Causes
A boil on the forehead develops due to the penetration of pathogenic bacteria under the skin. Our bodies are home to many beneficial and harmful bacteria, but it is usually Staphylococcus aureus that causes boils on the skin. It can penetrate in two ways:
- The infection travels along the hair shaft to the hair follicle in the dermis, where it is localized.
- Through untreated wounds, cuts, abrasions on the body. Damaged skin is the best conductor for bacteria into deeper layers and tissues.
If you come into contact with someone who is already sick, this does not mean that a boil will definitely pop up. There is a risk if you have chronic diseases such as psoriasis, eczema, diabetes. People with a reduced immune status, as well as those who do not follow hygiene rules, are more likely than others to be susceptible to bacterial infections. Long-term use of antibiotics, hormonal drugs and cytostatics also increases the risk of contracting a coccal infection.
Classification of abscesses
Soft tissue ulcers are classified in different ways. The main one is etiotropic systematization:
- Simple – monomicrobial with localized clinical data. The main pathogens are staphylococcus (usually aureus) and beta-hemolytic streptococcus. Most often they are small in size, located on the surface and are easy to treat.
- Complex - can be mono- or polymicrobial. The causative agent is staphylococcus in association with Escherichia coli, Proteus and other microorganisms, mainly anaerobic. Complex ones penetrate deep into tissues and follicles. According to ICD-10, soft tissue abscess and boils are combined into one category and have a common code.
Stages of abscess maturation and their symptoms
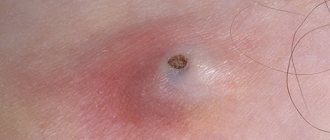
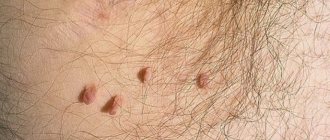
A classic boil on the forehead resembles a pimple or an insect bite, which grows over time, turns into a cyst, and is filled with pyogenic contents. It looks like a pinkish-red swelling, pulsating and painful to the touch.
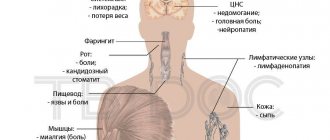
You should be alert to the following symptoms of the disease, in addition to the fact that a painful formation appears on the forehead:
- fever;
- nausea;
- chills;
- inflamed skin in the forehead area;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- release of contents from the abscess.
The maturation of a purulent abscess on the forehead occurs in 3 stages:
- Infiltration. The skin around the hair follicle turns red, swells, and becomes unbearably painful and sensitive due to the large innervation of the facial skin.
- Necrosis, purification. At this stage, a green rod is formed and rises above the skin. The boil with pus softens, opens, and its contents come out. After 2-3 days the root itself comes out. At this time, the patient feels especially bad, the temperature is elevated, the pain is intense and throbbing. After opening the boil, the painful symptoms subside, redness and swelling disappear.
- Healing. Within 4-7 days, the wound scars and heals.
There are situations when you do not need to wait for the boil to break out on its own, but you should immediately seek specialized help. If your lymph nodes are swollen, the pain intensifies and does not go away, new ulcers appear, the temperature does not subside, heart rhythm disturbances are observed, or you have a history of diabetes, you should immediately consult a doctor. These conditions pose a serious threat to life and health.
Clinical manifestations of an abscess
The general symptoms of abscesses are the same as with any inflammatory processes accompanied by the formation of pus. The severity of clinical manifestations is determined by several factors:
- The human condition. People have heterogeneous susceptibility to various pathogenic agents, and the response may manifest itself in different ways.
- Toxicity of the infectious agent. Some types of bacteria, even in very small quantities, can cause severe inflammatory processes.
- The extent of inflammation.
- Prevalence of necrotic changes.
With abscesses, both local and general somatic symptoms are observed.
- Hyperemia at the site of inflammation.
- Slight swelling.
- Increased temperature in the area of the abscess.
- Painful sensations.
- With deep necrotic changes, general malaise is observed, body temperature rises to 40 ° C with chills.
With tuberculous etiology, the purulent-inflammatory process spreads far from the site of origin. For example, a leaky abscess of the soft tissues of the thigh may occur (mainly on the medial surface).
Large ulcers that appear on the surface of the skin of the extremities affect their functionality. When walking or moving your arms, pain occurs, which severely limits physical activity.
An abscess of the soft tissues of the buttock, resulting from intramuscular administration of drugs, is usually accompanied by severe pain. The inflamed area may take on a burgundy or even blue tint. The formation of a hematoma prevents the capsule from breaking out and creates a risk of sepsis.
What are the dangers of such localization of an abscess?
The good news is that a boil on the forehead can mature, burst and heal on its own, without medical intervention. But the specificity of the location on the forehead and face is such that it requires mandatory treatment from a specialist. Due to the close proximity of the forehead to the brain, inflammatory phenomena must be neutralized at the very beginning in order to prevent such dangerous complications of the boil:
- meningitis, when the meninges become inflamed and swollen;
- Brain abscess, when pus accumulates in the tissue of the brain.
Our face is covered with a dense network of blood vessels. When you try to squeeze out a boil in the forehead on your own, pathogenic bacteria quickly enter the bloodstream supplying the human brain. If specialized assistance is not provided in time, this can even lead to death.
Under no circumstances should you squeeze out a boil located on your forehead. If the boil does not break out within 4-5 days, and your condition only worsens, consult a doctor immediately.
General information
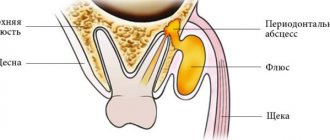
In certain areas of the body rich in vascular anastomoses, inflammation is especially dangerous. For example, skin abscesses around the nasolabial triangle can lead to cavernous sinusitis, meningitis, and brain abscess. Skin abscess on the face, let's look at the main symptoms, where the most dangerous location is and how to treat it.
The diagnosis of a skin abscess is made based on examination of the patient. In certain cases, additional basic tests are required, such as a general urine and blood test. Local treatment is carried out by an infectious disease specialist or surgeon.
Important! An abscess on the face occurs as a result of damage or inflammation of the skin on the face, mucous membrane of the mouth, lips, nose, and eyelids.
The resulting abscess is a protruding, protruding and brightly hyperemic area. The skin over it is thinned.
How to treat a boil on the forehead
To quickly get rid of a boil on the forehead and consolidate the result, they use medications, traditional medicine, and surgical methods. As a result of these manipulations, the boil should mature, break through and spew out its contents along with the stem. The wound itself is then healed using standard methods. In particularly severe cases, surgery under local anesthesia is required.
During the treatment of a boil on the forehead, the skin is carefully treated with disinfectant solutions, do not wet it, and monitor body hygiene. The patient's diet is enriched with vitamins and minerals.
Medicines
Treatment of a boil depends on the stage of maturation and the general condition of the patient. Does it make sense to get rid of boils with medication? If the infiltration process has just begun, the affected area should be treated with antiseptic drugs - hydrogen peroxide, furatsilin solution, salicylic or medical alcohol. The wound is carefully washed several times a day, do not rub or press. At the same time, UV and UHF procedures are performed, which suppress the development of the disease.
When a pustule with pus and a core appears above the surface of the skin, apply pulling compresses from ointment - Ichthyol or Vishnevsky - 3-4 times a day. For severe pain and fever, take anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drugs.
Antibiotic therapy is prescribed if the boil does not break out within a week, there is a risk of complications, or multiple rashes appear throughout the body. Before starting treatment, the doctor determines the type of staphylococcal infection and the type of antibiotic to which it is most sensitive.
The antibiotic of the penicillin group, dicloxacillin, has proven itself best in the fight against boils. If the bacteria are resistant to this drug, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used - tetracycline, erythromycin. Antibiotics are always supplemented with vitamin therapy and immunomodulators.
How to help at the clinic
Surgical treatment of a boil on the forehead is required if it matures for a long time, painfully, causes fever, rapid heartbeat, or a sharp deterioration in health. Removal of purulent contents is carried out in the clinic, under local anesthesia. Depending on the size of the boil, the doctor makes an incision or puncture, removes the rod with pus, cleans the wound, and applies a sterile bandage or stitches. After surgery, scars always remain, so surgery is resorted to only when absolutely necessary.
Traditional methods
Folk remedies for the treatment of boils on the forehead help only in cases where we are talking about getting rid of single abscesses, that is, until furunculosis begins. Their task is to accelerate the maturation and release of purulent contents. To get rid of a boil on the face, the following compresses made from natural remedies will be useful:
- gruel from baked onions, which is applied in the form of a warm compress and fixed with an adhesive plaster;
- crushed aloe leaves, which are applied 3-4 times a day to the boil site;
- tea tree oil compresses – its antibacterial properties suppress the development of pathogenic bacteria;
- Propolis is a natural antibiotic that quickly relieves pain and suppresses infection.
Before using folk remedies for treating an abscess on the forehead, a preliminary consultation with your doctor is necessary.
Features of treatment for children and pregnant women
The likelihood of contracting staphylococcus during pregnancy is the same as at any other time in a woman’s life. In 3-5% of cases this leads to infection of the fetus. The first thing to do if a boil appears on your forehead or face is to immediately consult a doctor. You will be prescribed penicillin antibiotics, which do not have severe side effects. They will prevent the infection from spreading and minimize the risk of complications. If you miss the beginning of the ripening of the boil, you will have to take strong antibiotics. And this is very dangerous for the developing fetus, sometimes it ends in premature termination of pregnancy and complications in newborns.
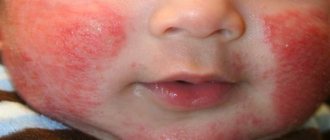
When boils appear on a child’s forehead, parents should be able to distinguish them from ordinary acne. Unlike a pimple, a boil always hurts a lot, pulsates, turns red, the body temperature rises, and nearby lymph nodes become inflamed. The child becomes lethargic and refuses to eat. To avoid wasting precious time, immediately show your child to a specialist.
Pregnant women and children are very vulnerable patients. Their immunity is weakened, and if infected, the infection quickly spreads throughout the body. Timely diagnosis and treatment of boils on the forehead will help avoid serious complications in babies and expectant mothers.
Soft tissue abscess
The disease is quite common. According to some data, about 14 million patients seek medical help every year with a similar problem.
The main difference between a soft tissue abscess (photo below) is the presence of a capsule (pyogenic membrane). Such capsules are characteristic of ulcers of any location, even those that appear in internal organs. The pyogenic membrane of soft tissue abscesses plays a very important role - it prevents the spread of the purulent-inflammatory process to nearby anatomical structures. However, an excessive amount of exudate can lead to thinning of the capsule, followed by its rupture and release of purulent contents into the surrounding spaces.
Another advantage of soft tissue ulcers is their localization. Abscesses are located on the surface, which facilitates the most accurate diagnosis with the prescription of adequate therapy.
According to ICD-10, soft tissue abscess has code L02. It also includes boils and furunculosis. International standards classify the disease as an infection of soft tissue and skin.
What is prohibited to do
The most important commandment when boils appear on the forehead is not to squeeze! You will not be able to completely remove all the pus, but pathogenic bacteria from purulent abscesses will enter the bloodstream and cause complications.
- Do not rub, do not comb, touch the affected area as little as possible. This will avoid secondary infection.
- Do not lubricate boils on the forehead with brilliant green, iodine or other coloring preparations. This will make it difficult for the doctor to make a correct diagnosis.
- If the boil on your forehead has already broken through and its contents have come out, you should not wet the wound. This will make scarring and healing more difficult.
Pathogenesis of purulent-inflammatory disease
An abscess occurs either in dead tissue, where autolysis processes occur (self-dissolution of cells under the influence of enzymes), or in living tissues exposed to the aggressive effects of pathogenic microorganisms.
When an infection enters the body, the immune system is activated. The main “defenders” are leukocytes (neurophilic, basophilic). 6-8 hours after the introduction of the infectious agent, neurophils move from the vascular bed to the mucous membranes. With the help of chemoattractants, neurophilic leukocytes penetrate to the inflamed lesion.
In the initial stage of the purulent process, the affected area is infiltrated (soaked) with inflammatory fluid and leukocytes. Over time, under the influence of neutrophil enzymes, the tissue undergoes melting, forming an internal space filled with exudate. The pus in the cavity is lysosomal enzymes from the remains of neurophils. The walls of a soft tissue abscess eventually form a two-layer pyogenic membrane. It prevents exudate from spreading to neighboring anatomical structures.
How to prevent an abscess from recurring
It is not always possible to avoid boils on the body, especially if you have reduced general immunity. However, some recommendations will help you avoid staph infections:
- carefully observe personal hygiene, take regular showers, and frequently change bed and underwear;
- do not use antibacterial soaps and detergents with triclosan - it kills beneficial bacteria on the skin and opens the door to infection;
- minimize the consumption of sugar in your daily diet - this will help cope with existing boils on the forehead and prevent the appearance of new ones;
- Properly treat any wounds, cuts or abrasions on the skin;
- avoid hypothermia;
- Strengthen your immune system and take vitamin complexes.
Even a single boil in the forehead poses a serious threat due to its close location to the brain. If home remedies do not work within 3-4 days, be sure to visit your doctor. To avoid the development of furunculosis and re-infection, strengthen your immune system and lead a healthy lifestyle.
What is the likelihood of complications?
In severe cases of purulent-inflammatory process with predominant intoxication, problems arise in determining the causes of the patient’s serious condition. There may be several reasons for this condition:
- Purulent-resorptive fever is the absorption of toxic decay products into the blood from the source of inflammation. When there is a significant accumulation of pus, it penetrates the membrane. Absorption occurs through lymphogenous and hematogenous routes.
- Generalization of infection or sepsis is a general purulent infection caused by pathogens and their toxins entering the circulating blood. The infection is characterized by intoxication, thrombohemorrhagic syndromes, and metastatic tissue damage.
- Another complication of a soft tissue abscess is phlegmon. The purulent process tends to spread. Cellulitis is characterized by general malaise, high fever, and pain in the affected area when moving or touching.
- Neuritis can occur as a result of purulent melting of the wall of a large vessel and the nerve trunk located in it.
- Osteomyelitis. When the purulent process spreads to the bones, inflammation of the bone marrow may develop.
Therapy
A boil is a disease that occurs in stages, therefore treatment is carried out in accordance with the stage of development of the purulent process:
1. At the initial stage, use:
- a course of penicillin antibiotics;
- injections of staphylococcal toxoid;
- physiotherapy: electrophoresis and ultraviolet irradiation.
2. When the boil matures and the abscess opens, local procedures are added to the treatment:
- mechanical removal of residual pus and dead tissue is carried out and the cavity is washed from the boil with aseptic solutions (salicylic alcohol, boric acid or a solution of furatsilin or hydrogen peroxide);
- a pulling ointment for boils (Vishnevsky, Levomekol or ichthyol) and antimicrobial (salicylic or erythromycin) is used.
3. At the healing stage the following are shown:
- vitamin therapy;
- UHF;
- biostimulants for skin resorption and restoration (with severe scarring).
Preventive measures
Abscesses are a rather dangerous disease. A breakthrough of the pyogenic membrane with the release of purulent exudate into the internal spaces threatens severe intoxication. The etiology of the disease has been well studied, which makes it possible to take measures to prevent it. Preventive measures are not specific and differ little from the rules of antiseptics.
- Timely and complete treatment of wounds.
- In case of burns and frostbite, therapy should be carried out by a doctor and the process monitored until complete recovery.
- Compliance with antiseptic rules during injections and other medical procedures.
- Adequate treatment of any diseases of infectious origin.
- If there are suspicious abscesses, consult a doctor immediately.