What causes the fungus to appear and how is it transmitted?
The following reasons for the development of fungal diseases are identified:
- associated with the external environment - high humidity, hot climate;
- associated with the characteristics of the affected organism - obesity, diabetes, age category, use of antibiotics or oral contraceptives.
The widespread spread of infection is associated with places where it reproduces. Often these are swimming pools, saunas, beaches, and gyms. And these are just the starting points of the entire list. Basic hygiene can protect against infection.
It is important to know that certain conditions are required for the development of mycosis. These include the presence of damage to the nail plate, tight and unventilated shoes, and high humidity.
Changes in, for example, nails can be caused not only by fungi, but also by other diseases. Therefore, if you have the slightest doubt, you should consult a specialist for advice.
To protect yourself from mycotic lesions, you should not forget the possible routes of transmission of infection:
- use of common manicure tools;
- general footwear;
- handshake;
- contacts with the patient;
- use of contaminated items and items.
Violation of sanitary standards in public places can cause the proliferation of microorganisms. And the presence of substrates for fungal growth increases the chances of inhalation infection. Sanitary conditions are key in the development of mycotic lesions.
At an appointment with a dermatovenerologist, the following is carried out:
- Diagnosis and therapy of skin diseases of various origins
- Early diagnosis of skin tumors
- Diagnosis and treatment of sexually transmitted infections
- The latest techniques in the treatment of nail diseases
- Removal of benign skin formations, warts, molluscum contagiosum (cryodestruction, radio wave surgery with the Surgitron apparatus)
To diagnose diseases, traditional and modern methods are used (cytological and histopathological examination, microbiological studies - microscopy, bacteriological and virological methods, molecular genetic studies, immunological methods, allergological methods), as well as instrumental diagnostic techniques that allow timely diagnosis of such diseases:
- Allergic dermatoses (contact dermatitis, allergic dermatitis, eczema, atopic dermatitis, neurodermatitis, urticaria)
- Fungal diseases of nails, smooth skin and scalp
- Bacterial skin infections (pyoderma)
- Erythema infectious, parainfectious, reactive
- Diseases of the sebaceous and sweat glands (acne, hyperhidrosis, recurrent hidradenitis)
- Nail diseases (infectious and non-infectious etiology)
- Hair loss (alopecia)
- Psoriasis
- Dyschromia (vitiligo)
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Herpes, viral warts, genital warts
- Lichen planus
- Scleroderma
- Angiitis
- and many other chronic dermatoses.
For early, accurate and objective diagnosis of skin diseases and skin formations, a non-invasive diagnostic method is used - dermatoscopy: the skin is examined without surgery under magnification in order to clarify the diagnosis and for the early diagnosis of malignant skin tumors.
The Federal Scientific Clinical Center provides comprehensive treatment (including various types of physiotherapeutic procedures) for skin diseases and sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
In the conditions of the physiotherapy department, therapy is carried out in the following areas: electrotherapy (electrophoresis, phonophoresis, magnetotherapy, inhalation therapy, ultraviolet irradiation, thermal procedures, EHF, EHF, ultrasound therapy.); polychrome light therapy; hydrotherapy; cryotherapy; reflexology, etc.
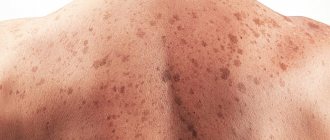
Signs of fungal infections
Although dermatomycosis does not cause acute pain, it still introduces some discomfort into the patient’s life. In order to find out how the fungus manifests itself, you just need to pay attention to some signs - the condition of the skin, nails, hair, internal organs.
If the disease is superficial, then lesions appear on the skin, hair, and nails. This is the result of changes in the stratum corneum of the epidermis. The disease can be provoked by increased sweating, diabetes, and obesity. Deep damage injures internal organs, liver, and brain.
The most vulnerable to infection are the feet, because hands are washed very often during the day. On the legs, the feet and nails may be affected. Fungus can be recognized by rough calluses and an unpleasant odor.
The general picture of the disease is represented by the following symptoms of the fungus:
- irritated skin between the fingers and its peeling;
- itching;
- altered nail structure;
- diaper rash;
- yellow spots on the body.
If such deviations from the norm are present, you should consult a dermatologist. For diagnosis, tests from infected areas of the body will be needed. Biological material is checked under a special lamp to determine the type of pathogen.
Indications and contraindications for taking scrapings for pathogenic skin fungi
The procedure is indicated for the purpose of preventive diagnostics for going to the pool, baths, saunas and other public places. The doctor prescribes a test if mycoses are suspected, in particular due to the patient’s complaints of cracks, rashes, itching and peeling of the epidermis. Using the study, you can detect microorganisms, determine their type and make an accurate diagnosis.
There are no contraindications to the manipulation, since it is painless and is carried out within a few minutes. Taking a scraping does not cause discomfort or other unpleasant sensations.
Indications for analysis
Only a specialist can prescribe scraping for skin fungus. A dermatologist treats fungal infections. If, as a result of examining and interviewing the patient, the doctor notes that the patient has symptoms of the presence of a fungus, then it is recommended to undergo an analysis to determine the type of infection.
A full fungal test is prescribed if the following symptoms are present:
- severe peeling of the surface of the dermis;
- increased sensitivity;
- hypothermia;
- feeling of pain when touched;
- change in skin tone in a limited area;
- itching of epithelial tissues (including the surface of the scalp).
Additional signs for examination are pathological processes:
- loss of eyebrows and eyelashes;
- changes in the shape, density and color of the nail plates;
- frequent damage to the dermis by inflammation (pimples, boils, etc.);
- damage to the mucous membrane by rashes of various types.
Although the analysis is considered practically harmless, the mechanical method of its implementation assumes the presence of contraindications in the form of problems with cell regeneration, the presence of open wounds and ulcers in the infected area, as well as the sensitivity of the dermis to mechanical stress.
Features of the analysis
Skin scraping for mushrooms is a procedure that involves cutting the thin top layer of the epithelium. The resulting cells are sent to a laboratory to be tested for infection or virus. Scraping can be done from different parts of the patient’s body.
The area most often affected by fungal infection is:
- faces;
- stop;
- brushes;
- heads.
The progression of the fungus on any part of the body, including mucous membranes, is possible.
For the most accurate result, you will need to undergo this diagnostic several times. The interval between procedures is 2-3 days. An analysis is also taken at the end of treatment to determine the effectiveness of therapy and the likelihood of residual infection.
Cultural examination
The material is inoculated on standard Sabouraud medium, often with added antibiotics. In the diagnosis of dermatophyte infections, it is customary to add cycloheximide to Sabouraud’s medium, which suppresses the growth of contaminant fungi coming from the air. Ready-made commercial media with added antibiotics and cycloheximide are available. It should be remembered that many non-dermatophyte molds and some Candida species do not grow on medium with cycloheximide, so it is recommended to inoculate on Sabouraud's medium with cycloheximide and on medium without it. Identification of species is usually carried out by microscopic examination of the grown culture or by subculture on selective media (Fig. 2-15). Rice. 2. Culture of the fungus T. rubrum isolated from affected nails. Obtained on Sabouraud medium (left) and corn agar (right) Fig. 3. Culture of the fungus T. mentagrophytes var. interdigitale isolated from affected nails. Obtained on Sabouraud medium. Rice. 4. Culture of the fungus Candida albicans. Obtained on Sabouraud medium. Rice. 5. Culture of the fungus Torulopsis glabrata isolated from affected nails. Obtained on Sabouraud medium. Rice. 6. Culture of the fungus Ulocladium sp., isolated from affected nails. Rice. 7. Micromorphology of Acremonium sp. isolated from affected nails. Rice. 8. Micromorphology of Fusarium sp., isolated from affected nails. Rice. 9. Micromorphology of Scopulariopsis sp. isolated from affected nails. Rice. 10. Micromorphology of Candida albicans isolated from affected nails. Rice. 11. Micromorphology of Altemaria sp. isolated from affected nails. Rice. 12. Micromorphology of Aspergillus sp. isolated from affected nails. Rice. 13. Micromorphology of Ulocladium sp isolated from affected nails. Rice. 14. Micromorphology of Chaetomium sp. isolated from affected nails. Fig. 15. Panel of nutritional compounds for the identification of dermatophytes (on the left - T rubrum culture, on the right - T mentagrophytes var. mterdigitale). From left to right: Sabouraud's medium, Baxter's medium, Christensen's medium, corn agar It should be noted that some molds, including dermatophytes, grow slowly in culture, within 2-3 weeks. Even if all the rules for collecting material are observed, with good equipment of the laboratory and highly qualified personnel, the number of positive results of cultural research is very small. According to foreign literature, the percentage of positive studies does not exceed 50. The percentage of positive results in the best domestic laboratories barely reaches 30. Thus, in 2 out of every 3 cases of onychomycosis, its etiology cannot be established.
How does the procedure work?
To analyze skin scrapings for fungus, specialists use a medical instrument that painlessly and accurately separates particles of the dermis in the most problematic areas.
Most often, a scalpel is used as a procedural instrument. If you need to take a sample from the area of the nail plates, then special needles or scissors can be used.
The procedure follows the following scheme:
- All instruments must be sterilized.
- Material is collected at the border where the infected tissue passes into healthy tissue (in rare cases, from the source).
When the nail plates are affected, cells are taken from the edge of the nail, as well as from under the nail. If damage to the scalp is suspected, then in addition to the epithelial cells, a hair (along with the bulb) is taken for diagnosis.
The process of taking material for analysis is absolutely painless.
Cell processing in the laboratory is carried out:
- dimethyl sulfoxide;
- caustic alkaline substance.
When using demethyl sulfoxide, the reaction of pathological microorganisms begins to be observed after 10 - 15 minutes. Exposure to alkali gives results within a day.
Preparation
In order for the results of the study to be as accurate as possible, it is recommended to prepare for the test. In two days you should not:
- use soap for hygiene procedures;
- apply cosmetics to the affected area;
- apply external medications to problem areas;
- drink alcohol.
Immediately before scraping, the laboratory technician himself cleans the surface of the dermis from dirt and sebaceous secretions with acceptable preparations. The use of antiseptic agents complicates the process of studying the material and can lead to false results.
Tissue particles taken from the patient are placed in a special container and sent to the laboratory. The study of cells is carried out using microscopes, through which the reaction of microorganisms to medicinal inoculation is monitored.
Where to get tested
In public hospitals, testing for fungal infection by skin scraping is most often not carried out. If a specialist gives appropriate recommendations about the need to undergo this diagnostic method, the patient sometimes needs to contact a private laboratory or bacteriological center.
Your doctor can recommend where to get tested. Often hospitals and clinics collaborate with laboratories that provide them with all the information about the diagnostic results of a patient referred from a medical institution.
The patient can independently choose the institution where he will be examined, but one should not trust unofficial clinics and laboratories, since further treatment depends on the accuracy of the results.
Preparation
A scraping of biomaterial is taken if there is a need to identify a parasitic mite and determine its type.
Before carrying out the analysis, it is necessary to carefully prepare for it. To do this, it is recommended to follow some simple rules:
- do not carry out water procedures three days before the start of the examination;
- do not use cosmetics (this includes tonics, creams, gels) for at least seven days;
- Do not consume water or food if blood is being drawn.
It is worth noting that ultraviolet rays have a negative effect on the tick, so during the daytime it tries to hide as deep as possible in the layers of the epidermis.
The activity of the parasite is noted in the evening and at night, as evidenced by its presence on the surface of the skin.
Considering these features, it is recommended to take scrapings for demodex in the evening, no earlier than six to seven hours. When taking an analysis during the day, the results may be unreliable.