Causes
In the vast majority of cases, tuberculosis of the skin and subcutaneous tissue is a secondary disease. Inflammatory agents enter the skin through the lymphohematogenous route from other infected organs. Less common are cases where mycobacteria enter the dermis from nearby organs. The most common variant of infection is exogenous. With this type of infection, mycobacteria penetrate the epidermis through damage (abrasions, scratches, wounds).
The risk of contracting tuberculosis increases in proportion to the decrease in immune function. The less the body is protected, the more likely it is to become infected. So the likelihood of infection is affected by:
- HIV positive factor.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
- Various infectious diseases.
- Disorders of the thyroid gland, that is, an incorrect balance of hormones in the body.
- Malfunctions of the nervous system.
- Lack of water, vitamins and minerals.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions.
- Bad habits (alcoholism, drug addiction, smoking).
It is also worth noting that the general conditions of a person’s existence have a tremendous impact on his immunity. For example, stress, anxiety, and panic attacks greatly affect the overall tone of the body as a whole.
Routes of infection with tuberculosis
In most cases, tuberculosis infection is caused by Koch's bacillus. There are several ways of transmitting the disease:
- Through the air - when talking with a sick person or carrier, during communication and inhalation of microparticles of saliva released when coughing or sneezing;
- Through the digestive tract - when a person eats food infected with mycobacteria. This type of transmission of tuberculosis is extremely rare;
- By the placental route - from a sick mother to the fetus or during the passage of the child through the birth canal.
When infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis by airborne droplets, a pulmonary form of tuberculosis develops, however, if the Koch bacillus is transmitted to a person in any other way, then tuberculosis of other organs most likely develops, in particular:
- Skin;
- Organs of vision;
- Musculoskeletal system;
- CNS or meninges;
- Digestive organs;
- Organs of the urinary system.
Symptoms
Each type of disease has its own symptoms. But there is a general clinical picture.
- The first signs are the appearance of numerous redness on the skin that hurt or itch.
- Decrease in the level of well-being of the body as a whole.
- A clear decrease in the body's defense response (weakening of the immune system).
- Frequent allergic reactions.
- Positive test for tuberculosis.
We recommend reading an article about methods for diagnosing the disease, namely mantoux and diaskintest.
If you experience at least one of the above symptoms for a long time, consult a doctor immediately. You may be infected, which is dangerous not only for you, but also for all people who come into contact with you.
Signs and symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis
The main symptom of pulmonary tuberculosis in adults is:
- Cough - from a slight cough to a cough with sputum, sometimes mixed with blood. In smokers with illness, the nature of their cough changes. A cough indicates damage to the bronchi.
- When the pleura is affected, chest pain and shortness of breath appear.
- When advanced forms are identified, all intoxication complaints, a sharp decrease in body weight, cachexia, anemia, and respiratory failure are evident.
Rice. 2. The main symptom of pulmonary tuberculosis is cough. When coughing, mycobacteria are released into the external environment.
Types
There are two clinical forms of cutaneous tuberculosis: primary and secondary.
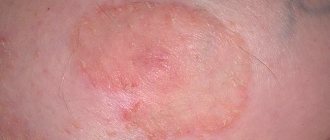
- The primary form of the disease appears extremely rarely. This fact is due to the fact that all people are vaccinated against tuberculosis in the first days of life. Primary tuberculosis in most cases occurs in children under fourteen years of age. Red-burgundy inflammations form on the body, in the center of which a whitish tuberculous chancre can be observed. Ulcers do not go away for a long time. After a course of treatment, obvious scars form at the site of inflammation. People with weakened immune systems are characterized by relapses, as a result of which the patient’s body takes on a terrible appearance, spoiled by numerous scars.
- The secondary type of disease occurs in patients who previously suffered from other forms of pathology. Skin tuberculosis is divided into localized and disseminated. Experts conclude that it is precisely these forms of the disease that are appearing more and more often recently. The most common type of disease is dermal tuberculosis, a type of lupus.
There are dry and wet forms.
When dry, the skin continues to carry out regeneration processes, replacing the affected areas with young layers of the epidermis. This form is also characterized by a very dry surface of the infected area, prone to damage.
When it gets wet, erosions form, which do not heal for a long time, and after elimination they form scars.
Tuberculous lupus
Tuberculous lupus or lupoid tuberculosis, as mentioned earlier, is the most common type of disease. This form of the disease takes a long time, is painful and has numerous exacerbations. The infection manifests itself as tuberculous inflammations, lupomas (yellowish tubercles, the size of which does not exceed one centimeter). In the initial stage of the disease, lupomas are located under the fat layer. Over time, they move to the surface of the epidermis. If you put pressure on the lupa, it will burst. This factor will be accompanied by heavy bleeding and severe pain.
- With a positive result of treatment, the inflammation gradually resolves, and in its place a thin layer of very dry skin forms.
- If negative, inflammation appears on the mucous membranes of the eyes, mouth, and nose. At first, lemon-colored plaques form on them, which subsequently lead to tissue necrosis.
There are also scaly and tumor-like types of tuberculous lupus.
Collicative
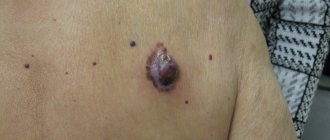
Colliquatic tuberculosis of the epidermis - mycobacteria enter the skin through the lymph nodes. Thus, small nodules are initially formed under the lymph nodes, which are absolutely painless, but over time they significantly increase in size and begin to cause concern to patients. Later, the nodules open, forming wounds from which pus mixed with blood clots is released. After the pus is released, an ulcerative wound is formed, which, when healed, leaves a scar covered with small papillary growths.
Ulcerative
Men are more prone to this type of disease. Pathogenic mycobacteria come from the sputum or other waste products of a patient infected with tuberculosis. In this case, the skin around the natural openings of the human body is susceptible to pathology. For example, around the mouth or anus.
First, indistinct tubercles form, which gradually fester, forming ulcers. The size of such ulcers can reach up to five centimeters in radius. The course of the disease is extremely difficult. Ulcers take a long time to heal, bleed and fester. All inflamed areas bring severe pain. Frequent relapses are possible.
Lichenoid
This type of disease is also called “scrofulous lichen.” Most often, this disease is observed in children under ten years of age with weakened immunity. Rarely in adults with other forms of tuberculosis. With the described form of the disease, rashes form, which often appear on the limbs and skin of the abdomen.
We recommend reading the article about scrofula on our website.
Warty
Warty skin tuberculosis is observed in people who have been in contact with the carcasses of infected animals. Mycobacteria penetrate the skin with the help of waste products of a dead animal. The disease occurs with numerous complications, and there is a high probability of relapse.
Papulonecrotic
Papulonecrotic tuberculosis of the skin most often occurs in young people. At the same time, small papules are formed on various parts of the body (chest, buttocks, armpits, etc.), the diameter of which can reach up to four centimeters. After healing, they turn into whitish scars.
Indurative
This form of the disease affects patients who suffer from tuberculosis of other internal organs of the body.
Be sure to read the article about extrapulmonary forms of tuberculosis on our portal.
The first signs and symptoms of tuberculosis in adults and children
The first symptoms of tuberculosis in adults and children are divided into general and local.
- General symptoms of tuberculosis (intoxication, fever and paraspecific reactions).
- Local symptoms of tuberculosis (depending on the location of the tuberculosis process).
At the initial stages, the clinical symptoms of tuberculosis are extremely scarce, and the signs of tuberculosis in adults and children have weak specificity. The symptoms of tuberculosis at an early stage are similar in nature to the symptoms that occur with a number of infectious diseases. Persons with an open form of the disease (infectious patients) have clinical symptoms in 95% of cases.
- Symptoms of intoxication appear gradually, increase gradually, and are manifested by weakness, sweating, poor appetite, weight loss, and low-grade body temperature.
- Neurovegetative disorders in tuberculosis are manifested by sweating of the palms and feet (distal dyshidrosis), tachycardia, excitability or depression.
- Decreased appetite and subsequent weight loss are associated with constant intoxication of the body.
- Fever in tuberculosis never occurs with a high temperature. Low-grade body temperature is usually noted.
- The first signs of tuberculosis can manifest themselves in the form of paraspecific reactions, which are more often recorded in children. Paraspecific reactions are more often recorded in children (read more below).
Diagnostics
If you experience any symptoms of cutaneous tuberculosis, you should consult a doctor who will prescribe you the following procedures:
- Mantoux test.
- Chest X-ray.
- Pirquet's test, which detects cutaneous forms of tuberculosis.
It is important to understand that tuberculosis is a complex disease that requires careful diagnosis. Therefore, performing only the Mantoux test in this case is not appropriate. Often, discharge from wounds and ulcers is also taken for analysis.
How to detect tuberculosis?
This viral disease can be diagnosed using tests such as:
- X-ray;
- fluorography;
- CT scan;
- research of biological materials;
- reaction of Mantoux et al.
Symptomatic tuberculosis is characterized by the following signs (clinical picture):
- complete indifference to things;
- general weakness;
- sweating (most pronounced at night);
- "lethargy";
- weight loss;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes, ulcer on the neck X-shaped chest
Anemia (decreased number of red blood cells) and leukopenia (decreased number of white blood cells) are found in human blood. Then symptoms characteristic of the affected organs appear. This could be, for example, a cough with sputum, a runny nose, difficulty breathing (pulmonary tuberculosis), constipation or diarrhea, blood in the stool (intestinal tuberculosis), etc.
Hand of a person with anemia (left) and a healthy person (right)
Stomatitis is one of the first signs of leukopenia
Treatment
There are various types of treatment for epidermal tuberculosis. Each of them is designed for a specific form of the disease.
It is important to understand that you cannot self-medicate. If you use traditional medicine methods, you can further complicate the pathology. Treatment should only be prescribed by a TB doctor.
The first and main rule of therapy is to be under the full supervision of specialists. Most often, general therapy lasts from ten months to one and a half years. Treatment can be divided into several stages.
- Four medications are prescribed for a period of two to four months.
- The number of medications is reduced to two medications, replacing them with others. This system is designed to prevent harmful mycobacteria from developing resistance to the active ingredients in medications.
- An important part of the treatment is strengthening the immune system and improving the overall tone of the body. To achieve this goal, doctors prescribe various vitamin complexes, a specialized diet high in protein and vitamin C. Experts also advise adhering to a certain water consumption pattern to maintain normal water balance.
Electrophoresis with the addition of anti-tuberculosis drugs is often prescribed. Such treatment gives the highest possible effect.
In extremely rare cases, surgery is performed.
Signs and symptoms of bronchial tuberculosis
The bronchi are always affected in pulmonary tuberculosis. As an independent disease, bronchial lesions are rarely recorded. Damage to large bronchi is diagnosed by bronchoscopy.
Clinical symptoms of tuberculosis of large bronchi are scant. The main symptom of bronchial tuberculosis is cough. Cough centers are always involved in the inflammatory process. Sputum scanty. Symptoms of intoxication are barely noticeable.
Rice. 3. Ulcerative tuberculosis of the right main bronchus, which developed as a result of the breakthrough of caseous masses into the bronchus from the affected intrathoracic lymph nodes (the fistula opening is indicated by the arrow).
Symptoms and signs of spinal tuberculosis
Symptoms of spinal tuberculosis and the clinical picture of the disease depend on the location of the process and the degree of organ destruction.
Symptoms of spinal tuberculosis and clinical picture in the prespondylytic phase
This phase is characterized by the fact that the process is limited to the body of one vertebra and does not go beyond its limits. Intoxication of the body manifests itself weakly, somewhat more clearly in children. Phenomena such as a feeling of heaviness and minor pain in the spine disappear after rest. During this phase, patients practically do not seek medical help.
Symptoms of spinal tuberculosis and clinical picture in the spondylitis phase
During this phase, the process spreads beyond the vertebral body affected by tuberculosis. Symptoms of intoxication appear clearly during this phase. Pain in the spine increases significantly and has different colors and irradiations. The mobility of the spine is limited. Muscle rigidity (tension) is noted, which occurs as a response to pain. The patient's gait changes. The usual body position (posture) changes. There is atrophy of the back muscles.
Symptoms of spinal tuberculosis and clinical picture in the post-spondylytic phase
Symptoms of the disease in this phase are caused by the development of degenerative-dystrophic changes, with the development of osteochondrosis and spondylosis. Muscle atrophy is pronounced. Kyphosis or scoliosis is obvious. The chest is sharply deformed. The spine is unstable. The patient experiences severe pain localized in the area of spinal curvature. Exacerbations of the disease are severe.
Rice. 11. A characteristic sign of tuberculosis is destruction of the vertebral body (indicated by arrows).
Rice. 12. A characteristic sign of tuberculosis is pronounced curvature of the thoracic region.
Signs and symptoms of skin tuberculosis
Cutaneous tuberculosis is represented by a variety of localized and disseminated forms that appear in previously infected people. Tuberculous lupus accounts for up to 75% of all cases.
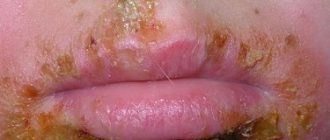
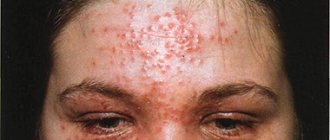
The disease affects the skin of the nose, face, neck, red border of the lips, mucous membranes of the mouth and eyes. The skin of the extremities is rarely affected. Tuberculous tubercles merge and form lupomas. The first signs of skin tuberculosis are the appearance of tuberculous tubercles, which merge to form lupomas.
Their color is yellowish-rusty. Size – up to 0.75 mm. At first, the lupomas are located deep, and then they begin to protrude above the skin. The shape of the lupoma is round, the consistency is soft, with significant pressure from the probe, the elements of the lupoma rupture, causing pain and bleeding. Lupomas often merge. Their surface is smooth and shiny. If you press a glass slide onto the affected area, the lupomas become the color of “apple jelly” (apple jelly symptom). With a favorable outcome, resorption begins in the center of the tubercles and replacement of the damage with thin skin in the form of tissue paper.
Rice. 6. Photo of lupoma. Lupoma is the main symptom of skin tuberculosis.
Rice. 7. The “apple jelly” symptom is the main symptom of tuberculous lupus.
Rice. 8. The photo shows skin tuberculosis (Lupus vulgaris).
Rice. 9. The photo shows skin tuberculosis. Lupus vulgaris.
Rice. 10. The photo shows skin tuberculosis. Consequences of Lupus vulgaris.
Tuberculosis rash photo
In medicine, skin tuberculosis is usually classified as a separate nosological entity that is widespread. The causative agents in this case are tuberculosis microbacteria that penetrate under the skin tissue. The most dangerous varieties are bovine and human tuberculosis (in medicine called Koch's bacillus). You can encounter a similar disease anywhere in the world.
With primary skin tuberculosis, the initial symptoms begin to appear only after a month. A red-brown papule appears at the site of the lesion, has a dense structure and subsequently transforms into a superficial ulcer.
This type of disease most often affects young children. After about three weeks, lymphadenitis or lymphangitis begins to appear.
By the end of the third month, the affected area of skin heals or, conversely, the process generalizes.