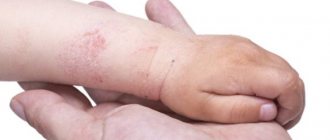
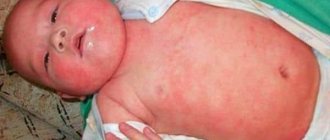
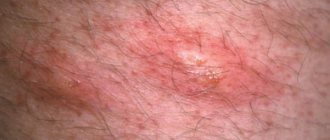
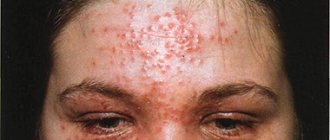
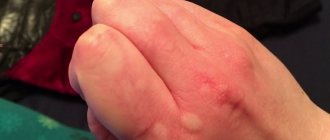
Eczema (from the Greek ekzein - to boil) is an acute or chronic non-contagious inflammatory skin disease of an allergic nature, characterized by a variety of rashes, burning sensation, itching and a tendency to relapse. Eczema or dermatitis is an umbrella term used to describe a group of different symptoms, it can be acute or chronic and occurs as a result of a variety of causes. The medical dictionary lists 21 types of eczema (dermatitis). Clinical signs are similar for all types of eczema and vary in the duration of the rash.
What is eczema
Eczema
(from the Greek ekzein - to boil) is an acute or chronic non-contagious inflammatory skin disease of an allergic nature, characterized by a variety of rashes, burning sensation, itching and a tendency to relapse.
Eczema or dermatitis
is a collective term used to describe a group of different symptoms, it can be acute or chronic and occurs as a result of a variety of causes. The medical dictionary lists 21 types of eczema (dermatitis). Clinical signs are similar for all types of eczema and vary in the duration of the rash.
Stages of eczema
— Acute eczema
manifested by: redness, swelling, rashes in the form of papules, vesicles (vesicles), exudation and soaking of lesions, usually with fuzzy edges, severe itching, peeling.
— Subacute eczema
manifests itself: erythema, rashes in the form of papules, plaques, peeling, itching.
— Chronic eczema
manifested by: erythema, peeling, lichenification, xerosis, hyperkeratosis, itching, hypo- and hyperpigmentation.
Dermatitis
There are a lot of ailments that affect the skin. Dermatitis in a broader sense is skin inflammation. There are two main types of this disease:
- Eczematic (eczema), which is difficult to eliminate if it is already in the body. Eczema and contact dermatitis are transmitted through tactile contact between people.
- Non-eczematic dermatitis can appear through direct contact with a sick person.
In addition, there is a classification based on the causes of diseases.
Types of eczema
Idiopathic or true eczema
It occurs at any age and is characterized by an acute onset with a chronic course and periodic relapses; it is impossible to determine the cause.
Dry eczema or eczematous dermatitis
It is caused by cracks and severe dryness of the skin. Dry eczema is characterized by a slow, chronic course. Exacerbations occur in winter due to low air humidity. Provoking factors include diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, stress and lack of vitamins.
Weeping or wet eczema
Weeping eczema sometimes transforms from the dry form. It manifests itself as extensive inflammation of the skin of a polyetiological nature, occurring as an acute form with areas of weeping with a macerated and exfoliating stratum corneum. May be the result of idiopathic or true eczema.
Atopic eczema or atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory recurrent skin disease accompanied by itching and exudative and/or lichenoid rashes. Most often it occurs in childhood and has characteristic age-related localization features. This eczema is hypersensitive to allergens and nonspecific irritants. Atopic dermatitis is hereditary and is often accompanied by other allergic diseases (bronchial asthma, hay fever). It has a clear seasonal dependence: in winter - exacerbations or relapses, in summer - partial or complete remissions.
Numular eczema
Happens quite often. This eczema has coin-shaped eczematous lesions. The extremities are most often affected, although the back and buttocks may be affected. Numular eczema occurs more often in young people who abuse alcohol, as well as in older men. In addition, it can occur in children suffering from atopic dermatitis, which is difficult to treat.
Allergic dermatitis or contact eczema
Allergic dermatitis is a disease that develops as a response of the patient’s body to exposure to a facultative irritant (i.e., a substance to which normal healthy people do not develop allergic reactions) through direct contact with the skin for even a fairly short time. A localized reaction is manifested by redness, itching, and burning in places where the skin came into contact with the allergen. After treatment (removal of the allergen), the symptoms completely disappear.
Seborrheic eczema or seborrheic dermatitis
It differs from seborrhea in that the initial cause is not a malfunction of the sebaceous glands of the skin, but an inflammatory disease of the skin itself. Seborrheic eczema is characterized by peeling skin and itching. It occurs due to hormonal imbalances, changes in diet and nervous stress.
Asteatotic eczema
It is observed in older people, especially with dry skin. Factors contributing to the development of the disease: low humidity, frequent washing, use of diuretics. More often it develops on the lower extremities in the form of a corrugated skin pattern or small cracks on an erythematous background.
Static (gravity) eczema or varicose eczema
Varicose eczema is most often localized on the lower extremities, accompanied by venous insufficiency (swelling, redness or bluish discoloration of the skin, lack of hair, induration, hemosiderin deposition and ulceration) and the development of hypersensitivity to external antibiotics and antiseptics.
Lichen simplex or neurodermatitis
Neurodermatitis manifests itself as plaques of lichenified eczema that appear as a result of rubbing or scratching as a habit or in response to stress. Often localized on the back of the neck, lower extremities and in the anogenital area.
Dyshidrotic eczema or dyshidrosis
It is localized on the palms, on the inner surface of the fingers and toes - recurrent blisters and blisters appear there, accompanied by severe itching. This form of eczema occurs in atopic eczema, simple contact and allergic dermatitis, but often this form can be idiopathic.
Microbial eczema
Formed in places of chronic foci of pyoderma (around infected wounds, trophic ulcers, fistulas, abrasions, scratches). It is characterized by the formation of blisters with purulent contents and rough, weeping skin.
Mycotic eczema
An allergy to fungal infections affecting the nails and skin develops. Localized on the feet and hands.
Sources
- Maryasis E. D., Dubrovsky A. A., Treatment of dermatoses in children. Publishing house "Book publishing house", 1986, Krasnodar.
- Sokolova N.G., Pediatrician's Handbook. Publishing house "Knizhkin Dom", Moscow, 2012.
- Team of authors (L. A. Aleksanyan, L. S. Biryukova, A. L. Vertkin, A. V. Glazunov, L. M. Gumin, V. G. Moskvichev, E. A. Prokhorovich, S. I. Rapoport , A.V. Topolyansky, Kh.M. Torshkhoeva, L.G. Turbinina), Therapist's Handbook. Eksmo Publishing House, 2008, ISBN 978-5-699-30442-4.
- Handbook of a practical physician, edited by A. I. Vorobyov, Moscow, Medicine, 1992, ISBN 5-225-02641-9.
Symptoms and signs of eczema
There are more than 20 genes associated with the process of eczema. This is why no two patients have the same symptoms or reasons for an outbreak. The most commonly affected areas are the flexor muscle area on the inside of the elbows and knees. Eczema can affect the entire body. The cause of the disease is still unclear, since there is no determining causative factor. But we know that part of the disease is caused by an overreaction of the immune defense system.
It is known that allergy sufferers have an imbalance between T-helper type 1 (Th1) and T-helper type 2 (Th2), which normally should balance each other. People with atopic dermatitis have excess Th2.
Symptoms of eczema:
redness, itching, papules and vesicles. If left untreated, symptoms will progress to the formation of scabs and discharge, peeling and thickening of the skin (lichenification). Pigmentary changes may also occur.
Remission and relapse are possible years later, developing into a chronic condition. Please do not confuse eczema with psoriasis, which has more defined features - silvery scabs.
Ointments
One of the most effective means of treating the disease are ointments. Today there are a significant number of ointments on the market for eczema and dermatitis on the hands, between the fingers and on other areas of the skin. Such medications are divided into hormonal or non-hormonal. The effect of the drug is primarily aimed at relieving redness of the skin. In addition, it relieves the symptoms of the disease that appear under the influence of various factors and causes. Ointments are good for treating eczema and dermatitis in the finger area.
Hormonal ointments are based on steroid hormones. Therefore, when used, their action occurs very quickly and effectively. The inflammatory process in the affected areas of the body is instantly stopped. However, the main negative consequence of such ointments is addiction. When the disease relapses, it is often necessary to change the main medication.
Non-hormonal ointments have shown very good effectiveness in the first stages of illnesses and mild symptoms. The bulk of drugs are based on zinc, tar, and naphthalene oil. Boron-naphthalan ointment, Meshchersky ointment, and so on are very popular.
Causes of eczema
Eczema usually appears in childhood, followed by a period of remission, followed by a relapse in adulthood. As a rule, people with reduced immune function, suffering from allergies, respiratory infections and allergic rhinitis get sick.
The cause of the disease can be anything, it is different for everyone, and usually, until the cause is found, the process of deletion continues. For some, the reason may be clothing, for others, temperature changes, dust and/or dandruff, detergents and even fruit juice.
Don't be afraid of the doctor
As soon as the patient notices dermatitis or eczema, treatment with traditional medicine or over-the-counter drugs usually begins immediately. But only a dermatologist will develop a truly effective course of therapy. Trying to treat dermatitis and eczema on your own can lead to complications.
The main result of visiting a doctor will be the diagnosis of the exact signs of the disease. As mentioned above, for any patient, identifying symptoms and prescribing a course of treatment occurs strictly individually. And this is the only way to effectively get rid of the disease.
A sensitive problem
One of the main problems is itching. Irritation from itching is similar to pain signals - they both affect the same nerve fibers. Scratching relieves itching because it blocks signals transmitted along the nerve to the central nervous system. In eczema, this same scratching leads to thickening of the surface of the skin, as well as damage to the skin and the release of more inflammatory mediators, causing even more itching. And so everything repeats itself - a vicious circle. Some of these mediators are serotonin, prostaglandin, peptides and proteinase - chemicals that are constantly present in the skin.
ethnoscience
Therapy is sometimes carried out with folk remedies for eczema and dermatitis. There are several typical examples:
- For eczema on the extremities, you can apply compresses to the affected areas: 100-200 g of oat straw stalks cut into pieces, brew 1 liter of hot water, hold for two hours, then use the tincture for compresses.
- Eczema and foot fungus are treated using a similar recipe: mix smokeless gunpowder and sour cream in a ratio of 1:0.5. The mixture should be thick enough; this ointment should be applied to the affected areas. Bandage it for three days.
- Traditional medicine also suggests treating eczema with warm compresses.
- For purulent eczema, folk remedies provide excellent support if you alternately apply urine lotions and bandage plantain leaves at night.
Treatment of eczema
Treatment of eczema should be based on the golden rule of dermatology - “treat wet with wet, and treat dry with dry.” Weeping eczema should be treated with lotions - various solutions, decoctions, tinctures, and they must be cooled in order to overcome local inflammation and reduce the activity of inflammatory processes. Dry eczema should be treated with ointments and creams.
Drug treatment of eczema
1. Over the years, many methods have been tried with varying degrees of success. Until recently, resin wraps were used. The other main method was phototherapy - PUVA therapy, which used ultraviolet light and a medicine called Psoralin. The same treatment was prescribed for psoriasis.
2. Topical and systemic corticosteroids have been used for many years despite side effects.
3. Topical antihistamines for itching and to reduce redness.
4. Topical immunomodulators are a new class of drugs that have been used over the past five years with great success. They change the speed of the immune reaction, which in more than 80% of cases helped get rid of all the symptoms of the disease.
5. There is a new subset of biologics that have proven themselves in clinical trials that are more targeted against T cells.
Aesthetic treatment
Diet for eczema
Stress and/or a lack of essential fatty acids (EFAs) have long been considered the main cause of eczema. Stress-reducing treatments combined with ingredients rich in essential fatty acids have been shown to work well in treating many forms of eczema. A lack of gamma-linolenic acid is also associated with this disease. You need to think carefully about fats (at least EFAs) when choosing anti-anxiety, sleep-reducing, or stress-reducing medications. Ingredients such as borage oil, evening primrose oil, rosehip seed oil, ceramides, lecithin, linoleic and linolenic acids are a good source of essential fatty acids.
Essential fatty acids help the skin in every possible way, keeping it soft and elastic. The hydrolipid balance and barrier functions of the skin also depend on EFAs. A constant supply of essential amino acids is essential to keep your skin in optimal condition. This is especially important when the normal functioning of the skin is disrupted, for example, by eczema. In addition, you need to eat foods rich in vitamin E and vitamin A.
A diet for eczema is absolutely necessary. You can tell your patients, casually, that eating plant-based polyunsaturated fats from nuts and seeds and different types of fish will be very beneficial. The idea needs to be presented this way, because you cannot put people on a diet if you do not have special education.
The use of scrubs and chemical peels for eczema is contraindicated, as well as classical massage; only lymphatic drainage massage is possible.
Hardware procedures are not contraindicated, although it is recommended to use the vaporizer with caution. Keep him at a greater distance from the client than usual, and not for as long. Remember that temperature changes can cause aggravation. Avoid using hydrotherapy and the like to treat patients with eczema or other dermatosis; the water should be warm or even cool - not hot.
Moisturizing skin for eczema
Be careful with transepidermal water loss (TEWL) due to the weakening of the epidermis, dehydration of the skin can occur. Therefore, blot the skin, do not wipe it dry. Apply moisturizer immediately (within three minutes). For skin with this condition, it is best to use oil-based products; do not use water-based lotions - they do not help much.
As you know, water does not moisturize the skin as well as water vapor, so wet wraps are more effective than immersion treatments. This is because when wrapping the relative humidity is maintained at almost 100%, therefore no water evaporates from the skin. This, in turn, keeps the skin hydrated. Once you've done this on a cleansed body, all that's left to do is apply an oil-based moisturizer and a broad-spectrum sunscreen. Especially if it contains zinc oxide, which has proven itself in the treatment of wet eczema. Don't let your skin dry out during treatment - use a toner between treatment steps to help rebalance your pH balance.
Skin pH
The normal environment of the skin is acidic (normal skin pH is from 5 to 6). Due to the constant loss of hydration associated with eczema, the skin environment can become alkaline. For this reason, it is not recommended to use soap. Water has an alkaline environment (pH = 8-10), so many find salvation in adding apple cider vinegar to it, which makes the environment neutral or slightly acidic (any vinegar will do, but it is recommended to use apple cider vinegar because it does not smell as strong as the others ). Products for cleansing and toning the skin should contain fruit acids; it is good if the cleanser does not need to be washed off with water, it is milk or cream.
If you are using a bath, jacuzzi, hydrotherapy or something similar, give the water time to "bubble" - this helps reduce the alkalinity to neutral.
Forms of release of medicines
When making prescriptions, the doctor takes into account the characteristic features of a particular dosage form. Ointments that have a fatty texture because they contain appropriate emollients (substances containing fatty acids) are especially effective for deep eczema. However, if the patient has high capillary permeability, it is dangerous to use these drugs - the medicine can enter the blood.
This will not happen with a cream whose texture does not allow it to be absorbed deeper than the epidermis and middle layer. Water-based gels penetrate inside to a minimum; the purpose of these products is to form a film that can protect the body from secondary infection.
Herbs and essential oils for eczema
Anti-inflammatory:
Calendula, chickweed, echinacea, nettle, red clover, essential oil of orange, cypress, jasmine, lavender are some of the possible ones.
Antibacterial:
Black walnut, calendula, chaparrel, hydrastis canadensis, tea tree oil, cloves, lemon balm, thyme.
Sedatives:
Flower and herbal extracts play an important role, especially during stress. Motherwort, valerian, bergamot, peony, radiola rosea, mint, lemon balm, St. John's wort, geranium, passionflower, hawthorn are very effective in combating stress. In addition, you can perform aromatherapy with essential oils.
Estheticians can do a lot for patients with eczema. I hope this information will be a kind of instruction for you on how to care for skin with this disease. Remember that ultimately this is a medical condition and sometimes advice to see a dermatologist is the best you can do for some people.
Possible complications
Due to the disease, the patient's skin becomes dry, microcracks appear on it, through which infection can penetrate. In particular, the risk of infection increases when scratching the inflammation.
The most common complication of eczema is staphylococcosis, in which a high temperature rises and a person feels a general malaise.
In addition to affecting physical health, the symptoms of the disease can affect the patient’s psyche. Due to severe itching, irritability, emotional breakdowns and sleep problems appear.