HPV type 16 is the most harmful of all strains of papillomavirus , which develops and multiplies in epithelial cells.
Important! This type of virus is oncogenic, and the target for damage is the cervix, which in 90% undergoes the development of a neoplasm. The disease manifests itself in the form of flat plaques, which are localized on the external reproductive organs of a woman.
The difficulty in diagnosing the disease lies in the length of time the virus remains in the woman’s body in an inactive state. The period when the virus does not manifest itself varies from a month to several years. HPV is activated due to suppression of the immune system, which occurs when taking potent drugs or when there is a systematic lack of vitamins and minerals in the body.
Causes of HPV type 16 infection
Scientists identify several ways of infection with papillomavirus:
- Intimacy with an infected partner.
- Infection through injured skin areas. Penetrating into damaged layers of the epithelium, the virus actively multiplies and causes harm to health. The conductor of infection is blood, saliva or sweat.
- Infection of the newborn. When a baby passes through the birth canal, the baby's weakened body can become infected.
Factors contributing to infection
- early onset of sexual activity;
- regular change of sexual partners;
- use of non-standard types of sex;
- weakened immunity;
- the presence of a disease such as AIDS;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- termination of pregnancy (abortion);
- high blood sugar;
- regular stress or depression.
Why is papillomavirus type 16 dangerous?
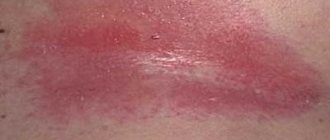
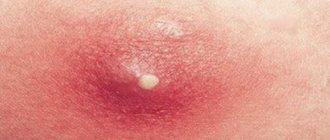
Photo 1: On average, after infection, cervical cancer can develop within 15-20 years, and if you undergo timely examination, the tumor can be cured in the early stages and the risk of relapse can be eliminated.
Source: flickr (Evgeniy rumedicalnews). HPV type 16 also provokes cancer in the following organs :
- vagina;
- rectum;
- vulva;
- larynx;
- breast.
The likelihood of developing cancer with HPV 16
Infection with this virus does not always lead to the formation of cervical cancer . Susceptibility to this disease is explained by reduced immunity and chronic diseases of the body.
With timely detection of HPV type 16 and proper treatment by a medical specialist, it is possible to prevent the development of a cancerous tumor, and the manifestation of the disease can be limited only to the formation of benign growths on the woman’s genitals.
Note! According to statistics, only 15% of patients got rid of this pathology without the disease developing into an oncological process.
Therapeutic measures
There is no universal medicine that helps cause the death of a cellular parasite, so the main emphasis in treatment is on strengthening the immune system. Today there is no single scheme allowing for complex therapy. In each specific case, all appointments are made taking into account individual indications. Most often, patients are prescribed immunomodulators and antiviral drugs. They are advised to protect themselves from hypothermia and stressful situations, and are advised to normalize their diet and maintain a daily routine.
If you have papillomas, condylomas, erosion or dysplasia of the cervix, you need to get rid of them. This can be done using cryodestruction or diathermocoagulation.
Stages of the disease
The human papillomavirus has 4 stages of development, each of which has characteristic features:
Stage 1
Infection stage. There are no obvious symptoms, which allows the virus to remain undetected for a long time.
Stage 2
The papilloma virus is actively multiplying. The presence of the virus can be determined using cytological analysis.
Stage 3
At the DNA level, the virus and a healthy cell exchange information. HPV type 16 penetrates deeply into the structure of body tissues at the cellular level.
Stage 4
The formation of atypical pathogenic mutated cells that grow, forming a cancerous tumor.
Symptoms, characteristic signs
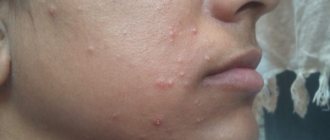
Photo 2: In the first months and even years, the disease may not manifest itself.
Gradually, single or multiple growths (papillomas) appear on the skin and mucous membranes. Source: flickr (David Anderson) The most common locations of pathological formations:
- vaginal walls;
- nasal or oral mucosa;
- décolleté area and face;
- armpit area.
Note! The formations have the appearance of a growth that rises above the level of the skin, which increases in size and merges with other identical formations.
When a woman’s reproductive organs are damaged, the following symptoms appear:
- itching and burning in the vagina and in the area of the outer labia;
- pain when urinating;
- the occurrence of scanty bruising after sexual intercourse.
This symptomatology is inherent in many infectious diseases, however, only when infected with HPV type 16, genital warts form on the mucous membrane of the genitourinary system .
How is it transmitted?
The main route of transmission of the virus is sexual. A less common method of transmission is household contact and vertical (birth) transmission. Most often, people who are just entering into sexual relations are infected. The first two years of sexual life account for a greater percentage of papillomavirus infection.
Transmission of the virus from a carrier to a healthy person occurs through damaged skin or mucous membranes. Virus particles penetrate deep into the epidermis due to damage to the natural barrier. Sexual intercourse is characterized by microtraumas through which the virus enters the woman’s body.
Diagnostic methods
To diagnose the disease, specialists perform the following procedures:
- gynecological examination;
- cytological analysis - determines the presence of atypical cells;
- polymerase chain reaction analysis - the DNA of the virus and the number of microorganisms are determined;
- Digene HPV test – determines the amount of virus in biological material;
- histological analysis - combined with a gynecological examination, allows you to assess the degree of tissue damage.
Analyzes
Any tests for HPV involve the collection of biomaterial obtained from the cervical canal. As a result of the analysis, the presence of the virus is detected, its strain and the level of viral load are determined. An HPV test is recommended for every sexually active woman at least once a year for prevention. After diagnosing papillomavirus, tests for infection must be taken every six months.
The primary test that women undergo is a Pap smear. This cytological study allows you to diagnose the presence of atypical cells in the body in the cervical area and suspect a viral effect.
The most common test aimed at diagnosing HPV is the PCR test. This is the widest range of diagnostic measures that allows you to identify the viral pathogen, its concentration and thereby select the optimal method of treatment.
The cost of such an examination will be from 700 to 2000 rubles, depending on the number of strains tested. The results are provided to the patient within 3 days after taking the biomaterial. For diagnostic reliability, the study must be carried out approximately in the middle of the menstrual cycle.
In this case, a contraindication for analysis is:
- menstruation period;
- recent sexual intercourse (less than 2 days ago);
- douching;
- recent colposcopy;
- use of antibacterial drugs (only after 2 weeks).
The results will be deciphered as follows:
Lg<3.0 – infection is absent in the body;
Lg 3.0-5.0 – viral particles are present, medium concentration level;
Lg>5.0 – the virus has a strong effect on the body, the concentration is high.
After receiving this data, it is possible not only to prescribe the correct treatment, but also to monitor the effectiveness of the therapy.
Treatment methods for papillomavirus type 16
Important! Treatment for HPV type 16 involves a combination approach that includes eliminating the virus, strengthening the immune system, and surgical removal of growths.
General therapy
The first stage in the treatment of HPV is aimed at destroying the virus. For this purpose, medicinal antiviral drugs are used - Cycloferon, Amiksin, Interferon (and other variations), Inosiplex. These medications not only effectively fight the multiplication of the virus, but also help strengthen the body’s protective function.
To treat cells that have been damaged by the HPV 16 virus, specialists prescribe the following drugs:
- Kondilin;
- Podophyllin.
The effectiveness of these drugs is due to the cauterizing effect on condylomas. The active substance causes necrosis of affected tissues and relieves the inflammatory process.
Hardware treatment
When removing genital warts, hardware techniques . These include the following procedures:
- electrocoagulation or cauterization of formations with electric current;
- laser removal;
- radio wave removal;
- cryodestruction.
Surgical intervention
Due to the increased traumatic nature of this method, surgical removal of condyloma is extremely rare. The only indication for surgery is the proliferation of cancer cells , which must be immediately removed from the body.
Is treatment possible with folk remedies?
Traditional medicine recipes can be used in the treatment of HPV type 16 only when combined with drug therapy.
Note! Self-medication can backfire and only make the situation worse. Under no circumstances should folk remedies be used to treat oncogenic papilloma without consulting an oncologist.
Celandine juice has cauterizing and disinfecting activity. To heal the wound surface after cauterization, you can use Kalanchoe or aloe juice.
In addition to the direct impact on the growth, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system. To do this, it is recommended to inhale essential oils of lemon, tea tree, cedar and eucalyptus.
Consequences of deletion
Surgery is usually prescribed for grade 2 and 3 dysplasia. At stage 1, conservative methods are used. In women with stage 2 HPV, treatment is also carried out with medications. If therapy does not bring any results, surgery is prescribed. The following methods of mechanical removal of growths can be performed:
- cryodestruction;
- radio wave therapy;
- diathermocoagulation.
Patients are very worried and ask the doctor what danger lies behind surgery. At stage 2 of dysplasia development, 2/3 of the epithelium is affected. The operation will not cause loss of reproductive function. At stage 3 of pathology development, most of the cells are affected. In this case, the reproductive organ may be completely removed. As a result, the woman will not be able to get pregnant.