Dermatovenerologist (1 KO, 1/35)
Kintaev
Azamat Samuratovich
7 years experience
Dermatovenerologist
Make an appointment
Mycoses are a broad group of diseases united by one characteristic - they are all caused by pathogenic fungi that parasitize the skin, mucous membranes and other human tissues. Among all skin infections, they rank first in prevalence, but despite this, many sick people cannot recognize the disease in time and see a doctor, which is why dermatologists often have to deal with advanced forms of pathology.
Types of disease
Currently, about four hundred different species of fungi are known that can be pathogenic to humans under certain conditions. Mycoses are classified according to the type of tissue affected:
- superficial, affecting the skin and mucous membranes:
- deep, the affected area is subcutaneous tissue;
- visceral, which parasitize the internal organs.
According to the types of fungi that parasitize humans, the most common diseases are the following.
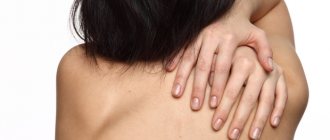
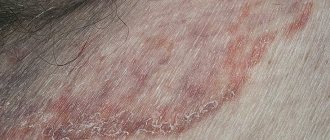
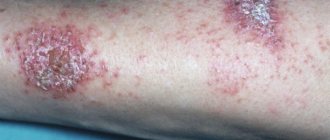
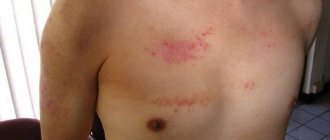
- Rubrophytia. The fungus rubrum trichophyton affects the spaces between the toes, feet, and less often settles in skin folds and on the head. The skin at the site of the lesion turns red and peels, nodules and small bumps appear on it. When the skin of the body is affected, it forms large patches of reddened skin with bright red concentric ridges.
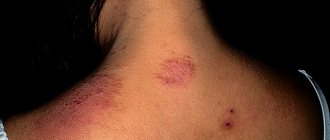
- Microsporia. As a rule, the fungus is transmitted from sick cats or dogs and affects vellus hair on the body, less often – the skin with the formation of a focus of inflamed skin with peeling and blisters, surrounded by a ridge. Microspores are resistant to external influences.
- Trichophytosis. The trichophyton fungus parasitizes the skin, affecting mainly exposed areas of the body - the face, hands. It is highly contagious. In humans, outbreaks of the disease are most often recorded in late summer and autumn during field work, when people come into contact with hay and straw that have been infected by sick rodents.
- Tinea versicolor. The most common cause of mycosis of smooth skin is Malassezia furfur. Lesions, as a rule, form on the chest and abdomen, less often on other parts of the body: small pink spots appear, the color of which then changes to yellow or brown. They are covered with coarse scales that look like bran. Multiple spots soon merge into large formations.
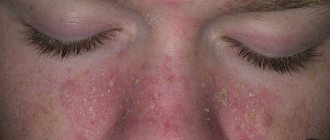
- Seborrheic dermatitis. This is a common mycosis of the scalp, affecting the scalp, including the skin of the eyebrows, eyelashes, mustache and beard, caused by Pityrosporum ovale. The variety Pityrosporum orbiculare parasitizes the smooth skin of the body. These are lipophilic fungi, the nutrient medium for which is sebum. The affected areas of the skin are marked by inflammation and flaky crusts.
- Candidiasis. Yeast-like Candida fungi settle in skin folds, on mucous membranes and form reddish spots covered with small blisters. After a while, eroded areas of bright red color appear in place of the bubbles.
There are many types of mycosis of the skin, subcutaneous tissues and internal organs, which are much less common than the listed types.
What is mycosis of smooth skin
This is a fungal infection of the upper layer of the epidermis, which is accompanied by an inflammatory process, swelling, and severe itching. The most common diagnoses are the following: microsporia, keratomycosis, lichen versicolor, trichophytosis, candidiasis, mycosis of the skin of the hands and feet. Localization of the lesion - the upper layer of the epidermis, smooth skin, folds, interdigital space. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the lungs and affect other internal organs.
Symptoms
We can only talk about the symptoms of mycosis in general terms, since each type has its own manifestations, which can only be recognized by an experienced dermatologist. With skin lesions, as a rule, the following appear:
- reddened and flaky areas of skin;
- severe itching in areas affected by the fungus;
- diaper rash in skin folds and interdigital areas;
- small bubbles that burst and dry out after a while;
- white, yellow or brownish crusts over inflamed skin.
With mycosis of the extremities, as a rule, the nails also suffer - they become brittle, split, then gradually become cloudy and darken.
Deep mycoses, as a rule, occur with the formation of deep ulcers, purulent inflammations, fistulas, etc. They are most common in countries with hot climates, and in Russia they are extremely rare. Visceral, depending on the location and degree of damage, can cause dysfunction of organs on which fungi parasitize - pulmonary diseases, digestive disorders, etc.
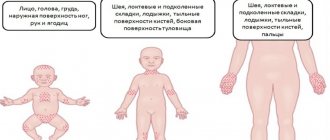
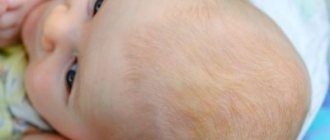
Mycosis of smooth skin in children
A characteristic illness can develop in a child, making him nervous and irritable, and disrupting the usual sleep phase. More often, microsporia develops in a child’s body, provoked by the increased activity of fluffy microsporum. A child becomes infected from an infected animal contaminated with spores of pathogenic fungi. The most common symptoms of the disease in childhood are presented below:
- round or oval spots have clear boundaries;
- the surface of smooth skin is distinguished by the presence of bubbles, later crusts;
- the size of pathological foci varies from 1 to 2 cm;
- the central part of the spot is peeling;
- There is a ridge along the periphery of the skin rash.
Reasons for the development of pathology
The main cause of mycosis is infection with a pathogenic fungus. At the same time, many types of fungi are constantly present in the body, and their growth is usually inhibited by the immune system. As control decreases, the fungus begins to grow on the skin or tissues of internal organs. This often happens due to:
- a chronic disease that weakens the body;
- non-compliance with hygiene rules;
- insufficient or unbalanced nutrition;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- exposure to external factors that weaken the body - hypothermia, excess ultraviolet radiation, poisoning, radiation damage, etc.;
- long-term use of antibiotics or certain other medications.
The only exception here is the so-called mycosis fungoides, which is not a fungal disease. This is an oncological tumor pathology, which is based on the degeneration of T-lymphocytes into a malignant form.
What does skin fungus look like?
If a pathogenic fungus appears in the upper layers of the epidermis, the skin changes its structure and has external changes. The presence of small scales, pink spots, and swelling prompts alarming thoughts about a fungal disease. Foci of pathology are localized on the thighs, legs, upper and lower extremities (feet, hands, palms) and have visible boundaries. Trichophytosis of the scalp is not excluded.
Transmission routes
There are many ways to become infected with fungal diseases. Most often this happens:
- in direct contact with the affected areas of the skin of another person;
- when sharing towels, slippers, personal hygiene items;
- through a contaminated manicure instrument;
- through contaminated clothing and shoes;
- through the soil, especially in the presence of skin microtraumas;
- in contact with pets.
Often, skin mycoses develop in people who visit swimming pools, saunas, showers at sports clubs, etc. Infection is more likely the worse the person’s immune system works.
Prevention
To avoid mycosis, it is necessary to take care of the child and accustom him to hygiene products.
The child's shoes must be clean and dry. Small children should not be wrapped tightly to ensure heat transfer through the air. If an excess amount of heat is released through sweat, the fungus will begin to actively multiply, because a humid environment contributes to this. Clothing, including shoes, should be made from natural materials and allow enough air to pass through. Your baby's nails should be trimmed regularly, preferably with individual nail scissors. When staying in public places with high humidity (swimming pool, gym), make the baby wear shoes. Prevention of mycoses is easier to implement than treatment of fungal diseases. A sufficient amount of attention given to a child should be enough to protect him from an infectious disease.
Diagnostic methods
As part of the diagnosis of mycoses, studies of scrapings of skin and nail formations, sputum, blood, hair, scrapings of mucous membranes, feces and other biomaterials can be performed, depending on the type and location of the lesion. For skin diseases, the following is usually performed:
- dermatoscopy - examination of affected areas of skin, hair or nails to identify characteristic signs;
- microscopic examination of scrapings to detect fungal mycelium;
- bacterial culture on nutrient media, which allows you to identify not only the type of fungi, but also the optimal drug for treatment;
- serological blood test;
- PCR test to detect the fungal genome.
Some types of fungi are quite easily diagnosed using UV radiation, which is generated using a Wood's lamp.
Simultaneously with determining the type of fungus, the patient undergoes a general examination to identify the cause of weakened immunity that led to infection.
Diagnostics
To identify an external fungus, a comprehensive examination of the child by a pediatric dermatologist or mycologist is necessary.
Microscopy of clinical material (hair, particles of the epidermis, horny masses of the nail bed) makes it possible to detect the presence of mycelium, spores or hyphae in it, confirm a fungal skin disease in children and determine its tissue form. Sowing scrapings on universal and selective media helps to isolate a pure culture of fungi and determine their sensitivity to drugs. Bacterioscopy of culture smears and biochemical analysis are carried out for phenotypic, species and intraspecific identification of the pathogen.
Examination of a child’s skin under a Wood’s lamp reveals a golden-yellow glow of particles in lichen versicolor, bright green in microsporia, and a weak glow in cases of trichophytons.
Differential diagnosis is carried out in order to distinguish skin fungus from dermatitis with similar manifestations: neurodermatitis, eczema, psoriasis, erythrasma, vitiligo, syphilitic leukoderma, seborrhea, alopecia areata, etc.
Treatment
Currently, there are many means and techniques for treating mycosis of almost all types. The main method is drug therapy, which includes general drugs and local agents, which are selected depending on the type of fungus, the degree of damage, the duration of the disease, the patient’s health status and other factors. Mycoses of the skin and mucous membranes are best treated: if you follow the doctor’s recommendations, you can get rid of the disease within two to three weeks, and sometimes in just a few days.
If nails are affected, the course of therapy lasts several months, and combination treatment is required: local drugs are combined with systemic agents. Local dosage forms are extremely varied: these are creams, ointments, gels, sprays, nail polishes, powders, drops. Systemic antimycotics are usually available in the form of tablets or capsules. In some cases, complete removal of the affected nail is required.
When choosing medications, the dermatologist must take into account the individual sensitivity of the pathogen to a particular drug. Independent use of certain drugs often does not bring the desired result, since before starting treatment it is necessary to determine the type of causative agent of the disease. For certain fungal infections, the patient’s diet becomes important. So, during the treatment of yeast and mold fungi, it is necessary to exclude foods that contain fast carbohydrates (sweets, flour products), fermented foods, alcohol and potatoes.
Classification of fungi
There are about 1000 species of fungi in total and each of them has its own characteristics. But doctors were able to identify several species, the development of which can occur on the skin of a child.
- Keratomycosis. It damages the surface of the baby's skin. Presented in the form of color lichen. The most basic symptom is peeling of the skin. Often in infants, peeling is present on the dermis of the head.
- Candidiasis. Its development occurs due to damage to the body by fungi of the genus Cand > Keratomycosis Candidiasis Mold fungus
Candidiasis is considered the most dangerous for a child. It can affect the body of children directly during delivery through the birth canal, when the mother is sick with thrush. Candidiasis is also transmitted through breast milk if the mother has been diagnosed with nipple candidiasis.
Mycosis in children
In childhood, the most common mycosis is microsporia or simply lichen. The cause of infection in most cases is contact with infectious animals. Moreover, these can be not only stray animals, but also domestic animals. The causative agent of the disease is fluffy microsporum.
Another important factor of infection is the long incubation period of the microsporum. If the fungus can take root on the body within 1.5 months, then in the ground or sand it remains viable for up to 3 months. That is, if an infected animal has visited this sandbox or a sick child has played in this sandbox, then the likelihood of picking up microsporum spores here will persist for the next three months.
Fungal infections – School of Dr. Komarovsky
Symptoms of mycosis in children
Microsporia in children manifests itself in the same way as in adults:
- Round or oval lesions;
- The presence of a convex edging around the affected area;
- The lesion itself may be covered with scales, blisters or pimples;
- When the scalp is infected, hair breakage and partial loss occur at the site of the lesion.
Most often, mycosis in children is superficial in nature, and therefore is treated only with local drugs.
Treatment of mycosis in children
The optimal algorithm for the treatment of mycosis in children is a combination of external medications. Here is a small example of effective elimination of microsporia or lichen:
- Treatment of lesions with iodine in the morning;
- Treatment of affected areas with salicylic or sulfur ointment in the evening.
Other antifungal ointments and creams can be used between these treatments, but this is not necessary.
In advanced cases, when vellus hair appears at the site of the lesion, the use of systemic medications is necessary. It could be Griseofulvin. However, if you have liver problems, it should be replaced with Lamisil. This drug acts more gently and the healing process will take longer.
Symptoms
The manifestation of fungal pathology in children occurs in different ways. It all depends on the location of the lesion. If the fungus has infected the throat, the following symptoms are observed:
- hyperemia (redness) of the mucous membrane;
- the presence of a small white rash of the curd type;
- gradual formation of white, gray or yellow plaque;
- the formation of ulcers after removing plaque through one’s own efforts or lack of adequate therapy.
If the fungus has damaged the nail plate, it can be recognized by the following clinical picture:
- roughness and peeling of nails;
- the upper layers of the epidermis of the nail bed become noticeably thick;
- nail color changes;
- Stripes and yellowish spots form on the nail plate.
When the fingers or toes are affected, the disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- burning, itching;
- hyperemia of the skin;
- rash in the form of blisters;
- the presence of erosions and ulcers on the skin.
Fungal infection on the legs of young patients can be recognized by the following clinical picture:
- small rash in the form of blisters;
- formation of ulcers, erosions on the skin;
- skin hyperemia;
- cracks in the skin;
- painful sensations when moving;
- itching, burning.
Folk remedies
Using alternative medicine, you can successfully cure childhood fungus. But they should only be used in combination with medications. The following recipes remain the most effective:
- You need to take 20 g of celandine. Add 1 liter of boiling water. Wait until the broth is infused. Warm it up and steam your feet in it for 30 minutes. If other parts of the body are affected by the fungus, you should soak a cotton pad in the infusion and then apply it to the damaged areas. Read more about celandine treatment...
- If your child has mycosis on his skin, you can use natural honey. Take it in the amount of 1 liter and 10 liters of water. Use the resulting solution for lotions. But this method must be used with extreme caution, since honey is a strong allergen.