Lipoma and skin atheroma are two common types of benign neoplasms. They require exceptionally attentive treatment, since in some cases (though, fortunately, not often) they can degenerate into malignant tumors. The appearance of atheroma may not cause suspicion - at first it usually does not cause much inconvenience. However, even if the tumor is not painful, you should still see a doctor. Often a lump (lipoma) on the neck or scalp gradually increases in size, in this case you need to visit a doctor urgently - the new growth will need to be examined to determine whether there is a risk of developing cancer.
Lipoma
and
atheroma
are often similar in appearance, and patients often do not distinguish them from each other, defining them under the general name “wen.” Let's try to figure out what the difference is between a lipoma and an atheroma, and also what to do if you have one of these formations.
Features of atheroma
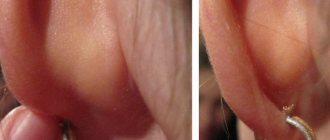
To independently distinguish an epidermal tumor from a wen, you should know the characteristics of atheroma, as well as its structure. This is a dense and mobile neoplasm, which consists of epithelial as well as fat cells. The formation rarely grows more than five centimeters. A skin cyst can appear in any part of the body where sweating is increased. These are the so-called seborrheic zones. Often there is a blockage of the sebaceous gland on the face; in most cases, the development of atheroma is often diagnosed in the forehead, upper eyelid, cheek, and wing of the nose. There is a risk of epidermal growth behind the ear or on the scalp. Epidermoid cysts of the coccyx and other parts of the back, groin, and armpit occur less frequently.
Atheroma tissue begins its development in the lower layer of the epidermis - the dermis. The tumor has a small hole that comes out and looks like a black dot. It is through this hole that infection often enters the tumor, causing an inflammatory process. The growth may have an oval or round shape; the base of the tumor has good adhesion to the skin, but inside the tissue it moves a little during palpation.
Features of lipoma
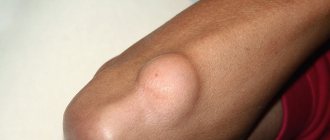
Lipoma is a benign tumor that is formed from overgrown adipose tissue, so it is advisable to call this neoplasm a wen. The neoplasm can be dangerous because it is difficult to distinguish it from a malignant liposarcoma tumor by its first signs. The formation grows slowly and can affect the back, arms, shoulders, and neck. The size of the wen can be very large (up to eleven centimeters), it can even develop on internal organs. The consistency of the neoplasm is soft-elastic, mobile during palpation, since it does not adhere to the skin.
We recommend reading: Kidney tumor - causes, symptoms of tumors, treatment
More often, the pathology has a multiple form; according to the type of content, the wen is classified into several varieties:
- fibrolipoma – to a greater extent, includes fibrous tissue;
- lipofibroma - consists predominantly of adipose tissue;
- angiolipoma – composed of adipose and muscle tissue;
- myelolipoma - consists of fatty as well as bone tissue;
- myolioma – consists of muscle tissue and a large number of altered blood vessels.
Fatty tumors that appear on internal organs are very dangerous, so they need to be diagnosed and removed immediately.
Places of education
As a rule, wen forms in places poor in adipose tissue. This is the upper back, shoulder girdle, outer thighs. Sometimes lipomas rapidly increase in size, which is typical for lipomas of the mammary glands, which can lead to its deformation.
Do you know the main symptoms of breast cancer? And how to diagnose the disease in a timely manner?
Every girl should know the symptoms of an ovarian cyst. After all, this disease does not like to wait.
Why is it so important to diagnose colon cancer in a timely manner? And how can this end? Information at: https://www.oncodisease.com/vidy-raka/kishechnik/simptomy-raka-kishechnika.html
ul
Common features
Lipoma and atheroma have a number of common features, which is why they are often confused.
The common features of these two neoplasms include:
- Benign - both growths are not malignant, however, with a combination of risk factors, a lipoma can be a precancerous condition of liposarcoma.
- Causes of occurrence - both neoplasms can occur due to metabolic disorders, mechanical damage, or genetic predisposition.
- Localization - these two tumors can occur on any part of the skin except the palms and soles.
- Absence of symptoms - apart from a visual defect, the epidermal cyst and wen do not manifest themselves in any way - they do not cause pain, itching or discomfort.
- Visual similarity - in appearance, these two neoplasms are practically indistinguishable from each other.
Based on the general characteristics, the patient is unlikely to independently determine the type of formation. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and then prescribe the correct treatment.
Differential diagnosis
The main differences between atheroma and lipoma are the mobility and density of these neoplasms. The wen is softer and has greater mobility.
A doctor can distinguish these two neoplasms by the following signs:
- a lipoma is an accumulation of adipose tissue, and a cyst is a capsule with fatty and epithelial contents;
- cystic formation has a tendency to inflammation and suppuration;
- the wen has a soft consistency, and the epidermal tumor is dense and elastic;
- the epidermal cyst moves during palpation;
- lipoma can be localized on internal organs, and atheroma occurs only in the layers of the epidermis;
- the cystic formation must be removed, as it can become inflamed, and the wen can be observed and not removed if there are no unpleasant symptoms.
We recommend reading Symptoms, causes and treatment of well-differentiated adenocarcinoma
Despite the similarity of these diseases, their occurrence requires consultation with a doctor.
Symptoms
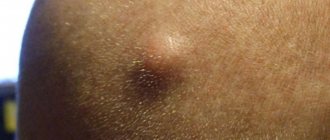
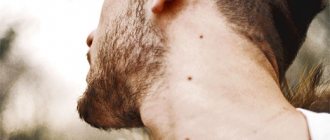
Lipoma:
- Soft, painless.
- Has not fused with surrounding tissues.
- The tumor-like formation can be freely moved back and forth.
The lipoma is shown in the first picture of this article.
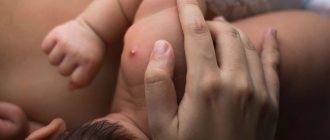
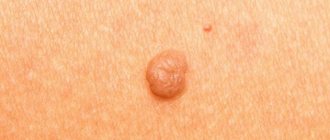
Fibroma:
- Firm, usually painless.
- Visible on the skin.
- Sometimes the tumor rises above the skin.
The fibroma is shown in the bottom picture of this article.
What is the difference between atheroma and wen
In order to accurately find out the type of formation, you need to visit a doctor, but by some distinctive features you can distinguish atheroma from lipoma yourself:
- the wen always has no inflammatory process;
- lipoma does not have an outlet;
- the cyst is harder and denser;
- the wen is easy to move;
- the epidermal formation is adhesive to the skin;
- the growth of an epidermoid neoplasm is more rapid than that of a fatty one;
- an epidermal cyst never develops on the surface of internal organs.
The fatty tissue does not have to be removed if it does not cause any aesthetic discomfort, since this type of neoplasm almost never leads to complications.
Reasons for appearance
Based on the cause of its occurrence, the doctor can determine whether the patient has a lipoma or atheroma. Wen occurs due to the fact that adipose tissue begins to grow rapidly. This can be caused by factors such as trauma to the localization site, metabolic disorders, and heredity. An epidermal cyst grows in places where there are a large number of sebaceous glands and occurs due to blockage of their duct with detritus. The patency can be disrupted by particles of the upper layer of skin or mechanical damage to the gland.
The appearance of atheroma is often associated with damage to the skin, with the introduction of particles from the upper layer into the deeper layers of the skin, as well as with an increase in the density of detritus. Cyst factors include genetic predisposition, metabolic disorders, neglect of personal hygiene, and improper use of cosmetics.
Appearance and structure
The visual manifestations of a wen and an atheroma (cyst) are similar, so outwardly they can be confused, but there are also some differences. A cystic neoplasm is often smaller in size than a fatty one. Purulent contents can be released from the opening of the epidermal cyst when pressed, which never happens with a lipoma. If you touch the wen, it has a softer consistency, because it is a growth of adipose tissue under the skin. The cyst has a dense capsule, so it feels harder to the touch. If you press on the wen, it will move to the side without any problems. The epidermoid cyst is fused to the skin; it can only be slightly moved relative to the deeper tissues.
Subjective sensations and symptoms
There are no symptomatic differences between these two neoplasms. They do not cause pain, itching or discomfort. Lipoma never becomes inflamed, which often happens with atheroma.
We recommend reading: What are nevi and what do they look like?
Symptoms of an inflamed epidermal neoplasm:
- Redness of the skin over the cyst.
- Swelling of the tissue around the tumor.
- Pain syndrome on palpation.
- Isolation of purulent exudate during purulent course.
If there is at least one sign of the development of an inflammatory process, you should immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment.
Risks and complications
Lipoma can have one complication. Very rarely, a wen degenerates into a malignant tumor, liposarcoma. An epidermoid tumor never becomes malignant, but it very often becomes inflamed. Detritus, which is located inside the capsule, is a breeding ground for the development of bacterial flora, so inflammation of the cyst is not uncommon. The purulent contents corrode the membrane of the tumor and the skin above it, and can break out or in. In the second option, soft tissue phlegmon develops. The inflammatory process can develop without infection. In such a situation, doctors first stop the inflammation with Levomekol or Vishnevsky ointment, and then remove the epidermal neoplasm.
An epidermoid cyst is dangerous because it ruptures, which can cause the development of an abscess. When localized in the genital area, both the wen and the cyst can disrupt the process of urination or cause difficulties during sexual intercourse. After surgery to remove an epidermal cyst, it may grow back. When removing an inflamed atheroma, there is a possibility that the doctor will not be able to remove the entire cyst membrane, which becomes the main reason for the development of relapses.
Methods for removing skin tumors
Removal of skin tumors is usually carried out using three main methods:
By cryodestruction method, tumors are removed using liquid nitrogen.
- Pros: the method is painless.
- Disadvantages - uncontrolled depth of impact, as a result of which the removal of the skin tumor may not occur completely, or the impact may be deeper than it should be. In this case, you will experience excess tissue scarring.
Removal of tumors with laser.
- Pros: slight bleeding after removal of the tumor.
- Disadvantages - as in the previous method, an uncontrolled depth of exposure to the laser beam may be observed.
In our clinic, we use only modern high-precision laser equipment to remove tumors. Its difference from an electrosurgical and cryogenic scalpel is that when used there will be minimal contact with the treated area. The laser beam reduces surgical injuries, improves homeostasis, and reduces pain.
Removal of tumors using electrocoagulation.
- Pros: controlled, fairly accurate depth of impact.
- Disadvantages - the risk of increased bleeding after removal of the tumor.
Removal occurs using a coagulator. After its exposure to the skin, a crust forms at the site of the neoplasm, which itself disappears after 7-10 days. If necessary, during the procedure anesthesia is performed using a lidocaine injection.
We remove tumors (warts, papillomas, moles, etc.) in our clinic in Yekaterinburg using a laser or electrocoagulation method.
>
Features of treatment
A lump or skin cyst can be completely and permanently removed only surgically or using hardware removal techniques. Doctors recommend cutting out atheroma, as well as lipoma, before complications arise. The method of removing atheroma depends on the size of the tumor. Small cysts are removed using laser or radio wave therapy. Treatment of atheroma by cutting with a scalpel is carried out only on closed areas of the body, since a scar remains after the operation. If the surgeon does not remove the entire capsule of the atheroma, relapse is possible, so surgical removal is performed less and less.
Puncture-aspiration removal
In some cases, they resort to the puncture-aspiration method of removing wen on the body. During the procedure, a wide-bore needle is inserted into the formation, after which the contents are removed with an electric suction.
The advantages of this technique include:
- No need for hospitalization (you can go home after 15 minutes);
- No stitches or need for further dressings;
- Absence of cosmetic defects on the skin after treatment (especially important for wen on the face).
But this method of treatment does not allow removing wen with a pronounced fibrous component.
With wen on the body, the prognosis is favorable. But there is no guarantee that after a lipoma is removed in one place, it will not appear in another.