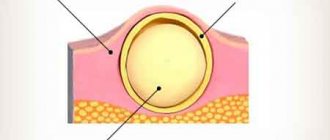
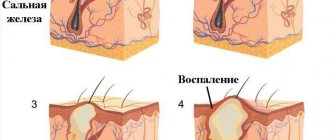
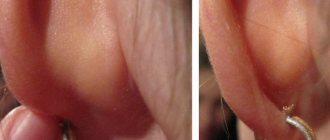
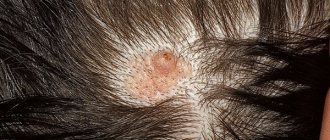
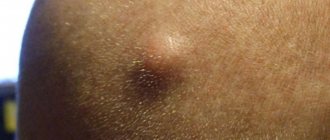
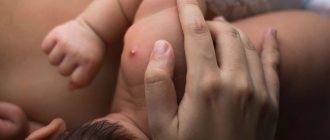
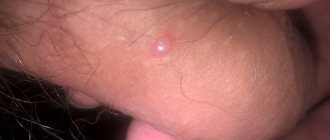
The location of atheromas is the skin, namely the sebaceous glands of the skin. For this reason, such a neoplasm can be detected on any part of the body, including on the chest in women. Breast atheroma accounts for no more than 1% of clinical cases, however, the pathology deserves special attention from the patient and specialists.
Varieties
In medical practice, there are two types of breast cysts:
- Congenital. Presented in the form of multiple formations, similar in size to lentil grains. On palpation, a dense structure is palpable, there is no pain.
- Secondary. We are talking about the expansion of the sebaceous glands of the skin, which is formed as a result of a violation of the outflow of sebum. Typically, this pathology worries patients with underlying ailments, for example, the oily variety of seborrhea. Secondary atheroma has a round shape, is dense, and hurts when pressed.
Consequences and prevention
Atheroma of the breast and nipples is a disease that does not cause complications if treated in a timely manner. But if a visit to medical specialists occurs in an advanced stage or after a capsule rupture, then negative consequences are possible in the form of:
- a purulent process that threatens tissue necrosis;
- spread of infection throughout the body;
- the development of inflammation, which can affect nearby lymph nodes.
On this topic
- Atheroma
The difference between lipoma and atheroma
- Olga Aleksandrovna Kalinina
- July 13, 2020
The tumor is a benign type of neoplasm, however, if it is not treated, there is a risk of oncology. At an advanced stage of the disease, the immune system is significantly weakened, and against the background of inflammation, cancer cells can be activated.
Preventive measures for pathology of the ductal glands of the breast (nipple) do not imply any special rules. Prevention is the elimination of the causes that provoke the formation of a tumor. All that is necessary to prevent the disease is maintaining a healthy lifestyle and observing simple hygiene standards.
Education on the mammary gland
A cyst on a woman’s chest reaches a size of 7-8 cm. The formation is motionless and has a dense structure. Itching and pain are absent in most cases. In advanced cases, the patient experiences redness of the skin in the area of inflammation, suppuration, and pain.
Attention! The peculiarity of formation on the mammary glands is the danger of inflammation moving to nearby lymph nodes localized in the armpits.
General information
The name “atheroma” itself is Greek and consists of two words: tumor and pulp (gruel). This neoplasm is also called a cyst, wen or steatoma. Age does not matter for the onset of the disease; it is diagnosed in children, even infants, and adults.
Divided into the following types:
- Trichodermal.
- Epidemoid.
- Follicular.
- Steacystoma.
In the international classification of diseases, atheroma is defined as a disease of the skin appendages. It is almost impossible to visually distinguish this type of benign neoplasm from similar ones; only a thorough diagnosis is needed.
Causes of pathology
The sebaceous glands of the human body continuously secrete a specific secretion, the main function of which is to moisturize the skin and protect it from harmful factors. Sebum is an element of the local immune system of the skin, without which it is difficult to maintain the stability of protective functions and maintain the necessary acidity of the skin.
When the channels are blocked, it is difficult for the secretion to reach the surface - it accumulates with a gradual expansion of the duct itself. The sebaceous gland begins to be surrounded by a sac filled with fluid.
Attention! The described problem is more common in women with increased sebum secretion.
Among the most common causes of deviations in the outflow of sebum are:
- mechanical damage to the mammary gland with the formation of scars on the skin of the breast;
- disruptions in hormonal levels (formation of deviations of the endocrine system with increased secretion);
- wearing tight underwear (local trauma to the skin, excessive sweating, blockage of the glands);
- neglect of the rules of personal hygiene (formation of an internal inflammatory process with the formation of pus).
Differences
How does atheroma differ from other formations? A dermatologist can distinguish an intradermal breast tumor from other neoplasms and make the correct diagnosis based on external signs.
But most often it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis with a lipoma. Distinctive features of intradermal formation:
- Appears when the functioning of the sebaceous glands is disrupted (lipoma is a benign tumor that occurs in adipose tissue).
- Inflammation in the capsule may develop (this is not a typical phenomenon for lipoma).
- It has the shape of a ball (lipoma is softer, flatter).
- Upon examination, gaps in the sebaceous canals are visible (with lipoma, they are not visible).
- Shifts along with the dermis (lipoma is inactive).
- Characterized by rapid growth (lipoma does not grow quickly).
To accurately diagnose the pathology, it is necessary to conduct a histology study (tissue is taken from the affected area): differentiation of lipoma, fibroma (growing in connective tissue), hygroma (in the sweat gland).
Also, the lesion, with the pus formed in it, must be distinguished from the inflammatory process in the hair follicle (furuncle).
Symptoms
Symptoms of deviation can vary significantly depending on the course of the process. In the absence of an inflammatory process, unpleasant sensations may be completely absent, and atheroma manifests itself exclusively in the form of a tumor.
If inflammation occurs, the woman observes:
- local swelling of a specific area of the breast;
- pain in the tumor area;
- local redness of the skin;
- purulent discharge from the tumor, which can cause intoxication of the body;
- elevated body temperature.
If a person experiences one or more of these symptoms, it is necessary to urgently consult a specialist to eliminate the risk of atheroma increasing in size.
Diagnostics
Atheroma progressing in the chest does not pose a risk to a woman’s life, but the lack of treatment can change the situation. In order to prevent the development of complications and exclude an oncological process, you should contact a mammologist or gynecologist in time and carry out a full diagnosis.
The examination of the patient begins after a detailed interview and examination at a doctor’s appointment. The specialist determines the general clinical picture and makes a preliminary diagnosis.
To confirm or refute the alleged diagnosis, an examination using laboratory and hardware methods will be required.
On this topic
- Atheroma
Everything you need to know about atheroma of the scalp
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- July 28, 2020
Laboratory diagnosis for atheroma of the nipples or breasts includes:
- general blood analysis;
- analysis ;
- Analysis of urine.
It is mandatory to undergo a hardware examination:
- mammography;
- ultrasonography;
- radiograph.
It is also possible to conduct a study for the presence of cancer cells. This is necessary to exclude the possibility of developing an oncological process.
A therapist, surgeon, dermatologist, and mammologist should take part in the process of diagnosis and determination of a treatment regimen.
Distinctive features of atheroma: how not to confuse it with a wen
An epidermal cyst is similar in appearance to a lipoma or wen, however, it has a different origin.
Formations can be distinguished upon self-examination by the following characteristic features:
| Features of atheroma | Features of lipoma |
| - remains motionless during palpation - has a dense consistency | - during palpation it is difficult to press down in a certain place - the wen tries to slide off - has a soft, plastic structure |
At the next stage, differentiated diagnostics is carried out by a specialist. In order to make a correct diagnosis, they resort to ultrasound of the breast or x-ray gammagram. These techniques reveal the presence of a formation, its contours, structure, contents and involvement in nearby tissues. In some cases, a biopsy of material from the cyst cavity is performed.
Possible complications
Not every person is aware of the dangers of the disease and possible complications. Let's consider what consequences can occur due to an epidermal cyst:
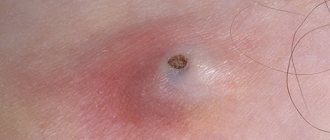
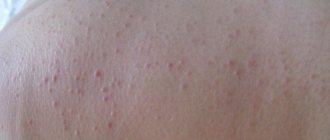
A complication of atheroma is its inflammation. Suppurating atheroma can provoke an abscess of subcutaneous tissue.
Photo of a suppurating atheroma under the skin of the back
Against the backdrop of what is happening, the patient’s temperature rises, their health worsens, and a purulent, sebaceous mass with a foul odor may separate from the formation.
With such a complication, it is necessary to carry out therapeutic measures as soon as possible, otherwise the risk of dissolution of the cyst shell and the release of purulent contents into the tissues increases.
Treatment methods
There is no drug treatment for breast atheroma; surgical or hardware removal is used. There are several methods of intervention, which are prescribed taking into account the size of the cyst and the general condition of the patient:
- laser radiation. The tissue is dissected with a narrow beam and the atheroma is subsequently removed using tweezers or the same laser. The main advantages of the method are: a short recovery period for the skin, the absence of scars and cicatrices. The disadvantages include the high cost of the procedure;
- radio wave removal. The cyst is drawn out using an electrode that passes high-frequency alternating current. This method also takes place without leaving any marks on the skin;
- surgical intervention. An incision is made using a scalpel, followed by cutting off the cyst from the surrounding capsule. The method is low cost, however, it provides for the future presence of a scar and marks from stitches. The postoperative period in this case involves taking antibiotics to eliminate the risk of developing complications of a bacterial nature.
The first two techniques are carried out using a local anesthetic and last about half an hour. After the procedure, the patient is left with small scabs that fall off after a couple of days without any medication. Among the indications in the postoperative period, it is worth noting the need to wear a sterile bandage (changed 2 times a day) and treat skin areas with an antiseptic solution.
Laser removal
1 Photo-coagulation
. To use this method, it is necessary to maintain the size of the atheroma, no more than 5 millimeters. It allows you to remove a cyst even with suppuration. The cyst evaporates, and a small crust remains on the skin, which falls off after the skin is tightened.
2 Excision of tissue with laser
. It is permissible to use this method to combat a cyst if its size is no more than 20 millimeters. During removal, a small incision is made so that the formation is visible. The cyst is then separated from healthy tissue and removed with tweezers. A drainage is placed at the site of the open wound and a cosmetic suture is applied.
3 Evaporation of a capsule by laser
. This method can only be used if the size of the tumor exceeds the threshold of 20 millimeters. During the surgical procedure, the doctor carefully makes an incision of such size that the cyst is completely visible, then the formation is cut and its contents are removed using cotton swabs.
Laser removal of atheroma has a number of advantages: removal takes place without blood, and there are no noticeable scar changes after removal. As a rule, the method is used for facial surgeries.
In addition to the methods described above, atheroma on the lower or upper eyelid can be evaporated by exposing the capsule to a laser. During the procedure, the cyst is opened with a scalpel, and it is cleaned of exudate.
Then the skin edges are moved apart, and the capsule shell is evaporated from the inside using a laser. At the end of the operation, the wound is sutured, and the sutures are removed on the 10th day.
However, laser evaporation of a cystic formation on the eyelid has some contraindications. You cannot carry out such an operation if you have:
- diabetes mellitus,
- immunodeficiency states,
- pregnancy,
- malignant tumors, etc.
Radio wave therapy makes it possible to prevent the re-development of pathology after surgery; the wound is not sutured when using this technique, it heals very quickly, and only a slight scar remains.
Preventive measures
Atheroma can be prevented by following simple advice from specialists. Necessary:
- observe hygiene rules, including regular water procedures using gels with an antibacterial effect;
- handle the skin carefully to avoid mechanical trauma to the nipples;
- consciously select sizes, shapes and materials of underwear.
Thus, breast atheroma is formed as a result of the accumulation of sebum in the duct. In some cases, the pathology is asymptomatic, sometimes the patient observes traditional symptoms of the inflammatory process. Therapy for cystic formation involves only removal of the atheroma.
Therapy for neoplasms
Atheroma on the mammary gland is one of those neoplasms that never go away on their own; they only need to be removed by any means, be it surgery, laser or radio wave method. Even if you pierce it with a needle and try to squeeze it out, only the contents of the cyst will come out, and the capsule will remain in place. Over time, it will begin to fill up again.
You cannot remove the capsule during a purulent exacerbation. At this time, it softens, it is easily damaged and partially left in the sebaceous duct of the gland, and this will lead to a relapse of the disease.
It is best to remove atheroma when it is small and not inflamed. Then you can completely remove the capsule without a visible scar on the skin. If the cyst is inflamed, but does not fester, the inflammation is first stopped, then it is removed. In the case of purulent inflammation, the atheroma is opened, the contents are removed and an open hole is left so that the pus comes out. The capsule is removed only after suppuration in the wound has stopped.
Local treatment
A subcutaneous cyst on the mammary gland is a neoplasm with a very specific structure that does not respond to either synthetic drugs or the healing properties of medicinal plants. You can find a lot of advice in the media on how to neutralize it. But the real facts are:
- Treatment of atheroma without surgery is a myth. All messages on this topic are, at a minimum, unprofessional, and at a maximum, cause great harm to health. Due to untimely consultation with a doctor, an inflammatory process begins in the cyst, then it results in a deep subcutaneous tissue abscess. As a result, she will still need to be operated on.
- If you believe in treatment with folk remedies, you will waste precious time and create conditions for the malignant degeneration of the lipoma (if that is what it is). At the initial stage, it can be difficult to distinguish between these two neoplasms. Only an experienced doctor can do this.
- Often a cyst in the sebaceous gland duct is mistaken for a subcutaneous pimple and they try to squeeze it out. This leads to injury to the capsule and its suppuration. New cysts form next to it, which is how atheromatosis appears - many small subcutaneous cysts.
- Often, after all kinds of “steaming”, the cyst on the mammary gland spontaneously opens and spews out its contents. But the capsule remains, and this leads to relapses of the disease.
- Theoretically, using films of raw eggs or Vishnevsky ointment, you can reduce the size of the cyst on the mammary gland. But in fact, they clog the clogged duct of the sebaceous gland even more, the capsule ruptures, and pus flows into the lower layers of the skin.
Today, the only way to completely get rid of an epidermal cyst is through surgery. This will eliminate the risk of inflammation and complications, and the procedure itself will not leave a noticeable postoperative scar on the skin.
Only the doctor decides how the atheroma on the chest will be removed. This depends on many reasons: the size of the cyst, its current condition and location - on the right or left breast. Cysts with a diameter of 2 cm or more are surgically removed using local anesthesia. If it is necessary to operate on a large purulent atheroma, the operation is performed in the clinic. The patient will be cut out of the capsule containing sebaceous masses with pus, stitches and a bandage will be applied. Complete healing will occur in 2-3 weeks.
What to do if a wen appears on a woman’s breast?
Wen is a common form of pathology in which fat deposits of any location become the site of development of a formation in the form of a nodule filled with tumor cells. Lipoma (the medical name for a wen) represents a class of benign tumors that, in very rare cases, become malignant.
The place where a lipoma appears can be the subcutaneous layer, muscle tissue, or tissue of internal organs. A favorable environment for development can be an accumulation of just a few fat cells, so the statement about the connection between the presence of excess weight and the tendency to the appearance of wen is incorrect. The greatest concern is a wen on the chest or face.
The content of the article: