In the modern world, papillomavirus is considered a fairly common infection that was known to mankind in the distant past. People suffered from an abundance of warts and tried to treat them in accessible ways. It was possible to isolate the pathogen only in the middle of the last century. Today, science knows about 130 strains of the virus, many of which have been studied in detail. Based on the classification, all types were divided into 3 groups. The greatest threat is posed by strains included in the third category due to their high oncogenic risk. One of them is HPV 56.
What is HPV 56
To explain in simple terms what HPV 56 is, it is a type of papillomavirus that is often transmitted during sexual intercourse and can cause the growth of benign skin thickenings (warts, papillomas, condylomas).
However, in medicine, the 56 HPV genotype attracts more attention from doctors, since it can provoke cancerous tumors affecting the human genitals. The significant danger of this viral infection is that its incubation period can last up to several years and manifest itself in full force after the body’s immune forces have weakened. Thus, a person may be unaware that he is a carrier of the disease and, because of this, infect his partners.
Discovered too late, varieties of this type have serious health consequences: cancer of the vulva and cervical canal lesions in women and cancer of the penis, rectum or prostate in men.
Prognosis of the course of the disease and precautions
The prognosis of the disease with timely treatment is usually positive. The virus is destroyed along with the growth and cannot provoke the formation of cancerous tumors. The main thing is to carefully follow the recommendations of doctors, do not forget about hygiene and carefully approach intimacy with unfamiliar people. Women need to undergo regular examinations with a gynecologist.
If strange growths appear on the body, you should immediately contact a specialist. This will allow you to avoid complications and get rid of the risk of developing the disease in time. In case of skin injuries, it is necessary to limit tactile contact with others and try to keep the sore spot sterile clean to avoid rapid transmission of the virus. You should not rely on the fact that there are no sick people nearby. HPV 56 often lies latent but can be transmitted.
Bed linen, underwear, and towels must be washed only in hot water and ironed well. You cannot wear other people's clothes or shoes. You should thoroughly wash your genitals after intimacy and pay attention to their condition. These simple precautions will significantly reduce the risk of infection with HPV 56 and help prevent the development of a malignant tumor.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Pathological threats
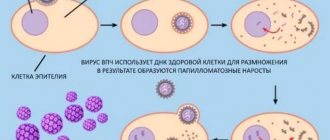
After penetrating the brain and blood, the papillomavirus infection remains in them without detecting itself. Bacteria belonging to HPV type 56 go straight to the brain, where they wait for favorable conditions for their development.
As soon as the human immune system weakens, the virus returns to the site of infection and begins its destructive activities. If a woman has concomitant diseases that affect the epithelium, it easily penetrates into the deeper layers of the tissue. Then growths appear on the mucous membrane - papillomas, which increase in size and spread to healthy cells of the body. Lastly, HPV type 56 attacks the carrier’s DNA, which leads to the development of genital cancer.
Among the accompanying factors that may contribute to the worsening of the situation, it is worth noting damage to the epidermis, skin sensitivity, and the introduction of additional infections.
It should be borne in mind that it is the 56 strain that causes cancer of the cervix, so therapy should be started at a very early stage.
Characteristics of the pathogen
As a result of the research, pathogens were divided into groups according to their degree of malignancy. The virus is a DNA-containing pathogen and has a high oncogenic risk. To understand the classification, you need to know what it is - oncogenicity and where it has the ability to cause cell mutations and malignant neoplasms.
The most dangerous types are considered 16,18,31,39,45,56,59,66,68,73,82. Strains of high carcinogenic risk affect the reproductive system to varying degrees. Half of cervical cancer cases are caused by types 16 and 18.
Pathogens of average oncogenicity 31,33,35, 51,52,58 are capable of causing severe complications in some people, including cancer, while in others they occur without complaints.
Low-oncogenic 6,11,42,43,44 strains cause the proliferation of benign papillomas, condylomas or warts, and malignant transformation is rarely observed.
It is important to understand the difference: the presence of high-risk HPV does not mean that the patient will definitely develop cervical cancer. However, the presence of cancer cells guarantees the detection of a highly oncogenic strain of the virus.
How can you get infected?
The most common way to become infected with human papillomavirus type 56 is through unprotected sexual intercourse. In addition, experts talk about other options for how this disease can be transmitted:
- upon contact of any mucous membranes;
- during pregnancy from mother to child;
- in the presence of damage to healthy epidermal tissue;
- failure to maintain personal hygiene (using other people's items or borrowing your own).
As mentioned above, the human papillomavirus in women, as well as men, can be present in the body asymptomatically and enter the active phase in the presence of accompanying factors:
- Depletion of immunity;
- Stressful situations and neuroses;
- Diseases of the urinary system;
- While carrying a child;
- Promiscuous and multiple sexual intercourse;
- Bad habits.
Methods for diagnosing strain 56 in women
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
A gynecologist can suspect the presence of HPV in women during a routine medical examination. To study the presence of strain 56 in the body, biological material is needed. There may be a smear of the mucous membrane of the cervix, vagina, urethra, rectum.
If the result is positive, papilloma is present in the female body, you need to undergo a medical examination by an oncologist, infectious disease specialist, or dermatovenerologist.
Symptoms
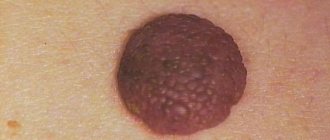
The main sign of the presence of HPV type 56 in women is the formation of genital warts. They often occur on the inner layers of the epithelium, so they are difficult to detect on their own. If a woman regularly visits a gynecologist, the specialist will determine their appearance immediately.
Otherwise, indirect signs may indicate the disease:
- Discomfortable sensations in the abdomen in the gynecological area;
- Bloody discharge during or after intercourse;
- Pain during sex or when urinating.
All these manifestations are caused by the fact that during sexual intercourse the growths are damaged and torn off from the epithelium. These symptoms cannot be called accurate for determining the presence of a disease in the human body, since they are also characteristic of a number of other, no less unpleasant diseases: cystitis, cysts, erosions or inflammatory processes. Only a medical professional can make an accurate diagnosis.
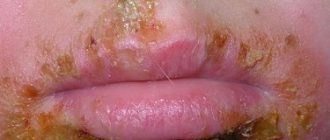
In men, this infection, as in women, provokes the growth of tumors on the genital organs, mainly on the head or foreskin of the penis. In advanced cases, when bacteria penetrate the urethra, urination may be impaired.
Warts have sharp tips that are located on thin processes. Sometimes they are adjacent to the mucous membrane or skin and, having a light color, are practically invisible. On the male body they can grow in places where the skin is thinner: armpits, the space between the fingers, wrists, and less often form on the neck.
There are other manifestations of HPV 56 symptoms in the male body:
- Bowen's disease, or Bowen's dermatosis - red spots of round or irregular shape with peeling;
- Bonevoid papulosis is a venereal disease, the distinctive feature of which is the formation of dark papules on the epidermis of the genitals.
Clinic
The disease does not manifest itself in any way at the initial stages. There is a high probability that warts, condylomas and papillomas become an accidental finding during a gynecological examination. A characteristic feature of viral growths is the appearance of elements in the places where the infection occurred - in the labia area, on the cervix.
Variants of unpleasant symptoms:
- pain during sexual intercourse, urination;
- contact bleeding;
- atypical growths on the genitals;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- precancerous conditions of the cervix: dysplasia, leukoplakia.
Diagnostics
To diagnose papillomavirus 56 strain, different methods are used.
- Examination by a specialist. A gynecologist or urologist can visually confirm the presence of neoplasms. Based on their presence, the doctor refers the patient for further examination to accurately determine its type.
- PCR or polymerase chain reaction. For this study, a smear is taken from any mucous membrane (anal, vaginal, urethral, nose or larynx). The biomaterial is sent to the laboratory, where, under the influence of the necessary drugs, they determine whether the virus belongs to a specific strain.
- Colposcopy . The examination is carried out using a special device - a colposcope. The condition of the mucous surface, blood vessels and tissues of the cervix is diagnosed.
- Cytology smear, Papanicolaou test, or Pap test. The material is collected using a smear from the cervical canal or an imprint. Allows you to determine cancer markers at an early stage.
- Cervical biopsy. A small fragment of tissue is used as a biomaterial if, after other studies, cancer is suspected.
- Digene test.
- Along with the listed procedures, competent doctors prescribe a blood test to check for additional infections. When an STD is detected, preliminary treatment is prescribed, and only then therapy begins.
Features of vaccination
Vaccination against HPV is the only way that can prevent the development of pathology. Most cases of transmission occur after the onset of sexual activity.
Two types of vaccines are registered in the country - Gardasil and Cervarix. Both are used to prevent infection from the most common oncogenic strains 16,18. Gardasil additionally includes protection against 6,11 species that cause cervical condylomas. The vaccine material contains no virus, so infection at the time of injection is excluded.
Immunization is carried out in three stages. The dose is re-administered two months and six months after the first administration. The most optimal period for drug administration is 11-12 years. The use of injections is officially limited to up to 26 years of age.
Many countries recommend immunizing boys and girls. This eliminates the risk of developing condylomas in the male population and further reduces the percentage of infection in women.
Treatment
Before starting treatment for HPV 56, you should learn about some of the features of this disease. Firstly, unfortunately, it is impossible to completely cure the disease. Since the virus is based in the brain and sometimes even the human circulatory system, drastic methods of removing it can lead to irreversible health consequences.
The main task of antiviral therapy is to strengthen the immune system to reduce the number of harmful bacteria in the carrier’s blood and get rid of external symptoms - removing papillomas.
People who have been diagnosed with type 56 papillomavirus should undergo regular examinations. As soon as the disease enters the active phase and growths appear, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.
The main methods of influencing diseases are drug and/or radical therapy. The drugs that are prescribed for patients are designed, first of all, to strengthen the body’s immune system, and secondly, to weaken the pathogen. An integrated approach uses antiviral drugs, immunomodulators, antibiotics and cytostatics (drugs that affect tumor processes).
Cardinal methods include surgical intervention:
- Electrocoagulation – exposure of growths to direct current;
- Removal using laser;
- Cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen;
- Exposure to chemicals;
- Electrosurgery – getting rid of affected areas using alternating current;
- Curettage is curettage of the cervix. This procedure is usually followed by electrocoagulation.
- Surgical excision method. Currently, it is used extremely rarely due to the risk of damage to internal organs and the possibility of bleeding.
HPV type 51
HPV 51 is an anogenital infection that primarily affects human epithelia and mucous membranes of the oral cavity and genitals. A distinctive feature of the course of the disease with this virus is the almost complete absence of pronounced symptoms .
In some cases, the formation of genital warts or condylomas is observed. As the infection progresses, patients experience bleeding, which often appears after sexual intercourse.
The danger of the virus lies in damaging not only the surface of the mucous membrane, but also the epithelial layer.
Active damage to the body is accompanied by the appearance of genital single or multiple genital warts. Symptoms may disappear for a while, but if the body's immune system weakens, the virus may reappear.
Prevention
The leading method of preventing papillomavirus 56 in people of puberty is the use of a condom during sexual intercourse.
In addition, women and men who have an active sexual life are advised to regularly visit specialists in order to prevent and early detect infection. Relatively recently, a vaccine has appeared in medicine that can protect against papillomavirus infection. If no infection is detected in the human body, doctors offer vaccination as a preventive measure. However, there are special recommendations: women are recommended to use this product up to 26 years of age, and men - up to 21 years of age.
As a primary method of prevention, the vaccine can be administered to girls under 12 years of age. The effectiveness of the vaccine has been proven in more than 90 cases out of 100.
Methods of secondary prevention (including after infection) include:
- Protected sexual contact;
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- Reducing or completely eliminating bad habits;
- Strengthening the immune system and hardening;
- Regular monitoring by an appropriate specialist.
Attentive attention to your health and timely preventive actions can maintain good health and prolong life.
Transmission routes and risk factors
In most cases, papillomavirus strain 56 spreads during sexual intercourse, including oral and anal sex. This occurs in conditions of disruption of the epithelium of the mucous membrane of the genital organs and oral cavity. The use of contraceptives does not guarantee complete protection, but it can reduce the likelihood of infection. Other ways contribute to the appearance of papillomas:
- contact-household, in this case, conditions for infection are created through direct contact with the carrier, if the person has lesions on the skin;
- during labor from mother to child - this route of infection is less common.
When penetrating the epithelium, negative agents can be destroyed by the body. However, this rarely happens, provided that immunity is not reduced.
With a 70-80% probability, the source of infection is a man, but a woman can also become a spreader of the disease, especially if genital warts have formed on her genitals, oral mucosa or lips.
In other cases, the virus begins to actively multiply, which is facilitated by external and internal factors:
- hormonal changes (pregnancy, lactation, menopause), diseases;
- regular stress;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- lack of nutrients;
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse);
- sleep disturbance;
- the presence of other sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV.
All these factors contribute to a decrease in immunity. This is the main condition under which the HPV virus is activated.