No one is immune from the human papillomavirus except those who have been vaccinated. Papillomas appear on the skin of the arms, legs, abdomen, and on the tongue and mouth.
The virus settles, and after a while appears on the rectal mucosa, and also forms on the anus.
The incubation period of papilloma in the rectum can vary from a month to as long as six months. Often people are unaware that they are carriers of the virus.
The human papillomavirus covers 80% of the world's population.
HPV in the rectum makes itself felt with unpleasant symptoms
General information, types of growths
Intestinal papillomas are benign neoplasms that arise as a result of the active action of the human papillomavirus (HPV). Every sixth person has HPV, but not everyone exhibits it. Most people are simply carriers of this virus, without even knowing it.
Some are less fortunate and in them HPV manifests itself as growths on the skin and mucous membranes. Infection caused by HPV is highly specific to humans. HPV is a group of viruses that belongs to the papillomavirus family and includes 27 species, 5 genera and more than 600 species.
Main types of growths:
- flat;
- pointed;
- threadlike.
How to distinguish HPV from a polyp?
Many people do not see the difference between a papilloma and a polyp, but it still exists. They have, at first glance, insignificant differences that are not given much importance. These neoplasms have only one common feature - they are benign.
A polyp forms on the mucous membrane of the intestines, colon, rectum and stomach as a result of hormonal disorders, as well as against a background of reduced immunity.
Externally, the polyp looks like a mucous formation on a stalk with a smooth surface, ranging in size from 1 to 5 cm. Polyps have many types and often undergo malignancy.
Papilloma is a benign neoplasm that most often affects the outer part of the rectum, but can also form on the intestinal mucosa as a result of penetration of the human papilloma virus into the body.
Externally, a papilloma looks like a formation that has a wide base with a striated surface, ranging in size from 0.1 to 2 cm. Unlike a polyp, papillomas do not have a wide variety and are less likely to malize.
Types of anal neoplasms
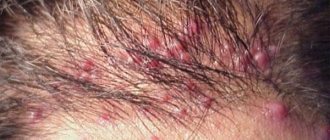
Localization of papillomas can be either in the anus itself or in the anus or rectum. Rarely, tumors appear in the colon and cause long-term constipation. They are divided into several categories depending on the classification criteria.
Thus, anal papillomas are distinguished by number:
- single;
- multiple.
To size:
- small, the size of which is a few millimeters;
- large single;
- large mergers of several growths.
Based on their appearance, growths are divided into:
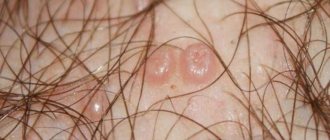
- Genital warts. Small neoplasms supported by a thin stalk. The shape may resemble a comb. Most often flesh-colored or pale pink.
- Tumor-like. The main feature is the swelling that accompanies the growth. In this case, papilloma is more like an inflammatory swelling.
- Papular. Externally, they are very similar to warts, they have a dark color and an uneven surface. They usually grow in the form of small tubercles. Have a flat shape
- Keratotic. The growths are hardened, dark-colored formations.
It is not difficult to diagnose the course of HPV infection in the presence of its external manifestations. However, problems may arise if papillomas are located in the rectum, the examination of which is impossible without the appropriate equipment.
Causes of pathology
Against the background of a decrease in the activity of the body’s immune system, the human papillomavirus is activated, which previously entered the body in the following ways:
- Sexual (the most common route of transmission).
- Transplacental (from mother to child).
- Contact (when touching household appliances, through abrasions and scratches).
- Autoinoculation (self-infection).
Due to the following reasons:
- Promiscuous sex and unprotected sex.
- Presence of bad habits (alcoholism, smoking, drug addiction).
- Presence of inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Emotional stress.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules in the presence of cracks, microtraumas, cuts, which can lead to HPV infection.
- Failure to comply with the diet and balance, excessive consumption of fried, spicy, salty foods.
- Uncontrolled use of potent drugs.
There are 2 opinions, one of them is that papillomatosis is congenital, and the other is acquired.
Prevention
The main preventive measure is barrier contraception, designed to reduce the risk of infection. It is also important to maintain the immune system in good condition, because it is on it that the containment of the virus’s activity depends. To do this, you need to give up bad habits, stick to a healthy diet, and be less exposed to stressful situations. It is also important to maintain good personal hygiene and keep your genitals clean.
Preventive measures include getting tested for HPV every 1-2 years. This will help to detect the penetration of papillomavirus at an early stage and begin timely treatment. If the virus is diagnosed while still in latent form, it will not have time to manifest itself, which prevents the appearance of anal papillomas.
Unfortunately, patients suffering from such a delicate problem are in no hurry to seek medical help. However, it is important to understand that there is no place for embarrassment here, because human health is at stake. The emerging papillomas not only cause discomfort in the anus, but can also lead to serious complications in the form of a malignant tumor. Therefore, qualified treatment is necessary here, which can only be provided by a specialist.
Symptoms
The disease can be asymptomatic for a long time due to the small size of the tumors. Therefore, patients come to us already at an advanced stage of the disease, when symptoms appear.
- Detection of bloody streaks in feces.
- Stool disorders (constipation and diarrhea, which either replace each other or appear separately).
- Discharge of blood after defecation.
- Pain of varying intensity can be either aching or cramping. It increases before the act of defecation, and then subsides.
- Dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, heaviness in the abdomen).
- Anemia occurs as a result of prolonged bleeding (weakness, headache, dizziness).
- Increased body temperature as a result of the development of the inflammatory process.
- When papillomas are localized in the anal area, the patient may be disturbed by the sensation of the presence of a foreign body and increased humidity in the anal area.
- Increased salivation.
Diagnosis of the disease and examination of the intestines
For diagnosis, objective examination data (often uninformative), laboratory and instrumental research methods are used.
Laboratory research methods:
- OAC (decrease in the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin, with inflammation, increase in ESR, leukocytes with a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left).
- Fecal occult blood test.
- Blood chemistry.
- PCR method (HPV detection).
Important!
When neoplasms are detected, it is imperative to do an analysis for HIV infection and syphilis.
Instrumental research methods:
- Colonoscopy is an endoscopic examination method that allows you to evaluate the mucous membrane of the colon using an endoscope.
- Irrigoscopy is an X-ray method for examining the colon by filling it with a barium suspension (contrast agent).
Important!
It is imperative to check with the patient whether there is an allergic reaction to barium.
- Sigmoidoscopy is an endoscopic method for examining the lower part of the sigmoid colon and rectum using a special tube.
- Ultrasound.
- Taking a biopsy for histological examination.
- CT and MRI.
Diagnostic procedures
With progressive symptoms of colon papillomas, the proctologist performs a rectal examination. The method allows you to determine the size and location. To compile a clinical picture, the specialist prescribes more informative methods: ultrasound, CT, urine and stool tests, tests for tumor markers.
Instrumental technologies are similar to each other, but each of them helps to obtain subjective information from each zone:
- Colonoscopy is performed under general anesthesia. The essence of the procedure is to insert a flexible hose with a camera inside.
- Sigmoidoscopy is performed using an endoscope through the anus.
- Anoscopy is not much different from the two previous technologies. The tube is pushed inside, and the area is diagnosed using a tip with a backlight, which opens a full view.
If a tumor is suspected, a tissue sample is taken using a biopsy for histological examination.
Therapy for papillomatosis
In the treatment of intestinal papillomatosis, I distinguish: conservative and surgical treatment.
Conservative treatment
Antiviral drugs that are aimed at suppressing the reproduction of HPV. Immunomodulatory and restorative drugs. As well as symptomatic therapy.
- Isoprinasine is an antiviral and immunomodulatory drug. Take 1000 mg 3 times a day for 2 weeks. After a month's break, you can repeat the course of treatment.
- Groprinosin is an antiviral and immunomodulatory drug. Take 500 mg 3–8 times a day for 14–30 days.
- Genferon is an antiviral and immunomodulatory drug. Available in the form of suppositories. 1 suppository 1 time per day for 10 days.
- Viferon - has high antiviral and immunomodulatory activity. 1 suppository 2 times a day for 5–10 days.
- Panavir is an antiviral and immunomodulatory drug. Taken in 3 doses during the first week with an interval of 2 days, during the second week in 2 doses with an interval of 3 days.
- Likopid is an immunostimulating drug. Take 10 mg once a day for 10 days.
Surgical therapy
The optimal method of treating papillomatosis is still surgical treatment. Methods of surgical treatment:
- Removal of papilloma using laser.
- Electrocoagulation.
- Cryodestruction.
- Radio wave therapy.
- Removing papilloma with a scalpel. The most traumatic method.
Folk remedies and recipes
In some cases, folk therapy has a beneficial effect on the treatment of papillomatosis. They have an immunostimulating, anti-inflammatory effect on the patient's body.
- Enemas with infusion of celandine. Preparation of infusion: pour 50 g of celandine with boiling water (50 ml), leave for 1 hour and strain.
- Baking soda solution. Acts as an antiseptic and disinfectant.
- Baths made from plants such as chamomile, St. John's wort, sage. For papillomas of the anus.
Is it possible to be treated at home and use folk remedies?
Due to the location of condylomas and papillomas, the anus, treatment at home is very difficult. Rarely does anyone get by here without outside help. Yes, and you can detect their presence yourself either with the help of a mirror (and even then, without any certain skill and plasticity, this is how it works out), or only during a medical examination.
Also, if you don’t want to experience the full range of feelings of a “scaled” horse, do not use Feresol and other burning agents. At home, it is recommended to treat formations with gentle patches, gels and suppositories (such as Viferon and others), and then so that the medication does not come into contact with healthy skin and mucous membranes.
Traditional medicine suggests getting rid of misfortunes with potato juice, celandine, rosehip decoction, tinctures of nettle, horsetail or plantain. Decoctions and tinctures are pre-frozen. The affected areas are treated with ice cubes or plant juices several times a day, but not more than 3 times.
Treatment with folk remedies can only be permitted with the permission of the attending physician. In this way, the patient will protect himself from an allergic reaction and the use of incorrect methods that are not suitable for his body.
Features of the treatment of papillomatosis in the rectum
In the treatment of rectal papillomatosis, medicinal, hardware and folk methods are used.
Medicinal method. Removal of papillomas using medications: cryopharm, feresol, wartner cryo, super celandine.
Important!
Medicines for removing papillomas are aggressive, so using them without consulting a doctor can be harmful!
Hardware methods:
- Using a laser.
- Electrocoagulation.
- Cryodestruction.
- Radio wave therapy.
- Surgical intervention (cutting with a scalpel).
Traditional methods were discussed above.