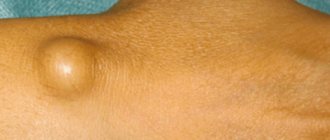
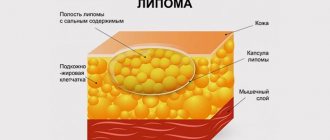
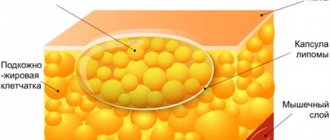
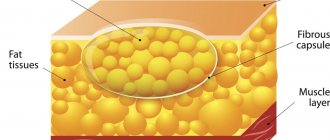
A fatty tissue (lipoma) is a benign formation that consists of a large number of lipid cells. Such a wen can appear in the subcutaneous tissue on any part of the body. However, more often this problem affects the legs, arms, and neck. The tumor itself is painless. But as soon as it begins to increase in size, the person experiences noticeable discomfort, and nerve endings may be affected. In this case, the wen on the neck becomes a real problem.
What is a lipoma on the neck: types of tumor
A lipoma on the neck, or, as it is also popularly called, a wen, is a benign neoplasm that arises under the dermis from fat cells and fibrous tissue. The tumor may hardly increase in size, or it may grow very quickly. This brings psychological and physical discomfort to the owner.
A lump on the neck is a soft tumor that is located under the skin.
Wen is most often located in those areas of the neck where there is a thin lipid layer:
- behind;
- on the throat;
- on the lateral surface;
- under the jaw.
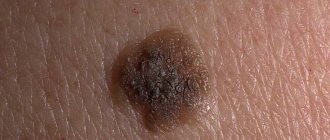
A lipoma on the neck causes discomfort to the owner
Classification of lipomas
Wen of different types may appear on the neck. They are divided into several types depending on the location of manifestation, structural features, their number and the tissues involved.
Types of neoplasms, their characteristic features:
- Soft wen is a classic form of neoplasm. It is a bubble formed from connective tissue directly under the skin. There is fat inside the bladder.
- A spilled, diffuse wen is a classic neoplasm without a membrane.
- Fibrous lipoma on the back of the neck is characterized by the proliferation of connective tissue, which causes the tumor to harden.
- Fossilized, or petrified, wen - is formed after the fat inside the bladder is saturated with calcium salts.
- Cavernous angiolipoma - a wen envelops a blood vessel.
- The perineural formation is a lipoma involving nerve fibers.
- Myolipoma is the presence of muscle fibers in the tumor.
- Ossified, or ossified, wen is diagnosed when the tumor covers the periosteum.
- Adenolipoma is a fatty subcutaneous formation that invades the sweat glands.
- Ring-shaped lipoma, or symmetrical lipomatosis, is a formation that looks like a “collar” around the neck, consisting of adipose tissue. The tumor can create quite a lot of pressure on the neck, making it difficult for a person to speak and breathe. Much more often this disease affects men.
- Bisha's hump, or widow's hump, is a rather massive lipoma that forms on the back of the neck, opposite the seventh vertebra. The mass may impede bleeding through the vertebral artery.
Single wen can appear on the neck from any side: behind, on the sides, in front under the jaw. More dangerous cervical wen of complex structure are distinguished by characteristic localization features. For example, painful lipomatosis (Dercum's disease) is characterized by many separate tumors that form on the head, neck and upper back. Many of these formations cover nerve endings, which causes discomfort in the patient.
What causes a benign tumor to occur?
Modern medicine has not yet established the exact causes of lipoma.
It is assumed that the impetus for tumor formation is:
- endocrine disorders;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- hormonal disorders. Lipoma often develops in women during menopause;
- genetic predisposition;
- metabolic disorder, namely lipolysis. As a result, fat formations under the dermis layer do not disintegrate, but grow;
- alcohol abuse.
Further growth of the wen on the neck occurs under the influence of a combination of factors.
Tumor growth is stimulated by:
- unbalanced diet (excessive consumption of carbohydrates, fatty foods);
- wearing tight clothing, which constantly injures the area of benign formation;
- wrong lifestyle.
Causes
To date, the cause of this pathology is unknown. As a rule, it appears in the thoracic or lumbar region, but in the cervical region it is quite rare. There can be many predisposing factors, but most often they are:
- Age over 30 years.
- Strong physical stress on the spine.
- Oxygen starvation of cells.
- Heredity.
- Increased levels of estrogen in the blood - most often this affects women.
- Climate change.
- Spinal injuries.
- High blood pressure.
Signs of lipoma on the neck
Wen is a benign formation of soft consistency. Lipoma does not affect nearby healthy tissues, but only slightly pushes them apart.
Lipoma is a soft, movable benign tumor
Features of a wen on the neck:
- located in places where a significant number of sebaceous glands accumulate;
- has a soft consistency;
- easily mobile;
- completely painless upon palpation (cause pain only in places of constant contact with clothing);
- grows slowly;
- has a size from 1 to 20 cm.
Multiple subcutaneous lesions (Madelung syndrome) can lead to:
- curvature of the cervical spine;
- compression of blood vessels and nerve trunks;
- dizziness;
- difficulty breathing;
- general deterioration of the condition.
Madelung's neck is observed in men over 40 years of age and is a reason for surgical intervention
Contraindications
Removal of the wen is not possible if there are certain indications. There are two groups of contraindications: absolute and relative.
Absolute contraindications include:
- localization of lipoma near vital vessels and organs;
- concurrent cancer;
- diabetes mellitus at various stages;
- pregnancy;
- immunodeficiency pathologies.
Relative contraindications include:
- diseases caused by the herpes virus;
- acute respiratory inflammation;
- menstruation;
- hypertensive crisis;
- chronic pathologies of internal organs in the acute phase;
- cardiac dysfunction.
Diagnostic measures
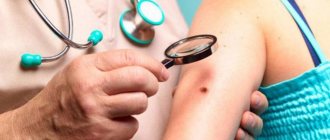
Diseases such as atheroma, cystic and malignant neoplasms look similar to a wen. Therefore, to establish the correct diagnosis, it is extremely important to consult a doctor. An experienced surgeon will issue a conclusion based on the data of the external examination and the absence of pain during palpation.
MRI is the most accurate study that allows you to clearly identify adipose tissue
If necessary, the doctor can clarify the diagnosis using ultrasound, MRI or CT. Additional studies make it possible to obtain valuable information about the size and density of the tumor, the relationship of the tumor with its surrounding tissues.
An ultrasound of the neck will make it possible to determine the structure and size of the tumor
Differential diagnosis is carried out in situations where the doctor doubts the correctness of the decision. To exclude malignant liposarcoma, as well as lymphadenitis, the patient may be prescribed a biopsy followed by histological and cytological examination.
Differential diagnosis
To make an accurate diagnosis, the formation must first be examined by a specialist. The diagnosis is confirmed if the tumor is located in areas of accumulation of adipose tissue, is mobile when palpated, does not cause pain and differs in the density of the tissue itself.
Then, to determine the nature of the formation that has arisen, the doctor takes a puncture. It is done using a thin needle, after which the tissue fragments are studied in the laboratory. If additional diagnostics of such a formation is required, the specialist may prescribe the following measures:
- ultrasound examination of the area of adipose tissue;
- X-ray showing cleared lesions;
- MRI of the tumor;
- electroradiography of soft tissue.
Such diagnostic measures will help to accurately identify the wen.
Treatment tactics
If you find a wen on your neck, do not rush to fight it yourself. Treatment should take place under the supervision of a qualified specialist. Only in this case the risk of complications is minimized. The decision to remove a lipoma should be made solely by a doctor.
If the formation is painless, does not grow into neighboring organs and does not change in size, it can be left untouched throughout life. The main thing is to closely monitor the tumor.
How to get rid of lipoma - video
Surgical removal
Surgical intervention is performed according to strict indications:
- rapid tumor growth;
- the size of a benign formation is more than 5 cm in diameter;
- compression of surrounding tissues, blood vessels, nerve endings;
- the presence of a wen on the leg;
- the appearance of inflammatory processes in the tumor area;
- cosmetic defect.
Surgical removal is the most common and affordable way to eliminate lipoma. Depending on the size of the tumor, the operation is performed under local or general anesthesia. The doctor cuts the skin with a scalpel, scrapes out the capsule with fatty tissue and applies sutures.
The disadvantages of the surgical method include:
- high traumatic rate;
- the appearance of scars that can spoil the aesthetic appearance of the neck;
- risk of bleeding.
Modern gentle methods include radio wave removal and laser treatment. These operations are safe, leave virtually no marks on the body, but have a higher cost.
Drug therapy and traditional methods
Drug therapy in the treatment of wen is ineffective and effective only in the initial stages. After an appropriate examination, the doctor, under ultrasound guidance, injects a substance into the tumor that will help it resolve. When resorting to drug therapy, you should not expect instant results, because the process of fat breakdown lasts from 2 to 3 months.
Traditional medicine and diets will not help get rid of lipoma. On the contrary, on a thinner body the tumors will be even more noticeable. Squeezing and piercing a wen at home is unacceptable!
Options for removing formations
If tumors are detected on the neck, there is no need to try to remove them immediately. To begin with, it is better to go for a consultation with a specialist who will accurately determine the type and origin of the growth and suggest the most effective way to get rid of this problem. Removal of cervical wen can be done through surgery or medication.
Surgical intervention:
- Operation. In this case, a scalpel or laser is used to remove the tumor. The traditional excision method is performed for large fatty tissues. The formation under the skin is removed along with the capsule. After the operation, a scar remains in this place. Most often, the procedure is performed under general anesthesia. Recovery after removal of the growth takes approximately 2 weeks.
- Laser. This operation is effective for removing small tumors. The procedure for removing a neck lipoma is practically painless, without bleeding, is carried out under local anesthesia, and leaves no scars. The patient's recovery period after surgery is up to 10 days.
- Puncture. Instead of dissection, in individual cases a puncture of the growth is made, through which the fat capsule is removed using an endoscope. The process takes place under local anesthesia. Small scars may remain after surgery. The postoperative recovery period is up to 2 weeks.
It is important to know that wound openings that remain after surgery can contribute to further complications, since infectious bacteria cannot be excluded.
Treatment of wen on the neck with medication is prescribed if the size of the formation does not exceed 3 cm in diameter. You can get rid of them without cutting them out. The essence of the process is that an injection with a special drug is made into the cavity of the wen. Under the influence of the medicine, fatty tissues are absorbed. A medium-sized tumor completely disappears after 4 months.
What danger does a lipoma on the neck pose?
A lipoma may not show any signs of growth for a long period of time. However, sometimes as a result of constant external influences, the wen may degenerate into a malignant neoplasm. Therefore, it is extremely important to carry out preventive monitoring of the tumor condition by a specialist 2 times a year. If you experience pain or notice active lipoma growth, consult your doctor immediately. With timely treatment there will be no adverse consequences for the body.
Removing a lipoma surgically will reduce the risk of its recurrence
Localization
Wen can appear in any part of the neck. It develops in areas with a lack of lipid layer.
Locations of pathology:
- Posterior – the tumor is most often detected in this part of the neck. The location of the lipoma makes it difficult to detect in the early stages of development. It is often confused with an enlarged lymph node. It is difficult to monitor its changes, but it must be done.
- In the front - lipomas in this part of the neck cause many symptoms and complications, since important vessels are located here, the esophagus passes through.
- Intermuscular - the wen may contain smooth muscle fibers. It's called myelolipoma.
The least complications are caused by a lump on the back of the neck. Although, if it is of a serious size, it can cause a lot of health problems.
Features of lipoma on the neck in children
As a rule, lipoma on the neck occurs in adults, but sometimes it also forms in children. The exact reasons for the appearance of the growth have not been established, but presumably the decisive factors are:
- genetic predisposition;
- blockage of the sebaceous glands;
- endocrine disorders.
If you find a lump on your child’s neck, you should consult a doctor. The growth of a lipoma can provoke circulatory problems in tissues and cause pressure on blood vessels.
Removing a lipoma yourself is extremely dangerous and should be done by professionals in a medical setting. Elimination of the tumor by surgical method is possible if the child is 5 years old.
Methods for dealing with neck lipoma at home
To cope with lipoma at home, you should pay great attention to strengthening the body. Folk recipes with immunostimulating properties can help with this.
It is very useful to drink rosehip decoction daily. This drink supplies the body with vitamin C, which activates the protective functions of the internal system. To prepare such a drink, you need to take a handful of rose hips, pour two glasses of boiling water over them, and keep the broth over low heat. When the tea is ready, you can add a spoon of honey to it.
It is effective to make compresses that will accelerate blood circulation in the affected area and thereby promote the resorption of the wen. Lotions based on medicinal herbs and plants will provide therapeutic results.
But under no circumstances should you rub the area with the lipoma.
Rehabilitation after lipoma removal
If the operation was small, the patient is sent home after 2-3 hours. When a large tumor has been removed, hospitalization for 1-2 days is possible. The patient should visit the doctor until there is no longer a need for dressings. Most often, it takes about 10 days for the wound surface to fully heal. In some cases, this process occurs faster.
Until the wound has healed, the patient should refrain from physical activity, so as not to provoke the sutures to separate. Superficial tissue fusion will be completely completed after 2 weeks. The wound will shrink inside within 2-3 months; more specific timing depends on the depth of the incision.
After laser removal of fat, a small pit may form in the place where it was previously located. Over time, it completely levels out.
Scars after laser lipoma removal are hardly noticeable. To make the skin look even more aesthetic, you can apply special gels or ointments that promote collagen production, smoothing out the scar.
The difference between a cervical lipoma and a lymph node
Lipoma of the cervical spine presents difficulties for self-diagnosis. The patient is often unable to distinguish a fatty growth from a lymph node. The true nature of a lipomatous tumor is revealed by the following signs:
- soft consistency of the wen contents;
- the ability to change color around the site of formation and the skin on the wen itself;
- the presence of inflammatory processes at a late stage of the disease;
- the wen is able to reach muscles and bone tissue as it grows progressively, putting pressure on nerve fibers and blood vessels;
- pathology can be located in any area of the human body, especially in places of maximum accumulation of fatty cell formations;
- the tumor can pose a risk of transformation into a malignant pathology;
- brings pain when pressed;
- at an early stage it does not benefit the body, and at a later stage it worsens the state of health, causing discomfort and unpleasant sensations in the cervical region.
A lymph node differs from a wen in the following ways:
- Warns of infection or virus entering the body, increasing in size.
- During inflammatory processes, the formation does not exceed the size of a pea.
- The skin is not susceptible to external changes and retains its color.
- Swelling and pigmentation of the lymph node were recorded during inflammatory processes.
- The anatomy of the formation is different: the bulk of the lymph node is lymphoid tissue. The presence of blood vessels, medulla, lymph and reticular fibers was discovered, which explains the density and elasticity of the lymph node.
- These formations are considered exclusively benign and have a beneficial effect on the human body. Being part of the lymphatic system, formations have a cleansing and antiviral effect on the human body. Inflammation of the lymphatic formations indicates the body’s fight against infections and viral diseases.
Arising on the left side of the neck, the wen is easily mistaken for a lymph node, since lymphatic formations most often arise on the sides of the cervical region.