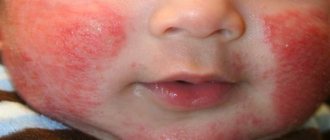
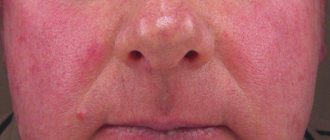
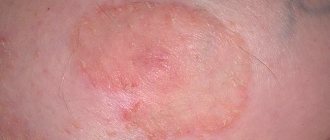
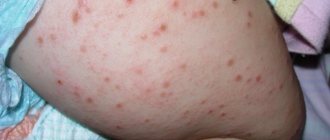
A skin allergy is an increased skin reaction that occurs due to contact with an allergen.
The most common allergens are:
- Honey;
- Milk;
- Animal fur (cats, dogs, small rodents, etc.);
- Dust;
- Mold;
- Nuts;
- Citrus fruit;
- Household chemicals;
- Plant pollen;
- Medications;
- Latex.
Allergies in children are extremely common; according to some data, every fifth child suffers from it. But recognizing childhood allergies is extremely difficult, because outwardly it is very similar to many other diseases, and the child himself is unlikely to explain the “atypicality” of his feelings. Treatment of children should be carried out by a specialist, because the complexity of the process and its duration prove that the treatment of a child is a skill of the highest level. Parents should not choose treatment on their own, because a lot of nuances that you do not know about play a huge role in this process. You may cause harm.
The main causes of allergies to antibiotics
Allergies may occur in certain people who are intolerant to certain components of the medicine. In this case, doses and administration will be carried out without violating the standards prescribed in the instructions. Allergy symptoms can appear for various reasons, the most common of which are:
- In the presence of an infectious process, namely mononucleosis, cytomegalovirus, and so on.
- The body's tendency to develop various types of allergies to animal fur, household chemicals, foods, exotic fruits, and medicine.
- Hereditary predisposition factor.
- Allergies occur during long-term antibiotic therapy, using either one or a complex of drugs.
A common occurrence is the development of allergies in young children. The child does not have a sufficiently stable immune system, which often malfunctions.
How does it manifest itself?
In the general form, the allergy affects the entire body and predominates in older people.
Allergies can express themselves in different ways; symptoms can be general or local.
An adult has a more stable immune system than a child. Local manifestation concerns only a specific organ or area of the skin. These manifestations occur in children and the elderly. Each person is different and there are exceptions. Common signs of a drug allergy are discussed below.
Signs of anaphylactic shock occur immediately after taking an antibacterial drug. Main signs: low blood pressure, lack of normal breathing, swelling of the epiglottis, itchy, red skin rashes.
Serum syndrome may occur two weeks after taking the medicine. Symptoms of manifestation: joint pain, skin rashes, enlarged lymph nodes and high body temperature.
Drug fever occurs 1-3 weeks after the antibiotic and manifests itself over several days. It is characterized by a significant increase in body temperature.
Epidermal necrosis is very rare. As it develops, the skin becomes covered with large watery blisters. After some time, the bubble bursts and a wound appears. To avoid infection, wounds require systematic treatment.
In some cases, Stevens-Johnson syndrome may occur. A rash occurs on the skin, an inflammatory process in the mucous membranes, and an increase in body temperature.
As a rule, severe forms of allergies occur very rarely; the manifestation is mainly local.
Local allergies in children often manifest themselves to penicillin antibiotics, and occur:
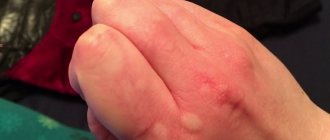
- Urticaria is the appearance of bright red spots with unbearable itching. Merging of several spots into one.
- Quincke's edema occurs immediately after an allergen enters the body. In which there is significant swelling of one of the skin areas. In this case, the skin turns red, itching with noticeable deformation is felt. There are no severe painful sensations.
- The photosensitivity effect occurs when exposed skin is exposed to the sun. It manifests itself as redness of the skin, itching and the presence of small watery blisters.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations can be divided into three groups of reactions:
- Acute type: appear immediately or within an hour after using the drug; These include Quincke's edema, acute urticaria, anaphylactic shock, an attack of bronchial asthma, and acute hemolytic anemia.
- Subacute type: appear within one day after taking the drug; accompanied by pathological changes in the blood.
- Protracted type: appear a few days after taking the drug; manifest themselves in the form of serum sickness, as well as allergic damage to the lymph nodes, internal organs, and joints.
The only manifestation of an allergy may be a prolonged, unexplained fever.
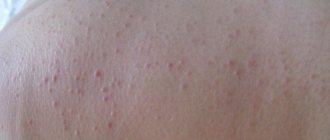
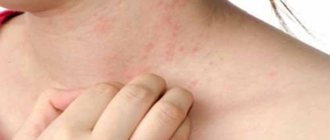
Allergic manifestations on the skin are characterized by polymorphism: there can be a variety of rashes (nodules, spots, blisters, blisters, extensive redness).
May resemble signs of eczema, exudative diathesis, pityriasis rosea.
Hives
It appears as blisters that resemble an insect bite or a nettle burn.
- There may be a red ring around the rash.
- Blisters can change location and merge.
- After the rash disappears, no traces remain.
Relapses are possible even without new use of the drug: this may be facilitated by the presence of corresponding substances in food.
Quincke's edema
Sudden swelling of the mucous membranes or skin and subcutaneous tissue.
Not accompanied by itching. It most often appears on the face, but can also be observed on other parts of the body.
Anaphylactic shock
This is the most severe acute reaction of the body to repeated use of the drug.
Appears 1-2 minutes after receiving the drug (sometimes after 15-30 minutes).
Manifested by the following symptoms:
- disturbances and increased heart rate;
- a sharp decrease in pressure;
- dizziness, headache;
- chest pain;
- severe weakness;
- visual impairment;
- abdominal pain;
- skin manifestations (skin swelling, urticaria, etc.);
- impaired consciousness (even coma is possible);
- bronchospasm and respiratory failure;
- cold clammy sweat;
- involuntary defecation and urination.
In the absence of emergency assistance, it can lead to the death of the patient.
Acute hemolytic anemia
Or “anemia” caused by the destruction of red blood cells.
Has the following symptoms:
- yellowness of the skin and sclera;
- weakness, dizziness;
- enlarged spleen and liver;
- increased heart rate;
- pain in both hypochondriums.
Toxidermy
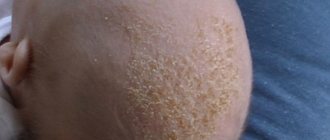
Has a variety of skin lesions:
- nodules;
- spots;
- bubbles;
- pinpoint hemorrhages;
- blisters;
- redness of large areas of the skin;
- peeling, etc.
One of the manifestations is ninth-day erythema (the appearance of widespread or patchy redness of the skin on the ninth day of use of the drug).
Lyell's syndrome
The most severe form of damage to mucous membranes and skin.
It consists of necrosis (death) and rejection of large areas with the formation of an eroded, sharply painful surface.
May appear several hours (weeks) after application. The severity of the condition increases very quickly.
Developing:
- dehydration;
- accession of infection with infectious-toxic shock.
The probability of death is 30-70%. The most unfavorable outcome is in elderly patients and children.
Using tablets if you are allergic to a medicine
allergy to antibiotics in the photo
If you have an allergy to medications, you must consult your doctor before prescribing drug therapy . Only a specialist can decide whether there is a vital need for the use of medications, or whether local drugs and antiseptics can be used.
To exclude a possible allergy to a drug, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics. Namely:
- Donating blood for laboratory testing.
- Checking the skin's reaction to the drug. To do this, a small amount of the drug must be applied to a cotton swab and glued to the skin using a patch. Monitor the reaction.
- Conducting skin allergy tests. The skin is scratched and an allergen is applied. If redness or itching occurs, this indicates the body is highly sensitive to the medicine.
- Blood test for the presence of immunoglobulin E. A positive result indicates the presence of an allergy.
Analyzing the diagnostic results, the doctor selects the safest and most effective antibiotic that will not cause an allergic reaction.
Drug rash: treatment in children and adults
The first thing to do after the appearance of hives is to stop taking the drug that caused it. If therapy involves taking several medications at once (both for internal and external use), it is advisable to temporarily stop treatment as such. After the “culprit” of the rash is identified, the doctor will select a safer analogue of the drug for the patient, which will differ in composition.
Treatment for drug-induced hives usually involves taking antihistamines. They are necessary to reduce the intensity of skin itching and burning.
In some cases, it may be necessary to use local hormonal agents. However, you need to remember that such ointments and creams are characterized by a rather aggressive effect, so they should not be used unless necessary. This is especially true for the treatment of drug rashes in infants and older children.
An important role in the treatment of rashes is given to the intake of enterosorbents, which absorb harmful substances and remove them from the body.
During treatment, you must follow a diet and drink enough fluids. It is advisable to exclude spicy, fried, smoked and salty foods, simple carbohydrates, and sweets from the diet.
Allergy to antibiotics in children
What to do if a child has an allergy? The symptoms of an allergic reaction are similar in both children and adults. Most often, young children have a reaction to Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Tetracycline, Penicillin.
When treating infants and newborns, antibiotic therapy should be used with caution for bacterial infections, and this should be done strictly as prescribed by the doctor. There is no need to give an antibiotic if the child simply has a stomach ache and diarrhea.
More gentle medications will help remove this symptom. Negative effects of antibiotics include disorders of the digestive system.
If a child develops an allergy after taking a medication, it is necessary to visit a doctor to avoid negative consequences in the future.
Treatment of skin allergies
How to treat skin allergies is an important and serious question. You should not treat yourself; your doctor will definitely know better how to help you. The most important thing in this difficult task is to protect yourself from the allergen. Without harmful effects, treatment will be easier and much faster.
Drugs
Drugs that promote treatment:
Antihistamines - relieve a general allergic reaction, stop the production of histamine, which is responsible for the occurrence of allergic reactions. Treatment of skin allergies in this way relieves symptoms, but does not fully cure.
Corticosteroids are hormonal drugs. They are used only as prescribed by a doctor, due to the fact that they are used as emergency aid and, as a result, they have significant side effects.
Immunomodulators are agents that help strengthen the immune system. To strengthen the immune system, they use not only medications, but also hardening, proper nutrition, sports, and giving up bad habits. Treatment of skin allergies with this method is very effective.
Folk remedies
There are also folk remedies to combat allergies. These methods mainly concentrate on the use of herbs, activated charcoal and aromatherapy. The effectiveness of these methods is highly controversial, because with such treatment you may stumble upon another allergen, which can even lead to death. Therefore, it is still recommended to use traditional medicine rather than witchcraft and herbal infusions.
So what kind of skin allergy remedy should you use? This is a purely individual feature and depends on what suits you best and what is more convenient.
Skin allergy tablets
Antihistamines include the following tablets for skin allergies:
- Zyrtec is a non-hormonal drug, contraindicated in pregnant women, lactating women, children under 6 months, elderly people and people with renal failure;
- Zodak is a non-hormonal drug, contraindicated for pregnant women, nursing mothers, children under 2 years of age, and the elderly;
- Fenistil is a non-hormonal drug, contraindicated in newborns, people with closed glaucoma, prostatic hyperplasia, bronchial asthma, pregnant and lactating women;
Also diazolin, loratidine, tavegil and the like.
Ointments for skin allergies
Ointments for skin allergies are hormonal and non-hormonal. Hormonal ones include:
- Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone (grade 1, weak effect). Can be used by pregnant women);
- Fluorocort, Afloderm, Cinacort (class 2, medium action);
- Advantan, Apulein, Elokom, Sinalar (grade 3, active action). Prescribed if necessary to immediately stop inflammation);
- Dermovate, Halcionide (grade 4, highly active). Applies only if the previous ones did not help.
Non-hormonal allergy medications include:
- Psilo-balm, Fenistil-gel (relieves itching);
- Fucidin, Levomikol, Levosin (bactericides);
- Videstim, Radevit, Actovegim, Solcoseryl (accelerate regeneration);
- Bepanten, Panthenol (promote healing);
- Skin allergy creams containing lanolin (reduce flaking, soften the skin).
When using any medications, it is recommended to consult an allergist, because self-medication is fraught with deterioration of the condition and the manifestation of numerous side effects. Value your health and the health of your loved ones.
Treatment
First aid depends on the type of allergic reaction.
It is necessary to act very quickly in case of acute urticaria, which quickly affects the skin. The first thing that needs to be done is to remove the pathological effect of the allergen on the body. To remove the medicine from the body, the patient needs to rinse the stomach and do a cleansing enema. The next stage is taking a sorbent, it can be activated carbon, Sorbex, Enterosgel. Afterwards, take an antihistamine to reduce allergy symptoms. Both the tablet and the injection will be equally effective.
Pathogenesis
In the pathogenesis of allergies there can be any variety or combination of allergic reactions, which can be explained by the individual reactivity of a particular organism, the presence of general somatic diseases, the nature of the allergen, the method of administration, etc., therefore, the division of allergic reactions into delayed and immediate types is partly arbitrary.
The simultaneous existence of 2 types of hypersensitivity due to the action of several groups of drugs can be observed. The severity and clinical manifestations of drug allergies depend on the predominant type of hypersensitivity at a certain stage of the disease or in its general course.
Drug allergies are manifested by immediate type reactions, when the main role is played by humoral antibodies. But quite often a delayed type of allergy occurs.
Clinical manifestations of the delayed type of drug allergy are extremely diverse, from local damage to the oral mucosa and skin to damage to entire organs and even systems (kidneys, respiratory organs, gastrointestinal tract, etc.).
Diet
If you are allergic to an antibiotic, you must follow a special diet. It will restore the functioning of the digestive tract, strengthen the body's protective functions and reduce the occurrence of vomiting and diarrhea.
Diet stages:
- For the first days, drink only water, then you can add a little porridge with water and bread.
- Gradual introduction of fermented milk products: kefir, fermented baked milk, low-fat cottage cheese.
- Taking mineral and vitamin complexes to replenish the body's reserves.
- After seven days of the diet, gradually introduce boiled meat and low-fat fish and eggs into the diet.
Prevention measures
To prevent the body from reacting again, the doctor makes a note in the medical history about the medications that caused the allergy. The patient is contraindicated to undergo drug therapy using several drugs at the same time.
It is prohibited to use antibiotics for prophylactic purposes. These medications are prescribed in the presence of a disease. An allergy to antibiotics can lead to a number of dangerous complications, including death. To prevent this from happening, treatment must be carried out strictly on the recommendation of a doctor and under supervision. In case of severe manifestations, you must immediately call an ambulance. For mild allergies, you should consult your doctor. It is important to follow preventive measures and avoid contact with the allergen in the future. Be healthy!
Features of the course of medicinal urticaria
Drug-induced urticaria can develop not only by an immunological mechanism. If you are sensitive to the components of the drug, the first entry of an allergen into the body is accompanied by the production of antibodies, which accumulate and attach to special mast cells and basophils. They store active substances - in particular, histamine and heparin, which are released into the blood upon contact with the medication. This causes the blood vessels to dilate and increase their permeability to blood components, which leads to swelling and blistering. There is also a non-immune mechanism for the release of histamine. It is realized due to the ability of some drugs (for example, Indomethacin, Aspirin, etc.) to act on mast cells directly, without the participation of immunoglobulins. The symptoms of non-allergic drug-induced urticaria do not differ from the manifestations of allergies externally, but have a number of diagnostic signs and relatively simple ways to solve the problem. One of them is to administer medications slowly.
Development speed
According to the speed of manifestation, drug-induced urticaria can be:
- instantaneous (the allergy appears after a few minutes);
- fast (1-2 hours pass from taking the medicine to the first symptoms);
- prolonged (may appear 1-2 weeks after the drug enters the body).
Cure time
As a rule, manifestations of drug-induced urticaria disappear several hours (up to 1-2 days) after the start of antihistamine therapy and the end of taking the drug to which the patient is allergic.