Features of the disease
Despite the symptoms characteristic of allergic skin manifestations, this disease is neither a type of allergy nor an autoimmune reaction.
Of course, with the development of atopic march or cascading forms of allergies in allergy sufferers, low temperatures can aggravate the inflammatory process. But then they are not the root cause, the main triggering factor.
Thus, three features of the pathology can be distinguished:
- cold turns out to be the only condition for the development of such dermatitis;
- implies climatic influence by cold, i.e. systemic - living in northern regions with a continental climate, where winters are long, low-temperature and dry;
- enters a state of stable remission when moving to regions with a warmer, humid climate.
Local exposure to cold on the skin can cause irritation, but it will quickly pass if there is no main external factor (severe dry winter).
Causes
Eczema is insidious due to its polyetiological origin, that is, this disease does not have a single cause of development - several factors contribute to the emergence of the pathological process.
The list of the main ones includes the following aspects:
- Genetic predisposition. In fact, this aspect is a single set of many criteria transmitted to the child from his parents, including a tendency to allergies.
- Endocrine diseases. Hormonal problems in the body often cause the immune system to react to various external and internal factors.
- Immune disorders that arise against the background of serious stress, weakness of the defense system, chronic infectious and inflammatory diseases, antibiotic therapy.
- Features of age. It is believed that the main active activity awaits a person between 20 and 50 years. It is at this stage that he comes into more intense contact with environmental factors, including not the most harmless ones. Most often this concerns women, since they are the ones who have more contact with detergents, laundry products and cosmetics.
- Chronic pathologies that provoke disturbances in the functional activity of vital systems: diseases such as hepatitis, HIV, diabetes mellitus and much more.
The conditions listed above inevitably lead to disruptions in the immune system. As if sensing deception, she lowers the T-lymphocyte titer. As a result, the immune system begins to perceive the skin as a foreign object, provoking pathological processes in them.
Once under attack, the epidermis grows, the blood fraction is released into the external environment, followed by keratinization of the skin, that is, a mechanism for the development of eczema occurs.
What causes itching?
itchy skin - often the effect of stress on the body
The culprits of this unpleasant symptom are the biogenic amine histamine and the neurotransmitter serotonin.
Leukocytes of various types actively strive for the focus of eczema. They trigger inflammation: they carry out phagocytosis, secrete proteolytic enzymes, cytokines, and prostaglandins.
A subtype of leukocytes, such as basophils (mast cells), contains granules with histamine. He can be freed directly and indirectly. In the inflamed area, basophils begin to degranulate, histamine binds to its receptors in skin cells, which leads to a feeling of itching. This is an indirect release.
Protease enzymes and complement factors selectively bind to basophil receptors and directly lead to the release of this biogenic amine.
The patient begins to scratch the skin, this leads to irritation of the nerve endings. Irritation from scratching leads to even greater degranulation of mast cells and a greater release of histamine.
An inadequate response to inflammation on the part of the autonomic nervous system leads to the release of serotonin by the nerve endings, which aggravates the process.
Histamine at the site of inflammation is needed in order to dilate blood vessels and cause an even greater influx of leukocytes for the normal completion of inflammation and healing. In a healthy human body, inflammation is suppressed by glucocorticoids - adrenal hormones. But in a person with a predisposition to skin diseases, the neurohumoral regulation of inflammation is impaired. Your own hormones are not enough to suppress this process.
Based on the main blocks of the pathogenesis of itching, the main directions of combating it are formed.
In order to relieve itching due to eczema, you must:
- Stop the release of histamine.
- Suppress inflammation.
The skin itches most severely during an exacerbation of the disease, but when the process subsides, in the place where the lesions were localized, the itching continues.
Allergy to cold
In autumn and winter, the problem of allergies to cold is especially relevant. However, it can occur even in summer. It can also be triggered by eating cold food and drinks, swimming in cool water, etc. It develops as a result of an inadequate response of the immune system to low temperatures that affect the body.
Allergic reactions to cold can be of the following types:
- Idiopathic. This pathological condition occurs independently. The causes have not been established. Occurs in most cases.
Purchased. Presumably associated with lymphoproliferative diseases and liver pathologies. It may appear after using certain medications (for example, Griseofulvin, contraceptives, etc.). The main category of patients are women over 27 years of age. Family. It is observed extremely rarely. Usually the immediate family also suffers. It begins to appear from the first year of a child’s life.
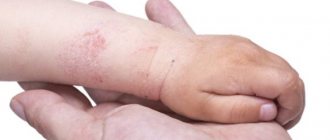
Rash on hands
Cold dermatitis on the hands is characterized by inflammatory changes in the skin due to exposure to low temperatures. Dry, scaly spots of a dark red or burgundy hue appear on the upper limbs. Their size can vary from two to five centimeters. Skin rashes are accompanied by a very intense sensation of itching and burning.
After some time, small cracks appear in the area of the rash on the hands and become crusty. The hands are most often affected, especially if the patient walks without gloves in the cold season. In some cases, with cold dermatitis, the rash spreads to other parts of the body (face, neck, legs, etc.). In parallel with the skin rash, sneezing, runny nose and lacrimation may occur, which disappear quite quickly at room temperature.
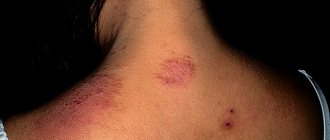
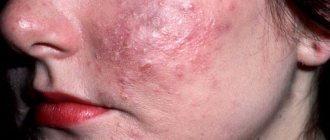
Eczema on the face
Quite often, an allergy to cold manifests itself as eczema on the face. The skin looks swollen and red. Small bubbles containing a cloudy liquid appear on it. After opening them, an erosive surface is formed. Then the affected area becomes covered with crusts. Pigmented spots may remain at the site of the rash.
The pathological process on the face is accompanied by severe itching. Allergic damage is usually symmetrical. In addition, the skin becomes dry and peels in places. Often there is a transition to a chronic form.
Hives
In most cases, cold urticaria is idiopathic. However, in some patients this allergic condition runs in families. Clinical picture of the disease:
- Due to cold water or icy air, the patient experiences burning, itching, erythema, blistering and/or swelling of the skin within a few minutes.
- Mostly these manifestations are found on the face and hands.
- Maximum clinical manifestations are observed during the warming process and usually disappear within an hour.
- Some patients develop persistent urticarial rashes (blisters), which appear almost immediately after hypothermia and persist for several days or longer.
- In addition to rashes, cold urticaria may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, drop in blood pressure, etc.
The severity of clinical symptoms determines the severity of the pathological condition. If the local form is noted, blisters and/or angioedema are detected on a limited surface of the skin. Cold erythema is characterized by severe pain and redness of the skin area. In this case, typical blisters and itching are absent.
Familial cold urticaria is often diagnosed in early childhood. In young children, an allergic reaction to cold is manifested by a rise in temperature, hives and joint pain. Clinical symptoms, as a rule, arise within an hour or two after the effect of the cold factor on the child’s body, reach maximum manifestations after 6-7 hours and disappear after a day. Conjunctivitis, excessive sweating, fatigue, headaches, thirst and nausea may also be present. Sometimes an attack is provoked by normal ventilation of the room. Mostly, exacerbations of the disease are recorded in the autumn-winter period of the year.
Folk remedies
For mild forms of the disease or to increase the effectiveness of conservative treatment, traditional medicine is used. They soften the skin and reduce the intensity of eczema symptoms.
Below are recipes for the most effective folk remedies.
- Bath with soda and salt: add 1-2 tbsp to 1 liter of warm water. l. sea salt, 1 tbsp. l. soda, pour in 50 ml of vegetable oil. Take a bath for 10–15 minutes. Carry out the procedure daily.
- Lotions with vegetable fat. You can use any oil - sea buckthorn, sunflower, olive.
- Chamomile oil: 50 g of dried flowers, pour 500 ml of warm olive or sunflower oil. Leave in a dark, warm place for 7–14 days. Strain and use as lotions.
- Compress made from a decoction of chamomile, sage and calendula. To prepare, mix 1 tbsp. l. dried plants and pour 200 ml of boiling water. The product must be left for 15 minutes and cooled, then it can be used.
- Lotions with carrot, potato or cabbage juice. Grate any of these vegetables and separate the liquid from the solid mass. Soak a cotton pad in the juice and apply to the sore skin for 15 minutes.
- Kalanchoe lotions: fresh juice of the leaves is applied to gauze and applied to the affected area. The result is observed after several procedures.
It is recommended to resort to folk remedies when the exacerbation stage has passed. Such methods are also used for prevention.
Symptoms of eczema
Acute eczema manifests itself in different ways, depending on its type. But there are also common signs:
- erythema - red skin, the area of which corresponds to the lesion;
- papules - red-pink nodules that rise above the redness;
- vesicles - bubbles filled with serous fluid;
- pustules - blisters with purulent contents;
- erosion - depressions that appear at the site of opened pustules and vesicles;
- crusts in place of eroded surfaces;
- hair loss in areas of erythema;
- exfoliation of crusts, the appearance in their place of pathological skin in the form of patches and dry plates built from the keratinized epithelial layer.
Let's take a closer look at the symptoms of eczema, depending on its type.
Idiopathic
A distinctive feature of this form of the disease is symmetrical eczema on the face, neck and hands. That is, the pathological process is localized in uncovered areas of the skin.
The initial stage of eczema is characterized by small blisters, which over time merge with each other, burst and form point erosions. Later, lichenification (induration, dryness) may form at the site of the lesion.
Atopic
With this type of eczema, the process begins with hyperemia and swelling of the skin, then blisters appear. After their opening, weeping eczema develops. The skin around the lesion peels off, crusts and scales appear. If the disease becomes chronic, patients complain that the eczema itches.
Professional
The process begins with the areas of the skin that were affected by the irritant, gradually spreading to the rest of the skin. The symptoms are similar to idiopathic eczema.
Microbial
Signs of this form of eczema develop due to excessive proliferation of microorganisms around wounds, burns and ulcers. The early stage is characterized by unilateral peeling of scales. Possible accumulation of serous fluid and crust formation. Itching is mild.
Dyshidrotic
The pathology is located on the palmar and plantar surfaces. Characterized by severe itching, burning, slight redness of the skin and dense blisters in its thickness. In case of infection with fungi or bacteria, local lymph nodes become enlarged.
Nummular
This type of eczema is named so because of its resemblance to a coin: the lesion is clearly limited and has the shape of a circle. Vesicles, papules, scales and other elements of the disease form in the area of erythema. Localization may vary. But more often the nummular form is characterized by eczema on the back, chest, and abdomen.
Intertriginous
With intergriginous eczema, lesions form in the area of natural folds: axillary, inguinal, under the mammary glands. The appearance is specific: severe hyperemia and cracks in the area of eczema.
Seborrheic
It forms in areas with sebaceous glands: on the head, face, armpits, and groin. The plaques are small or large, with a yellow tint.
Pruriginous
Typical localization is on the arms and legs, on the inside. Papules and vesicles are small. The rashes itch, but do not break out even when scratched. Lichenification does not occur.
Horny
More typical for women during menopause. Hyperkeratosis, cracks and itching form on the skin of the palms and feet. There are no vesicles or weeping.
Varicose
Develops with varicose veins, ulcers and sclerosis as a result. The process occurs on the lower part of the leg and occurs as a microbial form of the disease.
Eczema of the nipples and areola
The causes of this type of disease are injury to the nipple during breastfeeding or scabies. With nipple eczema, hyperemia, cracks, weeping, crusts and scales occur.
Children's
The disease develops at the age of 3-6 months. Manifests itself as a true, seborrheic or microbial form. Lesions on the skin initially appear symmetrically; hyperemia, oozing, crusts, and scales are visualized. The disease spreads from the forehead and cheeks to the head, shoulders, and limbs. Later, eczema forms on the back.
Proper nutrition
The diet for eczema deserves special attention, since the close relationship between the functioning of the digestive system and the condition of the skin has long been confirmed. First of all, you should exclude from your diet foods that are strong allergens, such as:
- Citrus.
- Dairy products.
- Fat meat.
- Chocolate and confectionery.
- Exotic fruits.
- Fish.
- Nuts.
Preference should be given to plant foods, cereals, vegetable soups, and fresh fruits. You can eat dietary meat: chicken or rabbit.
Since eczema can be triggered by allergic reactions, you should adjust your diet to limit your intake of these foods.
You should also give up smoked foods, fatty foods, fast food, fried foods, alcohol and carbonated drinks. This diet will not only cleanse the body, but also improve the functioning of all internal systems, which has a beneficial effect on the condition of the skin.
Symptoms
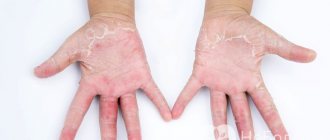
Dry eczema affects the upper and deep layers of the epidermis. It is usually localized on the arms: in the area of the palms, hands, between the fingers, and less often affects the feet and other parts of the body. The disease affects one or two or more limbs at the same time. The affected area gradually expands.
Initial signs are mild. There is dry skin, which is almost impossible to eliminate with moisturizing creams. The surface peels off and becomes less elastic. Over time, a burning sensation appears and severe itching occurs. Cracks of various sizes and depths form. Such lesions usually appear on the fingers. Microcracks heal very slowly and can expand and become inflamed.
Redness occurs. The affected area becomes covered with a crust, and a characteristic pattern appears on the skin. As eczema progresses, the symptoms become more intense. Soreness is noted. The scale of the defeat is growing. Numerous pink or reddish papules appear, which gradually merge to form specific plaques. After cracking, erosions appear in their place, which do not heal for a long time. Possible intoxication of the body, accompanied by headaches and fever.
To avoid complications, it is important to begin special treatment immediately. If therapy is not provided in a timely manner, dry eczema can turn into wet
This form of the disease increases the risk of fungal and bacterial infections with subsequent infection.
The disease can develop into a chronic form, which is characterized by frequent relapses. In summer, the symptoms of the disease subside slightly and do not require special treatment.
Features of eczema in children
Children's eczema (atopic dermatitis) is an allergic disease. Often, children suffering from eczema have a hereditary predisposition. If you or your relatives have bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, etc., then most likely your child has a very high chance of developing eczema. It is mainly diagnosed in the first six months of life. The first symptoms of childhood eczema are reddish spots on the cheeks, over time they increase and spread to the entire face, neck, and bends of the limbs. Severe itching bothers the child, scratching the spots causes them to become wet, and the risk of infection increases.
Types of eczema
Eczema can be called a “many-faced” disease, since it can have a different nature of occurrence. In addition, the symptoms of this disease can also vary, although not much. It all depends primarily on what became the main cause of the development of the disease.
There are these types of eczema:
- Idiopathic eczema. Its second name is true eczema. It can affect any part of the body and is characterized by the symmetry of the appearance of vesicles;
- Atopic eczema occurs in most cases due to a hereditary predisposition. Just like seborrheic is very common;
- Occupational eczema. It first appears on those areas of the skin that are exposed to allergens. In the future, it can spread throughout the body;
- Microbial eczema. Its occurrence is due to the presence of an excessive number of microbes in places where the human skin is damaged. This type of eczema differs from others in that such a symptom as itching is practically absent;
- Dyshidrotic eczema affects the palms and soles of a person. Has very clear symptoms;
- Nummular eczema. This type of eczema can develop in any part of the body. The lesions have a clearly defined rounded shape;
- Intertriginous eczema. The cause of its occurrence is the same as that of microbial eczema, however, there are some differences. It occurs in skin folds, and it is not at all necessary that there is a violation of the integrity of the skin at the site of the outbreak. Intertriginous eczema is accompanied by pain and the presence of cracks;
- Seborrheic eczema. One of the most common types of eczema. The lesions are located in parts of the body with the maximum amount of hair and on the face;
- Pruriginous eczema. The peculiarity of this type of eczema is its location. Foci of this type of disease are located exclusively on the inside of the legs and arms;
- Horny eczema. It occurs as a result of serious hormonal changes in the body. This is why horny eczema most often affects women during menopause;
- Varicose eczema. Arises as a consequence of trophic ulcers resulting from varicose veins;
- Mycotic eczema. The trigger for this type of eczema is all kinds of fungal infections. This type of eczema affects the hands and feet;
- Eczema of the nipples. Occurs as a result of regular trauma to the nipples, namely during feeding or when scabies occurs;
- Children's eczema. The first manifestations of childhood eczema begin in children from about 3 months of age. The main reasons for its occurrence are a congenital allergic predisposition against the background of age-related changes in intestinal flora.
Internal treatment for eczema and itching
Local treatment plays a huge role in the treatment of eczema. Treatment of itching, in most cases, does not bring long-term tangible results when using only external medications. The symptom can be eliminated if oral antihistamines are used in combination. The action of such drugs is aimed primarily at desensitizing the skin. The most common and most frequently prescribed medications for patients with eczema are:
- Suprastin;
- Diazolin;
- Fenistil;
- Zodak.
Since stress could be the cause or exacerbation of eczema, dermatologists often prescribe antidepressants and sedatives to patients. Patients are also recommended to include vitamin-containing medications in their treatment regimen. In any case, only a qualified specialist should prescribe drug treatment for eczema and itching. It is not advisable to use any means without medical advice. Self-medication can increase the manifestations of skin disease and aggravate the situation.
Symptoms
PþÃÂòûõýøà÷ðñþûõòðýøàÿþÃÂà ýð þñÃÂÃÂýÃÂàðûûõÃÂóøÃÂ, Ã¾Ã´Ã½à °ÃºÃ¾ øüõÃÂàÃÂÃÂô þÃÂþà±ÃµÃ½Ã½Ã¾ÃÂÃÂõù. Ã¥ðÃÂðúÃÂõÃÂýÃÂõ ÿÃÂø÷ýðúø ÃÂþûþ Keywords:
- ÃÂÃÂõú óþÃÂûð ø óÃÂñ ÿþÃÂûõ ÃÂÿþÃÂàõñûõýøàÃÂþûþôýþù ÿøÃÂø.
- ãÃÂøûõýøõ ÃÂøüÿÃÂþüþò ÿþÃÂûõ ÃÂþóÃÂõòðýøàúþöýÃÂàÿþúÃÂÃ¾Ã²à ¾Ã².
- ÃÂÃÂõú úøÃÂÃÂõù ÃÂÃÂú ÿþÃÂûõ úþýÃÂà°ÃºÃÂð àÃÂþûþôýþù ÿþòõÃÂÃÂýþÃÂÃÂàÃÂ.
- ÃÂþ÷ýøúýþòõýøõ ýð ÃÂÿøÃÂõûà¸Ã¸, ÿþôòõÃÂóÃÂõüÃÂàòþ÷ôõùÃÂÃÂò øàÃÂþûþôð, ÷ÃÂôÃÂÃÂøàòþûô ÃÂÃÂõù úÃÂðÃÂýþóþ ÃÂòõÃÂð.
- ÃÂÃÂø ýðöðÃÂøø ýð òÃÂÃÂÃÂÿðýøàþà½Ã¸ ñûõôýõÃÂÃÂ.
- áÃÂÿàøÃÂÃÂõ÷ðõàÃÂÿÃÂÃÂÃÂàýõÃÂúþÔ ÃÂúþ ÃÂðÃÂþò, ýõ þÃÂÃÂðòûÃÂàÿþÃÂûõ ÿþÃÂûõ õñàÃÂûõôð
- þñÃÂð÷ÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂàÿþòÃÂõüõ ÃÂÃÂýþ: ýð óþûþòõ, ÿþôþÃÂòðàýà¾Ã³, ûðôþýÃÂÃÂ. › ÃÂÃÂøÃÂÃÂõÃÂÃÂàò þñûðÃÂÃÂø ÃÂõø ø ûøÃÂà °.
- ÃÂýðÃÂøûðúÃÂøÃÂõÃÂúðàÃÂõðúÃÂøÃÂ, à¿ÃÂþÃÂòûÃÂÃÂÃÂðÃÂÃÂàò òøôõ þÃÂõúúà þýõÃÂýþÃÂÃÂõù ø ÃÂÃÂûþòøÃÂð, þñüþ ÃÂþúð, ÃÂà°ÃÂøúðÃÂôøø, ÃÂþúð.
- ÃÂÃÂõú ÃÂòøýúõ â ÃÂðÃÂÃÂþ òÃÂÃÂÃÂõÃÂð GALA ¸ ÃÂþûþôþòþù úÃÂðÿøòýøÃÂõ. › þÃÂõúð ýð ÃÂûø÷øÃÂÃÂÃÂà þñþûþÃÂúø ø úþöýÃÂõ ÿþúÃÂþò ÃÂ. › àÿøÃÂõòðÃÂøÃÂõûÃÂýðàÃÂøÃÂÃÂõüð, à¾Ã±Ã¾Ã»Ã¾ÃÂúø üþ÷óð, üþÃÂõÿþûþòà° àø ôÃÂÃÂðÃÂõûÃÂýðàÃÂøÃÂÃÂõüÃÂ.
àÃÂÃÂôõ ÃÂûÃÂÃÂðõò ýõþñÃÂþôøüð à½ÃµÃ·Ã°Ã¼ÃµÃ´Ã»Ã¸ÃÂõûÃÂýðàÿþüþÃÂÃÂ. ›
- þÃÂõúõ ÃÂõø;
- ÃÂòõûøÃÂõýøø ÃÂ÷ÃÂúð;
- ÿþÃÂòûõýøø ÷ðÃÂÃÂÃÂôýõýøù àô ÃÂÃÂðýøõü;
- óþûþòþúÃÂÃÂöõýøø.
The òûÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂàÃÂÿÃÂÃÂÃÂàýõúþÃÂþÃÂþõ òÃÂàµÃ¼Ã Ã¿Ã¾ÃÂûõ òþ÷ôõùÃÂÃÂòøàýð úþ öýÃÂõ ÿ þúÃÂþòàÃÂþûþôýþù òþôàøûø à ²Ã¾Ã·Ã´ÃÂÃÂð. ñþûÃÂÃÂøýÃÂÃÂòõ ÃÂûÃÂÃÂðõò ðûûõàóøàòþ÷ýøúðõàÿÃÂø ÃÂõüÿõÃÂðàÃÂÃÂõ ýøöõ 3 óÃÂðôÃÂÃÂþò.
áøüÿÃÂþüàøýþóôð ÿþÃÂòÃ"ÃÂÃÂÃÂà àø ò ñþûõõ ÃÂõÿûÃÂàÿþóþôÃÂ, õàûø ýð ÃÂûøÃÂõ õÃÂÃÂàòõÃÂõàøûø òûðöýþÃÂÃÂàòþ÷ôÃÂÃÂð ÃÂûøÃÂà òÃÂÃÂþúðÃÂ. ÃÂÃÂø ýðÃÂûõôÃÂÃÂòõýýþù ÃÂþÃÂüõ à¿Ã°ÃÂþûþóøø ÿÃÂþÃÂòûõýøàúÃÂÃ°Ã¿à ¸Ã²Ã½Ã¸ÃÂàòÃÂÃÂÃÂõÃÂðÃÂÃÂÃÂàôðöõ ÿÃÂø ÿþòÃÂÃÂõýýÃÂàóÃÂðôÃÂÃÂðàÃÂõÿûð.
› ñûÃÂôðÃÂÃÂÃÂàÿÃÂø ÿþóÃÂÃÂöõýøø ò à þûþôýÃÂàòþôÃÂ. ÿÃÂøüõÃÂÃÂ, ÿÃÂø ýÃÂÃÂÃÂýøø ò ÿÃÂþà ÂÃÂñÃÂ.
Cold dermatitis: treatment
Cold dermatitis is also known as frost eczema, cold allergy and frost dermatitis. This is an unpleasant and dangerous disease. The disease is similar to other types of dermatitis and manifests itself in the form of skin defects.
How to treat cold dermatitis? Medical treatment for cold dermatitis can include a variety of methods and techniques. Complex therapy may include medications, ointments, and various folk remedies.
Cold dermatitis: treatment in stages:
– Carrying out symptomatic therapy. This allows you to get rid of the appearance of dermatitis. This includes tablets and sprays;
– Using ointments, creams and gels to quickly heal wet spots and cracks;
– Taking vitamins that eliminate dysbacteriosis;
– Cosmetic skin care. Using fatty creams that can gently cleanse the skin.
It is very difficult to treat cold dermatitis in children. When frostbite occurs, a child constantly experiences pain that does not decrease throughout the day. It is necessary to use drugs that can reduce pain for a long time. When cold dermatitis appears, vascular drugs that improve microcirculation and antihistamines are prescribed. Don't forget to moisturize your skin!
Treatment of cold dermatitis is carried out by doctors: an allergist or a dermatologist. If the nature of the skin disease is not caused by dermatological reasons, you will have to be treated by an allergist. In addition, when treating cold dermatitis, a special therapeutic diet and physical therapy may be required.
Drug treatment of cold allergies
To quickly stop the manifestation of cold dermatitis, antihistamines should be used. The regimen for using drugs should only be prescribed by a specialist doctor. If the first manifestations of frost allergies are observed, you can use drugs such as: suprastin, tavegil, loratadine. After this, be sure to consult a doctor.
To improve blood circulation, the doctor may prescribe special medications that can increase blood microcirculation. When treating infectious foci, various antibiotics, sorbents, and antiparasitic agents are used. To increase immunity, the doctor may prescribe vitamins E, C, PP, A.
Treatment of cold dermatitis with ointments
When treating frost allergies, proven external remedies are used. These include: zinc ointment, Bepanten, Skin-cap or Fenistil gel - they eliminate allergy symptoms and heal itchy areas.
When you contact your doctor, you can get a prescription for antihistamine ointments containing hormones; you need to use them strictly according to the instructions, not exceeding the amount and duration of the course. A rich cream will help protect the skin from dermatitis before cold exposure.
Folk remedies for the treatment of cold dermatitis
There are several ways to treat cold dermatitis with folk remedies. The recipes below are the most effective.
– Tincture of medicinal herbs. Mix elecampane, marshmallow root and licorice in equal parts. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture into two glasses of boiling water and leave for at least ten hours. Take a third of a glass warm three times a day.
- Boiled egg shell. Pound the washed shells into powder or grind in a coffee grinder. You should take a teaspoon three times a day after meals. It is strictly forbidden to give such powder to people allergic to chicken egg white, especially young children.
– Horsetail. Pour a teaspoon of herbs into one glass of boiling water and leave. After cooling, strain the drink and take it in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Raspberry root decoction. Forty grams of dried raspberry bark must be poured with two glasses of boiling water and left for at least 30 minutes, then strain. Drink a quarter glass of infusion before going out into the cold, and also preferably at night.
How to treat eczema on hands?
Treatment is selected for each patient individually. In this case, the specialist takes into account the type of disease, how pronounced the inflammation process is, as well as the age of the patient, the presence of other diseases, etc. It is possible to bring the disease into a stage of stable remission only with an integrated approach to treatment.
- General therapy:
General therapy should include correction of existing dysfunctions of all organs, normalization of metabolism, and increase of the body's immune defense. It is important to pay attention to reducing the negative impact from the external environment.
Nonspecific therapy aimed at reducing the body's individual sensitivity to existing allergens has been recognized as effective. In this case, the patient is prescribed antihistamines, immunosuppressants, glucocorticoids, and cytostatics. In parallel, autohemotherapy, hirudotherapy, blood transfusion, and lactotherapy are carried out.
If the disease is severe, doctors refer the patient for plasmapheresis, hemo- and enterosorption.
- Therapy for neurotic disorders:
- Taking small doses of tranquilizers (Nozepam, Chlozepid, Phenazepam). The drugs can only be prescribed by a doctor, and the total course of treatment should not exceed 10 days.
- Bromcamphor and Sodium bromide are taken as sedatives for two weeks.
- Sedatives of plant origin are: Valerian extract, Persen, Novopassit, Sedasen, Peony tincture.
- Therapy aimed at eliminating intoxication of the body:
- Enterosorbents can be prescribed as a course for 10 days: Multisorb, Polyphepan, Polysorb, Enterosgel, Filtrum STI, Atoxil.
- Intravenous administration of calcium chloride or sodium thiosulfate is possible.
- If the disease is complicated by a fungal infection, then a solution of Hexamethylenetetramine is prescribed.
- Calcium gluconate is injected intramuscularly. The number of injections should not exceed 10.
- Therapy with hormonal drugs:
If there is an urgent need (if the disease persists), then the disease is treated with hormonal agents. Such treatment can only be prescribed by a doctor. The course cannot be long, since the use of corticosteroids has a number of side effects that can negatively affect a person’s overall health.
Particularly dangerous is the independent long-term use of hormonal drugs. If the eczema has not spread beyond the hands, then, as a rule, doctors limit themselves to local treatment only. For more extensive lesions, it is recommended to take hormones orally for a period of no more than 15 days. For this purpose, drugs such as: Triamcinolone, Prednisolone, Corticotropin, Dexamethasone can be used.
- Therapy with vitamins:
Any type of eczema on the hands is an indication for taking vitamins. However, they must be used with caution and only as prescribed by a doctor. For eczema, the following are prescribed: injection of B vitamins, taking Folic acid, taking Nicotinic and Ascorbic acid, taking vitamin E.
- Therapy using antiallergy drugs:
- During an exacerbation of eczema, Chloropyramine, Diphenhydramine, Promethazine are prescribed. Method of administration: parenteral.
- If the disease is of moderate severity, then oral administration of the same drugs is prescribed.
- As the inflammation process subsides, it is recommended to switch to third and second generation antihistamines. This could be: Cetirizine (Zyrtec, Zodak, Parlazin, Cetrin), Ebastine (Kestin), Loratadine (Dezal, Lordestin, Erius), etc.
- It is possible to take Ketotifen.
- Therapy using immunomodulators:
Immunomodulators are not prescribed to all patients with eczema. They can be taken only after undergoing an examination by an immunologist and performing all the necessary tests. The doctor may prescribe medications such as: Timomimetics (Imunofan, Timalin, Thymogen), phagocytosis stimulants (Lykopid, Polyoxidonium, Prodigiozan), as well as Plazmol, humisol solution, placenta extract, vitreous body.
- Therapy aimed at normalizing the functioning of the digestive organs:
Often eczema on the hands appears in parallel with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. To get rid of them, it is recommended to take drugs such as: Ermital, Pancreatin, Creon, Micrazim, Pangrol, Gastenorm, Biozim, Pepfiz, Pangrol, Enzistal, Festal, Solyzym.
If a violation of the intestinal microflora is detected, then a course of probiotics is indicated, for example, Lactobacterin, Hilak Forte, Rioflora-immuno, Bifiform, Linex, etc.
- Therapy for microbial eczema:
If a patient is diagnosed with microbial eczema, then it is impossible to do without the use of antibacterial drugs. Ointments with an antimicrobial effect are prescribed externally, and antibiotics from the following groups are recommended internally: cephalosporins (1st generation), macrolides, fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides. Antimycotics are prescribed when a secondary infection occurs.
Local therapy for eczema on the hands
If a patient is diagnosed with microbial eczema, then he needs to lubricate the crust on his hands:
- Brilliant green, Methyl violet solution, Gentian violet solution.
- Creams and aerosols: Panthenol, Polcortolon, Levovinisol.
- If the disease is chronic, lotions with a solution of Resorcinol or Ethacridine Lactate are recommended.
Lotion can have an anti-inflammatory effect and reduce itching with the application of the following compositions:
- Goulard;
- Burov's fluid;
- Resorcinol in solution up to 1%;
- Copper sulfate, zinc sulfate in solution 0.1%;
- Silver nitrate in solution 0.15%;
- Phenol in solution up to 5%;
- Citric acid in solution 1%;
- Metol solution up to 1.0%;
- Podophylline ointment;
- Diphenhydramine paste.
Effective means for relieving acute inflammation are powders with white clay, zinc oxide, and wheat starch. When the disease subsides somewhat, you can use zinc oil, as well as neutral ointments that do not contain active ingredients.
A solution of boric acid, a solution of tannin, and a solution of galascorbine helps eliminate swelling of the skin, reduce weeping, and remove redness.
To speed up the healing process at the stage of extinction of inflammation, you can use Lassara paste, zinc ointment with the addition of Naftalan paste, Ichthyol paste, Boron-zinc and Boron-naphthalan paste, Dermatol and Methyluracil paste.
As for corticosteroid ointments, to get rid of eczema on the hands, doctors often prescribe Elokom, Advantan, Skin-cap, Flucinar, Celestoderm. If the patient has microbial eczema, then it is best to use Trimistin, Lorinden S, Celestoderm with Garamycin, Travocort, Kremgen.
Hand eczema responds well to physical therapy. Therefore, such treatment methods as: baths with radon, with mineral water, diphenhydramine inhalations, electrosleep, general galvanization, diadynamic therapy, ultrasound treatment, laser therapy, utraphonophoresis with drugs, ultraviolet treatment, ozone therapy, magnetic therapy, paraffin baths, acupuncture are often used .
It is important to adhere to a therapeutic diet and avoid consuming large amounts of salt, excluding spicy, fatty fried and smoked foods. You should not consume chocolate, coffee, alcohol, eggs, as these products are potential allergens. Preference should be given to a dairy-vegetable diet.