There are two types of lichen that can affect the penis:
- Lichen planus;
- Pityriasis versicolor.
These diseases are caused by various causative factors. For lichen planus, the causes are not fully understood. Suspected provoking factors are:
- Viruses;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system and frequent stressful situations;
- Contact with chemicals and medications (beto-blockers, antimalarials, diuretics, antibiotics).
A number of scientists believe that lichen planus on the head is an autoimmune disease, in the development of which a disruption of the mechanism of skin cell division plays a leading role. More often, the disease develops in men over 50 years of age .
Pityriasis versicolor is a fungal disease. For its development, increased sweating in the groin area is necessary. The fungus that causes lichen can be contracted during sexual intercourse or by using the personal belongings of a sick person. Unlike lichen planus, pityriasis versicolor is seasonal (spring and summer) and most often affects young men aged 20-30 years. It does not affect older people due to atrophy of the sweat glands. In medicine, pityriasis versicolor is also called versicolor.
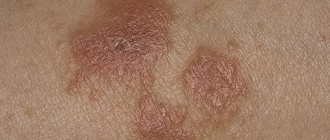
Pityriasis versicolor on the penis
Tinea versicolor (pityriasis versicolor) or versicolor (varicolored) is a common dermatosis. Characterized by multiple, small, oval, scaly spots measuring 1-3 cm in diameter. It is a benign superficial skin infection.
Most often found in young people during hot, humid weather, it is caused by the fungi Malassezia globosa and Malassezia furfur. The lesions may be light brown, reddish or white, hence the name versicolor.
Pityriasis versicolor (varicolored) on the penis is quite rare. The main localization of rashes is the back and abdomen. The genital rash is usually asymptomatic, although some patients complain of mild itching. Differential diagnosis includes inflammatory pigmentation and vitiligo.
Although the pathogenesis of the color change is not fully understood, the fungus is known to produce azelaic acid. This is a substance that interferes with the activity of tyrosinase and the subsequent synthesis of melanin.
The rash will clear up completely over time, but recurrences of this type of lichen are common. Sometimes spontaneous disappearance of the rash under the influence of ultraviolet radiation is possible.
Factors of occurrence
The reasons for the appearance of lichen on the legs can be different:
- fungal microspores;
- viruses;
- state of stress;
- genetic predisposition;
- interaction with infected people;
- metabolic disease;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules.
Wilson's lichen (lichen versicolor)
Lichen ruber planus or lichen planus . It can appear on any part of a man’s skin, and the groin area is no exception.
Lichen ruber on the penis is a chronic inflammatory, dermatous disease of unknown origin. It is characterized by various types of skin lesions (papules, nodules), more often in middle-aged people. The etiology of this type of lichen is still unknown.
Experts say that genetic, immunological and hormonal factors play a role in the formation of dermatosis. The most common lesions are purplish papules with well-demarcated borders. Commonly found on the wrists, lower extremities and genital area in men.
The disease is diagnosed by visual examination of the patient, and can additionally be confirmed using dermatoscopy. In some cases, a biopsy is recommended to help identify squamous cell carcinoma. This is a possible complication of genital lichen.
Lichen ruber planus localized on the genitals is rarely accompanied by extensive symptoms. Patients may complain of severe itching and the formation of bright papules on the head of the penis.
Treatment includes the prescription of hormonal drugs, steroids, antihistamines, and sedatives. The rash may persist for several months and appear periodically for many years.
Causes and epidemiology of lichen planus in humans
There is no exact statement why LP occurs. There are various versions of its origin. Some stand out in particular:
- Genetic path. It is believed that genes that store information about the disease remain inactive for some time in the body. Under the influence of internal and external negative influences, they enter the active phase, provoking inflammation.
- Immunoallergic. The organs' protective system is unable to distinguish between healthy and diseased cells. Produces antibodies against healthy epidermis and mucous membranes, causing immune inflammation (allergy).
- Intoxicating. The body is vulnerable to chemicals and drugs. This category includes: gold, antibacterial and anti-tuberculosis preparations. Intoxication can be caused by quinine, which is used in the treatment of lichen.
- Neurogenic. Occurs as a result of nervous disorders (neurasthenia). With neuritis, LLP can spill out along the branches of the nerves.
- Autointoxication. The cause is autoimmune diseases that disrupt the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine system, and liver. In patients with diabetes mellitus and hepatitis C, LP is often diagnosed.
- Iatrogenic (unforeseen or inevitable). Poor-quality fillings, dentures, and broken teeth disrupt the surface layer of the mucous membrane, creating the ground for the formation of lichen.
Wilson's lichen rarely occurs in the acute stage. Most often, it has a subacute and chronic form.
This type of lichen, in all cases, covers selected areas on the body.
Localization on the skin
Problem areas include:
- the area on the arm between the elbow and wrist on the inside;
- the area between the forearm and hand;
- the area on the leg between the pelvis and the knee on the inside;
- groin area, knee bend, armpit;
Dermatoses on the skin of the face (except the forehead), feet, inside of the hands, and scalp are not diagnosed as LLP.
Mucous
A quarter of patients complain of rashes in the area of visible mucous membranes:
- mouth (inner cheek area, red border of the lower lip, surface of the taste organ);
- cone-shaped end of the penis;
- the slit-like space between the labia majora and minora.
LLP on the mucous membranes can manifest itself as an independent disease, or can be combined with skin dermatosis.
Nails
Damage to the horny cover at the end of the fingers is not common and differs:
- ribbed striations along the horny cover;
- dark spots on the plate;
- hyperemia of the bed under the nail;
- increased fragility of the keratinized plate.
All these indications are typical for onychorrhexis (one of the types of lesions). Symptoms of onycholysis:
- slowing down the growth of the horny cover;
- complete destruction of the horny plate;
- growth of compacted epidermis on the bed.
Ringworm affects the nails of the upper and lower extremities.
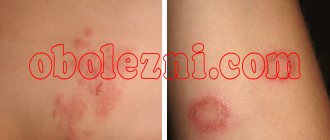
Pityriasis rosea
Zhiber's lichen or pityriasis rosea refers to infectious-allergic dermatous pathologies. Pityriasis rosea or Pityriasis rosea on the penis is characterized by the development of patchy rashes that can last up to 6 weeks on average.
There is an opinion that this type of lichen is contagious (infectious), but this judgment is erroneous. Pityriasis rosea can go away on its own, even without drug treatment. In some patients, scaly redness on the penis may persist for several months. Until they completely begin to regress over time.
In almost 90% of cases, the disease is asymptomatic, sometimes accompanied by itching. The development of pityriasis rosea can be facilitated by a decrease in immunity due to a viral or infectious pathology. More often the disease is diagnosed in men aged 10 to 40 years.
Additional measures and prevention
Since lichen ruber is a disease with a presumed immunoallergic nature, the most serious attention should be paid to strengthening the immune system, ensuring proper and nutritious nutrition, an optimal level of physical activity, and avoiding hypothermia and severe stress.
In addition, it is important to treat all identified infectious diseases in a timely manner, and suffer colds where they should be - that is, in bed, providing yourself with sufficient rest, sleep, plenty of fluids and a light, but vitamin-rich diet.
Shingles
Herpes zoster (shingles, Herpes zoster) is based on the reactivation of chickenpox infection.
Since the virus persists after the primary infection in childhood throughout life. Reactivation may be caused by stress or immunodeficiency. Shingles (Herpes zoster) on the penis is not uncommon.
The disease is accompanied by the formation of a rash in the form of blisters the size of a pinhead. After this, burning, itching and soreness occur in the skin area.
Approximately 4 days after the onset of the disease, erythema with uniform vesicles and papules is observed. After 7-12 days, the rashes dry out and form brown crusts. After 2-4 weeks, complete healing of the skin can be observed.
Shingles in the genital area requires special attention. To eliminate the risk of complications, it is necessary to begin a course of antiviral therapy as soon as possible.
Experts recommend starting to take antiviral drugs in the first 72 hours after the rash appears. Therapy is aimed at relieving symptoms and shortening the duration of the disease.
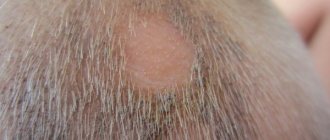
Lichen nitidus
Lichen planus is a rare and benign inflammatory skin condition first described in 1907 by Pincus. The prevalence is estimated to be about 0.34% of all dermatological conditions. Lichen nitidus usually occurs in children and young adults.
It is characterized by the presence of many asymptomatic, skin-colored or white, small, flat-topped papules that have a shiny surface. The most common sites affected are the arms at the elbow, the dorsal sides of the arms, and the genitals.
Lichen pelvis on the penis appears as small, dense nodules that are not prone to merging and spreading. The main localization of the rash is on the head of the penis. The disease is not accompanied by any special symptoms and does not cause genital itching or burning.
Lichen pellucida does not require special diagnosis and treatment. It is possible to prescribe symptomatic therapy, which will include taking steroids, antihistamines and immunostimulants. Patients with Lichen nitidus may be advised to take a course of physiotherapeutic treatment and take vitamin supplements.
Lichen sclerosus (lichen)
sclerosus is a dermatological disease of an inflammatory nature that occurs in a chronic form. Accompanied by changes in the histomorphology of the skin of the genital organs and the formation of scar tissue.
The main localization of the pathology is in the anogenital area; in men, such lichen occurs on the head of the penis. On other areas of the body, such as the back, arms or abdomen, lichen sclerosus is rare, occurring in about 6-15% of cases. The exact causes of the pathological process are unknown.
There are suggestions about hereditary transmission of the disease. It was found that 15% of patients with this diagnosis have relatives with the same disease.
Some researchers believe that lichen sclerosus may be an autoimmune disorder, where the immune system attacks its own cells and healthy tissue. Lichen sclerosus has also been found to be more common in women with other autoimmune diseases. Such as problems with the thyroid gland (thyroiditis) or diabetes, psoriasis.
Lichen sclerosus is a fairly serious dermatological disease that can lead to phimosis without appropriate treatment. Ringworm can also lead to more serious complications: urination problems, narrowing of the urethral canal, cystitis and other genitourinary diseases.
Long-term lack of treatment leads to the development of severe forms of the disease. This, in turn, can serve as a trigger for the formation of penile cancer.
Main symptoms: whitish spots and nodules (hyperkeratosis), which may coalesce into larger areas (plaques). It is also possible to develop severe itching.
Antibacterial drugs and mycotic agents are usually ineffective. In this case, a consultation with a urologist and determination of an individual treatment regimen is required.
Methods for diagnosing forms of lichen
To make an accurate diagnosis, differential diagnosis of various forms of lichen, including sexually transmitted infections, plays an important role. The first stage of the examination consists of a face-to-face examination of the patient by a dermatologist.
The doctor evaluates the characteristics of the rash, its structure and shape. To confirm the diagnosis, histopathological analysis is prescribed.
The histology of the affected area of the epidermis is based on a microscopic examination of the tissue and allows identifying atypical changes. The doctor can also perform a dermatoscopy; its picture will give a more detailed answer regarding skin lesions due to lichen on the penis. In addition, the study is aimed at identifying atypical changes in skin tissue that are not detectable with the naked eye.
Dermatoscopy is a simple, safe, non-invasive and publicly available examination method. Provides valuable information for the evaluation of epidermal lesions of vague origin.
A more simplified version of diagnosing skin diseases uses a Wood's lamp.
Additionally, a scraping can be taken from the surface of the rash for Giemsa or Tzanck analysis. If lichen is localized on the genitals, a test for STIs is prescribed; it is important to exclude the presence of sexually transmitted diseases. Blood tests for STDs can detect a specific type of pathogen or antibodies to it.
Treatment of various forms of lichen
Treatment tactics depend on the shape and type of skin lesion.
The therapeutic effect is selected by the doctor strictly on an individual basis. The specialist will provide a list indicating the necessary drugs for treatment, patterns of their use and dosage.
Next, the treatment of all forms of genital lichen will be described in more detail.
Treatment of pityriasis versicolor
Treatment of pityriasis versicolor on the penis is carried out using drugs of the mycotic group.
Your doctor may recommend topical antifungal medications. Such as Ketoconazole for oral and topical use.
Oral antifungal medications may cause side effects such as nausea and liver tissue damage. Therefore, medications should be taken strictly as prescribed by the treating doctor.
For patients with extensive damage to the epidermis and frequent relapses, Fluconazole is prescribed 150 mg / every seven days for 2 - 4 weeks.
Treatment of lichen planus (lichen ruber planus)
The following groups of medications are used in the treatment of lichen red:
- Corticosteroid creams or ointments. Reduce the severity of the inflammatory process, speed up recovery
- Vitamin RR. Improves skin condition, participates in cellular reactions
- Antihistamines. Reduce the severity of itching
- Antispasmodic or painkillers. Prescribed if necessary, when itching is accompanied by painful sensations
Therapy for Pityriasis rosea (pityriasis rosea)
Pityriasis rosea usually does not require any specific drug treatment. The rash may go away on its own within 6-8 weeks.
If the patient has unbearable itching, the dermatologist may prescribe antihistamines in the form of tablets or ointments. During the period of rashes, it is not recommended to stay in the sun for a long time and wear tight, synthetic underwear.
Treatment of herpes zoster
Herpes zoster is a viral pathology; antiviral drugs are prescribed to treat the disease. More often they resort to prescribing: Acyclovir, Ciclovir, Valacyclovir, Groprinosin.
Valacyclovir has been reported to have greater overall efficacy than Acyclovir.
Because it causes higher levels of antiviral activity in the blood. Thus, Valaciclovir may be a better alternative drug for patients at increased risk of complications.
Patients should avoid scratching the lesions to reduce the risk of scarring and keep the lesions dry and clean. At the time of therapy, it is necessary to exclude sexual contact to avoid transmission of infection.
Treatment of lichen planus
Lichen pellucida is characterized by a benign course. As a rule, rashes go away on their own and often require only symptomatic therapy.
Vitamin preparations and immunostimulants are prescribed, aimed at strengthening the immune system. As a local treatment, doctors recommend taking baths with a decoction of pine needles. Salicylic acid-based ointments are also prescribed externally.
If all of the above methods do not give the desired result, the doctor prescribes the use of a hormonal ointment, previously diluted in a baby cream.
Treatment of lichen sclerosus
Unfortunately, there is no treatment or way to completely get rid of this form of genital lichen.
However, there are ways to reduce or eliminate the clinical signs of the disease for a more comfortable life:
- Cortisone ointment. Applied to the penis area, it is aimed at reducing the severity of symptoms and to inhibit the development of the disease. Cortisone ointments should be used regularly, initially daily for 4-6 weeks, then once or twice a week even in the absence of symptoms.
Surgery. Most often prescribed to remove scar changes caused by pathology. Surgery can remove scars or adhesions, eliminate phimosis and narrowing of the urethral canal.
The patient will also need regular check-ups and visits to the primary care physician. This will allow you to control the disease and prevent complications.
For any, even minor changes in the skin or color or structure of the rash on the penis, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
If you suspect lichen on the penis, contact the author of this article, a dermatovenerologist in Moscow with many years of experience.
What are the risks for the sick person and his partner?
Whether it is possible to receive lichen as a “gift” through sexual contact with an infected person depends on the state of the person’s immunity, as well as on the type of disease. That is why such dermatoses are called conditionally infectious.
The most unpleasant ones on the list are the girdling and pink subspecies:
- Shingles cannot be contracted through airborne droplets; close contact is required, especially sexual contact. Using the patient's personal belongings also threatens with bad consequences. But these warnings apply only to the stage of the disease when a new rash appears. If the blisters are covered with scabs, the disease automatically becomes non-contagious.
- Due to little knowledge of the mechanism of activation of pityriasis rosea, it is not possible to accurately answer the question of its contagiousness. Therefore, it is assumed that this dermatosis is transmitted infrequently by contact. Doctors still recommend abstaining from sexual activity during illness, because sweat and water procedures are not the best companions for this dermatosis.