Allergy symptoms
In order to correctly understand which allergy medicine is best for your situation, you first need to determine what is happening to you. Allergies are accompanied by a general deterioration of the body's condition.
Most often, the cause is a specific irritant - a substance to which you are allergic. This happens due to the fact that its particles enter your body in the form of a separate food product, ingredient, dust, wool, microbe, and even a simple odor.
Respiratory symptoms include common sneezing, runny nose, and itchy airways. It can be more serious - respiratory wheezing and even bronchial asthma.
Modern and medical allergy medications can stop the reaction even at the stage of respiratory symptoms. Many chronic allergy sufferers keep one or more of these medications at home.
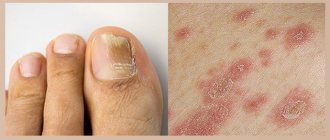
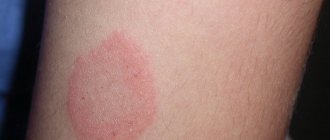
Next come dermatological manifestations. These include skin inflammation with local itching, blisters, rashes and even simple peeling. In addition, even swollen areas on the body can form.
Eye damage occurs due to conjunctivitis. At this time, your eyes may water, a slight, and then severe burning sensation may begin. The area around the eyes begins to swell, and direct rays of light cause pain.
When an allergy affects the stomach, attacks of vomiting, nausea and diarrhea begin. Sometimes the problem reaches the oral cavity, and then the tongue and even lips begin to swell.
Closing this list is anaphylactic shock. Probably the crown of everything that was mentioned earlier. The body's most violent and dangerous reaction to allergies. It can be caused by medications and insect or animal bites. Accompanied by severe vomiting, shortness of breath and even convulsions, which in turn lead to fainting.
Tablets for dermatitis
Systemic remedies for dermatitis are prescribed for moderate severity of the disease. Their components penetrate into the general bloodstream and therefore affect the entire body. The choice of tablets is determined by the cause of inflammatory reactions in the skin. For urticaria, antihistamines are prescribed, for seborrhea - antifungal drugs, and for pyoderma - antibacterial drugs.
Allergic form
To find out which pills to take for allergic dermatosis, you need to find out the cause of its occurrence. Antihistamines for dermatitis in adults are prescribed in cases where inflammation occurs due to contact with irritants. They relieve itching, rashes, peeling, and swelling of tissues. To make you feel better, the following tablets for dermatitis are used:
- Loratadine – for allergies to insect bites, nettle fever and itchy dermatoses;
- Claritin - to relieve manifestations of nettle fever, hay fever;
- Telfast - for the symptomatic treatment of seasonal allergic diseases;
- Exifin - for severe allergic dermatoses affecting the skin on the torso and limbs;
- Zyrtec – for atopic dermatitis in adults, which is accompanied by constant itching and exudative (blistering) rashes.
It is recommended to combine the tablets with local antiallergic agents based on natural ingredients - corn or linseed oil.
Allergic dermatitis does not occur suddenly, it develops within 2-3 weeks after exposure to a strong allergen, and for a weak irritant it can take months or even years.
If the rash spreads quickly, hormonal therapy is used. Corticosteroid tablets are taken in small courses of 3-5 days, which is associated with the risk of side effects. Nettle fever and other forms of allergic disease are treated with the following drugs:
- Triamcinolone;
- Prednisolone;
- Dexazone;
- Fortecortin;
- Megadexane.
They have pronounced anti-inflammatory properties, so they quickly eliminate swelling and redness on the skin.
Infectious origin
Allergic dermatoses of infectious origin are manifested by multiple rashes on the body, peeling, severe itching, and the formation of blisters with clear or purulent liquid. To eliminate them, tablets of etiotropic action are used, which eliminate the cause of inflammation - pathogenic flora. Most often it is represented by fungi or bacteria, so the following drugs for dermatitis are used to destroy them:
- Ampiox - combined antimicrobial tablets that eliminate purulent inflammation of the skin due to bacterial dermatoses;
- Terbinafine is a systemic antifungal drug that eliminates the manifestations of dermatophytosis, trichophytosis and candidiasis;
- Orungal - antifungal tablets for seborrheic dermatitis, candidiasis, pityriasis versicolor and other dermatomycosis;
- Flemoxin is a semi-synthetic antibiotic that relieves purulent inflammation of the skin due to bacterial dermatoses;
- Oxacillin is an antibacterial tablet that destroys staphylococcal infections.
Choice of medicine
Allergic reactions occur quite often, especially in families where there are people predisposed to it. The most important thing is to determine the source of the problem, and as quickly as possible. The more the allergy drags on, the more serious the damage can be done to the body.
People with frequent allergic reactions have skin and body allergy medications in their medicine cabinets that will help with known problems.
The worst thing is when you cannot identify the irritant during an allergy. In this case, you should consult a doctor who will help you find out the cause of your condition.
In addition, he will select safe allergy medications for you for both adults and children.
Drug rash: causes
The appearance of red spots on the skin that occurs after taking a certain medication may have the following reasons:
- Allergic reaction. According to statistics, about 10% of the world's population suffers from an allergic reaction to certain groups of drugs. After the initial dose of the drug, sensitization occurs, after the secondary dose, symptoms of urticaria develop.
- Intolerance to the drug or its individual components. A similar reaction develops in individuals with increased immunological reactivity. For example, aspirin intolerance is quite common among asthma patients.
- Side effects. Taking certain medications can lead to adverse reactions, including various skin rashes. Usually, the manufacturer indicates the possibility of such complications in the annotation for the drug.
Also among the prerequisites for the occurrence of drug-induced urticaria, it is worth highlighting the following:
- Treatment using immunostimulants.
- Complex therapy, which includes the simultaneous use of several medications and their incompatibility with each other.
- The patient has endocrine diseases.
- Diseases characterized by immune hyperactivity - for example, asthma.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Changes in skin microflora caused by taking antibiotics.
- Cross reactions. For example, if a person has previously been diagnosed with a mold allergy, there is a high likelihood of a similar reaction to penicillin and some other antibiotics.
Allergies in children
The situation with children is twofold. A small body experiences allergies more severely than an adult, which is why it is more difficult with children. But there is also a downside - the parent can take the child to the doctor, and he will determine the source of the problem and prescribe treatment.
In this place, it is often more difficult with adults than with children. Many people are confident in the reliability of traditional recipes for allergy medications, and therefore refuse traditional medicine.
This approach has both pros and cons. Yes, there are many folk recipes that can help you during allergies. At the same time, you can just as easily harm yourself.
The worst thing is when parents decide that they can deal with their child’s allergies themselves, but in reality they undermine his health with recipes that were recommended to them by relatives, friends, or read on the Internet.
Treatment of urticaria
Treatment of urticaria caused by medications begins with identifying and stopping the allergen. You can speed up the healing process with the help of enemas and enterosorbents (activated carbon, Polysorb). A diet that excludes alcohol, fatty foods and common food allergens (chocolate, nuts, eggs, red vegetables and fruits) is recommended.
Medications
Patients are prescribed the following drugs:
- Antihistamines (Suprastin, Cetirizine, Loratadine). They block histamine receptors and gradually stop the symptoms of urticaria.
- Antipruritic ointments (Akriderm, Fenistil). These drugs alleviate the patient's condition and reduce the chance of infection of damaged skin.
- Glucocorticosteroids (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone). Prescribed for complications and generalized urticaria.
- Miramistin solution for washing rashes on the mucous membrane.
Folk recipes
Traditional medicine is unable to help with the main cause of drug-induced urticaria, but can relieve symptoms and have an antiseptic effect on the skin. Baths with the following herbs have a calming effect:
- Chamomile. Pour 1-4 tablespoons of dried flowers into 0.5 liters of boiling water, leave in a water bath for 15 minutes and leave for another half hour.
- In succession. Pour 50 g of dry herb into 0.5 liters of hot water, cover with a lid and heat in a water bath for 20-25 minutes. Let it brew for an hour. Infusion and heating can be replaced by cooking for a quarter of an hour over low heat.
- Oak bark. Pour 80-100 g of raw material into 0.5 liters of boiling water and boil for 10 minutes.
Strained infusions can be added to a bath of warm water.
The intake of herbal decoctions internally is agreed with the attending physician . It is possible to use tinctures of valerian and hawthorn (dissolve 15 drops in a glass of water, drink before bedtime), calamus powder (0.5 teaspoon at night, washed down with water), yarrow decoction (1 tablespoon per 200 ml of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes, drink 3 times a day) and other remedies.
Allergies in pregnant women
With pregnant women, everything can be more complicated than with children, in terms of treatment. Any illnesses for pregnant women are undesirable. But the immune system during this period is greatly weakened, because you have to work for two people, and therefore it is difficult to avoid allergic reactions.
In this situation, you need to choose easier treatment options, with oral medications instead of traditional injections. All this should be done under the supervision of your doctor, and only after passing tests.
You cannot delay identifying the problem, because not only the mother, but also the child can suffer.
What to do to prevent the occurrence of drug-induced urticaria?
To protect yourself from developing a rash after taking medications, it is important to increase the body's defenses and not take medications uncontrollably. Among the preventive measures are the following:
- You cannot self-prescribe certain medications (especially antibiotics).
- You must take prescribed medications strictly according to the regimen recommended by your doctor.
- If you have had problems with a rash after taking medications in the past, be sure to tell your doctor.
- In the autumn-winter period, it is advisable to increase the body's defenses in every possible way, since it is the imperfection of the immune system that can lead to the development of a rash. To do this, it is recommended to take multivitamin complexes, eat fresh vegetables and fruits, drink natural juices, eat right and follow a drinking regime, play sports and spend time in the fresh air.
Allergy to medicine
After all, everyone has at least once read the list of side effects and possible reactions of the body to a particular drug. In nine out of ten cases it's just a warning on a piece of paper. It is this tenth patient that is important. Medicines can cause an allergic reaction not only after use, but also before.
It often happens that the simple smell of the medicine is enough to make a person start sneezing or watery. In this case, you need to check him for an allergic reaction from the drug.
In other cases, you have to endure unpleasant manifestations. We are talking about strong drugs that are used for serious problems with internal organs.
What is histamine
Histamine is a mediator that, during allergic reactions, is released from connective tissue and has a negative effect on the organs and systems of the body: skin, respiratory tract, cardiovascular system, digestive tract and others.
Antihistamines are used to suppress free histamine and are divided into 3 groups depending on the receptors they block:
- H1 blockers - this group of drugs is used in the treatment of allergic diseases.
- H2 blockers - indicated for stomach diseases, as they have a positive effect on its secretion.
- H3 blockers - used in the treatment of neurological diseases.
Currently, there are many antihistamines:
- Diphenhydramine Diazolin Suprastin Claritin Kestin Rupafin Loragexal Zirtec Telfast Erius Zodak Parlazin
You may also be interested in:
Photo of allergy medication
Description
The first drugs that block H1-histamine receptors were introduced into clinical practice in the late 40s. They are called antihistamines, because. effectively inhibit the reactions of organs and tissues to histamine. Histamine H1 receptor blockers weaken histamine-induced hypotension and spasms of smooth muscles (bronchi, intestines, uterus), reduce capillary permeability, prevent the development of histamine edema, reduce hyperemia and itching and, thus, prevent the development and facilitate the course of allergic reactions. The term “antihistamine” does not fully reflect the range of pharmacological properties of these drugs, because they also cause a number of other effects. This is partly due to the structural similarity of histamine and other physiologically active substances, such as adrenaline, serotonin, acetylcholine, and dopamine. Therefore, blockers of histamine H1 receptors may, to varying degrees, exhibit the properties of anticholinergics or alpha-blockers (anticholinergics, in turn, may have antihistamine activity). Some antihistamines (diphenhydramine, promethazine, chloropyramine, etc.) have a depressant effect on the central nervous system and enhance the effect of general and local anesthetics and narcotic analgesics. They are used in the treatment of insomnia, parkinsonism, and as antiemetics. Associated pharmacological effects may also be undesirable. For example, sedation, accompanied by lethargy, dizziness, poor coordination of movements and decreased concentration, limits the outpatient use of some antihistamines (diphenhydramine, chloropyramine and other representatives of the first generation), especially in patients whose work requires quick and coordinated mental and physical reactions. The presence of anticholinergic action in most of these drugs causes dry mucous membranes, predisposes to deterioration of vision and urination, and gastrointestinal dysfunction.
First generation drugs are reversible competitive antagonists of H1-histamine receptors. They act quickly and briefly (prescribed up to 4 times a day). Their long-term use often leads to a weakening of therapeutic effectiveness.
Recently, blockers of histamine H1 receptors (antihistamines of the 2nd and 3rd generation) have been created, which are characterized by high selectivity of action on H1 receptors (hifenadine, terfenadine, astemizole, etc.). These drugs have little effect on other mediator systems (cholinergic, etc.), do not pass through the BBB (do not affect the central nervous system) and do not lose activity with long-term use. Many second-generation drugs bind noncompetitively to H1 receptors, and the resulting ligand-receptor complex is characterized by relatively slow dissociation, causing an increase in the duration of the therapeutic effect (prescribed once a day). Biotransformation of most histamine H1 receptor antagonists occurs in the liver with the formation of active metabolites. A number of H1-histamine receptor blockers are active metabolites of known antihistamines (cetirizine is an active metabolite of hydroxyzine, fexofenadine is terfenadine).
First generation
The cheapest first-line drugs were developed by pharmacologists back in the forties of the last century2. They have a number of pronounced side effects:
- Drowsiness (severe);
- Weakness;
- Dizziness;
- Increased blood pressure (significant for people with hypertension);
- Headache;
- Psychomotor impairment.
Tablets are generally taken three times a day, which is not very convenient. However, their price still attracts a huge number of people. To treat severe allergic symptoms, it is better to choose another generation, whose effectiveness will be higher4.