Lichen sclerosus (lichen) or kraurosis, affecting the head of the penis, is a chronic, sluggish disease. Lichen sclerosus is a precancerous condition, so patients diagnosed with kraurosis should undergo regular examinations.
Lichen sclerosus develops mainly in adult patients. The average age of patients is 43 years. Lichen sclerosus of the penis is relatively rare. Thus, women suffer from kraurosis of the vulva 10 times more often than men from kraurosis of the penis.
Lichen sclerosus: causes of pathology
Why white spots appear on the skin (not to be confused with vitiligo) has not yet been established - there are several hypotheses. However, we can confidently say that lichen sclerosus is more often diagnosed in white women after the decline of childbearing function and in teenage girls , although cases of the disease have been recorded among dark-skinned women and Asian women. There is an opinion that the disease is a symptom of pathologies of the nervous, immune and endocrine systems , and also among the priority hypotheses about the infectious and autoimmune nature of the pathology . In addition, the following can lead to illness:
- habitual injuries of mucous membranes and skin;
- metabolic disorders;
- frequent allergic reactions;
- hereditary factor;
- disturbances in the blood supply to the mucous membranes in the genital area;
- diabetes mellitus, chronic infections, candidiasis, neurodermatitis.
Attention! The blood serum of patients who did not receive timely treatment for lichen sclerosus is characterized by increased levels of testosterone and androsterone, but the level of dihydrotestosterone in it is reduced. This suggests that the development of the disease is associated with a decrease in the activity of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which promotes the transition of testosterone to its active form.
Preventive recommendations
Special preventive measures that would avoid the appearance of lichen sclerosus have not been developed.
However, to reduce the risk of developing pathology, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- maintaining proper nutrition;
- eliminating bad habits;
- timely treatment of provoking (infectious) diseases;
- compliance with personal hygiene rules.
Lichen sclerosus: symptoms of the disease
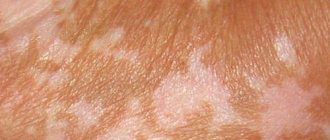
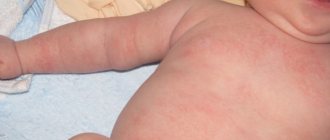
In the early stages of the disease, thickening of the epidermis and hyperkeratosis are observed, in addition, swelling of the mucous membranes, dilation of capillaries and decreased elasticity of the skin are observed. In women, depending on the form of lichen sclerosus, the spots are localized on the genitals (vulva, anus, inner surface of the buttocks, inguinal folds), on the neck, shoulders, abdomen, thighs and upper chest. In men, rashes are observed on the genitals, neck and shoulders.
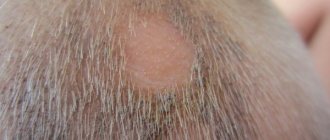
The initial stage of the disease is characterized by the appearance of small nodules of light gray color with a pearlescent tint, having a diameter of up to five millimeters and figuratively called “white splashes.” There may be several such nodules or papules, with closely spaced formations merging into spots (plaques), which at the beginning of the process rise slightly above the surrounding skin, and at the end are slightly pressed into it . The lesion becomes sclerotic, that is, the tissues lose elasticity, become dry and eventually atrophy. If the mucous membranes of the vaginal opening are affected, women suffer from severe itching and a feeling of tension due to the narrowing of the opening. In men, subjective sensations are usually absent, but the resulting narrowing of the foreskin causes phimosis.
If lichen sclerosus affects the area where there are hair follicles, then plugs resembling comedones are noted in their dilated mouths. In rare cases, the surface of the spots is covered with blisters, spider veins and small red spots (petechiae), and cracks appear in the folds of the skin.
Attention! The plaques characteristic of lichen sclerosus itch. If they are combed and torn off, an erosive surface is exposed, often covered with ulcers. The skin in the affected areas is thin and easily injured; if pathogenic microflora gets on it, the possibility of developing an inflammatory process cannot be ruled out, as a result of which lichen sclerosus is aggravated by dermatitis.
Diagnostics
If a rash appears on the pubis or genitals, you should contact a dermatovenerologist. The diagnosis of lichen can be made based on the following studies:
- initial examination, history taking;
- microscopic examination of a skin sample from the site of the lesion (for this, a scraping is taken);
- irradiation with a special lamp;
- clinical blood test.
Research helps to determine the nature of lichen - infectious, neurological or allergic, and to choose adequate treatment. Additionally, a test is carried out for the presence of sexually transmitted infections.
A blood test may be needed to make a diagnosis
How is lichen sclerosus diagnosed?
First of all, the doctor examines the patient and pays attention to the condition of the skin and mucous membranes in the genital area. The skin shrank and became like parchment; the anal area has acquired the appearance of an hourglass; there is obliteration (closure) of the foreskin in men and the labia minora in women - all these are signs indicating the development of pathology in the patient . It is clear that such changes are more likely to be detected by specialized specialists , although a consultation with a dermatologist would also not hurt, especially if we are talking about the extragenetic form of the disease.
Manifestations of lichen sclerosus may resemble vitiligo, scleroderma, lichen planus, candidiasis, diaper rash and some other dermatological diseases . To exclude them, a tissue biopsy is performed in the affected area with immunofluorescent staining of sections. In addition, when diagnosing lichen sclerosus, bacterioscopic, bacteriological and immunoenzyme studies of the material are carried out, as well as determination of the level of sex hormones and the immunological status of the patient.
Diagnostics
In advanced stages, it is difficult to confuse lichen sclerosus with any other disease.
At the same time, in the initial stages, the pathology has common symptoms with diabetes mellitus, vitiligo or vulvovaginitis. This may cause confusion. Diagnosis of pathology always begins with a questioning and examination of the woman. Already at this time, an experienced physician will be able to suspect the presence of lichen and make a preliminary diagnosis.
To confirm it, he may prescribe a regular or extended vulvoscopy (a procedure during which the tissues of the vulva are examined using a colposcope).
As for laboratory tests, they may include:
- blood test for glucose;
- PCR (to detect HPV);
- cytological examination of material taken from the tissues of the external genitalia (necessary to exclude cancer);
- immunogram (to understand whether the patient has immune disorders).
Forms of lichen sclerosus
There are two forms of the disease, which are determined by the location of the lesions: genital, characteristic of the genitals, and extragenital, affecting the skin of the body.
Genital lichen sclerosus in women affects the vulva and perineal area. The disease manifests itself as white or yellowish spots, plaques and nodules, but sometimes erosions and blisters appear on the skin. Healing of the affected areas is accompanied by tissue scarring, leading to “adhesion” of the labia minora and tissue cracking. In men, this form occurs only with preserved foreskin. The manifestations are similar to those mentioned above; the disease leads to the development of urethral stricture and phimosis. As a result of violations of hygiene rules, the course of the genital form of the disease is often complicated by bacterial and fungal infections.
Attention! The genital form of lichen sclerosus can malignantly degenerate into squamous cell carcinoma (mainly in older patients).
Extragenital lichen sclerosus is diagnosed in every fifth patient and manifests itself in the form of whitish pearlescent spots, which “sink” in the central part as they develop. Most often, rashes are observed in the upper third of the back, on the neck, abdomen (navel area), on the skin of the elbows and knees, as well as on the soles of the feet and palms.
The doctor's consultation
When the first signs of fungus appear, you should consult your doctor. In itself, penile lichen is not a dangerous disease, but if neglected, the disease can have extremely negative consequences, such as the localization of red spots or rashes not only at the genitals, but throughout the body; decreased immunity; may cause pain when urinating or during sexual intercourse, itching and burning. Therefore, if the first signs of infection appear, you should immediately consult a dermatologist or dermatovenerologist to rule out sexually transmitted diseases.
Do not wait until the rash spreads further to other areas of the skin. At the first signs, namely red rashes and itching, you need to seek help from a specialist so that he can prescribe the necessary treatment.
How to treat lichen sclerosus
Treatment is prescribed taking into account the patient’s age and the degree of damage to the skin and mucous membranes. Usually prescribed:
General strengthening agents, for example, Resorquin or Delagil.
Hormonal ointments . External therapy containing corticosteroids is used in short courses, not forgetting that steroids provoke thinning of the skin.
Injections . Improvements in skin condition are noted after a course of injections of triamcialone acetonide.
Pills. In advanced cases of the disease, it is advisable to use Acitretin (systemic retinoid).
External agents that improve blood circulation and increase tissue elasticity. A good effect is observed from the use of ointment with tacrolimus (0.1%), which, due to its non-hormonal composition, can be used for a relatively long time.
Supportive therapy . There is a beneficial effect on the condition of the skin of laser and ultrasound therapy, as well as selective photocoagulation and acupuncture.
Surgery. Used in rare cases, mainly in men.
Treatment
For the treatment of lichen sclerosus with the lesion located on the penis, the following is prescribed:
- Tocopherol acetate (that is, vitamin E) in high doses over a long course. The dosage and duration of the course are selected individually.
- Injections of retinol and lidase - in several intermittent courses.
Also, patients with scleroatrophic kraurosis are prescribed general restorative therapy and antimalarial drugs (resorquine, delagil). Ointments containing corticosteroids, agents that stimulate tissue traffic, are prescribed locally.
At the third stage of lichen sclerosus, if a urethral stricture is detected, surgery may be required.
Treatment with traditional methods
Medicinal herbs can also be used in the treatment of penile kraurosis. However, treatment will require long-term and regular treatment.
Baths with medicinal herbs for kraurosis of the penis. It is necessary to prepare a concentrated decoction of string, chamomile or calendula. You can also use a mixture of these dry herbs. The decoction is prepared at the rate of a glass of raw materials per liter of water. The composition is boiled for 5 minutes, after which it is left to cool completely. Next, you will need to strain the broth and squeeze out the herbs well. Use the decoction for local baths for scleroatrophic kraurosis of the penis, preheating it to a temperature of 39-40 degrees. The duration of the bath is until the water cools.
To treat kraurosis of the penis, you can use a tincture (alcohol) of celandine. Moisten a cotton pad with the tincture and wipe the sore areas. During the treatment, a burning sensation will occur. After wiping with the tincture, the areas of kraurosis are lubricated with an emollient cream, possibly for children.
What else you need to know about lichen sclerosus
- It is almost impossible to prevent the development of the disease , since the causes of the disease have not been established.
- Affected skin should be carefully cared for using neutral detergents and formulations containing moisturizing and softening ingredients.
- Make sure that covers do not come into contact with synthetic fabrics, and also avoid natural, but too brightly and unstablely colored linen and clothing.
- Be careful when choosing sanitary pads ; definitely avoid scented products, which often cause irritation and allergies.
- In most cases, lichen sclerosus can be cured; it is only important to contact a specialist in time , who will prescribe adequate treatment.
What are the risks for the sick person and his partner?
Whether it is possible to receive lichen as a “gift” through sexual contact with an infected person depends on the state of the person’s immunity, as well as on the type of disease. That is why such dermatoses are called conditionally infectious.
The most unpleasant ones on the list are the girdling and pink subspecies:
- Shingles cannot be contracted through airborne droplets; close contact is required, especially sexual contact. Using the patient's personal belongings also threatens with bad consequences. But these warnings apply only to the stage of the disease when a new rash appears. If the blisters are covered with scabs, the disease automatically becomes non-contagious.
- Due to little knowledge of the mechanism of activation of pityriasis rosea, it is not possible to accurately answer the question of its contagiousness. Therefore, it is assumed that this dermatosis is transmitted infrequently by contact. Doctors still recommend abstaining from sexual activity during illness, because sweat and water procedures are not the best companions for this dermatosis.