HPV type 68 in women is considered one of the most dangerous types of papillomatosis. Why? Because about 70-80% of cases of its diagnosis end in a complication in the form of cervical cancer. In this case, the disease occurs in a latent form, and is detected already at stages 3-4, when the symptoms are clearly expressed, or during a random examination by a gynecologist (periodic, during registration). That is, human papillomavirus type 68 is one of the most predisposed to subsequent transformation into a malignant tumor. It also occurs in men, but more often in women, in the mucous membrane of the genital organs (in particular, the cervix).
What is a virus, what is it?
HPV type 68 is one of the types of DNA human papillomavirus. In total, this virus has more than 100 strains, and the variant under consideration is the 68th genotype (strain). In fact, any HPV is an infection that causes the growth of wart-like formations (papillomas).
Initially, these formations are exclusively benign in nature, but later some of them are capable of transforming into malignant formations, and HPV 68 is the most prominent representative of oncogenic pathogens.
In general, HPV is considered one of the most common infections, and almost 2/3 of all women are infected with it. HPV 68 is much less common, but its degree of danger is very high. All papilloma viruses have an important feature - a normally functioning human immune system can easily cope with them, but they do not die, but go into a latent state, in which they can remain for decades.
Even medicines cannot completely eliminate them, but only “pacify” them. When immunity decreases, latent viruses are activated, causing the growth of papillomas. Thus, most women are carriers of the infection without even knowing it.
general information
Papillomavirus is an infectious lesion of the human body that cannot be completely cured. Doctors account for about 80% of people who are carriers of the human papillomavirus. Papillomavirus is divided into more than 100 strains, which have varying degrees of oncogenicity. HPV genotype 68 is one of the most dangerous infectious diseases, which often provokes cancer. Papillomavirus type 68 without treatment can lead to the following complications:
- development of cervical dysplasia and oncology;
- the appearance of a cancerous tumor in the anus;
- the formation of malignant neoplasms on the head of the penis;
- development of urethral cancer.
Papillomavirus type 68 develops especially actively in cases of weakened protective functions of the immune system.
The problem of infection in women
Infection with HPV 68 occurs from a carrier of the infection when the pathogen enters the mucous membrane, skin or blood of a healthy person. Representing a DNA virus, HPV in the human body is integrated into tissue cells, introducing its genetic information, which causes their abnormal development and the growth of papillomas.
In the vast majority of cases, women are infected with HPV 68 through sexual contact. It should be noted that even barrier contraceptives cannot provide complete protection against infection. Infection occurs with a high degree of probability during any type of sexual contact (traditional and non-traditional sex).
Much less often, infection occurs through contact and household contact. However, there is a risk when using common hygiene products and underwear, or when kissing a sick person. The probability of infection of the fetus during pregnancy or when a child passes through the birth canal of an infected woman is quite high.
Causes and routes of transmission
Human papillomavirus type 68 is transmitted primarily through sexual contact with a virus carrier. Pathogenic microorganisms can be transmitted during vaginal, anal or oral sex. Although doctors say that with the latter, DNA of type 68 papillomavirus is extremely rarely transmitted. Even less common is infection through household contact, in which a healthy person uses personal items of an infected person.
You can become infected with HPV type 68 through sexual contact with a patient or at home, with a weakened immune system.
In order for a pathogenic virus to be able to activate and multiply in the body, a weakened immune system is required, which will not be able to prevent the development of the virus. The main reasons for the development of the disease include:
- leading a promiscuous sexual life;
- presence of bad habits;
- secondary diseases;
- hereditary predisposition;
- unfavorable environmental situation in the region of residence;
- constant worries and stress that weaken the immune system.
How does infection occur?
Women are susceptible to HPV 68 attack in two characteristic circumstances - when the normal immune system cannot cope with an excessive number of invading pathogens or when the immune defense is significantly reduced.
In other cases, infection occurs, but the virus immediately goes into a latent state. Thus, the formation of papillomas can begin during primary infection or with the activation of a previously penetrated infection.
The group at increased risk of developing pathology includes women with the following factors:
- promiscuous sexual intercourse, frequent change of sexual partners;
- gross violation of personal hygiene rules, especially intimate places;
- alcohol abuse and drug use;
- frequent and severe stress, psychological overload;
- physical exhaustion of the body due to excessive physical exertion, lack of proper rest, thoughtless fasting;
- poor environment, harmful emissions in production;
- diseases of an inflammatory and infectious nature that can reduce immunity;
- hereditary predisposition.
The cause of the pathology can be any factor that can reduce immune defense.
Features of DNA virus symptoms
Features of the symptoms of the 68th strain of HPV depend on the stage of development of the disease:
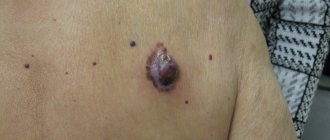
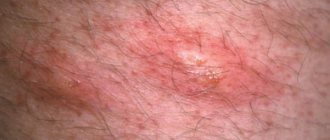
- Stage I (initial) . Symptoms practically do not appear. In rare cases, papilloma may begin to form in the genital area.
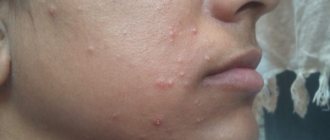
- Stage II . The first characteristic signs appear - spiky growths of a whitish, flesh-colored or pink hue. Typical localization is the genital organ, urethra, anus.
- Stage III (dysplastic) . At this stage, the DNA of the pathogen actively changes the structure of cells. Koilocytosis develops. Many papillomas of different types appear - flat, raised, loose.
- Stage IV . As a result of the rapid progression of papillomas, carcinoma arises. A benign tumor transforms into a malignant neoplasm.
If in the first 2 stages the symptoms are limited to a visible manifestation, i.e. the appearance of warty growths, then at the next stages a pathological picture with the following signs is added:
- gastrointestinal dysfunctions with stool disorders (constipation or diarrhea);
- pain and discomfort during bowel movements;
- increased gas formation, flatulence;
- bloody vaginal discharge not associated with menstruation;
- noticeable weight loss;
- general weakness, fatigue;
- unpleasant odor from the vagina;
- pain during sexual intercourse.
These symptoms indicate the presence of a serious danger of malignancy of the formations. When the first such signs appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Strain danger
Different types of HPV are classified according to their oncogenicity - low, medium and high degree of cancer risk. Type 68 virus is usually classified as highly oncogenic, with the probability of malignancy in women reaching 5-6 percent (this process is not typical for men).
Most often, in the absence of treatment, women develop dysplasia, and then cervical cancer. In addition, complications such as cancer of the rectum, anus, ovary, external genitalia, and urethra are possible. It must be taken into account that illness gives time to take effective measures. Malignancy of papillomas occurs no earlier than 9–12 years after the first manifestations of HPV 68. Timely and adequate treatment can completely eliminate the risk of transformation.
Diagnostic features
Most often, identifying papillomas is not very difficult; a simple examination is sufficient. It is important to determine the strain of the virus and its oncogenicity. For this purpose, a whole range of diagnostic studies is carried out:
- Colonoscopy. Using a special magnifying device (tenfold magnification), the surface of the mucous membrane is examined.
- General blood and urine analysis, venous blood test for HIV and syphilis, genital smear examination.
- PCR analysis. These studies make it possible to determine the type of virus, but the probability of error is also quite high in case of any violations during PCR.
- Digene testing or hybrid capture method. This is a fairly new technique that allows you to analyze the virus on DNA. This way you can give not only a qualitative, but also a quantitative assessment of HPV 68.
- Cytology. Examination of smears makes it possible to assess the degree of cellular destruction.
- Histology. Studying a biopsy taken from the affected area makes it possible to establish with a high probability the risk or onset of cell malignancy. This is the only way to establish oncology.
Comprehensive diagnostics allows you to accurately identify HPV and its type, as well as the stage of the pathology and the risk of complications. When conducting research, the participation of specialists such as a gynecologist, urologist, oncologist, and surgeon will be required. Also find out what indirect signs will help you identify HPV.
Type 68 diagnostic methods
A woman will receive qualified help only by contacting a gynecologist if she has dangerous symptoms. You can’t ignore the body’s alarm bells. The doctor will conduct an external examination of the genital organs, colposcopy (they use a device that magnifies the image of the tissues of internal organs tenfold), and prescribe:
- PCR diagnostics are carried out using enzymes that act on the pathogen in an artificial environment. Under the influence of enzymes, the virus is activated and grows, which is noticeable under a microscope;
- biopsy - performed if a cancerous tumor is suspected. Examine a piece of fabric;
- cytology - a smear is taken from the upper layer of the inner lining of the uterine mucosa. Makes it possible to determine the risk of cancer;
- molecular biological test - consists of studying chemical reactions that make it possible to identify HPV, benign and malignant formations.
Based on the study, the doctor determines treatment tactics. It is prohibited to prescribe medication for type 68 yourself.
An important stage of diagnosis is the examination of a woman for the presence of sexually transmitted infectious diseases.
Viral papilloma is often accompanied by concomitant illnesses: chlamydia, gonorrhea. If there is a concomitant infection, eliminate it, then treat the papilloma virus.
Treatment with medications
Modern medicine cannot completely rid a woman of HPV. Doctors are faced with a real task - to reduce the concentration of the pathogen as much as possible; completely suppress its activity, causing it to fall into a latent state; eliminate symptomatic manifestations, including papillomas; eliminate the risk of complications; Maximize immune defense. to prevent relapse of the disease. Treatment is provided by conservative and surgical methods. The choice of technique is made by the doctor based on reliable diagnostic data.
Drug treatment can be prescribed as an independent way to combat the virus or in addition to surgical treatment as symptomatic and immunostimulating therapy. Basic treatment is based on antiviral agents:
- Allokin-alpha. This is a solution with antiviral and immunostimulating properties. It is administered by intravenous injection.
- Groprinosin . Tablets with a pronounced immunomodulatory effect, allowing you to quickly eliminate papillomas.
- Viferon . Available in the form of an aerosol, ointment and suppository. The drug blocks the activity of HPV 68 and normalizes immune defense.
- Genferon . The drug contains benzocaine, taurine and interferon, which provide effective control against the causative agent of the disease. At the same time, immunity is increased and papillomas are eliminated.
- Isoprinosine . This remedy is aimed at stimulating the immune system.
In addition to drug therapy, folk remedies can provide real help. Symptomatic manifestations can be eliminated using lotions and compresses. Solutions based on garlic and lemon are used as effective remedies. Potato juice has a positive effect.
Therapy
Drug therapy for HPV involves the use of drugs that strengthen the body's immune systems and make the virus less resistant to its protective reactions. The drugs used in treatment include:
- “Novirin”, “Isoprinosine”, “Groprinosin” - help strengthen the immune system and reduce tumors,
- “Allokin alpha” – destroys the viral genome and strengthens the body’s immune forces,
- “Viferon”, “Interferon”, “Genferon” - suppress the processes of spread and reproduction of the virus, help cope with formations.
Surgery is used to remove large or cancerous tumors.
Removal can be done using:
- electrocoagulation,
- laser,
- surgical intervention,
- cryodestruction,
- radio waves
Surgical and other methods
The following technologies are used for surgical removal of papillomas:
- Cryogenic destruction . The growths are destroyed by exposing them to liquid nitrogen. This method cannot be used if you have cervical dysplasia.
- Electrical coagulation . The build-up is captured by a loop through which a high-frequency current is passed. The procedure is dangerous due to postoperative bleeding.
- Radio knife . Exposure to a tumor with a radiofrequency wave is considered one of the most gentle methods of surgical treatment. “Radio knife” allows you to remove papilloma using a non-contact method.
- Laser surgery . This is one of the most effective techniques that eliminates the risk of bleeding, because during exposure to the laser beam, the blood vessels are cauterized, i.e. clogged. This method has one drawback - the need for special equipment, and therefore the operation is performed only in specialized clinics.
- Surgical excision . A full-fledged surgical operation using a scalpel is performed with a large area of damage. You can’t do without it when identifying the real risk of cancer.
The doctor chooses a surgical method of treatment if there is no effect from therapy. The indication for surgery is the increased likelihood of complications.
How and with what to treat?
Drug treatment
Drug therapy can be either auxiliary during surgical removal or independent. Papillomavirus type 68 cannot be completely eliminated. With the help of drug therapy, it is only possible to stop the development of the papilloma virus and strengthen the protective functions of the immune system, which will not allow the disease to progress. The doctor prescribes the following pharmaceutical drugs:
Drug treatment for HPV type 68 is aimed at taking antiviral drugs.
- The Allokin-alpha solution has antiviral and immunomodulatory properties. The drug is administered to the patient inside a vein. When the product enters the bloodstream, the papillomavirus cells are destroyed.
- Taking Groprinosin in tablet form, which has an immunostimulating effect. With the help of such tablets, papillomavirus type 68 is treated mainly by women. After just a few days, the painful symptoms disappear and the tumor gradually shrinks.
- "Viferon" in the form of a spray, suppository or ointment. With the help of the drug it is possible to suppress the reproduction of papillomavirus type 68 and strengthen the immune system.
- Taking Genferon, which has an antiviral effect. The drug contains interferon, taurine and benzocaine, which restore immunity and allow you to quickly get rid of growths on the genitals.
- Taking Isoprinosine tablets, which increase the protective functions of the immune system. Often the drug is indicated for use as a prophylaxis.
Surgery
When a large growth is detected in a patient, which cannot be removed with medications, then prompt elimination of the problem is prescribed. Surgery is used when malignant degeneration of a neoplasm is suspected, which arose due to papillomavirus type 68. You can eliminate a growth on the genitals, anus or urethra in the following ways:
- cryodestruction removal;
- electrocoagulation;
- laser elimination;
- radio wave excision;
- surgical removal.
Cryodestruction
Cryodestructive removal involves exposing the formation in the genital area to liquid nitrogen. The temperature of the product is quite low and freezes the viral cells, which subsequently leads to detachment of the neoplasm. Although this procedure is painless and is used everywhere, even with growths on the face, it has contraindications. Cryodestruction is not allowed for women who have dysplasia. This is due to the fact that when removing nitrogen, the doctor is not able to control the deep penetration of the substance, which threatens relapse and complications.
Electrocoagulation
Recently, the procedure has been used extremely rarely, although it is comparatively cheap. With electrocoagulation, the tumor is removed using high-frequency current. The procedure is quite painful and bleeding is possible during the procedure. After removal, a scar may remain, which is then removed with plastic surgery if it causes discomfort.
Laser removal
With laser therapy, the tumor is eliminated using a laser beam that cauterizes it. The procedure is painful but does not cause bleeding. This is due to the fact that during the removal process the blood vessels are simultaneously cauterized. Doctors recommend using the laser method when removing genital warts, since there are no scars after it and relapses are extremely rare.
Radio wave removal
Radio wave treatment for HPV type 68 is almost always performed once due to the low risk of relapse.
The most gentle method for eliminating type 68 papillomavirus warts is radio wave therapy. The neoplasm is exposed to high-frequency radio waves, which destroy the pathogenic growth. Radio wave removal is non-contact. After radio wave removal, tumors in the genital area rarely reoccur.
Surgical removal
During surgical removal, the surgeon uses a scalpel. This method is the most painful and is followed by a long rehabilitation period. After removal, the patient is left with a large and noticeable scar, which causes discomfort. The only advantage of surgical excision is its affordable price. In addition, surgery is the most effective method for large or malignant tumors.
Prevention of pathology
Any woman should remember that HPV cannot be completely destroyed, and it remains in the body for life. Only preventive measures can avoid infection, as well as the activation of a previously penetrated virus. Preventive examinations with a gynecologist help ensure timely treatment at the earliest stages of the disease, which should be carried out regularly, without waiting for pathological manifestations.
To prevent HPV 68, it is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits, and maintain the immune system at a high level. Sexual intercourse should be carried out using barrier contraceptives. They do not provide a complete guarantee, but they significantly reduce the risk of infection. An important role is given to proper and nutritious nutrition. The body requires vitamin replenishment and essential microelements.
Papillomavirus genotype 68 is not very common, but it poses a great danger to the female body. It has a high degree of oncogenicity, and therefore, when it is detected, effective treatment should be started. Modern techniques make it possible to avoid serious complications during infection, but it is best for the woman herself to follow preventive measures to prevent it.
General characteristics
The presence of HPV type 68 DNA implies the presence in the body of a genotype of the papilloma virus, which poses a great danger due to its increased oncogenicity. There are currently 120 varieties of the virus, each of which poses a real threat to human health. However, not all of them provoke the development of cancer; the category of the most dangerous varieties includes 68, 51, 59, 31, 39, 18 and 16 types of the virus. A characteristic symptom of the presence of the virus are warts and papillomas that appear on various parts of the body.
In the absence of proper treatment, HPV 68 begins to mutate in the body, which ultimately contributes to the development of cancer in the reproductive organs. It is extremely important to undergo examinations on time and detect oncology in the early stages.
Papillomas are present on the body of almost every person and represent a direct source of infection. Such formations may not be noticeable at first glance, however, they can accelerate the entry of the virus into the body during contact infection. Most often, the infection penetrates through minor damage to the skin of the genital organs; the household method of penetration is much less common. Symptoms may not appear for a long time, but during this time serious changes occur in the mucous membranes of the body.
After receiving an immune response, a person has a chance to avoid infection if his immune system is able to cope with the attack of viral cells. With a decrease in protective functions, the first signs of infection begin to appear. Condyloma growths and warts form on the patient’s skin, the appearance of which depends on the category of the virus. Each type of HPV has a high, medium or low level of oncogenicity. Virus number 68 is included in the category of the most serious types, since it poses the greatest danger to women, causing cervical cancer.