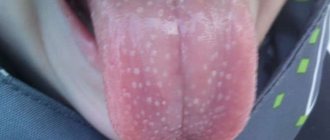
Symptoms of papillomatous nevus
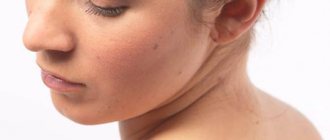
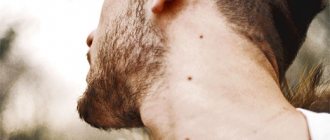
Papillomatous nevus, unlike simple moles, has an irregular shape and protrudes above the skin. Depending on the pigmentation, it can match the color of the skin or have a brown, brown tint. Black nevi are very rare. Sometimes pigmented hair passes through the papillomatous nevus. Papillomatous nevi occur both single and multiple. Most often, nevi are localized on the head, neck, and face, but there may be cases where they are located in other places of the skin.
A characteristic feature of a papillomatous nevus is its slow but constant increase in size. From the beginning of development it is not noticeable, but as it grows it begins to cause discomfort to a person. Nevus on the head are often injured when combing hair. As a result, inflammation may occur.
Papillomatous nevus is a serious cosmetic defect; it causes inconvenience and psychological discomfort to its owner. In adolescents and people with a delicate mental structure, this situation can cause prolonged depression.
Is HPV the cause of nevus?
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Intradermal papillomatous nevi resemble papillomas in appearance. The appearance of the melanocytic element is not associated with papillomavirus. Two similar skin growths differ in etiology and structure. Papillomatosis (code D 23 according to ICD-10) is a chronic infection caused by HPV activity. The pathology affects children and adults. The main route of transmission of the virus is through household contact, sexual contact, and intrapartum.
Melanocytic papillomatous intradermal warty nevus is formed by melanocytes. The reasons for its appearance on the human body are not fully understood. There are several theories of origin:
- According to the first theory, education is transmitted along the family line. Confirms the fact of similar localization in parents and children.
- The second theory is based on excess melanin secretion. Melanocytes accumulate under the skin in one place and begin to intensively secrete coloring pigments. Active production of melanin occurs under the influence of ultraviolet radiation.
- According to the third theory, the formation of an intradermal growth occurs in the prenatal period. The appearance of bumpy formations is provoked by the mother’s addictions, inflammatory diseases, and contact with harmful substances.
- The fourth theory associates the occurrence of growths with hormonal disorders. Melanocyte-stimulating hormone of the pituitary gland activates melanocytes, which begin to synthesize melanin.
Diagnosis of papillomatous nevus
For an accurate diagnosis, you need to consult an oncologist or dermatologist.
If a mole protrudes significantly beyond the skin, but does not cause discomfort, it should still be shown to a dermatologist. Accurate diagnosis of this type of skin formation is necessary in order to exclude melanoma and melanoma-dangerous nevi. Also, the type of tumor will help the doctor decide on treatment tactics. As a rule, a dermatologist will immediately distinguish a papillomatous nevus from an ordinary mole. Siascopic examination can be used for diagnosis. In difficult cases, a tumor biopsy, skin ultrasound and in-depth dermatoscopy are performed. In oncology, there are several types of nevi, depending on the size:
- small - up to 1.5 cm;
- medium - up to 10 cm;
- large - up to 20 cm;
- giant more than 20 cm.
A patient's risk of developing cancer directly depends on the size of the nevus.
Based on the place of their formation, nevi are divided as follows:
- epidermal - are an accumulation of melanocytes in the upper layers of the skin;
- intradermal - accumulation of melanocytes in the dermis;
- borderline - an accumulation of melanocytes between the upper layer of the skin and the dermis.
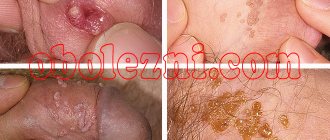
Differences between papilloma and nevus
To distinguish a mole from a papilloma, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist. Only a specialist can accurately determine the nature of the formation on the skin. However, a person can make a preliminary diagnosis independently, based on the following features:
- Moles can occupy an entire part of the body or be literally a few millimeters in size. In this case, the papilloma usually reaches 2-15 mm, increasing to 5-6 cm only in case of damage.
- Nevi have a hard and dense structure, while papillomas have a loose consistency and are soft to the touch.
- The basis of moles are skin cells, and papillomas include blood vessels.
- A mole is a feature of every person; in some cases, birthmarks are inherited. In this case, the spread of papillomas is carried out exclusively by infectious means - through household and sexual contact.
- Nevi can have different shades - pink, light, black, brown and even bluish. Papillomas are always light in color - flesh-colored or pink.
- Moles can affect any part of the body, including mucous membranes. The main localization area for papillomas is the mucous membranes and areas of strong friction.
- Moles should have an even, symmetrical shape - round or oval, while papillomas can have different shapes.
- Nevus appears at birth or in the first years of life. Papillomas develop several months after infection. Rapid formations can occur after 1-2 months, and protracted ones - after 4 months.
Treatment of papillomatous nevus
Due to the fact that the nevus is constantly exposed to external factors, it can become damaged and then inflammation will begin, which can be easily recognized by soreness and redness. If during the diagnostic process doctors managed to completely exclude melanoma, dermatologists recommend removing the nevus with mandatory further histological examination of the formation.
Removal of papillomatous nevus can be carried out using a laser, cryodestruction, radio wave, electrocoagulation or surgical excision. Typically, all of the above operations are performed under local anesthesia.
Modern methods of treatment
Papillomatous nevus is removed using the same methods as other types of moles:
- laser;
- radio wave knife;
- electrocoagulation;
- surgical excision.
Cryodestruction is not used in the treatment of papillomatous nevoid tumors. This type of mole is not very susceptible to the effects of liquid nitrogen.
The optimal technique is selected by a dermatologist-oncologist. To do this, he conducts a series of studies - dermatoscopy, biopsy of the affected tissue. Sometimes examining the mole is enough. The biopsy sample is taken using a scalpel or radio wave knife directly during the removal procedure. If other methods are used, the study is performed before the session.
Laser removal is good because it eliminates the risk of complications. This is a painless procedure that guarantees rapid wound healing. The same can be said about the radio wave method: it demonstrates a good rate of tissue regeneration and a low probability of complications.
Electrocoagulation allows for accurate histological analysis. It is used if there are symptoms of mole degeneration. One of the disadvantages of the method is that a scar forms after the procedure.
Surgical excision is used if the mole has reached large or gigantic sizes. The depth of removal is the entire thickness of the skin. With other methods, it is enough to remove the tumor to the upper layers of the dermis - the place where melanocytes accumulate. Wound care is standard for such procedures.
Papillomatous nevus in children
Papillomatous nevoid tumors in children are predominantly a cosmetic defect. They are removed using the same methods as in adults. The exception is cases requiring surgical excision. The operation is postponed until the child is 1.5-2 years old.
If the tumor is small in size, laser removal is recommended. This method is painless and has no age restrictions.
Papillomatous nevus during pregnancy
There are two situations worth highlighting here. The first is when a tumor appears in the expectant mother. The reasons are hormonal fluctuations caused by the restructuring of the female body in preparation for bearing a child, childbirth, and feeding. During this period, moles may appear or disappear. There is nothing abnormal in such changes.
If a new mole causes serious psychological or physical discomfort, you can consult a doctor about removing the papillomatous nevus. But it is better to postpone the procedure until the birth of the child. During delivery, another dramatic change in hormone levels occurs, which may cause the mole to reappear. The exception is when the formation suddenly changes shape, color, or size: then it must be urgently shown to a doctor. He will decide whether to remove the papillomatous nevus.
The second situation is when a neoplasm may appear in an unborn baby. To avoid it, a woman must follow a number of rules during pregnancy:
- If the expectant mother works in a workplace with toxic or potentially hazardous substances, she should definitely inform management about her situation. According to current legislation, while carrying a child, she should not have contact with such compounds, even if this is provided for by her position.
- If a woman likes to sunbathe, it is advisable to limit their time: avoid such procedures in the period from 11-00 to 16-00. And you can get a light and beautiful tan in the morning.
- If the expectant mother lives in an environmentally polluted area and near sources of radiation, it is better to move during pregnancy. Otherwise, there is a high risk of not only the formation of nevi, but also other anomalies of intrauterine development.
You can reduce the risk of tumors in your child by giving up bad habits - smoking and drinking alcohol. Doctors also recommend not to come into contact with aggressive household chemicals and to use rubber gloves when cleaning.
Surgical operations
Large papillomatous nevus undergoes surgical excision. The application of small cosmetic stitches after the removal operation guarantees minimal cosmetic defects. The possibility of relapse is excluded, since along with the nevus, the doctor also captures part of the healthy tissue when removing it. Giant nevi are also treated surgically. They are rare, but the risk of developing cancer in them is very high. Treatment of giant pigmented nevus is carried out in stages, with the involvement of plastic surgeons for further cosmetic operations.
Currently, there is no method that can prevent the appearance of a nevus. The only thing that can be avoided is the transformation of a nevus into melanoma. To do this, you just need to make sure that the nevus is not injured. Under no circumstances should you engage in self-extraction and self-diagnosis of nevi, as this may lead to undesirable consequences. Do not neglect your health, and if a large mole appears or damages an existing one, consult a doctor immediately.
Care after nevus removal
During surgical excision, it is recommended to seal the wound with a bactericidal plaster. The bandage needs to be changed 2-3 times a day. Also, before gluing, the mole site should be treated with alcohol. It is important to remember that during recovery not a drop of water should get on the wound.
If any other method was used, the wound should not be wetted for 5 days. Under no circumstances should you lubricate the wound with lotion or other cosmetic product.
After the crust falls off, young, pale pink skin will remain in its place. Try to protect it from exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Until the skin color at the mole removal site becomes normal, you should apply a high-level sunscreen to this area in the morning, afternoon and evening.
With improper care, multiple pigment spots appear at the site of the nevus.
general information
Intradermal nevi, which include the papillomatous variety, are in most cases melanoma-free. In the absence of provoking factors, the lumpy neoplasm does not degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Main locations:
- head, usually the scalp;
- neck area.
Less common:
- other areas of the body - axillary folds, the area under the mammary glands, in the groin.
Note! Intradermal neoplasms rarely appear on the arms and legs.
Often this type of mole is a noticeable cosmetic defect. Sometimes the formation is dark, almost black, with pigmented hair growing from the inside. Many people are embarrassed by the strange growth and try to remove it themselves, which often leads to serious consequences.
Find out all the details about methods of treating varicose veins on the legs with folk remedies at home.
The first signs, treatment methods and symptoms of mycosis of the foot are written on this page.
Appearance of complex nevi
The mixed type of moles are located in both layers of the skin, so they combine the characteristics of both intrademal and intraepidermal formations. The color of nevi is determined by the epidermal component and can vary from light brown to almost black. The convex shape raised above the skin, due to which moles are sometimes confused with an ordinary wart, is obtained due to the intradermal component.
Formations of this type have the appearance of a papule or a dome-shaped node of a round shape. The surface on which bristly hair often grows is in most cases smooth. Sometimes there are moles with a warty or keratinized surface.
As a rule, complex formations are located on the skin of the face and on the scalp (on the scalp), but they can often choose any, most unexpected location. The sizes of complex moles are usually small - up to 10 mm in diameter.
Prevention
The slightest changes in the tumor are considered a serious reason to visit a doctor.
Be attentive to your body and moles, so that if something happens, you will notice in time the beginning of the degeneration of a neoplasm into oncology.
Remember that timely seeking help will help you avoid many health problems. The main means of prevention is the exclusion of all kinds of mechanical damage to the formation and its traumatization. If the nevus is localized in a place where injury cannot be ruled out, it should be removed as soon as possible in an acceptable manner.
Causes
Scientists have been studying this type of benign neoplasm for many years. After heated discussions, they left one, the most likely version - a congenital malformation of intrauterine development.
What's happening:
- when a tiny organism malfunctions, an excess amount of coloring pigment accumulates in some areas of the skin;
- An intradermal nevus gradually forms. Under the influence of certain factors, a benign formation grows and becomes more noticeable.
The main causes of fetal development defects:
- exposure to high doses of radiation;
- poisoning by toxic fumes;
- prolonged exposure to the open sun;
- working with pesticides, using strong household chemicals.
What to do
Despite the fact that a mole itself is not a disease, a nevus requires serious attention and observation by a dermatologist. Treatment methods in each specific case are selected strictly individually and only by a doctor.
It is not recommended to use ointments or home remedies before visiting a dermatologist - self-medication can “blur” the picture and it will be more difficult for the doctor to make a correct diagnosis and prescribe competent treatment.
If the nevus does not bother or itch, does not increase in size, does not interfere or is not subject to friction, for example, by clothing, the dermatologist can simply observe the formation, recommending periodic visits for examination. When a mole is constantly injured, increases in size, or signs of melanoma appear, the doctor decides to remove it. Sometimes patients ask to remove an unsightly tumor for cosmetic purposes.
Modern medicine offers several methods of destruction (removal) of nevi:
- surgical excision;
- radio wave method;
- laser removal;
- electrocoagulation;
- cryodestruction.