A serious disease such as eczema can develop at any age. It is caused by a number of internal and external factors. Often the pathology occurs against the background of atopic dermatitis or diathesis. Eczema in children usually occurs in a severe form; children from two months to five years old are especially affected. It is important to promptly identify and treat the disease, since it brings a lot of suffering to the baby, and is often complicated by the addition of a secondary infection.
Childhood eczema: 5 types in children, newborns and infants, 9 treatment rules, video
Eczema in a child is a chronic skin disease caused by the influence of internal and external allergens. Young children often develop hypersensitivity to food allergens, especially cow's milk proteins, resulting in eczematous rashes.
According to the characteristics of its course, eczema is divided into the following types:
- dyshidrotic eczema;
- microbial eczema;
- seborrheic eczema;
- true eczema;
- Kaposi's eczema.
All types of eczema occur in children.
Diagnostic methods
If signs of eczema appear, the child should be shown to a pediatrician and dermatologist. Additionally, you may need to consult a neuropsychiatrist, allergist, gastroenterologist, nutritionist, endocrinologist, and other specialized specialists.
To confirm the diagnosis, the following studies are performed:
- general blood analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- fluid histology;
- allergen test.
Often, testing using an elimination diet is prescribed to rule out atopic dermatitis.
Eczema and its symptoms
Despite the wide variety of clinical features, it is possible to identify common features of the course of eczema in most children.
During the inflammatory reaction, blisters form in groups on the child’s skin. In an acute process, against the background of extensive redness of the skin and swelling, papular rashes appear, very quickly turning into blisters.
The blisters open, forming a wound surface on which a bacterial or viral infection quickly develops. After the weeping process decreases, crusts form. The child is bothered by itching.
Initially, foci of the rash may appear on the cheek, near-oral area, gradually moving to other areas of the face. As the process spreads, the lesions increase in size and become symmetrical.
Prevention
To prevent the development of eczema and prevent its relapses, certain recommendations should be followed:
Even during pregnancy, the expectant mother needs to carefully monitor her diet and not overuse food that causes allergies. The same rule applies during breastfeeding.
It is especially important to observe it for those who have a hereditary predisposition to allergies and skin diseases. The baby's clothes and shoes should be comfortable, made from natural fabrics and leather. When carrying out water procedures, it is best to use special hypoallergenic products. You can add chamomile or chamomile infusion to the bath, this will soothe irritation. It is important to provide the child with comfortable living conditions
Feeding and walking should be on schedule. It is advisable to do a daily wet cleaning of the room and ventilate the room.
Since it is much easier to treat eczema at an early stage, you should not wait for consequences. If polymorphic rashes appear, itching, swelling and redness develop, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Dyshidrotic eczema in children
Eczema on the hands of children in most cases is represented by the dyshidrotic type. The affected area is the palms and soles. The disease is observed in predisposed individuals (suffering from allergic diseases) against the background of emotional stress, weakened immunity, and during the period of recovery after a severe infectious disease.
Small bubbles filled with clear liquid form on the side surfaces of the fingers or toes. Subsequently, the number of bubbles increases and spreads to the palms and soles.
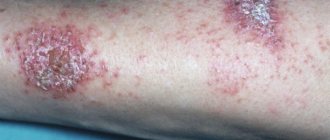
The blisters open to form a weeping surface, which, when dried, forms crusts and peeling, accompanied by burning and itching. Eczema on the legs of a child, represented by a cluster of blisters, also refers to the dyshidrotic form.
Flow options
Depending on the predominant symptoms in children, the following variants of the course of eczema are distinguished:
- intertriginous;
- microbial;
- seborrheic.
In the intertriginous form, blisters and weeping erosions are localized in large skin folds, for example, the buttocks. In this case, it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis of the lesion with candidiasis of the folds.
Microbial eczema is an allergic skin reaction that occurs in predisposed children with concomitant bacterial or fungal infections.
The seborrheic form appears at 2–3 weeks of life. It is accompanied by the formation of a large number of loose, fatty scales on the head. Skin itching is mild and occurs in rare cases. The peeling extends to the ears. The course of this variant is subacute, without pronounced weeping.
Kinds
Depending on the cause of the disease and its main symptoms, eczema can be:
- idiopathic;
- mycotic - with fungal infection;
- seborrheic - a rash covers the head, especially the scalp, ears, face in the area around the lips;
- dyshidrotic - affected palms, hands with deformation of nails and plantar parts of the feet;
- microbial - develops in the area of scratches, injuries, wounds or burns;
- callous (horny);
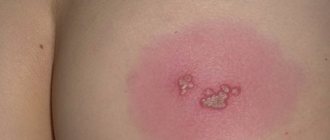
- coin-shaped - in the form of plaques with a diameter of up to 3 cm.
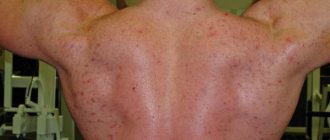
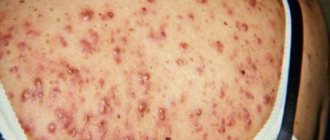
Experts note that eczema in a child is characterized by a large affected area and profuse rashes, as can be seen in the photo below.
Eczema in children: 8 photos, treatment, causes, symptoms, prevention
The occurrence of eczema in children is a common phenomenon; it occurs mainly against the background of diathesis as a dermatological manifestation of allergies. Children of any age, including infants, are susceptible to the disease. In the absence of proper treatment, eczema is dangerous by becoming chronic, which in turn is dangerous by developing negative consequences.
Internal factors:
- Chronic or acute diseases of internal organs.
- Disturbance in the functioning of the endocrine or nervous system.
- Bacterial or viral infections.
- Reduced immunity.
- Hereditary factor.
- Violation of the rules of the first complementary feeding or incorrectly selected artificial nutrition.
- Insufficient child hygiene, improper skin care.
- Hormonal imbalance – during puberty in adolescents.
External factors:
- Mechanical disorders of the skin - wounds/abrasions/diaper rash/wearing tight clothing or synthetic fabrics.
- Contact with chemicals (household chemicals); use of hygiene products containing aggressive components; abuse of antibacterial agents.
- Long-term use of potent medications.
- Burns/frostbite/prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
- Constant contact with the source of the allergy.
Many experts believe that a complicated pregnancy can cause eczema in the child, as well as the presence of serious diseases in the mother - diabetes, vascular and heart diseases, etc.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5fr4vPy7hXQ
The presence of helminths does not cause the development of the disease, but increases the risk of eczema.
Find out more
Treatment of eczema in children with folk remedies
There are many traditional medicine recipes for the treatment of eczema in children, but self-medication is unacceptable, even in relation to herbal medicine, because ignorance of the properties of some components can increase discomfort and harm the child’s health.
Often, alternative medicine recommends using herbs to make decoctions that should be added to water while taking a bath.
Common herbs that can be used are string, chamomile, calendula, hawthorn, motherwort, etc.
Prevention of eczema in children
By following simple preventive tips, treatment will be quick and effective.
When the first signs of eczema appear, you must:
- visit a doctor;
- follow the treatment to the end, without interrupting it even if the symptoms subside.
To prevent the development of the disease:
- follow the rules for caring for the child’s skin and teach personal hygiene;
- use clothes made from natural fabrics;
- air baths – prevention of most childhood skin diseases;
- strengthening or maintaining immunity;
- avoiding frostbite and ailments;
- monitor the quality of food for the child;
- exclude allergens.
Children are more susceptible to various dermatological diseases than adults, so ignoring any symptoms is unacceptable.
Therapy
Before starting treatment, the doctor must find out the cause of eczema in the child. After this, the influence of the stimulus should be eliminated:
- If the baby is breastfed, then the mother is prescribed a diet with restrictions on certain types of foods. For bottle-fed children, it is proposed to review the formulas consumed and, if necessary, switch to other options.
- It is important for preschoolers to stop eating allergenic foods. Exclude fatty broths, chocolate, citrus fruits, spices, and spicy dishes from the menu.
- The baby's clothes should consist of natural fabrics with a minimum number of seams to prevent irritation. Do not wear tight clothing.
- It is imperative to sanitize infectious foci, and if a helminthic infestation is suspected, deworming must be carried out.
Medicines
For treatment, local agents and systemic drugs should be used in combination.
- For weeping eczema, it is recommended to apply lotions several times a day with Burov's liquid or boric acid solution.
- After the affected areas have dried, you should use Skin-Cap, Eplan, boron-naphthalan ointments.
- The most commonly prescribed steroid drugs are Prednisolone ointment or Flucinar. They combine well with non-hormonal drugs.
The selection of medications for internal use is carried out taking into account the age of the baby, the type of eczematous rash and the severity of the process. The doctor takes into account the characteristics of the constitution, the degree of impairment of the immune response, the state of the nervous system, and the presence of endocrine abnormalities.
Groups of drugs that are used for childhood eczema:
- Sedatives. They help calm the child, improve his general condition and normalize sleep. Light remedies are used for this purpose (valerian tablets, Tenoten), but sometimes you have to resort to potent drugs - Meprobamate, Andaxin. VSD and neurotic disorders are relieved with Amizil or Tazepam.
- Antihistamines. They are selected according to age and given in a short course (about 10 days). Usually in this case Diphenhydramine, Tavegil, Suprastin, Fenkarol are prescribed.
- Anti-inflammatory. A 1% sodium salicylate solution is well suited for this purpose.
- Desensitizing therapy. Sodium thiosulfate is used for this; it is used to purify the blood.
- Products containing calcium. Calcium gluconate or glycerophosphate is combined with antiallergic medications.
- The addition of a purulent infection is an indication for the use of antibacterial agents. Broad-spectrum drugs (penicillins or macrolides) are usually recommended. Such treatment is not mandatory and is used only when complications develop.
- A pronounced process requires the use of systemic glucocorticoid therapy. They are prescribed for internal use in a short course (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone tablets).
To relieve especially severe forms, the use of hemosorption and plasmapheresis is sometimes practiced..
Traditional treatment
The use of natural ingredients is effective only at the initial stage of disease development.
- Kalanchoe juice is useful for external use. Soak sterile gauze with fresh juice and apply to damaged skin for five minutes. Repeat daily until signs of improvement appear.
- Grape pulp helps with eczema. The juice is squeezed out of the berries, and the remaining mass is placed in a bandage and applied for two hours. The course is 10 days, after which you should take a break.
- Infusions of string, motherwort, and chamomile are suitable for washing rashes and healing baths. To prepare, pour 3 tablespoons of the selected plant material into a liter of boiling water, keep in a water bath for 5-7 minutes, filter after cooling.
Traditional methods can have not only healing, but also negative effects, so you should not use home remedies without consulting a dermatologist or pediatrician.
Eczema in children: effective treatment and prevention. Eczema in children - causes, symptoms and treatment
class="clearfix">
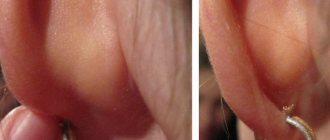
Eczema in children. Photo 1.
Eczema in children. Photo 2.
Eczema in children. Photo 3.
Eczema in children. Photo 4.
Complications and consequences
If you do not use special creams and ointments when treating eczema, there is a risk of deep scarring of the skin. In this case, marks of eczema may remain on the child's body forever.
If you do not take antibacterial drugs in case of microbial eczema, this can lead to infection of the entire body. Provided timely treatment and taking the necessary medications, the risk of complications of the disease and the development of negative consequences will rush to zero.
Treatment methods
Therapeutic treatment of microbial eczema should be based on taking medications, following a strict diet, and personal hygiene.
Therapy is prescribed for each patient individually. The doctor must determine the severity of the disease.
External treatment, ointments
For external treatment, use lotions on the skin with the addition of resorcinol (1% concentration solution), lead water, and an alcohol solution of brilliant green. The most effective medications for topical use are Castellani (fucorcin), which is recommended for use during the acute stage of the disease.
If the vesicles begin to get wet, then it is advisable to use naphthalan, ichthyol ointments, or tar-based preparations. If a bacterial form of eczema is detected, it is recommended to use antibiotic ointments - these are Bactroban, Dettol and Drapolene.
Below is a list of ointments that effectively kill fungi. They are prescribed to patients when diagnosing a fungal cause of the disease:
- exoderil;
- locoid;
- loceryl.
If inflamed lesions quickly spread to healthy skin, then it is advisable to use ointments and sprays with corticosteroids. They quickly relieve symptoms and swelling of the dermis.
General recommendations for patients:
You cannot stay in the sun for a long time, so as not to injure already damaged areas of the dermis; it is important to carefully monitor hygiene; you should not soak dry crusts of eczema for a long time; underwear should be made of natural material; change your diet (add more plant foods and dairy products to your daily diet); do not drink alcoholic beverages; limit drinking water and other liquids; exclude canned food and spicy foods.
Complications and diagnosis
Eczema in young children is dangerous due to its complications. If a herpes infection occurs at the site of the lesion, then Kaposi's eczema is diagnosed, which is so severe that it can lead to the death of the child.
Long-term use of hormonal drugs, especially for internal use, leads to tachyphylaxis, infectious complications, allergic reactions, skin atrophy, and obesity. Stretch marks appear on the skin, the child becomes sluggish, sleeps a lot and develops slowly.
The transition of childhood eczema to neurodermatitis is also dangerous. In this case, the disease does not go away as one grows older, but continues into an adult.
Timely treatment of acute eczema in children can prevent the development of a severe form. But only a specialist should prescribe medications and give recommendations.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor examines the small patient’s skin and asks the parents when and under what circumstances the rash occurred. In the card, he carefully studies the records of previous illnesses and the presence of allergic reactions. Blood and urine should be donated to the laboratory, a culture will be taken from the skin, and a test for skin allergens will be performed . In difficult cases, ultrasound or radiography may be needed.
Age specificity of childhood microbial eczema
Infants are much more likely to experience microbial eczema. Infants between 2 and 6 months are most susceptible to developing dermatitis. The consequence of immature immunity can undoubtedly be called an unformed intestinal microflora, a tendency to food allergies, and therefore a high level of skin sensitization.
Children of the older age group, from one to 6 years old, most often suffer from microbial eczema due to failure to comply with basic cleanliness rules. Among diseases of dirty hands in children, this pathology has become widespread.
The peak incidence of dermatitis occurs during puberty. Hormonal changes and constant fluctuations in the functioning of the endocrine system, as a rule, become the main causes of dermatological diseases. Young girls and boys can prevent eczematous manifestations on the arms and legs by avoiding damage to the epidermis and allergic reactions.
Common causes of development
A common cause of the disease is the immune system inherent during intrauterine development, which predisposes to the occurrence of acute allergic reactions. If the parents have the disease, the risk of the child developing the disease increases.
Most often, allergens that provoke acute manifestations of the disease are:
- plant pollen;
- dust;
- Food;
- washing powders;
- detergents;
- medications.
High sensitivity of the skin increases the risk of developing pathology. Congenital or acquired immunodeficiency can contribute to the appearance of eczema. Severe chronic infectious diseases can provoke this dermatitis.
Artificial feeding increases the risk of this problem in newborns. Breast milk contains substances that help improve immunity.
Often the cause of eczema lies in disorders of the central nervous system or endocrine system. Symptoms occur after suffering stress or an infectious disease.
Eczema on the face of a child
Symptoms of eczema on the face:
- A small area of severe redness appears on the face.
- A rash appears on the cheeks and forehead, which can spread to the eyelids, neck, and nasolabial triangle.
- Severe itching causes discomfort, and the child begins to scratch the wounds, which causes ulcers to form.
Typically, eczema develops due to allergic reactions to animal hair, food, medications, cosmetics, building materials (for example, if the apartment is being renovated) and clothes painted with bright dyes.
Important! Eczema can be caused by insect bites, various fungal and infectious diseases. The process of eczema occurring on the face may spread throughout the body
Treatment in this case will be difficult. Cosmetic defects may occur. Without timely treatment of eczema on the face, ulcers and erosions can become infected
The process of eczema occurring on the face can spread throughout the body. Treatment in this case will be difficult. Cosmetic defects may occur. Without timely treatment of eczema on the face, ulcers and erosions can become infected.
If a rash or sores occurs on any part of the child’s body, it is necessary to consult a specialist for an accurate diagnosis.
Eczema in children: 8 photos, treatment, causes, symptoms, prevention
The occurrence of eczema in children is a common phenomenon; it occurs mainly against the background of diathesis as a dermatological manifestation of allergies. Children of any age, including infants, are susceptible to the disease. In the absence of proper treatment, eczema is dangerous by becoming chronic, which in turn is dangerous by developing negative consequences.
Internal factors:
- Chronic or acute diseases of internal organs.
- Disturbance in the functioning of the endocrine or nervous system.
- Bacterial or viral infections.
- Reduced immunity.
- Hereditary factor.
- Violation of the rules of the first complementary feeding or incorrectly selected artificial nutrition.
- Insufficient child hygiene, improper skin care.
- Hormonal imbalance – during puberty in adolescents.
External factors:
- Mechanical disorders of the skin - wounds/abrasions/diaper rash/wearing tight clothing or synthetic fabrics.
- Contact with chemicals (household chemicals); use of hygiene products containing aggressive components; abuse of antibacterial agents.
- Long-term use of potent medications.
- Burns/frostbite/prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
- Constant contact with the source of the allergy.
Many experts believe that a complicated pregnancy can cause eczema in the child, as well as the presence of serious diseases in the mother - diabetes, vascular and heart diseases, etc.
The presence of helminths does not cause the development of the disease, but increases the risk of eczema.
Find out more
Treatment of eczema in children with folk remedies
There are many traditional medicine recipes for the treatment of eczema in children, but self-medication is unacceptable, even in relation to herbal medicine, because ignorance of the properties of some components can increase discomfort and harm the child’s health.
Often, alternative medicine recommends using herbs to make decoctions that should be added to water while taking a bath.
Common herbs that can be used are string, chamomile, calendula, hawthorn, motherwort, etc.