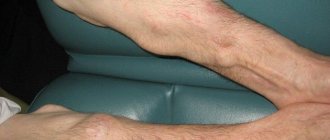
Atheroma behind the ear is considered a relatively safe formation, but requires timely treatment. As it develops, the size of the atheroma becomes larger, and if you do not give it due importance, without adequate treatment, various complications may arise, in particular, its transformation into a cancerous tumor. The formation of various types of neoplasms on the human body is not uncommon, and some of them not only cause cosmetic discomfort, but also pose a serious threat to health.
Atheroma is also called a skin cyst, which occurs due to blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands. This spherical cyst can appear in any part of the body, and the development of a cyst in the tissues of the ear is most often observed. If such a growth occurs, you should immediately seek medical help. An experienced surgeon can easily remove atheroma without leaving any traces behind. To prevent possible complications, you should find out in advance the symptoms, causes of occurrence and methods of treatment of such neoplasms.
Features of atheroma
Sebum, produced by the corresponding glands, performs a number of important functions:
- prevents drying of the upper layer of the dermis;
- moisturizes the epidermis;
- provides protection of the skin from the negative influence of the external environment;
- prevents infection of the body through the skin by pathogenic bacteria.
On this topic
- Atheroma
Let's find out what atheroma is
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- September 25, 2020
The concentration of sebaceous glands varies depending on their location. They are most concentrated on:
- head;
- face;
- back;
- chest.
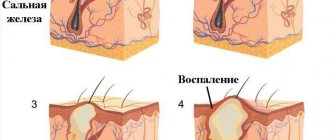
Sebum is removed to the surface of the epidermis through small ducts. In case of blockage of the latter, the secretion begins to accumulate, which provokes the formation of atheroma. This tumor is a cavity filled with fat. It occurs near the earlobe or inside the ear canal.
Reasons for development
Atheroma of the parotid region often develops against the background of metabolic disorders or hormonal imbalance. Both problems lead to blockage of the sebaceous glands. However, not only these factors contribute to the formation of atheroma.
A benign tumor near the ear occurs under the influence of:
- Disorders of the autonomic system. This failure activates the work of the sweat glands.
- Seborrhea. The disease often affects the scalp and is accompanied by the appearance of plaques on the surface of the skin that interfere with the normal functioning of the glands.
- Acne.
- Oily skin, which is often inherited.
- Pathologies of the endocrine system.
- Diabetes .
- Damage to the skin in the ear area.
- earlobe piercing technology This leads to the fact that the sebaceous glands, compensating for the negative impact, begin to actively produce sebum, which should close the wound.
- Active production of testosterone.
- Hypothermia.
- Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight .
- Insufficient hygiene . Because of this, small particles of dirt prevent the secretion of sebum for a long time.
On this topic
- Atheroma
All about atheroma removal
- Irina Nasredinovna Nachoeva
- August 19, 2020
Atheroma forms on the earlobe both in case of mistakes made during piercing and for other reasons:
- inflammation of soft tissues accompanied by an abscess;
- an increase in the concentration of granulation cells at the puncture site, as a result of which the tissue compresses the sebaceous ducts;
- formation ;
- hereditary predisposition to obstruction of the sebaceous glands.
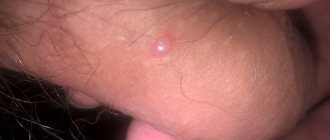
The maximum concentration of sebaceous glands is located near the earlobe. The tumor develops without obvious symptoms. This is due to the fact that the local sebaceous ducts are very narrow. Hormonal disorders in rare cases cause the formation of atheroma near the lobe.
The auditory canal, unlike other parts of the ear, also contains sebaceous glands in the subcutaneous layer. This area is located in a hard-to-reach place, so blockage of the ducts with sulfur occurs constantly.
In addition, there are many microscopic hairs that are associated with the sebaceous glands. Both circumstances cause the frequent occurrence of atheroma of the auditory canal.
On this topic
- Atheroma
How to remove atheroma on the face
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- July 28, 2020
However, for the formation of such a neoplasm, the influence of other factors is necessary:
- infectious infection of the ear, accompanied by an inflammatory process in the tissues;
- soft tissue injuries
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- metabolic disease ;
- hormonal imbalance;
- problems with the autonomic system.
Atheroma of the auditory canal is considered a more dangerous type of tumor. As it develops, the pressure experienced by thin cartilage increases. As a result, atheroma of the auditory canal can lead to a fracture of the latter.
Symptoms
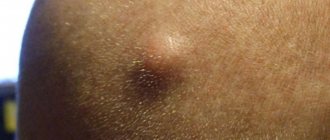
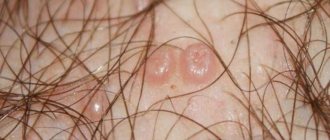
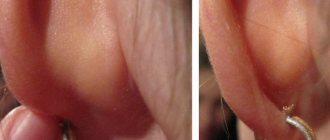
The most obvious sign of a neoplasm is the appearance of a dense ball. Its dimensions range from a few millimeters to several centimeters. But usually the patient ignores the occurrence of a thickening until it significantly increases in diameter. Pressing on the ball does not cause pain.
Dimensions range from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
However, as the cystic formation grows, the risk of developing a focus of inflammation and spontaneous rupture of the membrane increases. If this happens, the person will experience the following symptoms:
- the skin in the area where the pathology is localized turns red and its temperature rises;
- there is itching or burning in the ear canal area;
- the attachment site of the atheroma in the postauricular area swells;
- the temperature rises and chills appear;
- the cyst itself begins to hurt, this is especially felt when pressure is applied.
In addition to these signs, the development of the inflammatory process can be determined by general clinical symptoms. Feeling worse, weakness and headache appear, joints begin to ache, and appetite and sleep worsen.
Peculiarities
Postauricular atheroma occurs in approximately 0.2% of cases of diagnosing tumors on the head. Such a rare occurrence of a neoplasm is due to the fact that in this area there is a low concentration of sebaceous ducts.
Postauricular atheroma in appearance resembles adenoma of the salivary gland, which complicates the diagnosis of the pathology. If a tumor occurs in this area, he not only palpates the problem area, but also examines it by:
- CT;
- Ultrasound;
- x-ray;
- MRI.
It is not possible to distinguish atheroma from adenoma by external signs. Both tumors have a similar structure, and their development is not accompanied by pain. The only sign indicating the presence of atheroma is that in the affected area there is a small point of the sebaceous duct.
If a secondary infection occurs, the tumor becomes inflamed. The development of the tumor is accompanied by pain and causes an increase in body temperature. Inflamed atheroma has more specific features that allow it to be distinguished from other similar tumors.
The long course of the pathological process in the tissues of the area behind the ear leads to the formation of foci of suppuration. In this condition, the tumor often opens on its own, which leads to sepsis and death.
On this topic
- Atheroma
Everything you need to know about atheroma of the scalp
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- July 28, 2020
Postauricular atheroma is located in a place where there are many lymphatic ducts and blood vessels. This circumstance complicates the operation to remove the tumor.
More often, the tumor is operated on before the first signs of tissue inflammation appear. Performing surgery in later periods is not recommended, as they cause complications such as infection of the ear canal and damage to cartilage.
Prognosis and probability of relapse
The prognosis after therapy for atheroma that has arisen in the tissues of the ear is usually favorable, especially if the cyst was removed immediately after its appearance. But atheroma that occurs behind the ear, or in any other place, can recur. The likelihood of relapse largely depends on the chosen method of therapy and the quality of its implementation.
It is possible to prevent the reappearance of a sebaceous gland cyst 100% only if it is completely removed. Because the main reason for the re-formation of a cyst is the remaining fragments of the tumor in the affected area. Methods for removing such tumors vary, but the lowest risk of relapse is observed after laser burning. Also, to prevent relapse of atheroma, you should closely monitor your health and promptly treat chronic diseases.
Clinical picture
It is possible to diagnose atheroma behind the ear based on the following signs:
- the formation of a small tumor with a round shape;
- dense and elastic tumor;
- the presence of a dark dot (white if infection has occurred) on the surface of the atheroma;
- presence of small adhesions to the skin;
- a sensation of itching and burning as the formation grows.
In the case of a secondary infection, the clinical picture is supplemented by the following phenomena:
- redness of the skin;
- increased temperature ;
- discharge of purulent contents;
- headache ;
- attacks of nausea;
- general weakness.
On this topic
- Atheroma
All about atheroma on the chest
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- July 28, 2020
It is important to note that after the release of pus, the atheroma does not disappear. The cavity begins to fill with detritus.
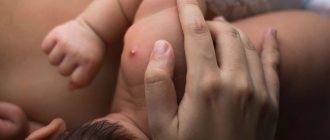
Atheroma on the earlobe is characterized by the following symptoms:
- dense neoplasm is formed in this area ;
- the development of the tumor is not accompanied by pain, it does not create discomfort.
In rare cases, a cyst on the lobe reaches a diameter of 40-50 mm. When a secondary infection occurs, suppuration occurs, as a result of which the size of the tumor increases. Such complications occur mainly in women due to the fact that they insert jewelry into the lobe.
Ulcers can be opened independently, which leads to devastation of the neoplasm. In this case, surgical intervention will also be required, since subsequently the secretion accumulates again in the emptied capsule, which leads to a relapse of the pathological process.
How to cure atheroma behind the ear using folk methods and at home?
It is impossible to remove a lump on the ear on your own, but it is possible to stop the growth and prevent inflammation of a small formation.
Treatment of atheroma at home consists of the following procedures:
- Aloe compresses - cut a leaf of the plant and apply to the desired area for 3 weeks.
- Lamb fat – use a water bath to heat the ointment, lubricate it up to 5 times a day.
- Dilute ammonia with water 1 to 1, moisten gauze and apply to the ear for 5-7 minutes.
- Ichthyol ointment - helps get rid of blockage of the sebaceous ducts, restoring patency.
- Eggshell - peel off the film from the inside of the shell and apply it to the formation.
These methods are used as auxiliary methods in the absence of redness and purulent contents, since improper treatment will worsen the condition and increase the risk of complications.
Diagnostics
The basis of diagnosis for suspected atheroma consists of measures designed to differentiate the neoplasm from other tumors that have similar external signs. To achieve this goal, the following is carried out:
- external examination and palpation of the problem area;
- collecting information about the patient’s condition, his complaints and concomitant diseases;
- radiography and CT scan of the skull;
- Ultrasound of lymph nodes located in the problem area.
On this topic
- Atheroma
Why is atheroma on the back dangerous?
- Olga Aleksandrovna Kalinina
- July 18, 2020
In case of damage to the ear canal, the following are additionally prescribed:
- dermatoscopy;
- cytological examination of the contents of the ear canal;
- otoscopy, which involves examining the problem area using a special instrument;
- audiometry for suspected hearing loss;
- pharyngoscopy, angiography and microlaryngoscopy (performed according to indications);
- histological examination of material collected during surgery.
These measures are designed to differentiate atheroma from other similar neoplasms:
- papilloma;
- fibroma;
- boil of subcutaneous tissue;
- lipoma and so on.
Before surgery to remove a benign tumor, the following are prescribed:
- chest fluorography
- blood and urine tests
- chemistry .
Despite the fact that atheroma cells do not mutate into cancer over time, this tumor is considered dangerous due to its specific location. If a secondary infection occurs, the neoplasm becomes inflamed, which threatens hearing impairment.
Possible consequences
Without treatment, the development of atheroma can cause the following complications:
- Gradual replacement of healthy connective tissue. This occurs against the background of the natural development of atheroma. The process of tissue replacement proceeds unnoticed. It does not cause pain. A dense nodule is formed in the problem area, which persists for a long time.
- Replacement with fibrous tissue against the background of inflammation. The consequence of this process is also the formation of a dense nodule, which does not disappear throughout the patient’s life.
- rupture due to purulent inflammation. The fluid penetrates deep into the ear canal and affects the middle and inner ear. This leads to deformation of the shell and destruction of cartilage.
If abscesses develop, there is a high probability of developing sepsis, which ultimately leads to death.
Treatment
Treatment of atheroma, regardless of its location, involves surgical removal of the tumor. It is highly not recommended to use traditional medicine methods or medications. This treatment leads to the development of an abscess in the problem area.
Even if with the help of medications it was possible to reduce the size of the tumor and remove the purulent contents, in the future the atheroma will again be filled with sebum and return to its original size.
Treatment of a tumor on the earlobe is carried out by:
- Enucleation. The method involves making a small incision in the problem area and removing the contents of the cavity. After this, the neoplasm tissue is excised. Full recovery after enucleation takes about a month.
- Laser removal. It is used when the tumor is small and not inflamed.
- Radio wave method. It is considered the most effective way to treat atheroma. It eliminates the possibility of relapse of the pathological process. Recovery after surgery takes about one week.
On this topic
- Atheroma
The difference between lipoma and atheroma
- Olga Aleksandrovna Kalinina
- July 13, 2020
Removing atheroma located behind the ear is associated with certain difficulties. Before the operation, the patient undergoes a detailed examination to determine the presence of contraindications to the procedure. Removal of such a tumor is carried out using:
- Surgical excision of the problem area. It is used mainly in the presence of purulent atheromas. After opening, the tumor is drained. Next, medications are prescribed whose action is aimed at suppressing symptoms (lowering temperature, eliminating pain). At the end of this stage, the tumor tissue is completely excised. After the procedure, a noticeable scar remains on the skin.
- Laser removal. Indicated if the tumor size does not exceed 3 cm and there is no inflammatory process.
- Radio wave removal.
After surgery, it is important to regularly treat the problem area with an antiseptic during the rehabilitation period to prevent infection.
Locations
Among tumor-like neoplasms of postauricular localization, atheromas are the most common, epidermoid cysts are less common. An adenolipoma (benign tumor) may also be found behind the ear, which is not easy to distinguish from atheroma.
Among all cysts of the outer ear, neoplasms can be distinguished:
- auricle (helix and antihelix, as well as earlobe);
- external auditory canal;
- parotid region.
When talking about a cyst behind the ear, they most often mean a cavity on the back surface of the shell, including one that extends to the lobe, or located in the postauricular fold.