Reasons for development
Papillomas develop when infected with HPV. About 90% of the population is infected with it, many of the people are only carriers.
Important: Infection occurs through household contact, sexual contact, and also due to non-compliance with hygiene rules.
For the occurrence of a neoplasm, contributing factors are required, the main one of which is a decrease in general immunity.
Against this background, HPV infects skin cells and mucous membranes. There are a number of body conditions that can provoke the development of squamous cell papilloma:
- Chronic infectious diseases, allergies. They cause a decrease in immunity and disrupt metabolic processes.
- Skin diseases. They are a damaging factor that creates conditions for the development of papillomas.
- Physical and chemical skin irritants. This can be prolonged exposure to the sun, in a solarium, photochemotherapy, contact with harmful substances in everyday life and at work.
- Hormonal imbalance. Occurs with endocrine diseases, taking hormonal contraceptives, during pregnancy.
- Elderly age. Old people are more likely to develop papillomas due to a decrease in the body's resistance.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle. Bad habits, alcohol, and poor nutrition also reduce resistance and immunity.
- Overwork and stress.
- Heredity.
Therapeutic techniques
Flat papillomas of the cervix, mouth and skin bring a lot of discomfort to a person. That is why most patients have a question: how to get rid of unattractive growths? The most commonly prescribed surgical treatment, the main types of which are:
- low temperature exposure;
- laser destruction;
- electrocoagulation;
- removal of papilloma with a scalpel.
It is often possible to remove large papillomas on the body only with the help of classical surgery. For these purposes, medical scissors or a loop-shaped instrument are used. Treatment of laryngeal papilloma can be carried out in two ways: open surgery and endoscopic intervention. The use of the second method shortens the recovery period and reduces the risk of complications. Growths present on the mucous membranes of the esophagus can be removed in the same way. The material removed during the operation is sent for histological analysis.
If there are papillomas in the area of the eyelids and lips, the attending physician may recommend radio wave destruction. The main advantage of this therapeutic technique is the low risk of injury to the skin and mucous membranes, as well as the penetration of pathogenic microflora. Tissue healing occurs without scar formation. To get rid of papillomas on the neck, various chemicals are used:
- trichloroacetic acid;
- potassium permanganate;
- silver or lead salts;
- hydrogen peroxide solution.
After surgery, treatment of papillomatosis continues. The doctor prescribes antiviral drugs, vitamins and immunostimulants. It is recommended to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, harden the body, and eat right. Is it possible to remove flat papillomas at home, what means are used for this?
Signs and symptoms
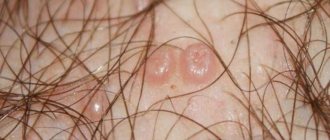
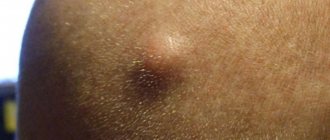
The appearance and symptoms of the development of squamous cell papilloma depend on the location in the body (skin, mucous membrane). It often appears in people of retirement age, and in young people with a decrease in general immunity. It grows slowly and rarely leads to cell degeneration (malignization). It is located on a thin stalk or has a wide base. It can be single or multiple formations occur. The color varies from light pink to dark red on the mucous membranes, and from grayish to dark brown on the skin.
Squamous cell papilloma
The main difference from other similar formations is its structure. Squamous cell papilloma is covered with squamous epithelium, at the base there are blood vessels and connective tissue. In other neoplasms, transitional epithelial cells are found.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Squamous cell papilloma (PP) is a non-cancerous disease prone to malignant transformation that affects the stratified squamous epithelium that covers the body, oral cavity, reproductive and internal organs of a person. The exact reasons why the mechanism of tumor formation is triggered have not yet been determined.
There are two main theories of their development:
- According to the first, PPs are formed in areas of the skin and mucous membranes that are regularly exposed to thermal, mechanical and/or chemical influences. With constant irritation of the epithelium, processes are launched that lead to its growth and, as a result, the formation of tumor-like formations.
- According to the second, PPs appear against the background of HPV activation. For infection, it is sufficient to have microdamages on the skin or mucous membranes and any close contact with the infected person or his personal hygiene products: shaking hands, using a towel, washcloth, kissing.
HPV does not activate immediately after entering the body. The first symptoms of the disease may appear a year or two after infection. And in some people they are absent throughout their lives, since strong immunity inhibits the replication of the virus - its activation is possible only during periods of decreased protective functions of the body.
HPV is oncogenic. It is his fault that the largest number of cancers develops. This virus infects about 60% of the world's population, and it is specifically responsible for the appearance of warts and moles, which can transform into melanoma - an incurable skin cancer.
The connection between HPV and cancer was first established by the German scientist Harald zur Hausen. He determined that about 25% of cancers occur in tandem with viral infections. The most typical example is cervical cancer developing against the background of HPV.
In the near future, Harald zur Hausen assumed, we will... open new connections. This does not mean that all oncological diseases are caused by viruses, but for a certain group of them, the viral factor can be designated as one of the reasons for the development of the tumor process.
Types and differential diagnosis
The structure of papillomas depends on the ratio of squamous epithelial cells, including keratinized ones, and stroma (vessels and connective tissue). There are:
- Keratopapilloma. Characterized by the appearance on areas of the body subject to friction, a contributing factor is skin microtrauma. Often stalked, may come off or cause inflammation and bleeding;
- senile keratomas are characterized by a dense crust that easily separates, leaving a dense bleeding base. Located on closed areas of the body;
- cutaneous horn. It is inactive and dense due to pronounced hyperkeratosis. It is difficult to separate the surface layer;
- fibropapilloma. The surface is wrinkled, located on a thin stalk. Can grow into dermal tissue;
- seborrheic wart. They are quite large, characterized by a dark color and a waxy sheen. May grow;
- vulgar wart. They are numerous and can disappear on their own, and papillomas develop slowly over several years, usually single.
For differential diagnosis, a histological examination or cytological analysis of scrapings can be performed.
Treatment with folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies
Squamous cell papilloma, like all other types of growths, forms mainly in elderly people. Surgical intervention is contraindicated for many of them. In such cases, the attending physician advises turning to traditional medicine. The most recommended means are:
- Freshly squeezed potato juice. Course – 2 months, take 100 ml, 2 times a day;
- Celandine juice. Course – 4 weeks, the affected area is lubricated with liquid several times a day;
- Fresh garlic. The cleaned slice is secured to the growth with an adhesive plaster for 2-3 hours.
Currant leaves, licorice root, nettle, lemongrass, plantain, garlic, beets, and carrots are actively used in the preparation of medicinal infusions. In addition to taking medicinal compounds internally, you can prepare salads and soups from medicinal plants and vegetables.
Squamous cell papilloma of the larynx
Squamous cell papilloma of the larynx occurs in both children and adults. In children, multiple formations on a thin stalk are usually observed, located in the anterior third of the glottis. Papillomas are soft, easily injured, usually light pink. Histological examination reveals inclusions of lymphoid tissue.
Their growth causes difficulty breathing and hoarseness. If they enter the glottis, they can cause spasm, which requires emergency treatment and can lead to death. When removed, there may be relapses, but sometimes they disappear on their own as the child grows older.
In adults, single papillomas occur. They grow slowly and can develop into a malignant tumor. Signs of hyperkeratosis are often observed. Such papillomas are dense and have a whitish tint. Relapses following removal are rare.
Why is the appearance of squamous cell papillomas dangerous?
For a very long time, a squamous wart does not manifest itself at all. However, if a patient with HPV does not go to the doctor on time, then such a skin growth (papilloma) sometimes becomes oncogenic.
According to statistics, HPV squamous cell tumors become cancerous in 7–12% of cases. It is this fact that indicates the danger of the formation of such a growth.
If a squamous cell tumor forms in the nose or mouth, then the person begins to suffer from oxygen starvation, and sometimes this disease leads to sudden death.
When such a wart occurs in the colon, under the influence of feces, the blood festers and becomes contaminated. This can lead to sepsis and subsequent death.
Thus, if a person has squamous cell papilloma anywhere, then he needs to urgently visit his doctor.
Squamous cell papilloma of the esophagus
Papillomas on the esophageal mucosa are more common in men. A predisposing factor for their development is: poor diet (spicy, sour, hot foods), bad habits (smoking, alcohol). They grow slowly and range from 1 mm to several centimeters in diameter, look like tuberous papillae, and may have a thin stalk. Rarely there are formations with increased keratosis. Usually they are single, but multiple ones can also occur. The favorite location is the middle third of the esophagus. With gastroesophageal reflux, they form in the lower third.
Important: Stomach diseases with high acidity (gastritis, ulcers) can cause the formation of papillomas in the esophagus.
In the initial stage, patients have no complaints. As the size increases, there may be discomfort in the esophagus, a feeling of a lump in the throat, increased salivation, dyspeptic symptoms (nausea, belching, vomiting) and pain behind the sternum or in the stomach. Large formations cause difficulty swallowing.
They are diagnosed by esophagoscopy, and can also be seen on contrast radiographs or MRI images.
What does it look like
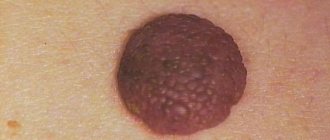
Squamous cell papillomas always rise slightly above the skin. Each growth has a small stalk on which is a wide base. The size of such papillomas usually does not exceed 2-3 cm, the smallest can be only 1 mm.
This type of papilloma often grows on the facial and cervical skin, as well as in the esophagus, mouth, uterine cervix and other human organs. In appearance, such a tumor is a round wart. Its color is flesh or dark brown
When palpated, papillomas do not cause pain. The growths are soft to the touch and do not differ in color from the tissues located nearby. However, the course of the disease can be complicated by the presence of hyperkeratosis.
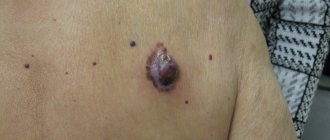
To the touch, squamous cell papillomas can be soft or hard, depending on the type of stroma (base). When injured, such a tumor often becomes oncogenic - a person develops cancer
In this case, keratinization of the skin is observed, and the papilloma itself becomes hard and begins to peel off. At the same time, it changes color to grayish, brown or brown.
PPs also differ in the depth of their location. They can grow deeply, localized under the epithelium, or they can be located on the surface of the skin.
Squamous cell papilloma of the uterus
The appearance of squamous cell papilloma in the uterus is dangerous, since there is an increased risk of its degeneration into a malignant tumor. The HPV strains that most often lead to cancer development have been identified.
The difficulty of detection lies in the fact that with small formations, women do not have any complaints, only later does itching and burning appear in the area of the external genitalia, the nature of the discharge changes, and regional lymph nodes enlarge. Papillomas are most often located on the cervix, adjacent to genital warts and erosion. They may appear and disappear periodically. Usually discovered during a routine examination.
When examining the vagina in speculums, the gynecologist can find them on the cervix, on the vaginal mucosa, and even in the labia area. The cervix looks lumpy and feels unevenly dense. Formations that arise during pregnancy must be treated immediately to avoid infection of the fetus with the human papillomavirus.
During diagnosis, in addition to a gynecological examination, colposcopy, histological and cytological examination are performed. The detection of squamous metaplasia and dysplasia indicates a high risk of cancer. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method allows you to detect the genetic material of the virus and determine its strain.
Important! 15 types of human papillomavirus can cause cervical cancer. Early detection of them using PCR allows you to start treatment on time. Malignization occurs within 2 years of papilloma development in 6% of cases.
Features of papillomas
Places where squamous cell papillomas can occur:
- skin: face, collar part of the neck, lower back, arm area;
- mucous membranes: oral cavity, larynx, esophagus, rectum.
Such formations grow slowly, do not cause any inconvenience and do not pose any particular danger to health. But if you are not careful, they can be injured, which can lead to the risk of papilloma transforming into a malignant tumor.
The main cause of papillomas is papillomavirus (lat. Papillomavirus). You can become infected with the virus in several ways:
- sexual intercourse;
- during childbirth;
- everyday life: touching, shaking hands;
- public places and establishments: swimming pools, saunas, baths, gyms;
- neglect of hygiene rules;
- self-infection: shaving or hair removal.
From the histological side, papilloma is an overgrown squamous epithelium and stroma, with uneven tissue atypia. It has a developed circulatory system in its structure. Papillomas do not appear immediately. The virus can remain in the human body for a long time, and manifests itself only in the presence of certain factors:
- weakening of the immune system;
- elderly age;
- dermatoses;
- allergies;
- infectious diseases;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- harmful environment;
- stressful situations;
- genetic predisposition.
Squamous cell papillomas are classified according to their location on the body:
- Squamous cell papilloma of the skin. Such warts appear in places of increased trauma: the skin of the face, neck, hands. Often it does not cause health problems. The question is more about aesthetic appearance.
- Papilloma of the mucous membranes. The problem here is more significant. The mucous membranes of the mouth, larynx, esophagus, and rectum are often irritated. This can lead to their traumatization and subsequent malignancy. In addition, they cause inconvenience, causing sensations of a foreign object, the inability to perform certain functions, and simply cause discomfort.
Squamous cell papilloma of the rectum
This disease is rare. If papillomas are detected in the perianal area and rectum, women should definitely be examined by a gynecologist.
The formations can be located either in the perianal area or on the rectal mucosa. While they are small, the patient has no complaints. Then itching, discomfort, and possible bleeding appear if they are damaged by feces. Microtraumas cause inflammatory processes and mucus, purulent, fetid discharge, and blood appear.
When diagnosing the disease, an examination of the perianal area and a digital rectal examination are performed. If compactions and dense growths are detected, then retromanoscopy should be performed. Squamous cell papillomas of the rectum are differentiated from condylomas lata in syphilis.
Diagnostic methods
Most neoplasms are diagnosed visually by a dermatologist, ENT doctor or gastroenterologist. If necessary, tests (smears, scrapings) and various studies of the stomach (endoscopy) are prescribed.
Based on the results of the initial diagnosis, a biopsy, tomography and histology may be necessary. Then an oncologist is involved in treatment. But that rarely happens. In general, you should not be afraid of any examinations; timely treatment is the right path to recovery and the key to success.
Types and methods of treatment
Treatment of squamous cell skin papillomas is carried out using conservative methods (antiviral drugs, traditional methods of treatment) or they are removed using various methods. When they form in the esophagus, on the cervix and in the rectum, surgical removal or destruction is indicated. Removal methods:
- Laser removal.
- Electrocoagulation.
- Cryodestruction.
- Radio wave removal.
- Surgical excision.
Important: Treatment for squamous cell papillomas is prescribed by a doctor! You cannot self-medicate, it is dangerous and can lead to malignancy.
General therapy includes: antiviral drugs, immunomodulators, vitamin therapy. They increase the overall resistance of the body. When the cervix is affected, cytotoxic drugs are often prescribed.
Complications of squamous cell papillomas can lead to disability and death, so it is important to consult a doctor when you notice the first symptoms of the disease. The human papillomavirus is active if the body's resistance is reduced. Therefore, a healthy lifestyle is the basis for disease prevention.
Places of manifestation of the disease
A distinctive feature of the various strains of papillomavirus (there are more than 100 genotypes) is their “wide geography” of distribution.
As a result, when a person is infected with HPV, various squamous cell papillomas often grow in the following places:
- on the skin;
- on the lingual surface;
- in the throat;
- in the rectum;
- inside the esophagus;
- on the genitalia.
If such growths appear inside the body, it is very dangerous. After all, they cannot be seen without the use of special devices, as can be done with external tumors.
Population risk subgroups
At risk are elderly and senile people who have a history of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, upper respiratory tract, skin and hormonal disorders. The disease is now diagnosed in people over 40 years of age. Those at risk include those who work in hazardous industries, lead an unhealthy lifestyle, or have a hereditary factor.
Video: “HPV Treatment”
In the presence of squamous cell papilloma of the bladder, in addition to the above symptoms of genital growths, itching and burning, pain when urinating and the presence of blood in the urine are added.
If the tumor is located on the skin, then modern methods are used as treatment. Among the most popular procedures are:
- laser therapy - laser exposure (especially relevant for complex cases, for example, removal of eyelid papilloma);
- cryotherapy – burning with liquid nitrogen;
- electrocoagulation - the use of electric current;
- destruction using a scalpel.
Surgical removal
The method remains one of the most effective to this day.
If the papilloma is located on the pharyngeal mucosa, treatment consists of removing it using medical scissors or a metal loop.
If the tumor affects the laryngeal mucosa, two treatment options are offered:
- extralaryngeal (open surgery);
- intralaryngeal (removal using an endoscope).
The second method of treatment is more effective and, in addition, reduces the number of complications after surgery.
Prevention and recommendations
To avoid contracting papillomavirus, it is enough to follow simple life rules. It is important to remember that HPV is transmitted primarily through sexual contact - through oral, vaginal and anal contact. The consequence is the appearance of papillomas on contact organs.
Attentiveness to the choice of a partner, consistency in relationships, and the use of barrier contraceptives play an important role in protecting against HPV. And taking care of your health, proper nutrition and rest, and maintaining good hygiene will increase resistance not only to the papilloma virus, but also to many other diseases.