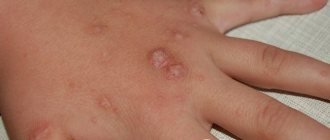
Many patients experience the appearance of papilloma on the abdomen. The cause of the formation of growths on the skin of the abdomen or in the navel is the papillomavirus. Today, scientists have isolated about one hundred strains of HPV. To determine the type of human papillomavirus that attacked the body, a technique such as PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is used. Such diagnostics allows one to determine the degree of risk of malignancy of the formation.
READERS RECOMMEND!!!
To treat papillomas, our readers actively use the remedy... Read more
The insidiousness of the papillomavirus in its long incubation period. For several months, and sometimes years, a person is unaware that he is a carrier of the virus. At this time, he is especially dangerous for people close to him.
After all, the main routes of infection are:
- Contact (direct contact with an infected person or problem area of skin through a handshake, hug);
- Household (failure to comply with hygiene standards: use of shared towels, washcloths, soap);
- Sexual (during sexual contact).
Reasons for appearance
Neoplasms on the abdomen appear due to papillomavirus. When the virus is dormant, it may not manifest itself in any way. However, after HPV enters the active stage of development, the virus penetrates the DNA of epithelial cells, as a result of which they grow and new growths appear on the body. Speaking about why the dormant papillomavirus awakens from hibernation, it is worth highlighting the following factors that contribute to its activation:
- decreased immunity and defenses of the body;
- age-related changes;
- hormonal imbalance;
- pregnancy;
- long-term use of steroid and antibacterial drugs;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- bad habits;
- promiscuous sex life.
Papillomas on the abdomen often appear during pregnancy and disappear after childbirth.
What are flat papillomas?
Flat papillomas are a specific manifestation of human papillomavirus infection on the skin. Penetrating into the body, pathogenic strains integrate into epithelial cells and gradually replace healthy cells. Under the influence of pathogenic activity, the natural regeneration of epithelial tissue is disrupted, and pathological growths are formed.
External manifestations of HPV are evidence of reduced immunity and various diseases of organs and systems.
Flat papilloma has some differences that make it possible to differentiate the growth from other neoplasms on the skin of a sick patient. Often the growth is confused with an ordinary mole, nevus and no attention is paid until symptoms of malignancy appear. Common types of papillomas and warts, as well as their main differences from moles, can be found in a separate article on our website.
There are a number of differences::
- dense structure;
- slight difference in shade from the main skin color;
- diameter no more than 8-9 mm;
- slight elevation above the surface of the skin;
- diverse localization;
- irregular form of neoplasm.
The surface of the growth is shiny, similar to a drop or bubble, and has no signs of hyperkeratosis. Flat papilloma forms on the neck, knees, back of the hands, face, and lower extremities. There are cases of flat papilloma appearing in intimate places, on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and genitals.
Routes of transmission of the virus
The most common routes of infection and transmission of HPV are:
- Contact. Contact with an infected person or problem area of skin is enough.
- Domestic. Neglecting personal hygiene rules can cause HPV infection, so you should never use other people’s hygiene products. If you have even small wounds on your body, it is not advisable to visit swimming pools, saunas, gyms, etc.
- Sexual. Most often, papillomavirus is transmitted sexually.
Another way of transmitting the human papillomavirus is from mother to child.
It is not uncommon for a child to become infected while passing through the birth canal.
Self-infection can also occur, during which the HPV pathogen is transferred from one part of the body to another.
An adult's appendage protrudes from the navel
- 01 August
- 0 rating
The umbilical region is a part of the abdominal wall, limited by horizontal lines connecting the ends of the X ribs above, the anterior superior iliac spines below, and vertical lines passing through the middle of the Poupart ligaments on the sides.
The navel is located in this area - a retracted scar that forms where the umbilical cord falls off. The navel covers the umbilical ring - an opening in the aponeurosis of the white line of the abdomen, through which blood vessels, the vitelline and urinary ducts penetrate the abdominal cavity of the fetus (Fig. 1).
After the umbilical cord falls off, the hole closes; the channels passing through it are deserted.
Rice. 1. Umbilical ring with passing germinal vessels and ducts, from the remains of which fistulas and umbilical cysts develop in children and adults: 1 - umbilical vein; 2 - umbilical-intestinal (yolk) duct; 3 - urinary duct; 4 - umbilical arteries.
Rice. 2. Congenital umbilical hernia.
In the navel area there can be congenital and acquired fistulas. The latter arise as a result of ulcers in the abdominal cavity breaking through the navel. Surgical treatment is excision of the navel along with the fistula.
Benign tumors in the navel area include lipomas, fibromas, adenomas and cysts from the remnants of the vitelline and urinary ducts.
Malignant tumors are often secondary - metastases of cancer of the stomach, intestines, uterus and its appendages.
The navel (umbilicus, omphalos) is a scar formed at the site where the umbilical cord falls off after birth. Located in the center of the umbilical region (regio umbilicalis), which is part of the anterior abdominal wall (see).
The skin of the navel serves as an outer cover for the umbilical ring, a defect in the linea alba, through which embryonic vessels (umbilical vein and arteries) and ducts: urinary and vitelline passed in the antenatal period of development (Fig. 1).
In the navel area there is no subcutaneous and preperitoneal fat - the skin is directly adjacent to the scar tissue that formed the umbilical ring. This is followed by the umbilical fascia (part of the transverse fascia of the anterior abdominal wall) and the peritoneum, fused to the circumference of the umbilical ring. In a third of cases, the umbilical fascia is absent (A. A. Deshin).
The location of the navel depends on age, gender, condition of the abdominal wall, etc. and on average corresponds to the level of the III-IV lumbar vertebrae. Newborn premature babies have a low navel.
Rice. 1. Umbilical ring with passing germinal vessels and ducts, from the remains of which fistulas and umbilical cysts develop in children and adults: 1—umbilical vein; 2 - umbilical arteries; 3—urinary duct; 4 - umbilical intestinal (yolk) duct.
The umbilical ring is one of the weakest areas of the anterior abdominal wall and the site of exit of hernias (see).
The color of the skin of the navel is of diagnostic importance: it is yellow with bile peritonitis, blue with cirrhosis of the liver and congestion in the abdominal cavity with insufficient compensation of collateral circulation, with intra-abdominal bleeding in patients with an umbilical hernia.
Preservation of the natural color of the navel during peritonitis indicates sufficient vascularization of the peritoneum and is a prognostic sign.
In emergency surgery, the symptom of “navel crepitus” is of great diagnostic importance. It is determined by the presence of air in the abdominal cavity (violation of the integrity of organs) and at the same time an umbilical hernia. Air escaping through the umbilical ring gives a crunching sensation when palpating the navel (as with subcutaneous emphysema).
Umbilical symptoms occupy an important place in the diagnosis of inflammation of Meckel's diverticulum - pain in this disease constantly radiates to the navel, intensifies when the abdominal wall is pulled anteriorly, in some cases swelling and hyperemia of the navel are noted.
In the umbilical region there are rich arterial and venous communications. The arteries are located in two “floors” - in the subcutaneous fat and the preperitoneal layer; there are anastomoses between both of these layers.
The arteries are branches of the superficial, superior and inferior epigastric, as well as superior vesical and umbilical arteries, which retain patency in a certain part in the postnatal period of development (G. S. Kiryakulov). Through them, contrast agents and drugs can be injected into the abdominal aorta.
The preperitoneal arterial circle is formed mainly by the inferior epigastric arteries, branches of the cystic and umbilical arteries. Between both “circles” there are many anastomoses that play a large role in the collateral circulation of the anterior abdominal wall.
Of the veins of the umbilical region, the portal vein system (v. portae) includes the umbilical and paraumbilical veins (v. umbilicalis et v. paraumbilical), the inferior vena cava system (v. cava inf.) includes the superficial, upper and lower epigastric (vv. epigastriacae superficiales sup., inf.).
Thus, extensive porto-caval anastomoses are formed around the navel, which expand significantly with intrahepatic portal blocks, especially with cirrhosis of the liver (Fig. 2), and have the appearance of a “jellyfish head” (caput medusae).
This symptom also has a certain diagnostic value in recognizing portal circulation disorders.
Source: https://papillomnet.ru/papillomy/iz-pupka-torchit-otrostok-u-vzroslogo.html
What types of growths are there and why are they dangerous?
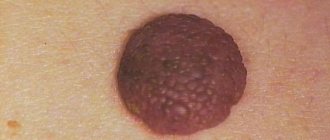
The color of papillomas in the navel and abdomen is flesh-colored or brown, and their shape can be convex or flat. The growths can reach 2 cm in diameter, but in most cases their size ranges between 1-2 mm. There are several types of tumors on the abdomen, which differ from each other in appearance and nature of the course.
Simple
Simple umbilical papillomas, also called vulgar, have a round shape with a keratinized surface, and their diameter does not exceed 1 mm. Such warts on the stomach cause virtually no discomfort.
Flat
Flat growths are characterized by a round or angular shape and a smooth surface. They may be flesh or light brown in color. The occurrence of such neoplasms is accompanied by redness and inflammation of the affected area of the skin, as well as severe itching.
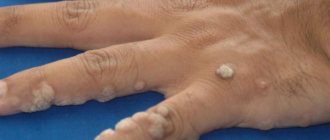
Filiform or acrochords
Filiform warts on the abdomen have an elongated shape, resembling a small bump. They grow up to 6 mm in length. Over time, papillomas can increase, which not only looks unsightly, but is also fraught with mechanical damage. For this reason, it is recommended to remove acrochords on the abdomen immediately.
The danger of tumors on the abdomen is due to the fact that over time they can degenerate into a malignant tumor if the HPV is of an oncogenic strain.
In addition, the appearance of warts in places where clothing rubs leads to the fact that they often tear and bleed, as a result of which the surrounding tissues become inflamed.
Possible complications
If the papilloma is frequently rubbed with clothing or scratched with nails, it can become injured. This usually manifests itself as redness of the formation, discoloration, and bleeding. In this case, the papilloma may be subject to external infection, which may contribute to the formation of a malignant tumor . The best solution in such a situation would be to remove the skin defect as soon as possible.
It is important! Another possible complication is malignancy of papilloma. In this case, papilloma cells acquire the properties of a malignant tumor. The basis of this process is a violation of the formation and proliferation of cells. If the growth of the tumor progresses sharply, it constantly bleeds and has an atypical color, consult a doctor as soon as possible!
Diagnostic goals
When papillomas appear on the chest and abdomen, a diagnosis must be carried out, the main goal of which is to establish the type of HPV that attacked the body. For this purpose, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique is used, which makes it possible to determine the timing of infection and the degree of risk of malignancy of these formations.
After the dermatovenerologist examines the skin on which there are the slightest defects, the patient will need to take tissue samples and blood for analysis. To do this, the following procedures are carried out:
- Biopsy. This procedure, during which tissue samples are examined, allows one to exclude or confirm the malignant nature of papilloma.
- Histology. Histological analysis is carried out after removal of the wart. Based on this, it is possible to make an accurate diagnosis.
Risk of degeneration into cancer
Doctors have noted the ability of papillomas to degenerate into melanoma under the influence of provoking factors, which can happen after several months or years. Malignant formation has its own characteristic signs:
- darkening of the growth is observed,
- by the diameter of the papilloma you can see redness (inflammation),
- there are no clear contours,
- the wart rapidly increases in size,
- pain is felt, discomfort can also manifest itself in a calm state,
- cracks appear on the surface,
- Fluid or blood is released from the papilloma.
If such symptoms appear, it is dangerous to delay consulting a doctor. The specialist will conduct an external examination and send for other diagnostic methods: colposcopy, biopsy, urine and blood tests. Only after this will a conclusion be issued and treatment prescribed.
Source
Should I delete it?
Many people mistakenly believe that if papillomas that appear on the abdomen cause only aesthetic discomfort, but do not hurt, itch or itch, then it is not worth getting rid of them. They don’t even think about the fact that neoplasms that appear on any part of the body indicate infection of the body with HPV. As the virus circulates in the bloodstream, there is a risk of papillomas spreading to other areas of the skin and even to internal organs, so doctors strongly recommend getting rid of growths on the abdomen immediately after they appear.
Features of clinical manifestations
If the virus is in a dormant state, then a person will not be able to find out about it until he passes the appropriate tests. The most pronounced symptoms of HPV are papillomas. They can occur in different parts of the body. At the same time, these can be either single or multiple formations. Depending on the type, they may look like bumps, thread-like processes, scaly growths, or ordinary warts.
In some cases, for example, when growths are traumatized, redness of the skin in this area, itching, soreness, and inflammation may be observed.
How to get rid of papillomas?
It is impossible to completely cure HPV, but through complex therapy it is possible to minimize the risk of malignancy of tumors and prevent their growth.
Mechanical removal
There are the following methods for removing tumors on the abdomen:
- Radio wave therapy. The tumor is removed using a non-contact method using the Surgitron device. During this painless procedure, the papilloma dries out and disappears on its own after a few days.
- Cryodestruction. Papilloma tissues are frozen with liquid nitrogen.
- Electrocoagulation. New growths are burned out by high-frequency electric current.
- Laser destruction. The growth cells are evaporated layer by layer with a laser beam.
- Surgical excision. The papilloma is cut out with a scalpel.
- Chemical method. To cauterize the growth, pharmaceutical preparations containing aggressive alkalis or acids are used.
Drug treatment for papillomavirus
Drug therapy for papillomavirus infection is carried out using a whole range of drugs that have bactericidal and cauterizing effects. This helps prevent further development of growths. The most effective medications for the treatment of this disease are considered to be solutions with a chemical composition that has a detrimental effect on papilloma.
These include:
- Feresol;
- Verrucacid;
- Super clean;
- Podophyllin;
- Cryopharma;
- salicylic acid;
- phenol in glycerin.
Folk remedies
You can get rid of growths on the stomach with the help of traditional medicine. However, before starting alternative treatment, you should definitely consult with your doctor.
The following products have proven themselves to be effective in removing formations on the abdomen:
- Celandine juice. Cut the plant and cauterize the growth with the sap that comes out of the stem. The procedure should be carried out 2 times a day until the tumor disappears.
- Garlic. To get rid of papillomas, garlic ointment is often used, which is prepared according to this recipe: a clove of garlic must be chopped and mixed with 1 tsp. baby cream The resulting composition must be applied in a thick layer to the problem area of the skin and fixed with a gauze bandage. After 2 hours, the ointment is washed off. You need to carry out a similar procedure 2 times a day for a week.
- Aloe. Cut an aloe leaf, squeeze out the juice, soak a cotton pad or gauze in it, and then apply it to the papilloma and secure it with a band-aid. The compress must be changed 3-4 times a day. The duration of treatment is 5-7 days, after which the growth should disappear.
Treatment methods
Contacting a specialist is required to establish the nature of the neoplasm and the causes of its occurrence. Treatment methods include physical therapy, medications and traditional medicine. Removal can be done:
These methods make it possible to remove formations after a single procedure; they are more often used when papilloma degenerates into melanoma. Due to the high price, few can afford these medical procedures to remove benign growths, so preference is given to medications:
- Super celandine;
- Verrucacide;
- salicylic or oxolinic ointment;
- Panavir;
- Solcoderm;
- Cryopharm;
- Salipodu.
Preparations can only be used after consultation with a dermatologist, since contact with healthy areas of the skin can cause damage.
Prevention of papillomas formation
To prevent the appearance of papillomas on the body and increase the body’s resistance to HPV, it is necessary:
- strengthen immunity;
- Healthy food;
- observe the work and rest schedule;
- follow the rules of personal hygiene;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- avoid casual sex.
By following preventive measures and timely seeking medical help, a person can protect his body from human papillomavirus infection and skin diseases.