What is ringworm in cats and what does it look like?
This disease is the collective name for fungal infections that mainly affect the pet’s skin and, less commonly, the claws. Moreover, it does not matter whether the animal goes outside or is completely domestic. The disease is transmitted by trichophyte and dermatophyte fungi, which is why lichen is also called microsporia, trichophytosis or dermatophytosis.
Lichen spores can only be examined under a microscope; they can be transmitted through the air and settle on clothing and any surfaces. Therefore, close contact with the carrier of the disease is not necessary - an animal can get sick if it rubs against its owner’s clothes or lies on the grass where a sick cat was previously sitting.
Tiny spores can remain for a long time in the grass and on the ground, furniture, carpet or clothing. They retain good viability for almost 2 years, and when exposed to favorable conditions (warmth and high humidity), they begin to actively reproduce and cause disease.
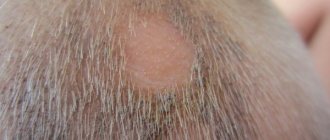
In order to detect the disease in time at the initial stage, you need to know what the sick animal looks like. The main symptom of lichen is breaking off and loss of hair on the affected areas of the skin. Bald and flaky pink spots on the skin resemble those cut with a clipper, which is how the disease got its name.
The following animals are most often susceptible to deprivation:
- small kittens;
- young individuals up to 1 year of age;
- adults whose immunity is weakened due to an inadequate diet and lack of nutrients;
- long-haired breeds;
- cats with malignant processes in the body.
Prevention and human behavior during the incubation period
The incubation period for lichen can last for quite a different period of time, ranging from several days to a couple of months. Most often, people experience the following problems that arise in the body with the onset of lichen:
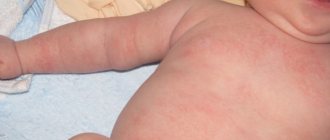
- The appearance of itching, which interferes with a person’s normal lifestyle. Pinpoint tingling of the skin appears and over time, characteristic spots from pink to red appear.
- In childhood, an increase in body temperature to thirty-eight degrees is quite often observed.
- After the spots appear in these affected areas of the body, characteristic vesicles begin to form, which are filled with serous fluid inside. Usually their location on the human body is linear.
- Within 10 days after the onset of the disease, serous blisters begin to gradually burst and a flaky crust forms in their place.
- In children during this period of development of the disease, there is a sharp increase in the size of the lymph nodes, as well as the appearance of catarrhal symptoms of various natures.
Treatment of the ringworm subtype should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. If proper therapy is not started in time, the disease can become chronic and constantly cause unpleasant relapses. Ointments for external use can be used as drug therapy, and individual inflamed lesions should be treated with alcohol tinctures of iodine. Various antifungal drugs can be prescribed internally.
Important! It is necessary to take precautions and preventive measures to protect yourself from contracting this disease. If there is a carrier of any form of this disease in the house, then the regime of compliance with preventive measures and caution should be increased, but it is best to temporarily avoid direct contact with a sick person or animal.
There are a number of preventive measures that experienced specialists advise to adhere to. If you are in the same room with a sick person or animal, you must:
- provide the sick person with separate household items, including towels, bedding, dishes, etc. Strictly protect yourself from contact with an infected person;
- all household attributes in the house should be disinfected as often as possible with specialized means, and clothes and bedding should only be washed at high temperatures in a washing machine;
- For healthy people who live with an infected person, it is best to start taking specialized medications that are stimulants and maintain a strong state of the human immune system
You can protect yourself from infection even while in public places. To do this, after every walk down the street, when you come home, you need to wash your hands with soap or another antiseptic. You cannot pet homeless animals on the street, swim in ponds or eat food directly from the shelves. It is best to dress in clothes that are made from natural fabrics and allow the skin to receive free access to oxygen.
Signs and symptoms
The incubation period of the disease is almost 3 months, so symptoms may not appear immediately. At the initial stage, it is almost impossible to recognize the first signs and determine lichen in a cat, but already at this stage the pet becomes infectious to the people and animals around it.
The main symptoms of ringworm in cats:
- deterioration in the condition of the coat is expressed in its breaking off, dullness and greasy;
- in some places bald spots appear, on which broken hairs are visible, gradually this area becomes more bare;
- bald areas become pink (less often gray-brown) and begin to become covered with scales and crusts;
- the animal loses its appetite, becomes lethargic and apathetic;
- due to constant itching, the cat begins to actively itch and bleeding scratches appear;
- when the claws are damaged, they become deformed;
- Over time, blisters may appear on the surface of the epidermis, which become covered with crusts, and if a secondary infection occurs, ulcers may appear.
The degree of damage to the skin and fur manifests itself depending on the state of health and immunity of the animal: in a healthy cat, only 1-2 spots are possible, in a weakened cat, lichen covers large areas of the body. The most commonly affected areas are the head, neck, muzzle, ears, back, tail and paws in the claw area.
Incubation period of pityriasis rosea
Pityriasis rosea photo
There is still debate about whether pityriasis rosea is contagious or not. Since cases of this type of infection have been recorded, entire families have been affected.
But it has not been possible to establish for certain which pathogen causes the manifestation of pityriasis rosea.
At the same time, there is a version that the transmission route for this disease is lice, bedbugs, and personal hygiene items.
The incubation period for pityriasis rosea in humans can range from 2 days to 21.
During the incubation period, lichen in adults and children manifests itself in the same way:
Symptoms of pityriasis rosea
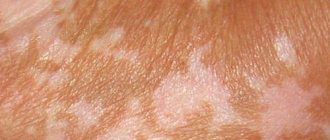
- an oval spot of bright pink color forms on the skin (maternal plaque);
- later, around the main spot, others, smaller ones, form;
- the skin in these places begins to peel, itch, tighten and crack.
Pityriasis rosea is localized in areas of increased sweating - under the arms, in the groin, under the breasts, on the thighs.
Treatment for pityriasis rosea is long-term – up to two months. But there is no secondary damage - a person develops immunity to this type of infection for the rest of his life.
Treatment for ringworm at home
A consultation with a veterinarian will help you find out how and how to treat ringworm in cats. After confirming the diagnosis in the laboratory and prescribing drug therapy by the doctor, the owner of the sick animal is recommended to take the following actions:
- try to isolate the sick pet from people and pets or minimize their contacts, prevent their presence on beds, sofas, etc.;
- be sure to examine all pets for signs of deprivation and take preventive measures;
- Until recovery, the cat cannot be bathed, because this will cause the spread of fungal spores throughout the body, with the exception of special medicated shampoos;
- treat the animal with gloves and do not stop treatment until complete recovery;
- improve the diet and living conditions of a sick pet to improve immunity.
Folk remedies also have a positive effect:
- An ointment based on wood ash and pork fat or butter (mixed in equal proportions). Used to treat the source of infection. A bandage is placed on top, which helps enhance the effect and prevent the cat from licking the medicine.
- Bathing in a solution of lime sulphide (1 tsp per 5-6 liters of warm water). The cat must be completely immersed in a container with the solution, and the diseased areas must then be moistened additionally. After the procedure, the fur should be blotted with a cotton towel or paper napkins and dried; do not allow the pet to lick itself. The method is not suitable for kittens, because... Possible side effects such as allergies, skin irritation or vomiting.
- Treatment of diseased areas with a solution of laundry soap (you will need 10-15 g of shavings per 1 liter of water). Wet a cotton pad and use it to remove dried crusts.
- Lubricating foci of infection with iodine or propolis 1-2 times a day. This method is contraindicated for pets with particularly delicate skin, because... burns may occur.
It is recommended to give a pregnant cat a decoction made from medicinal herbs (chain, nettle, violet, 0.5 tsp per 0.5 liter of boiling water). It is infused for 20 minutes, filtered and given to the animal 3-4 times a day.
The disadvantage of traditional methods of treatment at home is their low effectiveness, as a result of which the disease can become chronic. Therefore, for a faster positive result and complete cure, experts recommend using medications.
Ringworm
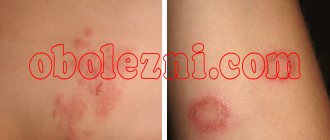
This species is not contagious. Sometimes it is called eczema because it is not a fungal infection, but a manifestation of an allergy caused by:
- detergents;
- ticks, fleas;
- hormonal disbalance,
- insufficient hygiene;
- stress.
The initial symptom of weeping lichen is painless reddish spots, then blisters with exudate appear on them. With proper treatment, they gradually disappear. In the absence of therapy, they open up, pathogenic bacteria enter them and ulcers form.
Ringworm in cats can be treated with external medications that remove inflammation and restore the skin. The following medicinal ointments are suitable for this:
- ichthyol;
- tar;
- salicylic;
- YAM BC;
- sulfuric
The preparations are lubricated on sore spots 1 – 2 times a day until recovery. To eliminate the disease, it is important to determine the cause of the allergy.
Reference. Shingles only affects humans; cats do not get it. Perhaps this is what other types of skin pathologies are mistakenly called.
Treatment with drugs
Treatment of lichen is carried out comprehensively and systematically using the following anti-lichen drugs prescribed by a veterinarian:
- Vaccines for the treatment of ringworm (trichopytosis and microsporia) - Vakderm F, Polivac TM, which are administered intramuscularly in the area of the femoral muscle 1-2 times with an interval of 2 weeks. Used at the initial stage of the disease.
- Ointments with antimycotic action. Used for local treatment.
- Special shampoos with antifungal ingredients (Nizoral with ketoconazole, Doctor skin shampoo, Antiseptic & Antifungal vet shampoo). They are an addition to the main course of treatment, because help reduce itching, have a positive effect on the skin and speed up recovery. Before use, the area around the affected area must be shaved and treated with an antiseptic.
- Sprays for animals (Fungin, Vakderm, Mycostop Provet). Medicines containing clotrimazole, which are applied to the affected area, the course is 1-2 weeks.
When choosing medications for complex therapy, the veterinarian takes into account several factors:
- the size and number of affected areas on the pet’s skin;
- severity of the disease and general condition of the animal;
- state of immunity.
You should know that antifungal drugs should be used in quantities of no more than 2 types and forms, so that the active ingredients do not accumulate in the animal’s body, because this can lead to toxic poisoning.
Symptoms
It is quite difficult to determine the incubation period, although many researchers provide figures from 10 to 35 days.
Initially, the disease manifests itself in the formation of bald areas on the skin. Size, texture, shape depend on the pathogen.
If the area is smooth, irregular in shape, and the hair is broken off, then we may be talking about microsporia. There is no itching, and the affected areas are on the head, withers, neck, and limbs.
If favus is called lichen, then the affected areas will be bald, and the dermis will be folded, red-cherry, often covered with crusts, adhesion of exudate with dried scabs. Itching may or may not be noticeable. The fungus chose the place of localization in the interdigital space, head, area around the lips and eyes.
Fungi of the genus Trichophyton (ringworm, trichophytosis) exhibit a clearly defined character. The inflamed areas have clear boundaries, there is no hair, the skin is dense, covered with dark crusts. The location does not differ from previous types of fungi, itching is clearly noticeable.
Mushrooms are especially dangerous for young animals.
Fur-bearing animals become ill with localized lichen lesions around the eyes, ears, and limbs.
In horses, the lesions are superficial, affecting areas of the head, back, and neck.
Tablets for lichen
Antifungal medications taken orally, in tablet form:
- Griseofulvin (analogs Gricin, Fulcin, etc.). Intended for the treatment of humans, but can also be used for cats. The dosage depends on the weight of the pet - 40 mg/kg, given half or a whole tablet crushed into powder twice a day with food. The medicine has side effects (diarrhea, nausea, liver damage, lethargy) and contraindications.
- Itraconazole (or similar drugs Irunin, Orungal, etc.). Available in tablets and capsules, for cats the dosage is ¼ tablet twice a day (for kittens - 1/8 tablet or capsule, depending on the pet’s weight 10 mg/kg). Give with food for 7 days, then another 2 weeks - every other day in the same amount. The course of treatment is from 4 to 6 weeks. Possible side effects such as nausea and decreased appetite.
- Terbinafine (analogs Lamisil, Exifin). It is given to animals at the rate of 30 mg per kilogram of weight for 3-4 weeks, and is also used in kittens. Side effects include loss of appetite and allergic reactions due to individual intolerance.
In addition, there are drugs in the form of injections. One of them is Dermikotsid, which is an antifungal drug for the treatment of microsporia and trichophytosis. Injections are given into the thigh muscles 2-3 times with an interval of 5 days. For kittens, the dosage is 0.5 ml, for adult pets - 1-1.5 ml. The drug has side effects in the form of an individual reaction on the skin (urticaria, rash), the appearance of redness in the eyes and mucous membranes of the mouth.
Lichen planus
This is a dermatosis that occurs in a chronic form, causing damage to the skin, mucous membranes and nails. Mostly women of different ages are affected. The cause of the development of the disease is not fully understood; provoking factors are disorders of the nervous and digestive systems, diabetes mellitus, pathologies of the liver, and pancreas. There is no incubation period for lichen because it is non-contagious.
Ointments
Before starting local skin treatment with gels or ointments, it is necessary to trim the hair around the diseased area and remove crusts, which will help improve contact of the medicine with the epidermis. To prevent the cat from licking the applied ointment, it is necessary to put a special collar or bandage on it.
To improve the condition of the epidermis and local antifungal action, the doctor prescribes an ointment for ringworm from the following list:
- Clotrimazole. The gel is applied to the affected areas three times a day for up to 30 days (if necessary, longer, until complete recovery).
- Sanoderm. A complex drug that includes a local antibiotic, an antimycotic drug and anti-inflammatory ingredients. Apply 1-2 times a day for 2-4 weeks (duration depends on the severity of the disease). Before using it, you should consult a veterinarian, i.e. the drug has contraindications.
- Miconazole. A remedy for the treatment of fungal diseases in people and animals, which need to be smeared twice a day on diseased areas, the course is 1-2 months.
- Fungin. An effective remedy in the treatment of trichophytosis and microsporia. Apply in a dosage of 0.2-0.3 ml per 1 kg of pet’s weight using a cotton pad and gently rubbing into the skin. Treatment should be carried out daily for 12-15 days.
- Sulfuric ointment. It is a simple, cheap and most harmless way to cure skin diseases, but is effective only for minor lesions. Apply 3-4 times a day to diseased areas of the skin.
- Ointment "Yam". It has acaricidal, fugicidal and keratolytic effects, applied in a thin layer to the skin and around the affected area (3-4 cm more) 1-2 times a day, the course of treatment is 8-10 days.
In chronic forms of lichen and severe bleeding scratches, a secondary microbial infection may occur and symptoms of purulent dermatitis may appear. In such a situation, the doctor prescribes antibiotics in the form of injections or tablets.
Treatment for ringworm takes at least 1-1.5 months. Evidence of a cat’s recovery is not the disappearance of external signs of the disease, but a negative result after testing scrapings taken from the animal’s skin (sometimes the testing procedure is carried out twice).
Types of lichen and their symptoms
For all types of lichen, a characteristic symptom is a violation of the normal pigmentation of the skin.
Pronounced spots with a color characteristic of a particular type of disease may appear on the body in different places.
As the disease progresses, the spots peel, crack, and in the area where the lichen is localized, skin tightness and itching are felt.
In medical practice, there are 5 main subtypes of the disease:
- ringworm - it is caused by a fungal infection of the genus dermatophytes and affects areas of the skin covered with hair;
- pityriasis versicolor - it is also called pityriasis versicolor because of the characteristic shade of spots protruding on the skin. The cause is yeast fungi. This type of lichen is not considered contagious;
- herpes zoster - the causative agent of this type is the herpes virus, and any spot that forms during the disease will be located along the nerve trunks;
- pityriasis rosea - this type of disease occurs with an inflammatory process, as it often occurs an hour or after an acute respiratory viral infection. And the question about the contagiousness of pityriasis rosea remains open to this day;
- lichen ruber - the nature of its occurrence is systemic autoimmune disorders in the body, therefore lichen ruber is not transmitted from person to person.
Is ringworm transmitted to humans?
The main danger of the disease is that lichen is contagious to humans. In this case, people can be affected in any part of the body (arms, legs, etc.), often the skin under the hair on the head. Pink spots appear with clear edges. They may be slightly raised above the skin. Hair on the spots always falls out and grows back only after the end of the course of therapy and cure.
Most often, children of preschool age, who have not yet developed immunity, and adults who have a weak immune system are infected with lichen. In people with a strong, healthy body and high immunity, fungal spores can live on the skin for quite a long time and remain in a suppressed state.
Shingles
This disease develops as a result of a viral infection; its causative agent is herpes zoster. Upon initial contact with the pathogen, a person becomes ill with chickenpox, then the virus remains in the body in an inactive state for life. With a sharp weakening of the immune system, the pathology worsens and manifests itself in the form of herpes zoster.
Can other animals become infected?
This easily transmitted disease is spread by fungal spores that can affect any mammals, which include dogs, cats, and rodents. Animals that live outdoors are at greatest risk.
When one infected pet appears, everyone around them is at risk of getting sick. The infection may quickly spread among residents of shelters or cat and dog kennels. Therefore, it is so important for the owner to isolate the sick animal from people and other pets.
Pathogenesis of microsporia in humans
To properly diagnose ringworm, you should consult a dermatologist . After the initial examination, a bacteriological examination of skin scrapings and analysis of several hairs from the lesion should be done.
When examining skin flakes and hair stumps, the presence of fungal spores is revealed. Also, the material taken for analysis can be sown in a special medium, where after a few days the microflora will grow.
Based on the results, not only the type of causative agent of the disease will be established, but also its resistance to certain antifungal drugs.
Routes of transmission of ringworm
Spores of the fungus that causes the disease can spread quickly through the air, in the aquatic environment and through clothing.
Main routes of transmission:
- in direct contact with a sick animal (if protective equipment is not used);
- with indirect contact, infection can occur through pet care items - a bed, food bowls, harness or leash;
- through other carriers of infection - rodents (mice and rats);
- in the environment, spores can spread with water or through the air, through soil, sand, garbage, upon contact with which the fungus begins to develop;
- through items of clothing or shoes of the owner or other people coming into the house.
Causes of development and pathogens
Ringworm is the common name for dermatophytosis. It is caused by dermatophyte fungi; the type of disease is determined by their appearance.
- Microsporia is a fungal infection caused by Microsporum fungi. The risk group is mainly cats, but dogs and other animals can become infected through contact with a sick cat. People are also at risk.
- Trichophytosis is a lesion of the body caused by the activity of Trichophyton. Kittens and puppies under one year of age are more susceptible to the disease. The pathogen can be transmitted to humans.
The main cause of dermatophytosis is contact with a sick animal. The risk group includes pets living in groups, rodent hunters and domestic cats on their own. The fungus is active at any time of the year, but peak incidence occurs in the spring and summer, especially in hot and humid climates.
Microsporia
A typical symptom of this pathology is the formation of round balding patches on the head and body. The fur in the affected area breaks off and thins, crusts and small rashes form in the lesion. As a rule, it affects the face, paws, and tail; it is rarely diagnosed on the body.
There are 4 forms of the disease.
- Superficial microsporia - affects only the fur, manifests itself in small round areas of alopecia, without skin inflammation.
- The follicular (deep) form is accompanied by severe lesions of the epidermis. It manifests itself as foci of baldness, inflammation, and the formation of dense crusts. Accompanied by itching, the animal scratches its body, thereby spreading Microsporum spores to healthy areas of the body.
- The atypical form of infection is manifested by small abrasions and injuries, without the characteristic round foci of alopecia.
- Latent lichen is a subclinical form in which the causative agent of the disease is present on the body, but there are no symptoms.
The hidden form poses a danger to all surrounding animals. A carrier cat does not have characteristic symptoms, but carries the fungal spores, infecting others.
Trichophytosis
Accompanied by fragility and hair loss, the clinical picture is very similar to microsporia. Localization of lesions: neck, head, paw pads. The areas are round, regular in shape, and quickly increase in size. The disease is accompanied by severe itching, so the cat scratches the body, the skin becomes inflamed, crusts and weeping wounds form. The addition of infection causes purulent inflammation.
Kinds:
- Superficial trichophytosis - does not affect the dermis, is diagnosed in adults.
- Deep form - affects young animals, accompanied by inflammation of the skin. Areas of baldness become covered with crusts, under which pus accumulates. It is characterized by a protracted course - from two months.
- Atypical form - occurs without dermatitis and itching, mainly in the summer. Small patches of alopecia appear on the body, there is no discomfort.
The disease is highly contagious; an infected cat quickly transmits spores to healthy individuals. All kittens are at risk, especially in spring and summer.
Prevention of lichen in cats
The main measures to prevent infection of pets with lichen include:
- good care and maintenance of the pet’s health and immunity;
- maintaining cleanliness in the room where animals live: regularly sanitize the bedding, house, feeder and drinking bowl, care accessories;
- when walking on the street, avoid contact with homeless and stray cats and dogs;
- carrying out preventive vaccinations that help protect the animal from ringworm and other types of lichen (these include Polivak TM, Vakderm, Microderm, etc.); with regular use of vaccines, the animal develops immunity to skin diseases;
- if your pet is suspected of being infected with lichen, it is necessary to provide personal means of protection against infection - wear a gown and rubber gloves when carrying out medical and other procedures for caring for a sick animal;
- After isolating a sick cat in a separate room, it is recommended to subject it to quartz treatment daily using a special lamp, and to carry out wet cleaning with a chlorinated solution (chlorhexidine or alcohol can be used).
The measures listed will help protect animals from infection, even in a situation where there is an animal with shingles in the house. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations and the proper quality of treatment and maintain the health of your pet, lichen can be cured and complications and the transition of the disease to the chronic stage can be avoided.
Transmission of lichen from animals
One of the most common ways to become infected with shingles is to catch it from animals. The carriers are often stray cats. Therefore, it is important to remember how shingles is transmitted. The incubation period for the disease is very long, and it can be very difficult to start treatment in a timely manner.
The symptoms are extremely unpleasant, and, as a rule, it is not possible to recover quickly and without consequences. Bald spots appear at the site of infection; severe hair loss is a prerequisite. But you can become infected through any, even the slightest, contact with an animal. The main thing is not to mistake this disease for severe dandruff, but in the early stages they are very similar. If you get carried away with dandruff treatment, you can seriously develop lichen.
The incubation period for lichen in a person infected by a cat can be several weeks. Therefore, it is best to completely avoid communication and contact with stray animals. Or if you decide to take an animal into your home from the street, then before bringing it into your apartment, visit a veterinarian. The specialist will be able to advise you whether the cat has lichen or other diseases, and will prescribe the necessary medications for both the animal and you and family members.
An extremely unpleasant disease is feline lichen. A person has a long incubation period, so the disease is usually started, and then they pay for a long time for their carelessness.
Prevention
- For prophylactic purposes, deep intramuscular injection of vaccines is used: “Vakderm” (dogs, cats and fur-bearing animals), “Vakderm F” (dermatophytoses of cats), “Polivak”, “Biocan M Plus” (microsporia in dogs), “Biofel M Plus” ( microsporia in cats) and others.
- Primary vaccination can be carried out starting from two months of age. The vaccine is administered: intramuscularly, initially - twice, with an interval of 10-21 days, in different paws (alternating - left, then right or vice versa), revaccination is done once a year, preferably within the 12th month, since it is stable immunity is maintained for 12 months, and it takes at least two weeks to develop an immune response after vaccination.
- Prevention plays a particularly important role for animals at risk. In particular, this applies to cats that walk freely and independently on the street, before exhibitions and mating (cats that have given birth can infect their kittens).
Remember: preventing diseases is always easier and cheaper than treating them. And what is also important is that prevention, unlike disease, does not harm the health of your pet.
Did you like the article? Share it with everyone! Thank you!
- Common cat diseases Cat diseases, ringworm or fungal skin infections
- Urolithiasis in cats or what pet owners need to know
- Calcivirus infection or calcivirosis in cats
- Panleukopenia or feline distemper