course, any disease must be treated and, it seems, chicken pox is no exception. The main thing is to cure the skin so that pus does not accumulate in the blisters under the skin and pustules do not form. Zelenka is an excellent antiseptic with fast-acting disinfecting properties. This is indispensable in the treatment of illness. It is worth smearing it on all affected areas, all pimples, and wait until crusts appear. Later they will begin to dry out, their appearance will end, and everything will pass. If you use various alcohol solutions, they are unpleasant for the skin, sting and irritate it.
When the body temperature rises, when the ability to tolerate it ends, they drink antipyretics in the form of syrup or tablets. Once you decide to wash yourself, you should not use rough washcloths, just pour some water over your body and add a weak solution of chamomile or potassium permanganate. Under no circumstances should you allow the body to be scratched, so as not to leave small scars. In addition to brilliant green, antihistamines, antivirals, and, in rare cases, antibiotics are also prescribed. Bed rest, rest, and taking medications on time will have a beneficial effect on the course of treatment of the disease.
If an adult is sick or children are sick, the local pediatrician or infectious disease doctor must visit them. A pediatrician treats children and adolescents aged 0 to 16 years. An infectious disease specialist treats infectious diseases, determines the congenital or acquired nature of the disease, diagnoses the causative agents of diseases, searches for the source of the disease, prescribes appropriate treatment and gives recommendations to those who have been ill.
After consulting a doctor, confirming the exact diagnosis and prescribing appropriate treatment, carefully monitor your health condition. If complications develop, you may be referred to an appointment with a pulmonologist who treats the bronchopulmonary system and respiratory system of those who have had chickenpox. In medical practice, cases of complications with chickenpox are very rare, and as long as the patient strictly follows medical recommendations, with proper treatment, a speedy recovery is guaranteed.
Rubella is a possible option
Rubella is a disease that is also similar to chickenpox.
Viral disease most often goes away in childhood, and quite easily.
However, there are rare cases when adults get sick and the disease is severe. The virus is very unstable: it dies from ultraviolet radiation in 12 minutes. Rubella can be contracted through respiratory droplets from an infected patient.
The only common symptom is a red rash on the body. The disease can progress in different ways, depending on the individual characteristics of the person. During the first 2 weeks, symptoms are not detectable. On the 12th day, you can notice a gradual spread of red spots on the body.
As soon as spots appear, body temperature immediately rises. Lymph nodes increase in size and become too sensitive. In general, the symptoms of the disease are similar to the common cold. The distinctive sign is a red rash.
To prevent infection, vaccines are given at a young age. However, the vaccine can only be valid until the age of 14, then it needs to be renewed. In addition, the vaccine causes many side effects and does not provide one hundred percent protection against the virus. Drugs such as Ervevax, Rudivax and others have been developed for the treatment of rubella.
Antibacterial drugs
For many years, brilliant green has been one of the most inexpensive and effective drugs for treating the disease. It has a disinfecting effect and at the same time slightly dries out inflammation, which promotes their speedy healing and subsequent recovery.
Some parents use iodine as an antibacterial drug, but applying it to pimples with chickenpox is prohibited, since such a medicine can cause severe itching on the child’s skin and cause the baby to scratch the resulting ulcers.
An alternative drug to brilliant green is potassium permanganate. The solution will help reduce itching and dry out rashes. You need to smear the skin with a 5% solution of potassium manganese, which can be purchased at almost any pharmacy.
Measles is a cause for concern
Rashes can also occur with measles, so it can easily be confused with chickenpox. You can catch the disease at any age. The virus is transmitted to a healthy person by airborne droplets.
The symptoms are similar to the flu or a cold, except for one sign - a rash. The patient develops a severe cough, weakness, and body temperature rises to 39 degrees. The conjunctiva turns red, the palate becomes covered with blisters, red spots appear on the body, which after 4 days begin to peel off.
You need to be treated at home; only patients with a severe form of the disease are allowed for inpatient treatment. During fever and fever, it is necessary to lie down constantly. There are no drugs that can cure measles. You can only alleviate the symptoms; the disease itself goes away on its own. You definitely need to eat fruits and vegetables. If you have a cough, an expectorant will do. You should not open windows as it irritates your eyes. You can drop Albucid into your eyes 3 times a day.
The main means of prevention is vaccination. It protects for up to 15 years. Complications after measles include bronchitis, bronchiolitis, keratoconjunctivitis and pneumonia. Rarely, hepatitis, myocarditis and glomerulonephritis occur.
Reduce itching
Ointments such as Acyclovir, Virolex and Gerpevir will significantly reduce itching and alleviate the child’s general condition. Moreover, the drugs have an antiviral effect, which has a positive effect in the treatment of chickenpox virus. Another good remedy is “Calamine”, which will relieve the child of itching and thereby prevent scratching and infection from entering the baby’s body.
Other effective remedies for chickenpox include Rivanol and methylene solution. For severe itching, chickenpox can be lubricated with glycerol. In some cases, doctors recommend treating smallpox with Vikasol, Rutin or calcium chloride. The use of these substances is advisable if the child’s rash becomes hemorrhagic (bleeding). The amount and frequency of application of the solution is determined by the composition chosen for application. Thus, “Rivanol” can be applied to wounds 2 times a day.
Light spots that remain after the end of smallpox can be lubricated with vegetable oil to even out the skin color and speed up the disappearance of traces of the disease.
For many years, brilliant green has been one of the most inexpensive and effective drugs for treating the disease.
The cause of the rash is whooping cough
Most often, children suffer from this type of infectious disease. Infection occurs by airborne droplets. Whooping cough develops very quickly. Its main difference from chickenpox is the risk of recurrence.
The first sign is fatigue, weakness and malaise. But it is difficult to identify the disease at the first stage. Later, more obvious symptoms appear. A person suffers greatly from a rough cough, which can lead to suffocation. Symptoms include a runny nose and fever. The patient becomes irritable. The cough is constantly getting worse, and tremors occur. During such periods, the tongue protrudes strongly, and the veins in the neck swell.
Although a person can die from such coughing attacks, whooping cough is not considered a fatal disease. Treatment is carried out at home. If the disease has reached a severe stage or if the patient is under 1 year of age, then treatment is carried out in a hospital setting. Antibiotics are used when the acute stage begins.
The most commonly used are erythromycin and azithromycin. You can use chloramphenicol and tetracycline. But not all of them are allowed for children. It is necessary to maintain bed rest, go for short walks, and take vitamins. It is necessary to eliminate all the causes that cause the cough.
Is it possible to get sick again?
Those who have had chickenpox have lifelong immunity to it and re-infection is impossible. If you are diagnosed with chickenpox for the second time, it means that one of the diagnoses was incorrect. Chickenpox can be confused with many other diseases, with streptoderma or herpes skin lesions, and other infections.
What you can get when you have chickenpox is shingles. Chickenpox viruses persist for life after illness in the nerve ganglia in the spinal cord. They can remain in a dormant state all their lives, or they can become more active when the immune defense weakens. This usually happens in the elderly, in people with immunodeficiencies, with HIV infection or other problems of the immune system. These people have chickenpox-like rashes on their bodies and can infect surrounding children and adults with chickenpox.
Smallpox as one of the reasons
This disease is considered one of the most terrible and dangerous in the world. Nowadays, thanks to treatment and vaccinations, outbreaks of infection rarely occur in the world. Virus samples are kept only in special storage facilities in Russia and the USA. Chickenpox used to be considered a mild form of smallpox, but later scientists and doctors discovered many more differences. It has now been proven that chickenpox (chickenpox) is a completely different disease.
Smallpox raged strongly at different periods of history. The countries that suffered most from it were China, Africa, and India. This viral disease is transmitted through household items and by airborne droplets. The virus is very resistant to environmental conditions: in severe frost or heat, it lives for up to a year and can even withstand drought. After the death of an infected person, the virus remained on the dried wounds, so the bodies were burned.
The main symptoms of the disease are:
- blisters on the body and red spots;
- crusts that remained from burst blisters;
- fever and heat;
- wounds and ulcers.
Every two weeks the situation worsened, accompanied by waves of severe pain. When purulent wounds appeared on the body, it meant that the patient would soon die if treatment was not started.
All children are vaccinated to prevent smallpox. To treat this disease, drugs such as immunoglobulin and metisazone have been developed.
Contagious period
During the incubation period of the disease, the patient is already infectious to the team. The carrier most often does not realize that he has become a latent distributor. During the formation of spots followed by the formation of blisters, the patient poses a greater risk of transmitting the virus to others. The active phase of the disease involves the simultaneous presence of several types of rash on the skin:
- flat spots of pink or reddish color;
- small pimples with clear liquid;
- larger blisters with cloudy contents;
- burst blisters with exudate;
- crusty wounds;
- healing wounds with detachable crusts.
It is important to know that a patient with chickenpox will be contagious to other people until all periods of the rash are over.
At the end of 6 days, when chickenpox last breaks out in children, young patients can visit the children's group. On the 6th day after the last rash has crusted over, the child is no longer considered infectious.
Since there is a certain sequence of stages of chickenpox disease in children, children's institutions begin quarantine measures from the moment visible signs are detected in the first sick child. The quarantine ends when the last patient from the children's team actually recovers.
What diseases in children are similar?
Chickenpox is one of the most common childhood infectious diseases, which most often affects children from 3 to 7 years old.
You can become infected through contact with a sick person, regardless of the season. The carrier of the virus becomes dangerous to others 2 days before the formation of the rash and continues to remain infectious for 5 days after the appearance of the last elements of the rash.
The incubation period for this childhood infection ranges from 10 to 21 days.
Classic chickenpox, as a rule, does not cause any difficulties in diagnosis:
- The disease begins with malaise - weakness, drowsiness, decreased appetite, increased body temperature to 37-38 degrees. Some children may experience symptoms of ARVI.
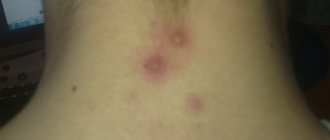
- On the second day, small reddish spots appear on the skin of the face, scalp, body and limbs. They quickly turn into single bubbles filled with a clear yellowish liquid.
- After a few days, the blisters burst, dry out and become covered with crusts, which fall off on their own, leaving behind areas of pigmentation.
A distinctive feature of typical chickenpox is the appearance of a rash on the scalp and mucous membranes (in the mouth, on the eyelids), as well as severe itching.
However, if chickenpox occurs in a pustular or rudimentary form, it can easily be confused with other diseases. Difficulties may arise when diagnosing the disease on the first day, when the rash that precedes chickenpox can lead to misdiagnosis.
The list of diseases similar to chickenpox includes:
- Simple herpes.
- Enteroviral fever (Coxsackie).
- Measles, rubella, scarlet fever.
- Streptoderma.
- Allergic reactions, including to insect bites.
The first signs of the disease before the appearance of a specific rash resemble the clinical picture of other viral infections. Headache, weakness, drowsiness, loss of appetite and fever occur with almost all diseases, ranging from colds to rare infections.
Until recently, thanks to mass vaccination, measles was considered a rare disease in children. In recent years, due to interruptions in the supply of vaccines and the popularity of the anti-vaccination movement, the incidence has increased again. Vaccination against measles does not guarantee lifelong immunity, so adults and older people can get this disease.
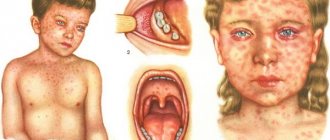
Measles is similar to the initial stage of chickenpox, as well as its rudimentary form. The pathology begins with fever, pain and sore throat, cough, conjunctivitis. Symptoms of ARVI are accompanied by the appearance of a specific rash on the buccal mucosa - Filatov-Koplik spots.
On days 3-5, a red spotty rash appears on the skin of the face and neck, the next day the rash spreads to the torso, and a day later to the limbs.
When a rash appears, the fever decreases and the patient’s well-being improves.
The main differences between chickenpox and measles:
- Measles rash does not appear simultaneously with fever, but on the 3-5th day of illness.
- The spots are large, bright red, and often merge with each other.
- Measles rash does not have blisters.
- With measles, the rash appears in stages.
In addition, the measles rash does not affect the scalp and mucous membranes, and the disappearance of the rash is accompanied by pigmentation and peeling.
Rudimentary chickenpox and rubella are very similar to each other in the morphological elements of the rash. Both of these diseases are accompanied by the appearance of pink-red spots on the patient’s skin.
Like chickenpox, rubella is caused by a virus. The incubation period in the presence of the latter is 11-24 days.
A person is contagious from the 7th day from the onset of the disease to 4 days after the complete disappearance of the rash.
The main manifestations of rubella are fever, the appearance of a small spotted pink rash, and enlargement of the posterior cervical lymph nodes.
Unlike chickenpox, rubella:
- The rash appears on the first day of the disease. This happens simultaneously with an increase in temperature.
- Mottled pink spots appear throughout the body, concentrated on the face, buttocks, and extensor surfaces of the arms and legs.
- Rubella is not characterized by pimples, crusts, or pigmentation.
Compared to chickenpox, the rash with rubella is smaller and is not accompanied by itchy skin.
The pathology is especially dangerous for pregnant women, as it can cause developmental defects in the fetus. That is why doctors recommend checking the titer of antibodies to rubella and, if necessary, re-introducing the vaccine to girls and women planning pregnancy.
Chickenpox leaves behind lifelong immunity, so in most cases it occurs once in a lifetime. However, many people believe that they have had chickenpox twice. This may be due to the fact that several decades ago it was mistaken for enteroviral fever caused by the currently known Coxsackie virus.
The source of infection is a sick person who is dangerous to others within 7-10 days from the onset of the disease. The peak incidence is recorded in late summer – early autumn.
When infected with the Coxsackie virus, the disease begins with symptoms of acute respiratory viral infection, fever, then itchy spots and a blistering rash appear on the skin, the same as with chickenpox.
The difference between enterovirus infection and chickenpox:
- The peak incidence of Coxsackie occurs in the hot season - August, early September, while chicken pox can be recorded all year round.
- The rash with enteroviral fever is most often localized on the flexor surfaces of the feet and palms, as well as in the mouth - on the tongue, palate, and gums.
- After the rash, the skin flakes and peels off like a sunburn.
Coxsackie infection, unlike chickenpox, is characterized by stomatitis - profuse blistering rashes on the oral mucosa.
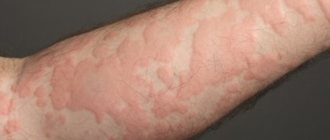
An itchy blistering rash, but not chickenpox, may indicate an allergic reaction - hives. This is a condition that occurs when there is an individual intolerance to a certain food product or cosmetic product. Reddish spots first appear on the skin of the body and limbs, then irregularly shaped blisters rising above its surface.
Differences between urticaria and chickenpox:
- Urticaria is not a contagious disease and cannot be transmitted from one person to another.
- An allergic reaction can occur in response to food allergens, cosmetics, pollen, and exposure to physical factors (cold, heat, solar radiation).
- Sometimes blisters appear in response to the development of microbial infections or the medications used to treat them.
- With urticaria, there are no symptoms of acute respiratory viral infection and rarely an increase in body temperature, however, upon examination, a local increase in skin temperature over the blisters may be noted.
Acutely developed urticaria requires mandatory medical consultation, because severe allergies can lead to serious complications such as angioedema or anaphylactic shock. Chronic, indolent urticaria also requires examination by a specialist to identify the trigger of the disease and select treatment.
Currently, in addition to classic childhood infections (chickenpox, measles, rubella, scarlet fever), sudden exanthema or sixth disease is distinguished.
Just like chickenpox, it is caused by a virus from the herpes family, which is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one. Most often this occurs through airborne droplets when talking, coughing, or sneezing.
Difference between chickenpox and roseola:
- The sixth disease begins with general malaise and increased body temperature. Unlike chickenpox, the rash does not occur during the fever, but after it subsides, i.e. on days 3-5 of illness.
- The rashes are small- and medium-spotted, pink in color, do not itch and do not form blisters.
- The typical localization of the rash is the torso and limbs.
The rash with sudden exanthema goes away on its own without any treatment 5 days after its appearance, leaving behind no peeling, areas of pigmentation or depigmentation. After roseola, as well as after chickenpox, stable lifelong immunity is formed.
Besides childhood infections and allergies, the symptoms of chickenpox are similar to those of some bacterial infections. In this regard, if pustular chickenpox is suspected, a differential diagnosis with streptoderma should be carried out.
The main differences between streptococcal impetigo and chickenpox are:
Streptoderma is not characterized by increased body temperature and general malaise. The rash usually affects the trunk and limbs. Despite the fact that streptococcal impetigo is a contagious disease, it is less contagious than chickenpox.
Diseases such as disseminated herpes and herpes zoster may resemble classic chickenpox.
However, with a significant decrease in immunity, for example, during treatment with immunosuppressants, with HIV/AIDS, or while undergoing high-dose chemotherapy, the infection can spread throughout the body and lead to the appearance of an itchy, blistering rash throughout the body.
Shingles is caused by the same virus as chickenpox. Most often it develops:
- After suffering serious illnesses.
- In elderly and frail people.
- Against the background of radiation and chemotherapy for oncological processes.
- While taking high doses of corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs.
A characteristic feature of herpes zoster, in contrast to chickenpox, is the thickening of vesicular rashes along the nerve trunks - on the face in the projection of the facial nerve, in the intercostal spaces, along the sciatic nerve.
If blistering rashes appear on the skin of the face, body and limbs, you should consult a doctor to establish the correct diagnosis and select treatment.