Staphylococcus aureus is an extremely dangerous spherical bacterium that can exist in the environment in a stationary form, and in the presence of certain climatic conditions, acquire volatile properties, moving along with air masses. Staphylococcus causes inflammatory diseases of the skin and all organs in adults and children. The microorganism received the name “golden” because when it comes into contact with a nutrient medium, in particular, one that has a protein base, it begins to emit a yellow glow. This effect can be observed in the laboratory using a microscope if bacteria are inoculated onto the material being studied.
Staphylococcus is found on almost all surfaces of environmental objects. If you carry out a sanitary inspection of the apartment, the bacteria can be sown on household items, children's toys, medical instruments, mucous membranes of the oral cavity and skin. Moreover, pathogenic microorganisms can be detected not only in a sick person, but even in those people who do not experience obvious symptoms of an infectious disease. Cases have been repeatedly recorded where harmful bacteria were sown even in mother's milk, which was a source of infection for the child in the first days of his independent life.
What it is
Staphylococcus aureus (lat. Staphylococcus aureus) is a bacterium that looks like a small ball. Approximately 2 out of 10 people are carriers of this infection. It can be in the nose, throat, genitals, or skin.
Enters the body by contact and airborne droplets. You can become infected in places where large numbers of people gather.
The main problem is that the bacterium produces a special toxin that poisons skin cells.
A completely healthy person has a powerful immune system that protects him from pathogenic bacteria. But when it weakens due to certain factors, a person can easily become infected with it.
How is staphylococcus treated?
Preventive sanitation is a very effective measure that is recommended for all carriers of staphylococcus to take regularly. Employees of children's educational and medical institutions take nasal swabs twice a year, and if the result is positive, sanitation is carried out, and then the analysis is taken again, trying to achieve the complete absence of staphylococcus in the upper respiratory tract. This is very important, because this is the only way to protect against the spread of the pathogen by airborne droplets.
If you or your child annually experience relapses of sore throat, furunculosis and other purulent-inflammatory diseases, the cause of which (according to test results, and not based on your guesses) is staphylococcus, it is worth replenishing your home medicine cabinet with means for local sanitation. With the help of these drugs, gargling, nasal instillation, placing cotton swabs in the nasal passages, irrigation or douching of the genital tract, wiping and lubricating the skin or mucous membranes, depending on the location of the carrier, are performed. For each case, you need to select the appropriate version of the drug and strictly adhere to the instructions.
Here is a list of all effective solutions and ointments against staphylococcus:
Oil solution of retinol acetate (vitamin A);
Staphylococcus can be the cause of many health problems - acne on the face appears very often in people who suffer from the disease caused by it.
If this disease is the cause of acne, it is worth knowing what it is and how to get rid of it, returning the skin to a healthy appearance.
Causes
The main reasons for how it is transmitted:
- deterioration of the body's protective properties due to frequent stressful situations, vitamin deficiency, use of antibiotics, side effects from certain medications;
- incorrect compliance with sanitary standards in the presence of open wounds on the body;
- eating vegetables and fruits that have been poorly processed;
- presence of chronic diseases.
The main problem with contracting this infection is that it is very difficult to treat.
Where can you get infected with Staphylococcus aureus?
Very often, this infection can be contracted from person to person in a hospital. Staphylococcus aureus enters the body both by eating food and by airborne droplets.
Infection occurs primarily through the skin, digestive tract, and respiratory tract. Bacteria spread throughout the body along with the bloodstream and affect other vital organs, such as the lungs, bones, heart, and brain.
Factors that provoke the disease
Unfortunately, not a single person has a chance to avoid the occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus. The problem also lies in the fact that microorganisms are capable of producing a special enzyme called coagulase. It is he who helps protect staphylococcus from the body's natural defenses.
There are several factors that significantly increase the chance of becoming infected with Staphylococcus aureus:
- drug use by injection;
- the presence of chronic diseases, including diabetes mellitus, circulatory disorders;
- weakened immunity in young children and older adults;
- use of medications that must be used intravenously;
- visiting places with large crowds of people (for example, a beauty salon, hospital, subway).
Traditional recipes for treating infection
How to treat? Staphylococcus aureus can be eliminated using traditional methods of treatment. You can cope with the infection with the help of juices, decoctions, and ointments. Treatment can act both to eliminate the cause of the disease and to strengthen the immune system.
To prevent the occurrence of this disease in young children, it is necessary to follow the rules of hygiene.
It is necessary to treat children's toys with antiseptic drugs. As soon as the mother begins to add some fruits to the child’s diet, the child’s body will be replenished with microelements and vitamins.
When staphylococcus appears on the skin, it is recommended to use herbs such as calendula, chamomile, St. John's wort, yarrow . They are used in the form of lotions and compresses. It helps to eliminate the infection in the initial stages of infection by treating manifestations with Fukortsin or Zelenka .
Nutrition
Fruits and berries are very beneficial for the body. They contain a large amount of vitamins necessary for the body. For example, black currant, apricot, rose hips.
Black currants contain a large amount of vitamins. It is recommended to use them to prevent the occurrence of disease and enhance the protective properties of the body.
Eating apricot promotes faster regeneration of skin cells. It helps increase vitality and strengthen the immune system.
Rosehip is a real Klondike of vitamins. It is recommended to be consumed as tea. It can even be used in autumn and winter as a prevention and treatment of colds.
Phytotherapy
You can eliminate general malaise and fever by taking decoctions and infusions.
- St. John's wort infusion . You need to take 1 tablespoon of the herb and add hot boiled water. Leave to infuse for an hour. You can take half a glass before eating.
- Infusion of burdock and comfrey leaves . You need to take 25 grams of burdock and comfrey leaves, pour a glass of hot boiled water. Take a glass before eating.
Staphylococcus aureus infection routes
The bacterium in question lives on the surface of the epidermis, mucous membranes, household items, medical equipment and even food. At the same time, Staphylococcus aureus is not always dangerous; the reasons for its active reproduction and toxic effect on the skin are a decrease in the activity of the immune system. A healthy person will not become infected with anything upon contact with a microbe.
Routes of transmission of the bacterium:
- airborne;
- direct contact with the carrier;
- consuming contaminated food or drinks;
- wounds, cuts, scratches;
- medical manipulations.
Staphylococcus - diagnosis
The described bacterium provokes symptoms similar to infection with streptococcus. To differentiate and develop the correct treatment regimen, an analysis for Staphylococcus aureus is necessary. When making a diagnosis, the following methods are used:
- coagulase test;
- scraping the epidermis with subsequent sowing of the resulting biological material on a nutrient medium;
- Vidal agglutination;
- Phagotyping.
In case of complicated infection by microbes and penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the deep layers of the dermis, additional tests are prescribed:
- blood;
- urine;
- feces;
- smears from mucous membranes.
How does staphylococcus appear on the skin?
Infection with the described pathogenic microorganism has several similar manifestations. What staphylococcus looks like on the skin depends on the location of the bacterial inflammation, its intensity and the state of the person’s immune system. The introduction of microbes into the epidermal integument is always accompanied by:
- suppuration;
- swelling of nearby tissues;
- pain syndrome;
- hyperemia.
The main symptom that provokes staphylococcus is a rash on the skin. They can take several forms:
- blisters (vesicles with exudate);
- acne;
- boils;
- extensive red spots (erysipelas);
- carbuncles;
- felon;
- phlegmon;
- pustules;
- abscesses and others.
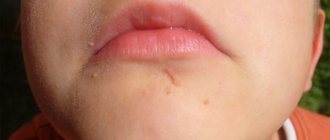
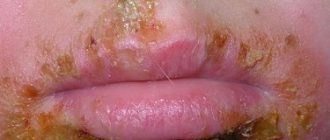
Staphylococcus aureus on the face
Infection with this microbe in the specified area is accompanied by a rapidly spreading rash. Staphylococcus aureus on the skin of the face causes a large number of acne. First, deep, painful inflammations form, which look like bright red bumps with severe swelling of the surrounding tissues. Signs of staphylococcus progress rapidly, and a white, purulent head appears in the center of such pimples. Over time, it turns yellow and opens, leaving a pit-shaped scar at the site of inflammation.
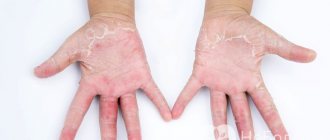
Staphylococcus on the skin of the hands
The main symptom of bacterial infection in this area is felon. Inflammation affects the fingers and periungual ridges and is often a consequence of a carelessly performed manicure. Staphylococcus aureus on the skin of the hands is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- accumulation of pus in the dermal layer;
- pronounced redness of the inflamed tissue;
- strong pain;
- twitching sensation in the affected area;
- swelling and swelling of the skin;
- change in nail color.
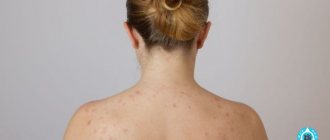
Staphylococcus on the body
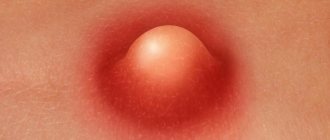
The most common form of infection is a purulent rash. It can form on any part of the body, but is more common in the upper half of the body (chest, back, abdomen). Staphylococcus on the skin in this case looks like a cluster of deep red pimples with white heads in the center. When pressing on such elements, intense pain is felt.
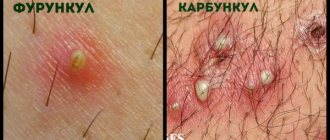
Cutaneous staphylococcus on the body can have other forms. A more severe type of inflammatory process is a boil (boil). It represents severe suppuration of the sebaceous gland or hair follicle. In the center of the abscess there is a deep purulent core. If it is not completely removed, bacteria will penetrate and damage the surrounding tissue.
Another type of staphylococcal infection is erysipelas. It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of a large red spot on the skin;
- swelling of inflamed tissues;
- local increase in body temperature;
- painful sensations;
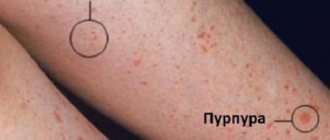
- small pinpoint hemorrhages at the site of the lesion;
- sometimes the presence of translucent blisters with a purulent mass on the epidermis.
Features of the disease
The most pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus has its own characteristics in different groups of people, which are important to know about. Although in general the treatment regimen looks approximately the same, doctors must take into account the points listed below.
Most often, staphylococcus begins to manifest itself when the immune system is weakened or exacerbation of existing chronic diseases. Women typically experience an increase in acne due to staphylococcus before menstruation. During this period, the face can literally become covered with them, and from days 5-7 of the cycle the number of rashes decreases.
Provoking factors that can act as a trigger and cause the appearance of staphylococcal acne on the skin are also:
- severe hypothermia, colds, ARVI;
- skin trauma, including during shaving;
- autoimmune and oncological diseases, HIV;
- severe hormonal imbalance;
- increased sweating and oily skin;
- abuse or use of someone else's decorative cosmetics;
- failure to comply with basic rules of personal hygiene.
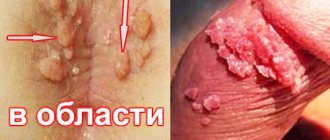
Most often, acne caused by staphylococcus appears on the face. But often the hairy part of the chest, the area around the nipples, armpits, back, and delicate intimate area are affected.
For them, Staphylococcus aureus is especially dangerous, since newborns do not yet have a strong immune system. They may not have the characteristic small purulent staphylococcal acne, but one of its other forms will appear:
- Richter's disease. The infection affects large areas of the epidermis with its subsequent detachment. Moreover, this form of the disease is caused by a certain type of toxin - exfoliatin, which the baby is not yet able to cope with on his own.
- Pemphigus of newborns. Externally it has some similarities with chickenpox. It is also characterized by the formation of many fluid-filled bubbles. But when they burst, inflamed purulent wounds form in their place. With this form, the risk of sepsis is very high.
Moreover, a baby can become infected with the bacteria in the womb, but more often this happens during childbirth due to the negligence of staff or failure to maintain sterility in a medical institution and especially in the delivery room.
Sycosis – this type of disease most often occurs in men. It has a clearly defined localization - around the mouth, on the chin and in the cheek area - exactly where stubble is usually shaved. Sometimes the infection spreads to the scalp.
Purulent inflammation affects the hair follicles. This can lead to their death and the development of alopecia. Unfortunately, in this case one begins to suspect the presence of staphylococcus quite late, when the disease is already rapidly progressing. At this stage, it is difficult to treat and often relapses.
What is the disease
Staphylococcal infection is the infection of the body with Staphylococcus microbes. These can be both mild and complex forms of pathological processes.
During their life, microorganisms produce large amounts of enzymes that are toxic to the body. More often this affects the condition of the skin, less often the functioning of the nervous system.
These microbes are highly resistant to environmental influences and antibiotics.
Symptoms
The symptoms of cutaneous staphylococcus depend on its location and the state of the immune system. In some cases, symptoms may vary, and it is extremely difficult to determine their nature.
| Symptom | Characteristic |
| Pyoderma | It is more common in newborns due to lack of normal care. Manifests itself in the form of small purulent blisters. When they burst, pus flows out and affects adjacent, healthy tissue. This condition is accompanied by deterioration of health and increased body temperature. |
| Furunculosis | The most common symptom. It develops due to damage to the skin by a microorganism that provokes inflammation and tissue necrosis. The most dangerous boils are in the neck and face. |
| Felon | Inflammation of the periungual fold, affecting the nail plate and nearby tissues. Due to the inflammatory process, it is characterized by redness, fever, and pain. When the inflamed area is opened, pus will begin to flow out of it. It can spread to other fingers and penetrate deep into the skin. |
| Phlegmon | Accompanied by severe swelling and redness of the inflamed area. Body temperature rises and health worsens. In advanced stages it causes necrosis. |
| Erysipelas | The most serious symptom. Accompanied by high body temperature, nausea, and vomiting. Typically, inflammatory processes occur on the legs, are red, hot to the touch, and have miniature rashes. |
Symptoms and signs of infection
Symptoms of infection in the face:
- Staphylococcus bacteria cause redness and swelling,
- increased temperature in the affected area,
- pores are enlarged and look larger, skin texture resembles orange peel (cellulite),
- areas of the face affected by staph infection are enlarged and painful to the touch,
- the patient experiences itching on the swollen skin,
- cervical lymph nodes are sensitive to touch,
- Some patients with staph infections on the face have a sensitive, swollen tongue,
- A bulla (blister) often appears on the reddened area and red streaks are visible that extend from the affected area.
Of the 30 strains of staphylococcus, only three lead to disease. The most dangerous are considered golden, epidermal, saprophytic.
Each type of staphylococcal disease is distinguished by the presence of characteristic signs:
- folliculitis is an inflammation deep in the skin in the area of hair follicles, accompanied by reddening of ulcers and pustules with yellow-green discharge,
- boil is an inflammatory process that is accompanied by the appearance of pus in the cavities of the skin, sometimes multiple foci appear, which indicates the presence of furunculosis,
- carbuncle-funnel with pus inside, the skin becomes bluish, nausea and vomiting begins, weakness and loss of consciousness are possible, delay threatens with an abscess of the soft tissues of the face, the development of osteomyelitis,
- impetigo - yellow (red) rashes in the form of conflicts (bubbles), bumps, blisters leaking out,
- Hidradenitis is a disease accompanied by an inflammatory process in the area of the sweat glands on the face, suppuration in the form of pimples appears on the surface of the skin, swelling and pain appear.
Is a staph infection on the skin contagious?
This type of microorganism is always present on human skin. In case of any violation of the integrity of the skin, it penetrates into the blood and becomes the cause of the development of inflammatory processes.
You can become infected:
- using non-sterile medical instruments;
- eating dirty, unprocessed food;
- by airborne droplets;
- by household means in case of non-compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- sexually.
A weakened immune system is the main cause of infection.
Are they dangerous?
Can acne cause other health problems?
Abscesses that appear on the body due to a staphylococcal infection are very dangerous, and in extremely severe cases can lead to the most dire consequences.
- The infection can enter the bloodstream and cause infection.
- The greatest danger is posed by ulcers located on the head, face and especially in the area of the nasolabial triangle. This is due to the proximity of the brain, infection of the tissues of which can even lead to death.
Therefore, under no circumstances should you squeeze out such pimples (and with subcutaneous pimples, this is also useless, since they do not have a duct outward, and the action itself causes intense pain).
Staphylococcal infection on the face and head
The danger of this infection lies in its resistance to antiseptic and antimicrobial drugs. The infection can affect both children and adults. Staphylococci can affect any organs, causing inflammatory processes.
Purulent lesions form on the skin; due to lack of treatment, they spread to nearby areas and infect them.
The bacterium can cause blood poisoning, which leads to the development of serious pathologies. People with weakened immune systems are most susceptible to infection; the body is unable to independently resist the microorganism.
Description of the disease
Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium that can cause a lot of harm to the body.
Together with the blood, the infection spreads throughout the body, affecting the internal organs. This bacterium lives on mucous membranes, such as the mouth.
If staphylococcus begins to actively multiply, it will cause serious diseases.
Dysbacteriosis, blood poisoning, sore throat, pneumonia, and various skin rashes may appear.
Often staphylococcus occurs in doctors and those who have recently been in the hospital. Who is at risk? Primarily people with weakened immune systems. For example, those who have recently been treated for a virus or even a common cold. Staphylococcus can appear in women during pregnancy.
In such a situation, it is important to defeat the infection in time to preserve the child’s health. A gynecologist should take part in the treatment.
In infants, while their immunity is still too weak, this disease also often occurs, so any rash on their skin should not be ignored.
People who abuse junk food are also at risk. Improper nutrition can cause staphylococcus.
You need to monitor your diet and eat only high-quality foods that contain many vitamins and minerals.
Various injections can also cause the disease. For this reason, diabetics are at risk. They should monitor the condition of their skin and their well-being in order to diagnose Staphylococcus aureus in time if it appears.
Any purulent processes, inflammation and acne can provoke the spread of infection in the body. Staphylococcus is a consequence of a person’s weakened immune system. It is important to diagnose the disease in time in order to select effective treatment.
Staphylococcal skin infection in children and newborns
After infection, the child develops:
- at an early stage, vomiting, bowel movements and fever;
- later there are purulent formations throughout the body.
This serious infection can provoke the development of purulent formations, infection of internal organs, infection of the mucous membranes, and the development of sepsis.
Sometimes recognizing the signs of staphylococcus is extremely difficult. Usually they are similar to the development of diathesis, ARVI, dysbacteriosis. To determine the pathology, it is necessary to undergo a laboratory examination, after which the doctor will be able to select adequate treatment methods.
Treatment is not aimed at eliminating symptoms, it must neutralize the infection that caused them.
Why does a staph infection appear on the skin?
The following factors can provoke the appearance of the disease:
- decreased immunity;
- bad ecology;
- infection with pathogenic microflora;
- stress;
- hypothermia;
- endocrine and autoimmune diseases.
In addition, the cause of staphylococcal pathology is increased sweating and improper skin care. To reduce the likelihood of developing the disease, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle. If inflammation is detected, you must contact a dermatologist and conduct a diagnostic examination.
Pathogenic flora for skin disease can be Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus. The presence of excessive bacteria is determined during a diagnostic examination.
Who is at risk
If a person has a weak immune system, is in contact with someone who is sick, or does not take care of their hygiene, then the risk of developing a staphylococcal infection increases significantly. Resistant strains of staphylococcus are found in hospitals and clinics. To prevent the occurrence of the disease, it is enough to monitor your immunity.
How to cure skin disease?
Staphylococci, which cause skin diseases, are pathogenic bacteria; therefore, the treatment of such ailments is based on local and/or systemic use of antibacterial drugs. But treatment should still be comprehensive and include:
- Compliance with general hygiene and lifestyle recommendations.
- Use of local medications.
- Taking systemic medications.
- Additional measures depending on the recommendations of the attending physician.
It is important to remember that when treating a staphylococcal infection, it is necessary not only to fight pathogenic microbes, but also to strengthen the immune system by all means. If the body works correctly, such bacteria will not be afraid of it.
General treatment recommendations
Staph infections can easily spread across the skin and cause a lot of discomfort. To quickly cope with the disease, doctors recommend:
- Limit water treatments. Most doctors advise against washing affected areas during the acute stage of the disease to avoid the spread of bacteria. Soon after the start of antibacterial therapy, this restriction is no longer relevant.
- Regularly wipe the affected areas with antiseptics. The best option for this would be brilliant green. Although it leaves green, indelible stains on the body, it actually destroys staphylococcus bacteria. As an alternative to brilliant green, you can use a weak solution of potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide, Chlorhexidine or Miramistin, but you should not expect a miracle from them.
- Stick to a healthy diet. The menu should be based on eating healthy foods that are well digestible and cover the body’s needs for minerals and vitamins. Fresh vegetables, fruits, berries and herbs will be beneficial. It is better to avoid frankly harmful foods, as well as alcohol.
- Take enough regular clean liquid. Maintaining a drinking regime will help remove toxins from the body as quickly as possible.
- Observe basic hygiene rules. Hands should be washed regularly with soap and avoid touching affected areas.
- Take multivitamins and medications that help strengthen the immune system as recommended by your doctor.
Following general recommendations will help you quickly cope with a staphylococcal infection and avoid complications and relapses.
How to treat with local remedies?
To combat staphylococcus on the skin, you can use local antibacterial drugs:
- Ointments with mupirocin. This is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, which is the main active component of several drugs - Bonderm, Supirocin and Bactroban ointments. Such drugs perfectly destroy pathogenic bacteria and rarely cause unwanted side effects.
- Baneocin ointment. This medicine contains two broad-spectrum antibiotics - neomycin and bacitracin. It is believed that when applied topically, such substances are practically not absorbed into the blood, but accumulate well at the site of application, fulfilling their intended purpose. However, it is worth noting that Baneocin ointment can only be used for application to limited areas of the skin (no larger than the palm of the hand), otherwise the drug can cause serious side effects.
- Fuzidin cream. This medicine contains sodium fusidate or fusidic acid. It perfectly destroys pathogenic bacteria and can be used to treat rashes on the face. Fusidine practically does not penetrate into the blood, so it cannot cause dangerous side effects.
- Erythromycin ointment. This is an affordable and effective medicine that can be purchased at every pharmacy. The drug perfectly suppresses bacterial activity and helps get rid of skin infections.
- Levomekol. This ointment is popular among the population, and it can really be useful in the treatment of diseases caused by staphylococcus. The drug contains the antibiotic chloramphenicol, which fights bacteria, as well as methyluracil, which activates cellular regeneration processes and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
A doctor will help you choose the most effective medicine in each specific case. Sometimes local medications are enough to cope with staphylococcus on the skin.
How to get rid of it with systemic medications?
What are the symptoms of infection?
When infected with a staphylococcal infection, the manifestations depend on the type of disease and its location. Staphylococcus can lead to the following pathologies:
- furunculosis;
- vesiculopustulosis;
- sycosis;
- phlegmon;
- erysipelas;
- felon.
Each disease has its own symptoms and characteristic features during development. After the examination, it becomes known what exactly the staphylococcus led to.
Vesiculopustulosis
Vesiculopustulosis is a disease that is diagnosed in newborns. Staphylococcus causes inflammation in the area of the eccrine sweat glands. In this case, the following manifestations appear:
- purulent inflammation in the form of a small rash;
- malaise;
- itching;
- temperature.
The causes of vesiculopustulosis are considered to be imperfect immunity and improper hygiene of the newborn. The pediatrician should select a treatment regimen, taking into account the individual characteristics of the baby.
Furunculosis
Furunculosis is a purulent inflammation of follicular and perifollicular tissue. It is characterized by the appearance of a boil, which develops in several stages. As it forms, symptoms of the inflammatory process appear, among which are:
- pain;
- swelling;
- suppuration.
Body temperature may increase. A few days after the appearance of the boil, the boil opens. A large amount of pus comes out of it, and an ulcer forms. From this moment on, the disease declines.
Even one boil can bring a lot of inconvenience to a person. With severe immunodeficiency, severe furunculosis occurs, which is characterized by the appearance of several inflammatory elements. The disease is most dangerous when localized on the neck or face. In this case, serious complications (purulent meningitis or sepsis) may occur. If you find a boil on your face or neck, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Phlegmon
Under some circumstances, staphylococcus can cause cellulitis. Cellulitis is inflammation of cellular spaces and adipose tissue without clear boundaries. The inflammatory process can spread to muscles and tendons. Cellulitis poses a great threat to human health. When it appears, the following symptoms occur:
- severe swelling;
- subcutaneous compaction;
- heat;
- general malaise.
If phlegmon penetrates into the deep layers, it can lead to necrosis. Treatment of inflammation is carried out in a hospital setting. It is necessary to open the phlegmon and remove the purulent contents. The sooner a person seeks help, the less likely it is to develop dangerous complications.
Erysipelas
Erysipelas is an acute infectious disease that causes damage to the skin or mucous membranes. The main distinguishing feature of erysipelas is the intense redness of the affected area.
In addition, the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- temperature 38-39 degrees;
- headache;
- malaise and nausea;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
In most cases, the cause of erysipelas is a streptococcal infection. When staphylococcus is added, the course of the disease becomes more complicated. In the absence of proper treatment, abscesses, ulcers and phlegmon begin to form in the area of redness. This can eventually lead to sepsis. Timely treatment is required, otherwise erysipelas will cause serious harm to health or even cause death.
Felon
Panaritium is an acute purulent-inflammatory process that is localized in the tissues of the fingers and toes. With felon the following manifestations occur:
- pain;
- edema;
- redness.
The cause of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus. In the initial stages, panaritium is characterized by inflammation. If adequate treatment is not undertaken, suppuration occurs. If an abscess occurs, it will need to be opened. This can only be done in stationary conditions.
A simple cut or crack on a finger can trigger the development of felon. After the addition of staphylococcus, inflammation begins. At an early stage, it is enough to use antibacterial agents to stop the damage.
Sycosis
Sycosis is an inflammatory disease that is more often observed in men. The reason for the appearance of Staphylococcus aureus is endocrine disruption and reduced immunity. Characteristic manifestations of sycosis are:
- inflammation of the follicles;
- redness;
- swelling.
Sycosis begins with the formation of single inflammations, which quickly disappear. They are localized on the face (in men in the beard area, in women on the eyebrows and the inner surface of the wings of the nose). In the presence of a constant infectious agent and a malfunction of the body, the disease becomes chronic. Redness becomes constant, pustules fester and form ulcers. Severe sycosis leaves scars on a person's face and therefore requires immediate treatment. Men due to sycosis cannot shave, as the inflamed area of the skin is injured.
What do acne caused by staphylococcus look like?
- Pimples caused by a staph infection are inflamed, red bumps.
- They rise above the surface of the skin in the form of a cone, and the top represents a cavity filled with pus. It is usually white in color, but can also have a greenish tint.
Such rashes appear on any part of the body, but more often on the face, back, and chest.
But acne caused by Staphylococcus aureus can be localized anywhere; they can be found on the upper body, butt, and thighs.
They have their own symptoms:
- the pimple is located very deep under the skin;
Photo: deep subcutaneous acne
- due to deep localization, the purulent cavity may not be noticeable, but is defined as a subcutaneous ball or nodule;
- the pimple causes severe pain, which intensifies when pressed;
- the resulting tubercle has signs of inflammation and is red in color;
- if several follicles are infected, then the pimple is large and may resemble a ball;
- Body temperature may rise, digestive disorders (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) may appear.
It is better not to self-medicate such acne. They require immediate medical attention.
How is diagnostics carried out?
Laboratory tests are used to detect staphylococcus on the skin. First of all, the doctor conducts a visual examination, determining the extent of the damage. Based on the initial examination, a preliminary diagnosis is made and additional examinations are prescribed. The following tests are used to diagnose staphylococcal infection:
- bacteriological culture;
- blood test for staphylococcus proteins;
- General and biochemical blood test.
Visual manifestations of staphylococcal infection are:
- purulent inflammation;
- redness;
- swelling.
It is worth noting that there are many other bacteria that cause diseases with such manifestations. It is laboratory tests that make it possible to determine the type of pathogenic flora and methods of treating it. During bacteriological culture, the sensitivity of the infection to various medications is determined.
Based on the results of the diagnostic examination, a treatment regimen for the disease is determined.
Visual inspection
The initial examination is carried out by a dermatologist or therapist. The degree of damage is determined. If the doctor detects phlegmon, he may recommend treatment in a hospital. When a person comes in with a boil in the neck or face, the most optimal treatment method is selected. In some cases, the doctor can immediately open the abscess.
Through visual examination, it is possible to determine the location of inflammation and associated diseases. An accurate diagnosis will be made after laboratory tests.
Laboratory research methods
For laboratory research it is necessary to obtain material. To do this, a scraping or fluid released from the lesion is taken. The degree of damage and the condition of the human body will be determined by a general and biochemical blood test. Acute infectious inflammation affects the number of leukocytes and erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Blood tests are taken on an empty stomach in the morning. To obtain material for laboratory tests, it is necessary to stop using local medications the day before scraping or taking purulent fluid. The doctor will tell you in detail what needs to be done to make a correct diagnosis.
Diagnostics
The definition of staphylococcal infection is based on external clinical signs of the disease:
- the presence of ulcers;
- redness and swelling of the skin;
- high temperature up to 40 degrees;
- weakness and malaise.
- bacteriological culture (in order to identify the pathogen, secreted fluid is taken from wounds and studied in various environments);
- serological analysis (studying the patient’s blood to find staphylococcal proteins there). Additionally, a consultation with an infectious disease specialist or surgeon may be scheduled.
To identify staphylococcus, blood is taken for analysis.
Laboratory tests are also carried out under a microscope:
How is staphylococcus treated?
Regardless of the location of the disease and its severity, antibiotics and antiseptics are used. After a diagnostic examination, the most effective medicine is determined. In case of serious damage, systemic antibacterial agents are used. For minor inflammation, apply antibacterial ointments topically. When treating staphylococcal infections, the following principles must be adhered to:
- always complete treatment;
- stimulate the immune system;
- avoid provoking factors.
Many types of staphylococcus are resistant to antibacterial agents. It is necessary to accurately determine a drug that will be effective against the bacterium. The treatment regimen should include not only antibiotics, but also drugs that stimulate the immune system.
A person must adjust his lifestyle in order to achieve results in the treatment of chronic infection.
Tablets and injections
Antibiotics in tablets or injections are used for severe staphylococcal inflammation. They are used in cases of erysipelas and severe furunculosis. The most commonly prescribed medications are:
- Clarithromycin;
- Azithromycin;
- Amoxicillin;
- Tetracycline.
To treat resistant strains, the latest generation antibacterial agents (Levofloxacin, Roxithromycin) are used. It is worth remembering that antibiotics are toxic and have a lot of side effects, so their use is limited.
Ointments and antiseptic solutions
For local treatment of the inflammatory process, ointments and antiseptics are used. The following medications have proven themselves well in the treatment of staphylococcal diseases:
- Gentamicin ointment;
- Chlorhexidine bigluconate;
- Levomekol.
For purulent-inflammatory lesions, it is recommended to use Levomekol. It suppresses infection and promotes speedy healing.
Local agents are used throughout therapy. It is necessary to choose the right ointment in order to achieve a good effect in the treatment of skin staphylococcal infections. The treatment regimen should be drawn up by an experienced dermatologist or therapist. It is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of a person.
Surgery
If the disease is advanced and poses a threat to human health, surgical treatment is performed. During the operation, the abscesses are opened and the internal cavity is cleaned. After surgery, antibiotics are taken and the wound is cleaned daily.
To treat chronic skin lesions, it is necessary to use a complex effect. Therapy can take time and take a lot of energy. A person must change his lifestyle and follow all doctor’s recommendations.
Immune stimulation
To help the body's defenses, a person can use vitamin complexes and dietary supplements. In some cases, the doctor may prescribe immunomodulators or immunostimulants.
To improve immunity, a person should:
- Healthy food;
- give the body a small load;
- use supplements.
If the disease is acute, then you need to adhere to bed rest and drink plenty of fluids. Despite the lack of appetite, you must adhere to your normal diet.
Questions and answers
If it is proven that acne is caused by a staphylococcal infection, then you should not:
- squeeze out pustules, this can lead to the spread of infection and blood poisoning;
Photo: if you have a staphylococcal infection, you should not squeeze out pimples yourself
- make masks from clay, it is better to dry the pustules with a solution of salicylic acid using a cotton swab;
- do facial cleansing, and it is better to refuse other cosmetic procedures.
Staphylococcus causes purulent acne on the face.
Your doctor can recommend effective remedies based on your specific situation.
- This could be antibacterial ointments, lotions with bacteriophage, or possibly taking antibiotics orally.
- The skin needs careful care during the treatment period. Use products with zinc or salicylic acid, which have anti-inflammatory and drying properties.
- During the period of active rashes and maturation of pustules, peelings and scrubs should not be used. They can help spread the infection.
To detect the pathogen, give:
- feces for microflora determination;
- contents of a ripe pimple.
Why does Helicobacter cause acne? Find out here.
Why does a pimple on my nose not go away for a long time? Read on.
Using these results, the doctor prescribes treatment.
Among all the causes leading to the formation of acne, staphylococcal infection is one of the most dangerous.
It is this that causes purulent formations in any part of the body. In this case, without consulting a doctor and special treatment, it is rarely possible to cope with acne. Therefore, it is better not to delay a visit to the clinic.
The human body can serve as a home for thousands of microbes and bacteria, and such proximity does not necessarily end in disease. The immune system reliably protects us, restraining the activity of uninvited guests and forcing them to follow the rules of good manners. Staphylococcus is no exception; it is normally found in about a third of the world's population, but does not manifest itself in anything for the time being.
A weakened immune system, simple hypothermia, or the presence of another infection in the body against which antibiotics were used are the reasons why staphylococcus can go on the offensive. Therefore, it is important to understand two things: you cannot be treated with antibiotics in case of the slightest ailment or cold, and it is simply pointless to use them against staphylococcus as a preemptive measure. You still won’t get rid of the carriage, but you will introduce your staphylococcus to antibacterial drugs and negate their effectiveness in the future, when they may really be needed.
The only reasonable measure to prevent staphylococcal infections is local sanitation of the skin, mucous membranes and upper respiratory tract during the cold season, as well as taking medications that strengthen the immune system. The prescription of antibiotics is justified only in the case of severe, life-threatening diseases: pneumonia, endocarditis, osteomyelitis, multiple purulent abscesses on the skin and soft tissues, boils on the face and head (in close proximity to the brain). But before choosing an antibiotic against staphylococcus, a qualified doctor always performs a bacterial culture.
At a sanitary and epidemiological station, a skin and venereal disease clinic or a medical office of a specialized specialist (ENT specialist, dermatovenereologist, gynecologist, urologist, pulmonologist, gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist), a bacterial culture is collected from the site of localization of the staphylococcal infection. This can be a swab from the throat, purulent skin abscess, vagina or urethra, as well as a sample of blood, sputum, urine, saliva, gastric juice, semen and other bodily fluids.
The resulting material is placed in a nutrient medium, after some time the colony of staphylococci multiplies, and the laboratory assistant can determine what type of pathogen it is and what antibiotics it is sensitive to.
The culture result looks like a list in which one of the letter designations appears next to the names of all current antimicrobial drugs:
S (susceptible) - sensitive;
I (intermediate) - moderately sensitive;
R (resistant) - stable.
First aid
It is necessary to have local first aid products in your first aid kit in case of infection. Any staphylococcal lesion is characterized by the appearance of suppuration. If a person discovers a boil, the first aid in getting rid of it will be to apply an antibacterial ointment. If the situation does not improve within 4 days, you need to make an appointment with a doctor.
Self-medication can be done only with minor inflammation of the skin and complete confidence in the diagnosis.
Prevention measures
Prevention in the fight against staphylococcus is extremely important - doctors note that every year the virus becomes more and more resistant to antibiotics, so to speak, it develops its immunity. Plus, a long course of taking antibiotics reduces the body's defenses.
Doctors call the following points the main preventive measures:
- Timely treatment of skin damage - wounds, cracks and cuts, boils and ulcers.
- Strengthening the body's defenses and immunity - sports and proper nutrition, giving up bad habits.
- Careful observance of all rules of personal hygiene, careful processing of all food products, compliance with the technology of their preparation.
- Treating all surfaces in the house with antiseptics, which is especially important if there are small children and pets.
Staphylococcus is a pathogenic bacterium that infects human skin in severe forms. And the most dangerous is Staphylococcus aureus, but with timely diagnosis and the right course of therapy, it will be easy to deal with.
Prevention of staphylococcal infection
To prevent the appearance of staphylococcus on the mucous membranes and skin, it is necessary to carry out prevention. You will need to do the following:
- support immunity;
- maintain hygiene;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- Avoid contact with things of sick people.
Prevention is aimed at preventing infection and stimulating the immune system. In order not to encounter staphylococcal disease, you will need to avoid stress, hypothermia, excessive physical activity and other factors that provoke a decrease in the body’s protective function.
If you suspect a staph infection, it is advisable to make an appointment with a dermatologist. He will conduct a visual examination and prescribe tests. At an early stage, getting rid of inflammation of the skin is extremely simple.
Staphylococcus is present on the skin and mucous membranes of all people. A healthy body controls its amount, so the bacterium does not cause any harm. If there are malfunctions or decreased immunity, the risk of developing the disease increases. If a person constantly suffers from furunculosis or sycosis, this is a reason to conduct a full examination of the body.
Staphylococcus aureus symptoms, causes and treatment:
Symbiosis of bacteria and humans
One of the factors leading to such changes is the bacterial flora. Different types of bacteria are constantly present on the surface of our body. A certain symbiosis between humans and microorganisms is created. The smallest living creatures help stabilize local immunity, thereby protecting the body from adverse external influences. However, under some conditions, excessive proliferation of bacteria occurs, as a result of which inflammatory changes appear. One of these microbes, capable of surviving at the expense of the host in a certain situation, is staphylococcus. Such a variety as Staphylococcus aureus of the skin, the symptoms of which are parasitized, we will consider further.
Characteristics of rashes on the face
Types of rashes:
- spot (skin color changes, degree of pigmentation, fuzzy edges, no irritation),
- tubercle (a compaction without a cavity in the deep layers of the dermis, tissue destruction, possible scars),
- blister (a cavityless element, the result of inflammatory edema of the upper layer of the dermis, disappears during the day, leaves no traces),
- node (red spots, provoke inflammation),
- pustule (a rash resulting from inflammation, filled with pus, appears in the face and back, forms scars and creates uneven pigmentation),
- papule (a pink nodule on the surface of the skin up to 3 cm in size).
General strengthening agents
A strong immune system helps resist microorganisms and bacteria. Taking multivitamin complexes, herbal preparations of adaptogens (ginseng, eleutherococcus), intramuscular transfusion of purified own venous blood (autohemotherapy) will help maintain the body’s defense at the proper level. Complex combinations of synthetic immunomodulators are also used when ready-made immune preparations (staphylococcal immunoglobulin) are administered.
What's bad and what's good
There is a myth that oily skin does not need to be moisturized. You need to moisturize: the more you dry your skin, the more oily sheen appears and the pores become clogged.
Let's look at what is bad and what is good in treating acne.
- Overdrying the skin causes even more oily shine to appear.
- Use oils as they clog pores.
- Drink more than two glasses of milk a day - milk provokes inflammation.
- Don't look for the cause of acne.
- Frequent facial cleansing and exfoliation.
- Choose care based on the advice of friends, not doctors.
- Squeezing pimples can cause an infection.
- Use medicinal or professional cosmetics for your skin type.
- Get tested.
- Visit doctors.
- Watch your diet.
- If you are worried about acne, consult a therapist.
- Trust your dermatologist.
Ways to prevent diseases
Preventive measures and a number of precautions will help reduce the risk of developing staphylococcal infections:
- strengthen the immune system (diet and regular exercise),
- personal hygiene (wash hands thoroughly), personal care products and personal wardrobe (do not use other people’s toothbrushes, clothes, sports equipment),
- treat skin lesions, use sterile bandages and plasters for bandaging, the bandage will prevent the spread of microorganisms beyond the wound, will prevent the entry of new infections,
- wash clothes, children's toys, bedding in hot water,
- heat treatment of products and compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards during the cooking process.
Acne is a skin disease
It is wrong to consider acne only an aesthetic defect. Acne is a skin disease. In medicine it is called acne, or acne.
There are different stages of acne: mild, moderate and severe. Depending on the stage, the dermatologist selects individual treatment and care for each patient.
Acne treatment is a long process. It may take several months or even years. Clinical improvement occurs only after a few months. You can’t take pills, buy new cream and wake up with a clean face.