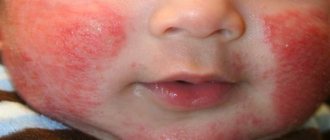
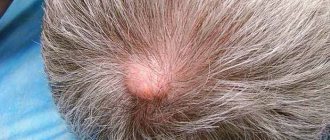
Atheroma is a benign formation of a round shape, noticeably protruding above the surface of the skin. Inside it is a capsule with a white or light gray liquid. If, when pressing on the tumor, exudate with a fetid odor is released and pain occurs, then the person is diagnosed with suppurating atheroma.
General information
When suppurating, a benign growth sometimes opens on its own. In this case, an open wound forms on its surface, through which pathogenic bacteria can enter the body. If the capsule bursts inward, then the fluid it contains enters the bloodstream, causing life-threatening sepsis.
A growth formed from fatty tissue appears on any part of the body covered with a large number of sebaceous glands. Areas with hair, behind the ears, chin, frontal part, neck, and tailbone are often affected. Suppurating atheroma of the back is often encountered, but it does not occur on the palms and soles.
A formation based on fatty tissue is not the tumor that many compare it to. Atheroma is a non-inflammatory pathology of the sebaceous glands, the development of which results in a cystic growth. In most cases, the wen undergoes surgical excision. It may not bother a person for a long time, but under favorable conditions it becomes rapidly inflamed with severe suppuration.
Features of atheroma
To independently distinguish an epidermal tumor from a wen, you should know the characteristics of atheroma, as well as its structure. This is a dense and mobile neoplasm, which consists of epithelial as well as fat cells. The formation rarely grows more than five centimeters. A skin cyst can appear in any part of the body where sweating is increased. These are the so-called seborrheic zones. Often there is a blockage of the sebaceous gland on the face; in most cases, the development of atheroma is often diagnosed in the forehead, upper eyelid, cheek, and wing of the nose. There is a risk of epidermal growth behind the ear or on the scalp. Epidermoid cysts of the coccyx and other parts of the back, groin, and armpit occur less frequently.
Atheroma tissue begins its development in the lower layer of the epidermis - the dermis. The tumor has a small hole that comes out and looks like a black dot. It is through this hole that infection often enters the tumor, causing an inflammatory process. The growth may have an oval or round shape; the base of the tumor has good adhesion to the skin, but inside the tissue it moves a little during palpation.
Causes
The cyst appears and develops due to disruption of the sebaceous glands. There are many reasons for its occurrence. The most common of them include:
- insufficient personal hygiene;
- hormonal imbalance in the body with an increase in testosterone levels;
- violation of the integrity of the skin;
- cystic fibrosis.
Quite often, pathology is observed in women who have reached menopause. The reason in this case lies in the decrease in estrogen production.
Suppuration of atheroma can also occur due to acne, trauma to the skin, excessive sweating, regular contact with harmful chemicals, and metabolic disorders. The inflammatory process often occurs as a result of an attempt to independently eliminate the wen.
Forms of atheroma
Atheromas are classified depending on the composition of their contents and histological structure. There are four forms of formations:
- sebaceous gland cyst;
- dermoid;
- atheromatosis;
- steacytoma.
All these cysts are characterized by the same signs and course. Doctors do not use this classification in their practice, and the types of atheroma are of interest only for scientific research.
Specialists involved in treatment use the division of cysts according to their location and characteristics of appearance. This approach divides neoplasms into congenital and acquired.
Congenital ones look like small cysts, not exceeding half a centimeter in diameter. But their number is multiplicity. Localized in the areas of the pubis, scrotum, and scalp. Their appearance is caused by a genetic disorder in the structure of the sebaceous glands.
Acquired ones are formed due to blockage of the ducts. They can be provoked by a change in the consistency of sebum towards thickening, against the background of injuries, hormonal imbalance, inflammatory processes of the skin and other factors. These atheromas are often single, take a long time to develop and grow to significant sizes.
Common symptoms
Suppuration of atheroma is considered a common phenomenon in people prone to developing dermatological diseases. Leading experts recommend getting rid of such formations immediately after their appearance. Although inflamed wen does not cause pain, it can fester at any time. This process is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the tumor enlarges, the skin above it noticeably stretches, causing discomfort;
- adjacent tissues swell greatly, turn red, and become hot to the touch;
- the patient almost always has a fever;
- the area with the inflamed cyst causes discomfort, aches or pains;
- if lymph nodes are located in the immediate vicinity of the problem area, they also become inflamed and enlarge;
- The patient complains of weakness and general malaise.
It is forbidden to treat festering atheroma with traditional medicine, since they can only worsen the person’s condition. At the first symptoms of the inflammatory process, you should consult a surgeon.
Lipoma, atheroma, hygroma, fibroma - what's the difference?
When a subcutaneous nodule resembling a lump appears, almost all patients think about a wen, but dermatologists and surgeons identify up to a dozen varieties of subcutaneous growths, differing not only in filling, but also in structure, morphology, and the risks of serious complications.
What is lipoma?
Lipoma is a subcutaneous neoplasm of an initially benign nature without pronounced symptoms; it tends to spread and then unite into nodular conglomerates. Typical locations are the arms, head, groin, genitals, forearms and neck. There are cases of lipoma of internal organs.
Lipoma is characterized by unstable filling, subcutaneous migration and mobility, risks of malignancy and transformation into liposarcoma, unlike other benign neoplasms.
Based on the nature of their filling, there are several main types of lipomas.:
- Lipofibromas – filling is up to 85% adipose tissue;
- Myolipomas - as part of the pineal growth, fatty and muscle tissue, an abundant vascular component, found on the kidneys;
- Myelolipomas - the structure consists of adipose and bone tissue, localized in the adrenal glands, peritoneum;
- Fibrolipomas - the internal composition includes fibro-adipose tissue localized on the lower extremities, buttocks, inner and outer thighs.
Lipomas of internal organs carry the greatest danger due to their structural features. Being growths on a thick stalk, they are capable of twisting, leading to necrosis, trauma, and internal bleeding.
Subcutaneous lipomas become malignant under the influence of various negative factors. Read more about what a fatty lipoma is here.
What is atheroma?
Atheroma is a subcutaneous capsule-shaped neoplasm of limited localization with an exclusively benign course. The structure of the tumor consists of subcutaneous fat and epithelium. Atheromas are called wen, skin cysts.
Main localization:
- back,
- face,
- ears,
- neck,
- mammary gland,
- lower abdomen and genitals.
The size of the atheroma varies between 0.5 cm and 3 cm. Unlike lipoma, the filling of the atheroma is stable and does not change, which is responsible for the low oncogenic risks. However, the risk of infection remains due to contamination and dust. Atheromas are more common in men of different ages.
Hygroma
Hygroma (translated from Greek as liquid + tumor) is a benign neoplasm - a cystic component with dense walls and viscous contents. The internal filling resembles a jelly-like mass. Hygromas are localized in tendon cavities and large joints.
When the tumor is small, it does not manifest itself in any way, but with intensive growth and compression of the nerve roots, they are accompanied by pain and disruption of innervation.
Hygromas occur mainly in young women; up to 65% of all benign tumors are hygromas of the wrist joint.
In general, the prognosis is favorable, but, unlike other benign neoplasms, the risk of recurrence after removal is extremely high.
Fibroma
Fibroma is characterized by a nodular formation consisting of connective tissue fibers, typical of almost the entire body. Based on the base of the fibroma, the localization of the tumor can be multiple.
The exact causes of fibroids are unknown, however, there are several defining theories of their occurrence.:
- hereditary factor
- hormonal disorders,
- injuries and metabolic disorders.
The classification of fibromatous neoplasms involves several main forms:
- Soft , which contains cellular elements with a low concentration of connective tissue, in appearance resembles a fibrous skin polyp;
- Dense , consisting of collagen fibers with a low content of cellular elements, resembling a mushroom in appearance;
- Desmoid is a dense tumor with a localization typical of the peritoneum, characterized by aggressive growth, the risk of cell malignancy and high recurrence after excision.
Each type of tumor - atheromas, lipomas and other fatty tissues - requires mandatory diagnosis and examination by a dermatologist, surgeon, or oncologist. Self-treatment and inadequate removal methods lead to infectious complications and cell malignancy.
Manifestation of complications
Growths with filled capsules do not pose a danger to humans. The situation is different with abscessing atheroma, which entails a number of complications, although it is benign. If a large number of bacteria accumulate in the problem area, an abscess may develop. With a gradual increase in the volume of exudate, the capsule decomposes, leading to the opening of the formation. When fluid enters the blood, you may experience:
- general intoxication of the body;
- the development of phlegmon, in which purulent diffuse inflammation occurs not only in the soft tissues, but also in the subcutaneous tissue;
- identification of the opened wen;
- thrombosis affecting the brain, which can cause death;
- if the cyst is located on the head or face - intracranial abscess.
To avoid life-threatening complications, it is necessary to consult a specialist immediately after the occurrence of atheroma. As soon as an epidermal cyst appears, it must be removed immediately.
Complications that atheroma can cause
Sebaceous cysts on the back, as a rule, do not affect the patient's quality of life. However, if complications develop, they can cause problems for the patient. The most common complication is inflammation of the atheroma.
Inflammation of the sebaceous gland of the back can be septic and aseptic. It depends on the nature of the factors causing the reaction. In aseptic inflammation, the process is triggered by physical factors; in the development of septic inflammation, the main role is played by infection of the formation by bacteria from the environment.
In both cases, you need to consult a specialist to prevent phlegmonous process or the occurrence of ulcers on the surface of the skin. Before receiving the necessary medical care, it is better to cover the area of skin on the back with a bandage soaked in Levomekol solution or Zinc ointment.
The purulent contents of the capsule and it itself must be urgently removed. Without surgical intervention on the back, a new growth will soon appear in the same place, which will quickly become inflamed.
A cyst filled with pus is particularly dangerous because it serves as a source of infection and serious complications: abscess, phlegmon and even sepsis. As the condition progresses, a rise in temperature and fever may occur.
The size of the atheroma on the back does not always affect the degree of complications. To avoid such problems, it is necessary to notice the cyst in time and seek advice from a specialist.
Diagnostic measures
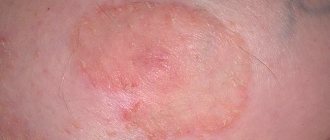
To make a diagnosis, the patient must visit a surgeon. The specialist must examine the neoplasm and make sure that it is not a fibroid, lipoma or inflamed lymph node. Atheroma has clear contours, it is round and noticeably rises above the skin. In its center there is a characteristic black dot, indicating a clogged and non-functioning sebaceous gland.
It is worth noting that the wen formed in the thickness of the skin is mobile and moves with it. Upon palpation, a soft and elastic consistency is felt. The exact size of the growth is determined during ultrasound examination. If a malignancy is suspected, a puncture with histological examination of the material taken is required.
What is suppurating atheroma?
A suppurating atheroma is a benign, round cyst that protrudes above the skin. It is a capsule with white or greenish contents, characterized by an unpleasant odor. Externally, it does not differ from other tumors: hygromas, fibromas, lipomas.
Since cysts appear in the skin and consist of epidermal structures, they are also called epidermal. Despite the fact that the formation is growing, it is not a tumor. For this reason, atheroma is not malignant and does not turn into cancer. The mechanism of their occurrence is fundamentally different.
If, when you put pressure on the cyst, a pasty substance with a pungent odor comes out of it, and the formation itself is painful, then you can definitely say that this is a suppurating atheroma.
On this topic
- Atheroma
Let's find out what atheroma is
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- September 25, 2020
Such a neoplasm is a reason to see a doctor, because with further development, an abscess of the sebaceous gland may appear.
Suppuration is a dangerous process, it is necessary to get rid of it. But before starting any action, the inflammation should be removed. Only after this is removal carried out in case of danger to human life.
First aid
A growth without any signs of inflammation can wait for some time, but a festering cyst must be treated immediately. When exudate gets inside, vital organs are affected and the general condition worsens.
It is unacceptable to pierce, squeeze or cut an inflamed capsule at home. Such procedures are performed only by a specialist in a medical facility and using sterile instruments. Moreover, upon completion of the operation, the doctor prescribes treatment based on antibiotics, antimicrobial drugs and vitamin complexes.
If an inflamed atheroma is detected, you must go to the hospital in a timely manner. To avoid unpleasant consequences, it is recommended to treat the neoplasm with Vishnevsky ointment or Levomekol and cover it with a sterile bandage.
It is believed that if atheroma forms and develops in the subcutaneous space, then its diagnosis and treatment is carried out by a dermatologist. This opinion is erroneous, since the surgeon studies the formations on the skin filled with exudate. If suppuration occurs on weekdays, a person should contact a specialist at a clinic located at his place of residence. When the cyst becomes inflamed after hours, the patient needs to visit an emergency hospital, where the doctor on duty will carry out the necessary therapeutic measures.
Under no circumstances should you wait until Monday or the next morning. A festering wen can burst open in just a few hours, causing serious complications for the body.
What to do and how to relieve inflammation?
If you notice redness on the atheroma , immediately begin taking steps to relieve inflammation. You can get rid of it at home. Here are the most popular recipes:
- Use Vishnevsky . It is applied to the wen and left for several hours. After this, the cyst bursts and its contents come out.
- Melt the lamb fat and rub into the inflamed formation.
- Mix garlic gruel with vegetable oil and apply to the area with inflammation; as a result of this treatment, the wen should break through.
- with aloe juice twice a day . The method is especially effective when a wen appears on or near the earlobe.
- Apply levomekol or ichthyol ointment .
- Baked onion applied to the atheroma and sealed with a band-aid on top helps Change the compress 2-3 times a day. The duration of treatment will depend on the degree of inflammation.
Attention! To prevent inflammation from developing, it is important to follow a diet. Eliminate fatty, spicy and salty foods from your menu.
It is also prohibited to heat or steam the wen in order to quickly “ripen” it. Water can spread germs further throughout the body, so it is not recommended to wet the inflamed wen .
After the wound heals, you can take a shower and wash with baby soap. Other cosmetic soaps with fragrances are prohibited until the wound has completely healed. This also applies to taking a bath.
Surgery
Atheroma is completely eliminated only by complete excision. Without this, any therapeutic actions will not bring the expected result. Surgical intervention is necessarily indicated in the presence of purulent wen. It is necessary to understand that surgery is possible only after complete relief of inflammation. However, in difficult and emergency situations, the doctor can immediately remove the atheroma. There are several methods to eliminate the inflamed growth:
- Standard surgery using a scalpel. The specialist opens the tissue and takes out the wen. If the neoplasm does not suppurate, then sutures are placed in its place, which will need to be removed after 5-7 days. When it comes to a growth filled with purulent exudate, healing by primary intention should occur in the surgical area.
- If an atheroma of small diameter is to be removed, then it is appropriate to use laser therapy. The doctor uses a narrow laser beam to treat the lump, which after a while is destroyed along with the accumulated fluid. The occurrence of relapses is minimized.
- Radio wave treatment is carried out by exposing the problem area to radio frequency waves. This method is convenient because when it is used, scars are either completely absent or almost invisible.
- Electrocoagulation is aimed at destroying the inflamed cyst with high-frequency electric current. At the end of the procedure, sometimes a small burn remains.
- A new technique in the world of medicine is argon plasma coagulation. It consists of using a special scalpel that delivers a directed plasma beam. The procedure prevents bleeding and healthy tissue remains unaffected.
General anesthesia is not used when removing atheroma. If the operation lasts no more than 20 minutes, then local anesthesia is used. An antiseptic is applied to the excision site. Drainage must be installed. In the absence of complications, the wound heals after 15 days, and the individual characteristics of the body should be taken into account.
Wen lipoma and atheroma: differences, causes of appearance and removal methods
Wen lipoma and atheroma: differences, causes of appearance and removal methods
What we are used to calling the general word “fat” can actually mean completely different diseases. For example, it could be a lipoma or atheroma, which are so similar in appearance that patients often do not distinguish them from each other. Meanwhile, each of these formations has its own developmental characteristics, which means treatment and removal methods may also vary. In addition, both types can cause complications in the future, therefore, if you discover a formation of any kind, it is recommended not to self-medicate, but to consult a specialist.
When should a lipoma be removed?
If you consult a dermatologist about a lipoma, then be prepared to be referred to a surgeon. It is this specialist who must confirm the diagnosis. It is recommended to remove any lipomas, as they tend to increase in size. As for lipomas located in internal organs, it is necessary to remove them. The main danger of lipomas is that they can degenerate into a malignant formation. As a rule, to exclude an error, you will be prescribed a puncture followed by a cytological examination or histological examination (this is after removal of the lipoma). It is impossible to treat lipomas with a therapeutic method; there are also no cases of “self-resorption” of lipomas in medical practice. A lipoma must be urgently removed if:
- it is painful;
- it quickly increases in size;
- it disrupts the functioning of important organs;
- it is a noticeable cosmetic defect.
How are lipomas removed?
Small lipomas are removed under local anesthesia. In this case, hospitalization is not required - the patient will spend only 1-2 hours in the clinic. A large lipoma located in a hard-to-reach area is operated on under general anesthesia.
Atheroma: symptoms, complications, removal methods
Atheroma is a benign subcutaneous formation that has a round shape, is dense and mobile to the touch, and does not exceed 5 centimeters in size. Atheromas develop in the sebaceous gland duct. Such tumors are often called a fatty cyst. Atheroma is usually located in those areas of the body where there are sebaceous glands - on almost the entire surface of human skin, except for the feet and palms. The main difference between atheroma and lipoma is that atheroma is always formed only from the sebaceous gland located under the skin, due to blockage of its duct or thickening of sebum. If something interferes with the removal of sebum to the surface of the skin, then it accumulates in a kind of bag (capsule) - this is atheroma. The composition of atheroma is always the same: fatty substances (sebum), epithelial cells and the sebaceous gland.
Complications of atheroma
Typically, these small, painless lumps are harmless and almost never turn into anything cancerous. Dangerous complications of atheroma are:
- Inflammation. Since the contents of atheroma are a breeding ground for bacteria, if they penetrate the atheroma capsule, inflammation develops very quickly and pus appears. Pus may break out. If it spreads under the skin, it can cause soft tissue phlegmon. It happens that atheroma becomes inflamed without infection. In this case, before removal, it is first necessary to relieve inflammation.
- Break. Rupture of atheroma requires immediate medical attention, as an abscess may develop.
- Discomfort. Atheromas can cause serious physical discomfort. For example, atheroma on the genitals can interfere with normal urination or sexual intercourse.
- Removal of atheroma
Modern medicine knows only one way to treat atheroma - removal. Therapeutic and traditional methods of treating atheroma have not proven effective. Removal methods can be different: surgical, laser and radio waves. However, if the wen is inflamed and suppurates, then only surgical intervention will help. In this case, the atheroma is opened, cleared of contents, and then subjected to drug treatment. The operation to remove atheroma is simple, it is performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis and lasts about 15 minutes. The atheroma is removed only together with the capsule, since if even a fragment of the capsule remains under the skin, this will inevitably lead to a relapse of the disease. Doctors recommend removing atheroma without waiting for it to grow or break through - this can significantly complicate treatment and reduce the cosmetic effect.
Prevention of atheroma
Since atheroma is a wen and occurs due to the impossibility of sebum flowing through clogged pores, the main preventive methods are aimed at carrying out cosmetic procedures to clean the pores. They can be special masks, scrubs, steam baths. To reduce the greasiness of the scalp, you can use drying shampoos. Also preventing atheroma is establishing proper nutrition. If atheromas appear frequently, you should consult an endocrinologist.
We treat ingrown toenails and prevent their occurrence
The disease develops as a result of pathological changes in the nail, its matrix and surrounding soft tissues. It is accompanied by a complex of clinical symptoms and functional disorders. Before the age of 30, the disease is more common in men. An ingrown toenail occurs in 3-10% of the population and is one of the reasons to consult a surgeon. In an outpatient setting, they usually have to treat an ingrown toenail.
A chronic disease, prone to relapse even after surgical treatment, causes a lot of suffering and represents an important socio-medical problem, the relevance of which is confirmed by the presence of a large number of conservative and surgical treatment methods (more than 200), which are often ineffective. Even incomplete statistics indicate a trend towards constant growth. Ingrown nails rank second in the structure of inflammatory and purulent diseases after injuries complicated by infection.
Clinical manifestations
The disease can affect any toes, but, as a rule, it affects the big toe of the right foot (in right-handed people), sometimes the big toes of both feet. More often, the outer edge of the nail plate grows into the soft tissue, less often - both edges. Localization on the thumbs of the hands is even less common. There are three degrees of severity of the disease after the nail grows into the finger:
- I degree - mild pain while walking, inflammatory reaction of the soft tissues of the cushion in the form of slight swelling and hyperemia (redness).
- Stage II is associated with an increase in the acute angle of the nail plate and its further ingrowth into the roller. This leads to increased redness and swelling of the tissues, the occurrence of a purulent-inflammatory process and ulceration.
- III degree - formation of bloody-purulent granuloma (excess granulation in the form of a reddish nodule that bleeds easily). In the case of a long-term chronic course of the inflammatory process, under the influence of the pressure of the granuloma and the enlarged (as a result of edema) lateral fold, the nail plate bends and becomes thicker and duller.
When inflammation spreads to the soft tissues of the posterior ridge, paronychia (purulent inflammation of the transverse ridge, which is adjacent to the base of the nail), felon of the finger, phlegmon, lymphangitis (inflammation of the lymphatic vessels), erysipelas, osteomyelitis of the nail phalanx, addition of papillomavirus or fungal infection, hyperkeratosis may occur. , malignant formation. The severe course of the disease often leads to loss of ability to work.
Predisposing and contributing factors
Methods of treatment and prevention
Due to insufficient knowledge of the etiology and pathogenesis, the disease, the relapse (exacerbation) of which, according to various authors, ranges from 2 to 50%, is difficult to treat. An ingrown toenail is treated comprehensively, depending on the degree and severity of the pathological process, as well as the reasons that contributed to its occurrence. Existing methods are divided into:
- Conservative.
- Orthopedic.
- Surgical.
Conservative methods
Their main goal is to combat purulent-inflammatory processes and reduce the intensity of pain in the affected area of the finger, prevent its injury and create conditions for the unhindered growth of the nail plate. For this, lotions with antiseptic solutions, hot foot baths with potassium permanganate or anti-inflammatory infusions of plant origin (calendula), Levomikol, antimicrobial drugs, for example, Baneocin in the form of ointment or powder containing neomycin and batitracin are used. The drug penetrates deeply into the nail bed, has an effective antimicrobial effect in the absence of a negative effect on the processes of epithelization (healing) of the wound.
All this is combined with the displacement of inflamed soft tissues overhanging as a result of edema, the application of gauze rolls and/or placing under the sharp edge of the nail plate (if possible) gauze strips or thin rolls soaked in ointment or a solution containing antiseptic components. During the treatment process, it is necessary to periodically trim the nail correctly, observing antiseptic measures and using loose shoes.
The use of conservative treatment is usually ineffective. After it, frequent relapses occur again. Therefore, it is justified only in the initial stages of the disease, as well as in cases where the patient refuses more radical methods or is unable to use them for some reason.
Basic rules for pedicure
Trim the nail correctly without rounding the edges
Surgical removal of an ingrown toenail
This method has received the most recognition. There are many variations of it. The basic principle is a marginal wedge-shaped resection of a section of the nail or the entire nail plate with simultaneous electrocoagulation of the matrix (growth zone). Methods used:
- classic or traditional - using a scalpel;
- laser removal of ingrown toenails;
- radio wave method.
Surgical removal
In the first case, the operation is characterized by high trauma, a long healing period (for many weeks), persistent pain, increased tissue sensitivity even with slight pressure, which makes it difficult to use ordinary shoes. As a result of such seemingly radical treatment, relapses were noted in 47% of cases or more.
Laser use and radio wave therapy
The effectiveness of the surgical method is significantly increased when laser removal of an ingrown nail is performed, in which its evaporation and tissue dissection is less traumatic. Due to the photocoagulating effect, there is no bleeding, which facilitates the overview of the surgical field and, therefore, reduces the duration of the operation.
The laser allows you to accurately and carefully remove areas damaged by granulation, minimally damaging neighboring areas. In addition, the CO2 laser destroys fungal spores, has a pronounced bactericidal effect and minimal damaging effect. These properties contribute to faster (2 times) healing, reducing the frequency and risk of complications compared to classical surgery. Relapses occur much less frequently.
Removal of ingrown toenails using the radio wave method using the Surgitron device is also used. Some experts consider its advantages (compared to laser) to be higher accuracy and controllability of the effect, as well as the absence of thermal damage to neighboring tissues.
The most effective is the combined use of conservative, orthopedic and modern surgical treatment methods.
Pre-registration by phone: +7 (4217) 34-20-30, +7-929-419-20-30. Be healthy!
Preventive methods
It is not difficult to prevent the re-development of suppurating atheroma of the face, neck, back or other part of the body. Simple rules will help you stay healthy:
- cleansing problem skin with special cosmetic products;
- reviewing the diet, avoiding fatty, fried and salty foods;
- the use of shampoos that have a drying effect;
- maintaining personal hygiene;
- removing makeup from the skin before bed, periodically taking a break from makeup;
- regular walks in the fresh air in gas-free and dust-free places;
- compliance with protection and safety requirements in hazardous industries.
When removing newly appeared atheroma, antibiotics and other drugs are not needed. Treatment of festering wen is more complex. A clogged sebaceous gland must be removed immediately, otherwise it will pose a serious threat to health and life.
How to distinguish by appearance
There are some signs by which a person can independently recognize the type of a certain growth.
The size of the atheroma is usually much smaller and may have pus discharge. This symptom is not possible with a lipoma. It is also worth paying attention to the structure of the growth. Wen is softer, it easily changes its location under the skin. Atheroma is characterized by growth dynamics; this characteristic is not characteristic of wen.
Regardless of what kind of education a person has, the main action is going to the doctor.
Only a qualified specialist can provide relevant assistance in solving this problem. Ignoring symptoms or attempting self-treatment can lead to complications. The article has been verified by the editors
Removal of formation using laser surgery
A laser knife is used to remove inflamed and suppurating small atheromas. Methods used in laser surgery:
- Photocoagulation
– used to remove small inflamed atheromas (up to 5 mm). In this case, stitches are not required; after the postoperative scab falls off after 1-2 weeks, an area of skin without damage remains underneath it.
- Excision of the cyst along with the capsule
– used to remove formations 5-20 mm in diameter. First, an incision is made, then a laser knife is used to separate the capsule from the surrounding tissues, evaporating the boundary of the adhesions with the surrounding structures. After the atheroma is released, it is removed, drainage is installed, and the wound is sutured. After a few days, the drainage is removed, the stitches are removed after 1-1.5 weeks. As a result of this manipulation, an inconspicuous scar is formed.
- Vaporization (evaporation) of the capsule
– used to remove atheroma over 20 mm in diameter. After opening the cyst and removing the contents from it, the surgical field is drained, the wound is stretched and the capsule shell is evaporated using a laser. At the end of the operation, a drainage tube is installed, and stitches are applied for 1-1.5 weeks.
After using the laser knife, an inconspicuous seam remains and the tissue surrounding the cyst is not injured.
Atheroma on the back, its clinical manifestation and treatment
Quite often you can hear about atheroma as a benign tumor, as well as about the possibility of its degeneration into a malignant formation. This statement can be proven or disproved only after histological examination. However, there are still certain criteria by which it is possible to distinguish atheroma from other neoplasms.
Visually, atheroma is similar to a large number of pathological formations, but it is far from a malignant tumor. The most characteristic distinguishing feature of a malignant process is uncontrolled rapid growth. In addition, cytological examination reveals atypical cells that are not inherent in the organ where the disease develops. They appear due to mutations under the influence of provoking factors. These signs are not characteristic of a benign process.
Atheroma is a pathological formation formed due to the lack of outflow of secretions from the sebaceous gland. The secretion of the gland is constantly produced, and due to the presence of a barrier that prevents its removal, it accumulates in the formed cavity. The structure of atheroma is more reminiscent of a cystic formation, which has a capsule and contents. The filling of the cavity is represented by a grayish thick mass.
Diagnosis of the disease
Only a doctor can diagnose atheroma. At the beginning of the visit, a visual examination of the patient is carried out. The doctor pays attention to the pain of the formation, its size, density, and degree of mobility. A comparison with other possible skin defects must be carried out.
Diagnostics includes ultrasound examination, which determines the structure of the tumor contents and its homogeneity. If a cavity is detected, with a high degree of probability we can talk about a cyst.
Laboratory tests in this case do not show a clear picture, unless inflammation develops.