A boil on the mammary gland can appear for various reasons, but most often it is not dangerous. Let's figure out why boils appear and how to deal with them.
First of all, you need to know that a boil on the chest is no different from inflammation on any other part of the body. From a medical point of view, this is a purulent inflammation in the upper layers of the skin caused by an infection in the hair follicle or sebaceous gland.
What does a boil look like?
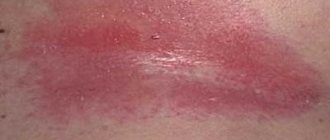
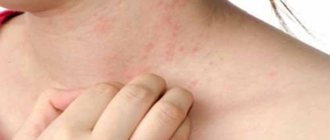
At the first stage of the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, a slight redness appears on the skin, reminiscent of a regular pimple. However, after a short time, the diameter of the formation increases (the surrounding connective tissue also turns red) and becomes denser, as a result of which a white dot forms in the middle of the “bump”. This point is the very necrotic core, inside of which there is purulent content.
IMPORTANT! You should absolutely not touch the boil, especially try to squeeze it out.
Time passes, the formation “ripens” and the rod comes out on its own. And with it all the pus and blood.
Are breastfeeding and pustular lesions compatible?
Whether you can breastfeed or not depends on what kind of boils have formed on the breast, that is, whether the lesion is deep, whether necrosis is pronounced, and the location of the abscesses in relation to the nipples. It is important to understand that the cause of furunculosis on the body is most often staphylococci. This pathogenic microorganism can be transmitted to the baby during feeding.
It is very dangerous for newborn babies to receive a portion of milk containing Staphylococcus aureus. The microbe easily takes root on the intestinal villi and provokes dysbiosis with subsequent symptoms of acute enterocolitis.
If there is one small abscess on the mammary gland, and it is distant from the nipple, then you can not interrupt breastfeeding. It is important to wash your hands thoroughly, not touch the surface of the boil, and treat the nipple before feeding so as not to provoke the transmission of infection to the child.
If there are several boils, it is recommended to conduct a microbiological examination of the milk, that is, check for the presence of bacteria in it. The study will help determine further feeding tactics. The result of the analysis will have to wait about 7 days.
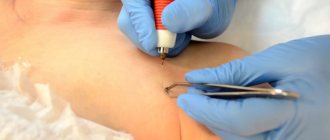
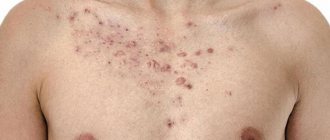
Photo
The photo shows what a boil on the chest looks like:
Preventive measures
The topic of preventing the appearance of boils is relevant for many people, but it is especially paramount for the following categories of patients:
- Pregnant women.
- Nursing mothers.
- With a weak immune system.
It is important to follow the following rules:
- Properly organized GW.
- Avoid nipple cracks.
- Be sure to do air baths for your breasts.
- Don't forget about regular personal hygiene.
- Give preference to special bras.
And most importantly, if a boil does appear on your chest, do not self-medicate in any way.
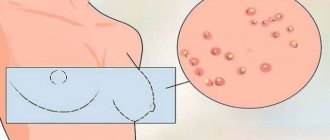
Where is the boil on the chest located?
Theoretically, a boil can appear anywhere where there is hair or a sebaceous gland. The breast falls under both risk factors.
Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should be especially careful. Their immunity is somewhat weakened by the special condition of the body, and its defenses cannot cope with staphylococcus. As a result: a boil is formed, the development of which is accompanied by pain and characteristic itching.
Following the localization of the inflammatory process, boils are diagnosed:
- on the nipple;
- on the skin of the breast;
- on the areola;
- under the mammary gland.
Ulcers on the breast
Even a single boil can provoke a whole range of unpleasant sensations (pain, general malaise, dizziness, increased temperature) if it is located on the skin of the mammary gland. There are many reasons for this:
- the boil comes into contact with clothing;
- the skin in this part of the body is very delicate;
- Pregnant women's breasts are incredibly sensitive;
- The nursing mother is also forced to latch on to the baby/express milk.
On the nipples
Considering the fact that nipples have many nerve receptors and are often injured during breastfeeding, boils on them are accompanied by slightly different patient complaints:
- the pain is shooting in nature (due to abundant innervation);
- pathological fluid is released from the breast, which is especially dangerous during lactation;
- axillary lymph nodes enlarge;
- the nipple may become deformed.
How to treat a mass on the sternum
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Treatment of a boil on the female breast is carried out in two ways: medication and surgery. The choice of method of influence depends on three factors: the stage of formation, the severity of the process, and medical restrictions on the use of the proposed therapy.
Drug treatment can reduce the unpleasant manifestations of the disease, speed up the release of pus, and wound healing. Effective means of combating boils on the chest include:
- Local preparations with drawing properties make it possible to remove pus from the necrotic area and promote the activation of reparative processes. Compresses are made with them, which are changed 2-3 times a day. Local preparations with a pulling effect include Vishnevsky's liniment, Ichthyol ointment and Levomekol.
- When applying a compress to a boil, it is important not to introduce a new infection into the inflammation site and to reduce the number of microorganisms inside the formation. Disinfecting liquids such as Fukortsin, Chlorhexidine, and hydrogen peroxide cope with this function. The listed means are used to treat the inflamed area and surrounding breast tissue before applying antibacterial, wound-healing drugs.
- In the second phase, it is necessary to speed up and facilitate the exit of the pustular rod. Doctors advise using Himopsin.
- Staphylococci are the main cause of breast boil formation. To achieve recovery of the patient, they resort to the use of antibiotics locally and systemically. Penicillins, Macrolides, and Cephalosporins in tablets, powders, and ointments are used for treatment.
- In order to restore tissues damaged by pathology, Solcoseryl gel is used.
Surgical treatment is indicated in the following cases:
- The patient developed complications of the disease.
- The breast boil does not break out for a long time.
- There were signs of systemic damage.
- There are several boils in one place.
Surgical intervention is carried out as follows:
- The pathology site is treated with antiseptic drugs (iodine, Betadine, Miramistin).
- The breast boil is injected with local painkillers such as Lidocaine, Novocaine.
- When the anesthesia takes effect, they begin to open the boil.
- The surgeon cuts the abscess and removes the pathological contents.
- Then he places a drainage and bandages the postoperative area.
- Discusses the dressing days with the patient and gives recommendations on wound care.
To prevent the recurrence of breast boils, doctors advise taking preventive measures:
- Purchase your own hygiene items. They should not be given to anyone.
- Daily bath procedures are the key to beauty and health. Microbes will not be able to resist the local immunity of well-groomed skin.
- Skin lesions of varying depths must be promptly treated with antiseptic drugs.
- A balanced, fortified diet will help strengthen the body's protective functions.
Timely treatment of furunculosis and proper skin care provide a favorable prognosis for the pathology.
Reasons for appearance
Medical sources say that the main reason for the proliferation of Staphylococcus aureus/white is a decrease in immunity. This category includes:
- diseases of various types (diabetes mellitus, colds, thyroid diseases, cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis);
- metabolic failures;
- obesity;
- chronic fatigue, sleep deficiency;
- lack of vitamins/nutrients;
- poor nutrition;
- bad habits (addiction to alcohol, smoking history, taking narcotic drugs);
- being under stress, nervous exhaustion, emotional instability.
However, a weak defense system of the body is not the only reason why boils appear. Their causative agent is a pathogenic bacterium that needs to penetrate the skin. This happens by infecting the body through injury/damage. It could even be a microscopic scratch that the patient simply will not notice.
The lack of basic hygiene also plays an important role. Especially when in the hot season a person sweats, but does not shower often.
Will vitamins help with boils?
Since the occurrence of boils is closely related to a decrease in immunity, it is recommended to take a vitamin course to keep the body in good shape. This will strengthen the immune system, promote rapid relief from the inflammatory process, and also reduce the severity of negative symptoms.
Currently, there are many high-quality, combined drugs on the shelves of pharmacies, including components specially selected for each other. Vitamins for adults are prescribed by a doctor, since he can choose the drug that suits you best, and you can use it for prevention, without waiting for the possibility of a boil or other pathological condition.
Important:
You should clearly define which vitamins you should take, and not mix different medications together.
For an adult without serious health problems, fasting may be recommended for boils. Under no circumstances should pregnant women fast, as the fetus must absorb nutrients.
Symptoms
The main symptom of the disease is a painful cone-shaped lump, which goes through several stages of development:
| Stage of development of soft tissue infiltrate | There is a slight swelling, the skin turns red, and a formation resembling a pimple appears. |
| Stage of suppuration of the hair follicle/tissue necrosis | The boil thickens, the skin on it shines, and a white dot appears in the middle. This is the necrotic core, which indicates suppuration of the hair follicle and necrosis of surrounding tissues. The body suffers from general intoxication. |
| Necrotic core exit/healing | The pus presses on the walls of the boil, as a result of which it “opens”, releasing a purulent core. If the wound is well cleaned, the breakthrough site will heal quickly enough, filling with granulation tissue. |
Every patient can tell about the accompanying symptoms of the “ripening” of a boil, since they are often individual in nature:
- moderate/severe pain (depending on the location of the boil);
- decreased ability to work;
- temperature increase;
- weakness/malaise;
- headache.
Development of infection
The development of a boil on the chest is no different from if it appeared on another part of the body. After staphylococcus penetrates the hair follicle and as a result of its vital activity, the inflammatory process begins. Initially, it occurs in deep layers and is invisible on the surface. Then a slight redness begins to form, which very quickly increases in size. And already on the 3rd day, a pustule is formed in the form of a cone with a white lid at the top. The diameter of the neoplasm can be several centimeters. The boil causes significant discomfort due to soreness and tightness of the skin. When touched, it feels like the pustule is filled with pus, as its walls spring back when pressed.
The boil develops in the same way as in other parts of the body.
The head of the purulent core becomes more and more distinct, and after a few more days the abscess breaks through and the pus flows out. You immediately feel relief as the pain and redness subside. If you look more closely, at the bottom of the ulcer you will see a funnel with the remains of a necrotic core. This fact makes it possible to distinguish a boil from other pustular skin lesions.
The residue gradually disappears, and the wound begins to heal with connective tissue. This process is quite long and depends on the general condition of the body. Since the cavity after a boil is quite deep, there is a high probability of scar formation. It can be either sunken or convex. The scar initially has a dark red, bluish color, but gradually the color evens out.
There are many nerve endings in the chest area and even one boil can be painful. With multiple ulcers, the general condition worsens and symptoms of intoxication appear: headache, nausea, weakness.
If the boil is not treated, symptoms of an abscess may develop - when a cavity filled with pus forms subcutaneously. It is characterized by pain, swelling, and redness.
The pus in the capsule does not spread to neighboring areas, but if there is too much of it, the abscess can burst and form phlegmon - a diffuse purulent lesion of the tissue or muscles.
Complications
The localization of ulcers on the chest is associated, first of all, with the close location of the lymph nodes. Accordingly, inflammatory purulent processes can provoke diseases such as lymphangitis/lymphadenitis.
Patients with a history of heart disease, kidney disease, diabetes mellitus, as well as cancerous tumors should also be extremely careful. A severe course of the purulent process will only aggravate the clinical picture and provoke complications of an infectious nature, sepsis, and death.
Single boils rarely pose a threat even to a weakened body, but their mass distribution is too dangerous even for young people.
Effective treatment
Treatment usually involves taking individually selected medications. Before prescribing therapy, the doctor may order a general blood test and microbiological examination of the infectious agent.
The following treatment methods are currently used:
- Physiotherapy: electrophoresis, IR irradiation.
- Taking antibiotics, in tablet form or topically as an ointment.
- Surgical removal.
Surgery may be required if the infection threatens to spread through the vessels or lymphatic ducts. If you apply on time, surgical treatment will not be necessary.
What you should pay special attention to
Sometimes, in most cases in women, unpleasant small pimples may appear in the nipple area. They should not be touched: the area is too delicate and sensitive. But if the pimple is quite large, something periodically comes out of it, it smells unpleasant, or asymmetric changes in the shape of the nipple are observed, consult a mammologist. It is likely that nothing bad is happening. But sometimes this is how some tumor diseases begin. And the sooner you find out what we are talking about, the better.
To summarize, it is worth noting that in most cases, acne appears due to insufficient hygiene, allergies, poor diet and (or) hormonal disorders. Often they go away on their own, but in order to accurately determine the cause and save yourself from unpleasant rashes, you need to consult a doctor.
We are being treated by a doctor
There are three ways to treat boils:
- local;
- general;
- nonspecific.
In the first case, the affected area is treated with alcohol solutions and bandages moistened with antiseptic liquids are applied. In the second case, suppuration can be treated by using bandages, ointments and compresses, which can quickly get rid of the boil. You can reduce pain with the help of medications administered around the inflammation with a syringe (needling).
Large ulcers in the mouth, tongue, face, head, back and other parts of the body must be treated surgically. The procedure consists of opening the cavity, clearing out the accumulated necrotic masses from it and removing the rod. The measures are carried out in a hospital setting by an experienced surgeon. Treatment with this method is necessary in several cases:
- severe inflammation;
- soreness of the area;
- impossibility of rejection of the rod in any other way.
Non-purulent discharge that may cause concern
The discharge is not always purulent, although sometimes in consistency and shade it actually resembles pathological exudate. But if the leakage of fluid from the nipples is not accompanied by severe and obvious inflammation, and there are no other symptoms, then most likely it is not pus.
Possible situations in which fluid similar to pus may be released from the nipples:
- Pregnancy. In the second half of the breast, colostrum begins to form, which the expectant mother may notice on her underwear. Its discharge does not cause concern, and the liquid itself has a fairly thick consistency and a yellowish-transparent color.
- Lactation. Leakage of milk between feedings is completely normal and should not be a cause for concern.
- If the discharge is very scanty and extremely rare, almost transparent or slightly yellowish, has no odor and is released when you press on the nipples, then this can also be considered a variant of the norm. In the mammary glands, even outside the lactation period, a small amount of a special secretion is secreted, which can come out through the milky tubules. The volume of discharge may increase due to overheating, intense physical activity, as a result of stimulation of the mammary glands, or after certain procedures.
- Galactorrhea is the spontaneous release of milk outside the period of breastfeeding. Normally, it can be released for some time after the end of lactation, but, as a rule, no longer than 6-12 months (in some cases 1.5-2 years). If a woman has not breastfed for a long time, and especially has never breastfed, then galactorrhea is caused by hormonal disorders, namely an increase in the level of prolactin, which is responsible for lactation. An increase in its amount in the body can be a consequence of an abortion or miscarriage, taking oral contraceptives and other hormonal drugs, diseases of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands or pituitary gland, liver failure (this organ ensures the utilization of hormones), certain gynecological or oncological diseases.
- Mastopathy. With such a common disease, discharge from the nipples can also be observed, but in most cases it is not purulent in nature.
- Ectasia of the milk ducts is their pathological expansion, most often developing in women over forty-five years of age. With this pathology, the resulting secretion does not dissolve in the chest, as in the normal state of the ducts, but rushes along them to the tubules located in the nipples and comes out. In some cases, deviation requires medical intervention.