Home > Urology > Epidermal cysts
- Treatment of prostatitis
- Pearly penile papules
- Fordyce granules
- Fordyce angiokeratomas
- Epidermal cysts
- Excision of the foreskin
- Short frenuloplasty
- Treatment of hydrocele
- Treatment of varicocele
- Removal of oleogranulomas
Epidermal cysts are a common type of cyst that can form on the scalp, face, neck, torso and genitals, as well as in areas of frequent friction. It is a flesh-colored tumor-like neoplasm, reaching a size of 5 cm. They are equally common in both men and women.
What is an epidermal cyst
An epidermal cyst is a benign pathological neoplasm that resembles a small ball. The pathology can be localized in any part of the body, most often growing on the head and in the back. Neck cysts are much less common. One patient may have from one to two or three cysts. The causes of the disease are varied - from neglect of personal hygiene to hormonal disorders.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications
Timely detection and treatment of a tumor will prevent the complication of the disease - degeneration into a malignant neoplasm. The disease occurs equally often in both men and women, and is less common in children.
Atheroma is diagnosed by appearance, histological examination, and ultrasound and MRI are prescribed to clarify the diagnosis.
Therapeutic measures depend on the size of the tumor: for larger sizes, the lesion is removed surgically (radio wave method, laser destruction and electrocoagulation are used). The prognosis is positive.
LASER REMOVAL OF PIGMENT STOCKS
After the procedure, the patient must follow the doctor's recommendations. Otherwise, there is a risk of infection or scarring of the tissue (if you wet it or pick off the scab).
The list of mandatory recommendations includes the following:
do not wet the wound or pick off the scab;
avoid situations in which the wound may become wet (visiting a swimming pool, sauna, open water, taking a bath, all water procedures - with caution);
do not apply cosmetics to the wound (for example, foundation or powder for the purpose of masking);
choose clothes in such a way that the fabric does not rub the wound;
In case of purulent discharge, swelling, redness, pain, you should immediately show the wound to a doctor.
The duration of rehabilitation depends on the size of the removed atheroma. The smaller the cyst, the faster the recovery will be. In any case, after laser removal, the healing process will not last long.
Causes of epidermal cyst
An epidermal cyst is formed in the process of blocking pores when the outflow of secretions from the sebaceous glands is disrupted. Most often diagnosed in patients prone to acne.
To better understand the mechanism of tumor formation, it is worth considering the functioning of the sebaceous glands, which produce a secretion that protects the skin from pathogenic bacteria. When the duct is blocked, the secretion accumulates inside and causes expansion of the walls of the gland, followed by inflammation.
An epidermal cyst externally looks like a round-shaped node with an unchanged or reddish skin color. The pores are enlarged and visually visible. The size of the formation is from 0.5–5 cm to a full apple.
The main causes of clogged pores:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- low-quality cosmetics that cause clogged pores;
- hormonal imbalances;
- metabolic disease.
The appearance of a cyst on the ovary is associated with embryonic malfunctions in the intrauterine development of the fetus. It can occur in women and is associated with physical and emotional stress, ovarian dysfunction and constant abortions, triggered by inflammatory processes.
Clinical picture
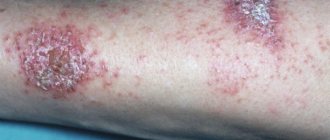
As mentioned above, an epidermal cyst resembles a large pimple (up to 5 cm) or a rounded nodule. The appearance of the formation is usually characterized by hyperemia (redness) of the skin next to the atheroma. Upon careful examination, you can see enlarged pores, as well as networks of capillaries on the cyst.
The formation is soft to the touch, resembling a balloon. At the same time, there is no pain or other unpleasant sensations during palpation. Another feature of an epidermal cyst is its mobility. If you touch the surrounding tissues and move them, the atheroma will move with them.
Sometimes a clear liquid can be seen next to the formation - this is discharge from the epidermal cyst, called atheromatous masses. The smell of discharge is usually associated with spoiled cheese.
Most often, epidermal cysts appear in certain places:
- The scalp.
- Face.
- Neck.
- Chest area.
- Upper back.
- Scrotum.
Sometimes formations are also found on the feet, fingers, earlobes or eyelids.
Classification
Epidermal skin cyst has a classification:
- True tumor. It is formed from appendages of the epidermis, has a congenital nature of origin and is diagnosed in women on the head. The growth of the tumor is slow, the risk of degeneration into malignant atheroma is very low.
- False tumor. Appears due to excessive secretion of sebaceous glands, which accumulates in the pores, forming a plug. The usual location is on the back, but it occurs on the face and scalp.
There are cases where an epidermal cyst has formed on the labia. The patient should be observed by a specialist. If the tumor grows quickly, the lesion is removed surgically.
An epidermal cyst can be localized in the perianal zone, which affects the area around the anus. Occurs infrequently.
False forms of cysts quickly increase in size, and the percentage of degeneration into a malignant neoplasm is high.
Causes and clinical manifestations
The causes of an epidermal cyst are a violation of the outflow of sebaceous gland secretions and/or its excessive production. In turn, depending on the reasons for such a violation, they are conventionally distinguished as:
- Primary, or true, which represent a developmental defect. They develop from the epidermis, usually hair follicles, as a result of its “unlacing” during embryonic development. They are most common in children of any age with equal frequency in boys and girls.
- Secondary, or false, which are characterized by rapid development. The main reason for their formation is traumatic damage to the hair follicle or dermatological diseases (seborrhea, acne), less often - metabolic disorders, hormonal imbalance, adverse environmental influences, application of a significant amount of cosmetics to the skin, especially with low quality, as well as violation of basic hygiene rules.
Clinically, epidermal cysts are mobile (displaceable to the sides), painless, smooth, oval or round-shaped compactions with a diameter of 3-5 mm to 1 cm, less often up to several centimeters, protruding above the surface of the skin, which is unchanged above them. Their contours are smooth and clear, the consistency is densely elastic, in the center you can often find a black dot, which is a clogged outlet
opening of the dilated duct of the sebaceous gland.
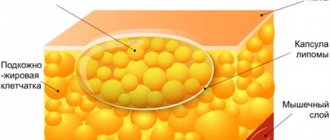
Morphologically, they are located in the dermis or subcutaneous tissue, well delimited by stratified squamous epithelium with a clearly formed layer of granular cells. Their contents are a cheesy mass of thick consistency with an unpleasant odor of rancid cheese (lamellar horny detritus), including a large amount of keratin and lipid derivatives, and having a grayish-white or yellowish-white color.
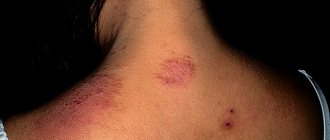
1. Epidermal cyst in the postauricular area that developed in a child 2. Multiple epidermal cysts
Most often, these elements are localized in the scalp, on the face (in the superciliary, zygomatic and temporal areas, on the eyelids), in the parotid region, along the back or front surface of the earlobe. In this area they often reach large sizes (up to 2-5 cm), and are prone to both aseptic and purulent inflammatory processes.
On the body, epidermal cysts are usually found in the axillary region, on the back (between the shoulder blades), sometimes reaching 10 cm, on the anterior surface of the upper chest, somewhat less often - in the groin (in men 2 times more often than in women ) and in the perineum, on the scrotum in men and the labia majora in women.
There are a lot of sebaceous glands on the mammary gland, but epidermal formations in this area develop quite rarely, especially in the area of the nipple areola. In this zone, they are formed in women and men, mainly in the presence of hormonal or metabolic disorders, as well as in women during breastfeeding, much less often due to non-compliance with the rules of individual hygiene.
Very rarely they form in the area of the palmar surface of the hands and the plantar surface of the feet. In these areas, their formation is associated mainly with traumatic injuries to the skin.
Epidermal cysts can be multiple, especially if they are localized on the head, and single, as a rule, on other parts of the body. The peculiarity of multiple formations is their small size, which increases slightly over a long time. In contrast, single elements can grow over a long period of time, reaching very significant sizes.
When irritated by external factors (friction by clothing, mechanical pressure), an aseptic inflammatory process may develop, accompanied by pain, redness of the skin in this area, and an increase in the size of the tumor formation due to edema. As a rule, such a non-infectious inflammatory process goes away on its own, but the formation itself usually increases in size after this and becomes denser due to thickening of the capsule and compaction of the surrounding connective tissue.
Single formations
In some cases, the cyst can open on its own, releasing a cheesy yellowish-white mass as a result of the accumulation of secretions and rupture of the capsule and the thin layer of skin above it. This process resolves on its own without complications if there is no bacterial infection attached.
The rupture of the capsule not outward, but in the direction of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue causes pain and an increase in the formation in size, and when infectious pathogens (staphylococci, streptococci) are attached - to the formation of an abscess or phlegmon. The formation, localized in the scrotal area, can sometimes become calcified.
Symptoms of an epidermal cyst
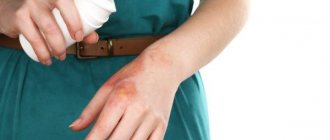
Epidermal cyst photo.
Epidermal cyst is the most common neoplasm. True atheroma visually resembles a subcutaneous node; the surface of the skin is clogged with pores. It can be located on the cheeks, ears, back and other parts of the body.
The node quickly grows and opens into the dermis, which causes severe pain and inflammation. The growth of the pathology is slow, the lesion has a tendency to thicken. A false epidermal cyst grows quickly.
You should consult a doctor if the following signs appear on your skin:
- inflamed nodules;
- pain in the tumor;
- rapid cyst growth.
A quick response and medical assistance will protect the patient from possible complications.
ADVANTAGES OF LASER REMOVAL OF atheromas
- Minimal risk of bleeding due to the ability of the laser to coagulate damaged vessels
- Minimal risk of postoperative complications associated with infections - the laser destroys bacteria and microorganisms, thereby creating a sterile environment in the operating area
- Fast recovery - healing occurs approximately twice as fast as after surgical removal
- Ability to remove atheromas of any size
- Subtle (in the case of large atheromas) scarring on the skin or complete absence of scars (in most patients)
Diagnostics
An epidermal cyst is diagnosed after an external examination. For unclear etiology, the following is prescribed:
- ultrasound examination of the tumor - the presence of a cavity and its size are determined;
- Magnetic resonance imaging - required in rare cases of cyst localization.
After examination and detection of rapid growth or large size of the tumor, the lesion is eliminated through surgery. After removal, a mandatory histological examination is carried out.
When making a diagnosis, differentiation is made from lipomas, hydromas, paronychias, adenophlegmons and dermatofibromas.
Treatment of epidermal cyst
An epidermal cyst cannot be eliminated mechanically. If the lesion is squeezed out, after a while it forms again in the same place. To prevent relapse, the tumor should be surgically removed along with the capsule.
If the cyst is severely inflamed, treatment will be as follows:
- eliminate the inflammatory process;
- conservative therapy.
The purulent inflammation is opened with drainage; only after the wound is cleansed and healed is it possible to remove the capsule to prevent the risk of blood poisoning.
The operation is performed with local anesthesia and can have the following types:
- traditional surgical removal;
- use of laser;
- radio wave technique.
Classic surgical removal involves cutting the skin over the cyst. The surgeon, using a special clamp with a gauze swab, carefully peels off the surrounding tissue from the cyst and removes the lesion along with the capsule. Stitches are then applied.
The following techniques are used to eliminate pathology with laser:
- Photocoagulation. Applicable for cyst diameters of no more than 5 mm. It is removed along with the capsule without suturing. During healing, a crust forms, which disappears at the final stage.
- Excision with capsule. Prescribed when the tumor is from 0.5 to 2 mm. Removal is similar to surgery, but a laser is used instead of a surgical instrument. The wound heals quickly.
- Vaporization of the capsule. The procedure is performed with a tumor larger than 2 cm.
It is worth undergoing treatment in a high-quality clinic with modern equipment and experienced staff.
LASER REMOVAL OF atheromas in “EL. EN."
Do you want to get great results?
Choose laser removal of atheromas with short rehabilitation and no scars. Our surgeon will recommend the optimal laser treatment method and perform the procedure. 1 Photocoagulation
The method is suitable for eliminating atheromas with a diameter of up to 5 mm. High-intensity laser radiation is directed (non-contact) to the neoplasm; as a result of the impact, the capsule and its contents are completely evaporated. After the procedure, a crust remains at the site of the atheroma; no stitches are required. After a certain time, the crust disappears, the resulting wound gradually heals, and the skin becomes even.
2
Excision
The method is most often practiced in situations where the diameter of epidermal cysts is up to 20 mm (but there are exceptions). The surgeon cuts the skin (with a laser knife or scalpel), stretches the cyst shell and evaporates the tissue around it with a laser - this is how the atheroma is separated from healthy structures. Then drainage is placed for several days.
3
Evaporation
It is practiced when the diameter of atheromas exceeds 20 mm. The surgeon opens the capsule, removes its contents, and then acts on the capsule with laser radiation - it evaporates. The operation is completed by installing drainage and suturing.
Our clinic also performs laser removal of ingrown toenails - the cost starts from 6,000 rubles. Sign up online or by phone.
Possible complications
An atheroma or epidermal cyst can transform from a benign tumor to malignancy. There is a high risk of wound infection if you try to get rid of the pathology yourself.
Suppuration of the tumor is dangerous - without disinfection, the inflammatory process can worsen. Large cysts on the head often cause vision problems and regular headaches.
For prevention purposes, you should carefully monitor your personal hygiene, use high-quality cosmetics, visit beauty salons and clean your pores, and consult a specialist in a timely manner.
WHY ATHEROMAS NEED TO BE REMOVED
- Many of our patients want to get rid of atheromas due to discomfort. When large, the cyst begins to come into contact with clothing, which causes discomfort.
- Another reason is aesthetic. An ugly “bump” on a noticeable part of the body or on the face clearly does not enhance one’s appearance.
- The absolute indication for removal of atheroma is its suppuration. In such cases, it is better not to delay treatment. If the atheroma becomes inflamed, swelling, pain when pressed, and redness of the skin over the formation appear. With purulent inflammation, body temperature often increases, and general health deteriorates sharply. The resolution of such a process involves the spontaneous opening of the cyst with the outpouring of pus, and not always to the outside - it is possible to overflow into the deep tissues with all the ensuing consequences.
- Therefore, the presence of an epidermal cyst (suspicion) requires contacting a dermatologist for diagnosis and subsequent removal of the tumor. Ignoring the problem and postponing a visit to a specialist can lead to a purulent abscess and a more serious course. The atheroma will still have to be removed, only the cyst will be large (remember that it grows quickly), drainage will have to be installed, and there will be a risk of a scar appearing at the site where the tumor was removed.
What to do
If you think you have an Epidermal cyst
and the symptoms characteristic of this disease, then doctors can help you: therapist, surgeon, dermatologist.
We wish everyone good health!
Diseases with similar symptoms
Median neck cyst (overlapping symptoms: 2 out of 5)
Median neck cyst is a rarely diagnosed congenital malformation. It is characterized by the appearance of a neoplasm with liquid content in the neck area. There are lateral and medial pathologies of the neck. The lateral forms are recognized immediately after the birth of the child, while the middle ones can appear as the child grows. Most often, the formation can be eliminated through surgery, which is performed in adults and children.
Did you like the article? Share with friends on social networks:
Prevention
The disease is called a congenital anomaly of the fetus and a newborn baby acquires it at birth, and therefore it will not be possible to protect him from developing the disease. Preventive measures consist of constant, timely examinations of the child by a doctor. Examinations by a doctor begin from the first months, this way pathology can be identified more quickly. The sooner a lump is detected, the easier it is to remove it without waiting for it to grow and become inflamed.
Try to protect your child from injuries and bruises in the larynx and neck area. This way you can prevent the active growth of the lump (if any) or the onset of the inflammatory process.
From time to time, an adult child should examine himself by palpating, and parents of children under seven years of age should carefully examine his neck on their own. A child’s visit to an otolaryngologist and dentist should be carried out at least once every six months.
There are currently 64 reviews on this article, average rating: 4.05 out of 5