The neoplasm, which is popularly called a wen, is called atheroma by doctors. This tumor can occur on any part of the body where there are many sebaceous glands: behind the ear, in the genital area, on the head, neck and face. Sometimes a large atheroma appears on the back.
Such a benign tumor is an accumulation of fat, cholesterol, and dead epidermal cells. The sebaceous glands of the upper layer, especially rich in them, become clogged. A capsule is formed, which is gradually filled with sebum.
What is atheroma?
Atheroma is a pathological cystic formation. It appears due to the fact that the ducts of the sebaceous glands are clogged and the outflow of constantly produced secretion does not occur. As a result, it accumulates in the resulting cavity (capsule).
It is filled with secretions of the sebaceous gland - a thick (cheesy) mass of grayish color with an unpleasant odor.
Atheroma on the back develops without causing discomfort, so it can be difficult to detect it in a timely manner. The formation can grow to the size of a chicken egg.
This benign sebaceous cyst is a fairly common skin problem.
In its most common location, on the back, there are many ducts that secrete sebum. Penetration of infection into atheroma is dangerous because pus mixed with blood appears in its contents.
In the future, an abscess may develop. Men are more susceptible to the disease, since testosterone affects the functioning of their glands. More often, atheroma is diagnosed in patients aged 20–30 years, as well as during puberty. In childhood, wen formation is rare; this may be a consequence of congenital pathologies.
Prevention measures
To prevent the appearance of atheroma, experts advise limiting the consumption of fats and carbohydrates, which will reduce the production of sebum. For example, it will be useful not to indulge in flour, fatty and sweet foods. And in general, you should pay attention to your diet so that the food is balanced and contains all the necessary vitamins and microelements. It is also important to take care of the skin of your back, observe good personal hygiene and not wear synthetic clothing; these measures will reduce sweating and reduce the risk of developing the disease. At the first signs of illness, it is advisable to consult a doctor, because the sooner the operation is performed, the less traumatic it will be.
Speaking about the prevention of atheroma, it is important to recall the undesirability of squeezing out pimples and other formations on the skin on your own, because during this process you can introduce an infection and provoke the development of a neoplasm.
Reasons for appearance
There are many reasons for the development of atheroma, but in general they are divided into two groups: internal factors and factors acting from the outside, that is, external causes.
External factors include:
- damage to the sebaceous gland canal and blockage of its ducts;
- skin injuries;
- weather influence - high air temperature, high humidity;
- unfavorable working conditions – frequent stay in a hot and stuffy room;
- the use of cosmetics that contribute to the narrowing and blockage of the sebaceous gland ducts;
- insufficient body hygiene.
Internal factors include:
- increased sweating (hyperhidrosis);
- dermatological problems - acne, acne, seborrhea;
- disruption of metabolic processes in the body;
- hereditary predisposition;
- changes in hormonal levels, especially during certain periods - puberty, menopause.
Alternative medicine
If a cyst is detected, treatment with traditional methods can only be carried out if there is a small neoplasm that has not yet led to central nervous system disorders and has not provoked displacement of the vertebrae.
Elecampane is considered the most effective remedy for the appearance of a sacral cyst. In this case, it is used in the form of an infusion, which is prepared as follows: take 1 tbsp. l. raw materials, pour 3 liters of boiled water and infuse for several days in the refrigerator. After this, the infusion is filtered and taken ½ glass 2 - 3 times a day.
Thistle, or rather its juice, is also an equally effective remedy in the treatment of this disease. To obtain it, the plant is crushed, minced in a meat grinder and infused for 72 hours. The juice that comes out must ferment. It should be taken 20 - 30 ml before each meal.
It is necessary to understand that cysts that occur in the spinal column are dangerous and can lead to serious health problems. Therefore, you should never self-medicate. Alternative medicine can be used exclusively as complementary therapy and only after consultation with your doctor.
Symptoms
It is worth noting that atheroma does not have characteristic, pronounced clinical symptoms. These cysts do not cause any discomfort, and when they are located on the back, they are usually noticed late, when the formations have already reached a large size.
Inflamed atheroma does not cause pain, but is a purely visual, cosmetic inconvenience.
External signs of a cyst are:
- the wen looks like a bulge protruding above the surface of the skin;
- the lump has a clearly defined contour;
- the shape of the cyst is round, and to the touch it is dense and elastic;
- atheroma is mobile, it can be slightly moved from its location;
- the size of the formation is different - from a pea to a chicken egg;
- on the surface of the atheroma you can see a clogged duct of the sebaceous gland - a black dot.
An inflamed wen has its own symptoms:
- swelling and redness are observed;
- atheroma becomes painful;
- sometimes it can open and then the purulent contents, which have an unpleasant odor, come out;
- the process is accompanied by a general deterioration in health and an increase in temperature.
Diagnostics
Specialists such as a dermatovenerologist and surgeon will help determine the disease. The diagnosis is made by a doctor upon examination of the patient. But to distinguish atheroma from other neoplasms that manifest themselves in a similar way, differential diagnosis may be required.
During the examination, the specialist observes a mobile cyst with a dense structure and clear contours. An excretory duct is observed in the center of the formation. In difficult cases, during an operation to remove a cyst, the surgeon may take material for histological examination.
In general, the diagnostic procedure can be represented as the following points:
- During the initial examination, the doctor identifies the main characteristics of the pathology - location, color, size, contours;
- Next, the specialist tries to find a blocked duct (it is its presence that indicates that the patient has atheroma, and not some other neoplasm);
- Then palpation is performed to determine density, mobility and soreness.
If, after performing all the above measures, the clinical picture remains insufficiently clear or there is a suspicion of cancer, a biopsy is performed, during which cells are taken for histological examination.
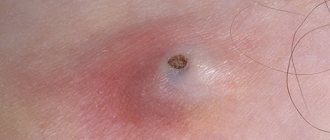
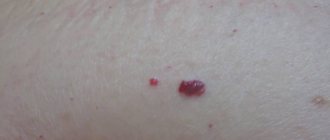
Photo
You can find out what atheroma looks like on the back in the photo below:
Treatment
Do those who have encountered atheroma have any hope that it can be cured with folk remedies? Or maybe there is a possibility that it will resolve on its own?
Unfortunately this is not possible. Even if you manage to open this cyst, after some time it will appear again. The fact is that the subcutaneous capsule will remain and will produce secretion that fills it. The process of formation of atheroma on the back will begin again.
Today, the following treatment methods for sebaceous cysts are possible:
- Removal using laser.
- Radio wave therapy.
- Surgical excision.
increasingly popular - it is safe and does not entail any complications. The recovery period does not exceed 5 days; no traces of the removed atheroma remain, since the procedure does not require incisions or punctures of the skin.
Laser treatment is recommended for mild forms of atheroma , when the size of the formation is small. The method is bloodless, there are no scar formations after its use. After laser therapy, relapses are extremely rare.
Laser and radio wave treatment are conservative treatment methods. When they don't help, the only option is surgery.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia. It does not last long and includes the following stages:
- a small incision above the surface of the cyst;
- opening the capsule;
- removal of the capsule with its contents.
After surgery, the doctor applies stitches and bandages until the skin heals. All procedures are carried out only under sterile conditions.
After surgical excision, antibiotic therapy is often prescribed. Local drugs that have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and healing effects are also used - for example, Levomekol or Vishnevsky ointment.
If the atheroma is inflamed, it cannot be removed immediately. First, suppuration therapy is carried out - the cyst is opened and the purulent masses are removed. The drainage is left for some time (up to several days). The patient usually requires a course of antibiotic therapy.
A few months after treatment of the inflammatory process, the atheroma can be removed.
ICD10 code
ICD10 is an international classification of diseases that collects coded information about diseases. The list is updated at regular intervals; today’s version of classified diseases is already the 10th.
The ICD was created to facilitate the work of medical specialists; it includes all diseases, including skin diseases, which include atheroma.
This disease is included in the section on neoplasms of the skin and appendages (benign). In the ICD-10 encoding it is included in the interval from L72 to L72.9.
Various shapes
Pilonidal
This form is an anomaly in the development of the skin in the coccyx area. The disease has another name - epithelial coccygeal duct. The disease can be suspected by retraction of the skin in the intergluteal fold.
Exacerbation occurs against the background of injuries and hypothermia. The fistula tract begins to become inflamed and suppuration appears. But most doctors are of the opinion that a pilonidal cyst is a congenital defect in the development of the ectoderm (outer germ layer).
The main method of treatment is surgery, but it can only be performed during remission. If a severe inflammatory process is observed, then anti-inflammatory therapy is first prescribed.
Perineural
The cyst is located in the spinal canal and is filled with various fluids inside. The structures are compressed, which causes discomfort. As the formation grows, the symptoms become more pronounced.
Therapy is required with medication, but if a perineural cyst ruptures on the spine, surgery is performed.
Arachnoid
This formation is distinguished by the presence of an arachnoid membrane on the walls of the formation. Formed from parts of the spinal cord. Spinal arachnoid cysts are often found in the lumbosacral region. There are cases of congenital forms of pathology.
Radicular cysts of the spine can be treated with medication. When the formation is more than 2 centimeters, pressure is exerted on the nerve endings, which causes clinical manifestations.
If the arachnoid cyst of the sacral spine grows large, then surgical intervention is required.
Periarticular
This type of formation is most often localized in the area of intervertebral joints. A periarticular cyst of the spine often forms after trauma or pathological changes. Taking into account the synovial epithelium, the following is diagnosed:
- Synovial cyst of the spine. The area of the intervertebral joint bursa is separated after injury or debilitating loads. There is a synovial lining inside the cavity.
- Ganglionic. The lining is missing due to loss of connection with the main bag.
If the formation is large, surgical intervention is required; in other cases, conservative therapy is carried out.
Liquor
A cerebrospinal fluid cyst of the sacral spine is a formation with cerebrospinal fluid inside. Formation begins against the background of complicated osteochondrosis, after serious spinal injuries or a decrease in the speed of cerebrospinal fluid movement.
Symptoms depend entirely on the location of the formation. In the absence of rapid growth, conservative therapy is indicated.
Aneurysmal
It forms inside the bones and is filled with blood, often venous. The pathology is dangerous for the development of malignant tumors and destruction of bone tissue. Can be localized anywhere.
The diagnosis is often made in childhood, mainly in females. Among the main causes, injuries occupy the main place. Swelling is noticeable; it often forms at the site of cyst formation, and there is an increase in temperature. There are pathological fractures in the same place.
The main method of therapy is surgical removal of the tumor. There is no other way to treat this pathology.
A pseudotumor of the spinal column is a benign formation, but the pathological disorders to which it leads can cause human disability. To avoid this, complex treatment of perineural cysts of the spine is required. Depending on the type of formation and the severity of symptoms, a method of therapy is selected.