Benign papillomas in children are not uncommon. A caring parent should immediately take their child to see a specialist immediately after identifying a viral rash. But, as practice shows, many adults try to independently cure the growth caused by the papillomavirus. Some still manage to cope with the disease on their own. It is only after a while that the neoplasms appear again, since the main reason for the spread of the virus throughout the child’s body is very difficult to eliminate using home methods.
Infecting a child with HPV
The main way of infection with the papilloma virus in adults is oral-genital, anal sexual contact.
If, when planning a pregnancy, a woman takes tests for viral infections and undergoes treatment, the baby is born healthy.
Infection of a child with HPV occurs when the mother has genital warts of the genetic type while passing through the birth canal.
Until recently, it was believed that this was the only way of transmitting the strain. Doctors have found that it is capable of penetrating the placenta and attacking the fetus in the womb. The evidence was provided by neoplasms in infants born via cesarean section, when contact with the mucous membrane of the mother was a priori excluded. Papilloma-like growths on the skin and mucous membranes of infants occur in 10 out of 1000 newborns.
Doctors explain the peculiarity of the strain being transmitted through contacts in everyday life due to its tiny size. The agent easily penetrates even through the five-micron pores of the condom. In the postnatal period, the pathogen is more often transmitted through untreated instruments and blood. Older children become infected at home when visiting places with high humidity. A child can become self-infected if he bites his nails, sucks his fingers, scratches wounds until they bleed, or uses the personal belongings of a virus carrier .
Development mechanism
For a long time the pathogen does not manifest itself in any way. Papillomas in children form under certain conditions after six months. After the agent enters the body, a 3-week incubation period begins. With good immune resistance, papillomas do not manifest themselves for years. The pathogen often develops after a cold, stimulating the formation of formations on the skin of various forms.
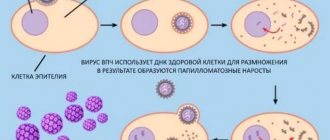
The mechanism of formation of papillary growths is simple. They are provoked by strains with low oncogenic risk - Papoviridae, Papillomavirus. They affect epidermal cells - keratinocytes, which serve as a biological barrier between the internal and external environment.
During differentiation, the virus encodes keratin cells and displaces them into the upper layer of the dermis. On the skin and mucous membranes they form epithelial growths of various configurations with small elevations with a diameter of 2 mm.
This group of strains is diverse and does not pose any particular danger. By themselves, they are harmless until, under the influence of certain factors, they transform into melanoma. This type of cancer rarely occurs in children. Adolescents with congenital atypical nevi, xeroderma pigmentosum, and those who have been subjected to immunosuppression (suppression of immunity) due to systemic diseases, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders are more susceptible to the disease.
Provoking factors of virus activity
The appearance of papilloma in a child is facilitated by frequent acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections, which reduce cellular and humoral immunity. Poorly differentiated lymphocytes cannot restrain the aggression of a foreign antigen and the growth of encoded cells. In this case, interferon loses its ability to suppress protein and viral RNA synthesis and regulate the interaction of immune cells.
Inhibit protective biological functions:
- bronchitis,
- tonsillitis and adenoiditis;
- tuberculosis;
- allergies and asthma;
- diabetes:
- dysbacteriosis:
- stress;
- long-term use of antibiotics.
Vulgar and simple papillomas in adolescents after puberty may disappear without a trace or remain unchanged.
Prevention
Since most children and adults are infected with the human papillomavirus, almost everyone should take preventive measures to control the spread of the disease. To prevent the appearance of benign neoplasms in a young child, his parents must follow the following rules:
- Accustom your baby to regular walks in the fresh air;
- Give him vitamins that boost immunity;
- Treat even minor wounds on the skin that can lead to infection;
- Create a healthy diet for your child that is enriched with healthy foods;
- Teach your child to do exercises and exercise in the morning;
- Limit your child’s consumption of unhealthy foods and drinks that contain large amounts of additives and dyes;
- Introduce him to the rules of personal hygiene;
- Closely monitor the child's emotional state. He should not experience serious stress, as it greatly weakens the immune system.
When parents take care of their children, they manage to avoid such health problems. If papilloma does appear, there is no need to panic right away. The first step is to make an appointment with your pediatrician. He will tell you how to act in this case and what to do to prevent the occurrence of new viral rashes.
Types of papillomas in children
Benign skin formations differ in external characteristics - shape, color, location. They grow like bumps, sacs or droplets. They can be single or multiple, localized throughout the body except the head.
Doctors classify several subtypes of skin growths:
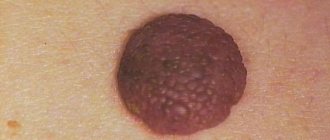
- Vulgar - rounded bumps with keratinized epidermis of flesh or dark brown color. The sizes of warts range from 2 mm to 1 cm.
- Flat papillomas are hemispherical formations 2-10 mm in size with a lumpy surface with papillary growths that match the color of the skin. In infants they are very itchy and lead to hyperemia.
- Plantar papillomas on a child’s body with dark patches are shaped like corns with a villous core in the center.
- Filiform papillomas (acrochords) grow with a stalk. In shape they are similar to a droplet or papilla with a fine-grained structure of pale pink or flesh color.
- Juvenile long growths form after 3-6 months with localization in the mucous membrane of the glottis after vertical infection during childbirth.
- Epithelial ones are almost indistinguishable from juvenile ones in appearance. They are localized on the inner surfaces of the cheeks, lips, and under the tongue, causing severe discomfort to the baby.
- Warty dysplasia is the most dangerous type, since the risk of malignancy is 30%. The virus is able to penetrate the chromosome of a cell and provoke atypical cell division.
Regardless of the type of human papillomavirus, treatment is necessary in young children.
Causes of growths
In childhood, papilloma appears only due to HPV infection. This infection is transmitted to children in several ways.
- Vertical. The virus can enter the child’s body as it passes through the birth canal of a pregnant mother. In such a situation, the neoplasm can be detected approximately 3-5 weeks after birth.
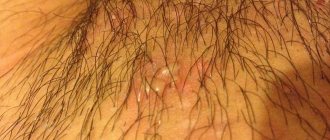
- Contact and household. This route is relevant in the process of close contact between a child and a virus carrier. Provoking factors include playing with infected children, using common personal hygiene products, swimming in a pool, etc.
- Self-infection. In childhood, this phenomenon is observed much more often. This particularly applies to children in preschool age. Having discovered a papilloma on the nose or arm, the child begins to rip it off or pick it. As a result, the infection that is inside the tumor will spread to healthy skin, causing the formation of new growths.
Signs of infection
Papillomas on the child’s body and face appear suddenly without previous symptoms. Parents often don't notice them until he starts picking and combing them. Subcutaneous nodules are formed one or several at a time, then unite with each other. If their number does not exceed 2-6, this is considered the norm. With low immunity, they spread throughout the body and mucous membranes.
Associated symptoms:
- loss of appetite;
- lethargy;
- tearfulness, capriciousness.
Diagnosis of HPV in a newborn - how to recognize infection?
When it comes to preparing for the birth of a child and preventing HPV, it is extremely important to carry out a specific examination of the woman even during pregnancy planning , so that there is time to undergo treatment if the diagnostic data are positive.
It is better if the woman undergoes examination at least six months before the expected conception . It should be borne in mind that the full course of treatment for HPV takes 4 months - this is exactly the period of development in the body for this virus.
So, a woman can be prescribed the following diagnostic procedures:
- Gynecological examination to detect external signs of infection - warts, genital warts.
- Cytological examination of smears from the vagina and urethra may show abnormal cells that are present in cases of HPV infection.
- Vaginal swab for PCR (Polymerase chain reaction).
- Screening Digene test is a cytological examination of epithelial cells from the cervical canal, taken by scraping. Shows both the degree of concentration of the virus in the body and its oncogenic activity.
- Histological examination of tissue samples taken by biopsy.
There are frequent cases of false-positive or false-negative diagnostic results for the human papillomavirus, especially in the absence of external symptoms. In these cases, if the presence of HPV is suspected, a complex of examinations using several methods is necessary, as well as repeated examinations after a certain period of time.
How is a child tested for HPV?
Papillomas in the throat of a newborn
If characteristic papilloma-like formations are detected on the skin of a newborn child, the diagnosis can be made immediately, with a visual examination.
To confirm the presence of human papillomavirus in the body of a newborn child and for differential diagnostic purposes, it is sometimes necessary to perform a PCR screening test .
To confirm laryngeal papillomatosis, a diagnostic procedure of direct laryngotracheoscopy .
Localization of neoplasms
Epithelial growths do not cause discomfort if they do not come into contact with clothing. When localized in the inguinal fold or near the anus, it causes irritation. To avoid scratching and inflammation, it is important to monitor the hygiene of the baby.
Simple papillomas form on the child’s hands: palms, between the fingers. Much less often - in the nasolabial triangle. Plantars occur near the big toes. With movement and external pressure they become painful.
With respiratory papillomatosis, thread-like warty processes form on the mucous membranes of the larynx and respiratory tract. They are mobile and can easily block the larynx when inhaling.
For the baby:
- the voice becomes hoarse;
- attacks of stenosis occur;
- breathing becomes difficult.
The pathology is difficult to treat. Papillomas on the palms and arms, feet resembling rough red-brown spots are signs of dangerous warty epidermodysplasia.
Vulgar, filiform, flat warts usually grow in the auricle. Later they grow and change structure. Thread-like papillomas in newborns on the ear appear in the form of yellow plaques. Over time they harden, change shape and volume. Flat (youthful) ones more often grow in schoolchildren. Warts have a smooth texture and a flat oval top. Localized in the auricle, near the tragus, on the outside of the ear.
How does papilloma manifest itself and is treated in a child?
However, there is agreement that children have papillomas that cause a visible cosmetic defect on the face or are located in a place where they are often removed, papillomas in the mouth or papillomas on the tongue, ear, which require treatment at a very early age.
The essence of the problem
Papillomas in children are benign wart-like growths of the skin that are almost always caused by infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). This is common among children of all ages—even newborns are not surprised to see papillomas.
A child becomes infected through contact with the virus, i.e. through direct contact with a carrier of the virus or through ordinary toys in kindergarten, clothing, and everyday items.
In this case, the penetration of the virus is facilitated if the skin breaks through in the form of abrasions, cuts, and scratches.
You might be interested in: How to give an enema to cleanse the intestines at home?
Papillomas in newborns are most often caused by intrauterine infection through the mother's body.
A virus that penetrates the skin causes active growth of epithelial cells, which leads to the formation of warts. When HPV is activated in children, the reasons are associated with a decrease in immune defense and the creation of favorable conditions for the virus. Such conditions are ensured by the following factors:
- frequent skin damage;
- colds;
- digestive problems;
- poor nutrition;
- allergic sensitivity;
- stress;
- metabolic disorder;
- solar radiation;
- hygiene disorder.
In adolescents during puberty, the growth of papillae is associated with hormonal changes.
How do childhood papillomas manifest?
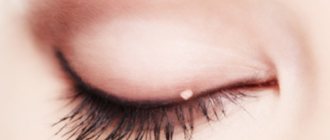
Papillomas in children usually appear 6-12 months after HPV infection, but their appearance is always unexpected. Warts in children are accidentally discovered in hidden places - in the folds of the skin, in the armpit area, between the fingers. The most common location of papillomas in infants is the soles, hands, and face. At the same time, papilloma in children can appear in unexpected places: the mouth and nose, larynx, bronchi. In newborns, congenital papillomas in the eye area, eyelids, ears, face and tonsils are most often “hereditary”.
Depending on the shape of the node, etiology and localization, the following main types of childhood papillomas are distinguished:
- Common (vulgar) type: a round, dry wart with a rough surface, most often on the knees, buttocks, arms, but which can appear anywhere on the body.
- Flat-type papillomas in the form of clearly defined spots that hardly rise above the surface of the skin - in infants, such defects are sometimes accompanied by itching and inflammatory reactions due to frequent scratching.
- Basic type: has the form of a small, hard yellow wart with a dot inside, localized on the surface of the sole or in the form of dry calluses without internal dots - causes pain when lying on the foot, especially when walking on an uneven surface.
- Hanging, digital papillomas in the form of small papillae on a thin leg may have a pink tint, but the predominant color of the flesh is more common on the face, neck and groin.
Diagnosis and treatment methods
For papilloma-like formations, the dermatologist makes a conclusion after a visual examination. To confirm the primary diagnosis and differentiation, a screening PCR test is performed and a blood test is prescribed. In case of laryngeal papillomatosis, he is sent for laryngotracheoscopy.
In difficult cases, a specialist examines tissue under a microscope for the cytopathic effect of the virus and nuclear inclusions, the type of interaction of the subtype with the cell. The presence of atypical koilocytes and altered nuclear cells are indicators of HPV activity. The virus itself is recognized using the DNA method. If oncology is suspected, histological studies are performed.
The technology for treating papillomas in children is determined by:
- size of epithelial growth;
- depth of lesion;
- location.
During diagnosis, several types of HPV are sometimes detected. Each of them requires an individual treatment regimen. A priori, there is no universal way to eliminate the virus from the body. Experts are inclined to carry out conservative therapy with an emphasis on immunomodulators, vitamins, and antiviral agents even with single fragments.
Conservative methods are aimed at suppressing the activity of the pathological agent and increasing defenses. When the biological functions of the immune system are restored, 90% of the skin cleanses itself. In special cases, radical measures are used. In case of inflammation, suppuration, formations in the larynx, eyelids, ears, the growths are removed.
Drug therapy
Not all adult treatment programs are suitable for children. Local immunomodulatory antiviral agents are contraindicated due to toxicity.
Formulas that activate the production of natural interferon are considered safe:
- Aminiksin (from 7 years), Likopid, Viferon, Isoprinosine.
- Injection drugs - Panavir, Cycloferon, Galavit, Taktivin.
For the treatment of papillomas in children, the antiviral Panavir with phytoformula is indicated in different dosage forms: on an ointment basis, in the form of rectal and vaginal suppositories, injections.
Local remedies
To remove simple warts, ointments with antiviral formulas are used:
- Viferon inhibits the activity of the virus.
- Aerosol "Cryopharma" acts with cold.
- Dermavit burns with celandine extract. The product is not intended to get rid of papilloma in a child in the groin, armpits, or near the mouth.
- An analogue is the herbal medicine “Supercleanness”. It acts more gently without leaving marks.
Solutions of salicylic acid and Feresol are suitable for schoolchildren. They have a cauterizing and mummifying effect, causing a short-term burning sensation. Viral warts are locally treated with solutions 3-4 times a day until completely eliminated. Solcoderm, which contains several types of acids and copper nitrate in the formula, will help get rid of papilloma in a child. The principle is the same: apply the product many times with an applicator and wait until the leg dries.
A proven remedy is a lapis pencil. Before use, the conical tip is moistened and the surfaces of the brushes and soles are treated. Do not use to remove skin defects on the face, as a scar may remain on delicate skin.
Removal of tumors
There are several radical ways to remove papillomas in a child:
- Laser ray. With its help, multiple formations in any location are removed absolutely painlessly in one session.
- Plasma coagulation. The non-contact method is characterized by speed and a small area of damage to adjacent tissues. The principle is to evaporate tissue with a plasma arc discharge.
- Cryodestruction. One of the best methods for removing warts from hands and face. Using liquid nitrogen, the cells are frozen and destroyed. After a week, no trace remains of the skin disease.
The chemical method for a child under 7 years old involves the use of acidic solutions - Solcoderm, Duofilma. For older children, Feresol is allowed. The technology is relevant for burning single specimens.
Folk remedies
In addition to pharmaceuticals, home remedies are used. Frequently treating the surface with tea tree ether burns the wart off at the root.
They help remove papilloma from a child’s foot:
- tar soap;
- propolis;
- whipped egg white.
They lubricate the problem area. seal with gauze overnight.
Decoctions help remove human papilloma viral infection in adolescents. Valerian, lemon balm, hop cones, coriander, linden are infused, take a glass a day. Every day it is useful to eat 5 walnuts, take 6 tablespoons of onion decoction with a spoon of honey, and rosehip infusion.
Clinical picture
The main sign of the disease is the appearance of a tumor on the mucous membrane or skin. More often there are no symptoms. But small papillomas are capable of uniting into colonies of overgrown epithelium, the length of which reaches 6 centimeters. When they are damaged, the virus spreads throughout the skin, causing infection of the wound.
Pustules appear on the skin. The following signs are observed:
- problems swallowing;
- difficult nasal breathing;
- speech delay;
- problems with walking;
- decreased hearing and vision.
Some types of HPV (16, 18 and 52) are characterized by degeneration into a malignant process. To prevent papilloma from appearing in a child, Komarovsky advises vaccination at the age of 13, before the start of active sexual life. If the growth is already present on the skin or mucous membrane, a comprehensive diagnosis is indicated:
- PCR. Determining the concentration of the virus in the circulatory system using its DNA.
- Biopsy. Identification of the peculiarities of tissue formation and the nature of the localization of its layers.
- Histology. The diagnostic result helps make a prognosis by assessing the likely risk of cells transforming into cancer.
A blood test is prescribed to determine the type of virus. It is recommended to treat papillomas in a child after consultation with an oncologist and surgeon.
Virus activation factors
Children with permanent injuries, cuts and abrasions are most susceptible to infection, since the virus cannot penetrate through healthy skin. But the virus “sleeping” in the body is not always activated; this requires certain conditions that reduce immunity. Papilloma in a child occurs under the influence of certain factors:
- allergic reactions;
- helminthic infestations;
- endocrine system disorders;
- exacerbation of gastrointestinal diseases;
- frequent colds.
To understand why growths appear in young children, you should undergo diagnostics. It will show what became the provoking factor for the activation of the HPV virus.
What symptoms does papillomavirus cause?
Childhood papilloma does not appear immediately after infection. Parents may not detect a growth on the baby’s body for a long time. After some time, when education begins to cause discomfort, the child may complain to adults.
The disease manifests itself in the formation of growths, warts, and condylomas on the body, which do not differ much in color from the skin tone.
Associated symptoms include:
- itching, burning, redness of the skin;
- increase in body temperature (slight).
With papillomatosis of the larynx the following are noted:
- the occurrence of hoarseness in the voice;
- difficulty swallowing and breathing;
- dyspnea.
A one-year-old baby can already show his parents what bothers him, where it itches or hurts, but papillomas in a baby are more difficult to detect. Therefore, pediatricians recommend examining the baby’s skin at least once a week after bathing.
The disease is recognized by its characteristic external signs:
- growths resembling a papilla or mole;
- often the shade of the formations does not differ from the color of the skin;
- the size of warts may vary, but do not exceed 5 mm;
- condylomas differ from warts in their intensive growth and damage to a large area of skin (in large numbers), most often this is the name for rashes in the mouth and on the mucous membranes of the genital organs;
- warts have a soft surface and do not become rough;
- The shape of the growths is different: on a stalk, elongated, flat, in the form of a fungus.