Atheroma in a child is a subcutaneous neoplasm that is formed due to blockage of the excretory ducts. It is often called wen. A benign tumor can be localized on different parts of the body, even on the nipple. This type of compaction can be congenital (due to intrauterine development disorders) or acquired (due to the influence of certain factors).
A benign tumor can be localized in different parts of the body.
Description of the disease
Atheroma is one of the relatively harmless tumors due to the fact that it does not transform into a malignant neoplasm.
However, there is a risk of significant increase in size, so medical attention is required in all cases. Teenage children are more likely to experience this problem. Boys and girls get sick about the same. The main reason why parents first turn to a surgeon is the presence of a visually noticeable tumor.
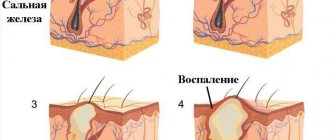
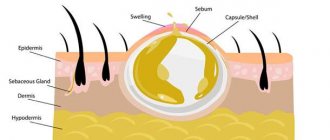
The atheroma itself is a small capsule filled with pasty contents. It is sebum, which, due to blockage of one or more glands, did not come out, but remained in the subcutaneous tissue.
Can atheroma disappear spontaneously?
Many parents, rightly fearing the effects of anesthesia, try in various ways to postpone surgery to remove the tumor. In medical practice, there are cases where the contents of the capsule were poured out due to regular mechanical stress. In this case, the cyst decreases in size so much that it becomes almost invisible. However, after a short period of time, its capsule, remaining under the skin, begins to fill with secretions again. Atheroma recurs. In this case, postponing surgical intervention is simply unacceptable. As long as the capsule remains under the dermis layer, neoplasm will occur.
Symptoms of atheroma in children
In 80-85% of cases, apart from the visual defect, children do not present any other complaints. Uncomplicated atheroma is characterized by:
- painlessness;
- mobility;
- elasticity upon palpation.
The skin over the surface of the tumor is smooth and does not fold. The clinical picture may change when the contents of the atheroma become inflamed against the background of the addition of bacterial flora. In this case, patients may note:
- pain when pressed;
- redness and increase in size of the tumor itself;
- local increase in body temperature.
If the above symptoms occur, you should immediately seek help.
This situation threatens the penetration of infection into nearby tissues and blood with the spread of microorganisms to distant areas of the body and can cause a deterioration in the general condition of the child. Atheromas occur in areas of the skin that are rich in sebaceous glands. Therefore, they especially often have the following localization:
- scalp;
- face and neck area;
- shoulder girdle, armpit area;
- back.
Neoplasms occur less frequently in the groin area and scrotum (in boys). In these areas they have the appearance of a skin growth and require differential diagnosis with other skin tumors.
Why does the disease appear?
When atheroma appears in newborn babies, the cause of the disease is heredity. Impaired functioning of the sebaceous glands develops due to the fact that the child’s hormonal system is not yet fully formed. The parents' mistake, which becomes a factor in the development of the disease, is improper hygienic care of the baby. This often occurs when using a large number of children's cosmetics. In addition, the reason is the parents’ desire to remove dry crusts from the baby’s head. To do this, they use a comb with fine teeth, which injure the baby’s skin. Another condition can cause atheroma:
- oily or dry form of seborrhea;
- the appearance of prickly heat due to impaired thermoregulation of the body.
Causes of atheroma in children
Atheromas in children occur due to a violation of the secretion of sebum by the corresponding glands.
When the excretory duct is blocked, the secretion of the gland has nowhere to go. It is secreted into the subcutaneous space, where a dense capsule is formed around it. Common causes of atheroma development in children are as follows:
- Using children's cosmetics (creams, ointments, moisturizing masks) in excessive quantities. Sometimes parents, in an effort to protect their child’s skin from harmful external factors, use cosmetic products uncontrollably. This leads to dysfunction of the sebaceous glands with blockage of their excretory ducts.
- Hormonal changes in the child's body. Infants and teenage children are traditionally at risk. It is during these periods that changes in the concentration of sex hormones occur. Against this background, acne appears, the function of the sebaceous glands is disrupted, and conditions are created for their blockage.
- Seborrhea. This is a dermatological disease that leads to dysfunction of the sebaceous glands in a certain area of the skin.
- Genetic predisposition or congenital structural features of the skin. Atheromas most often occur in children after 3 years of age. If neoplasms are detected in children immediately after birth, the doctor may assume the presence of problems with the sebaceous glands that developed in utero.
In addition, factors that increase the risk of developing atheromas are poor personal hygiene, metabolic disorders (obesity, diabetes) and frequent mechanical damage to the skin.
What to do and who to contact?
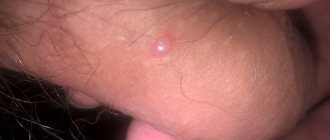
Atheroma is a common occurrence in a child under one year of age and even a newborn. In infants, pathology in most cases occurs on the head. A characteristic feature of an epidermal cyst is:
- round shape;
- the seal is soft to the touch;
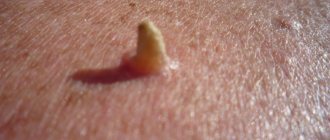
- a dark dot, often in the center of the swelling (blocked duct);
- inactivity;
- when pressed, white curd-like contents may be released. If the neoplasm becomes inflamed, the purulent discharge may have a different shade (yellowish or even brown) mixed with blood;
- sometimes the autopsy itself occurs.
Atheroma is easily confused with a lipoma. These neoplasms are very similar in appearance, but their nature of occurrence, content and consequences have significant differences:
- Both tumors are benign, but lipoma is a pathological growth of adipose tissue (wen), and atheroma is a cystic formation in the epidermis containing the secretion of the sebaceous gland.
- Lipoma grows very slowly.
- The lipoma feels more elastic to the touch.
- The inflammatory process is more often observed than in lipomas.
- The lipoma practically does not move when you try to displace it.
- Atheroma must be removed due to its frequent inflammation and suppuration. Lipoma often does not show signs of development, so it is not always removed, but only monitored with regular examinations.
- Lipoma can be localized on internal organs, which does not happen with atheroma.
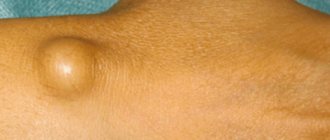
The size of the atheroma ranges from a few millimeters to a large chicken egg. If a neoplasm is detected on a child’s body, it is necessary to consult a surgeon. The specialist, after making sure that the lump is atheroma and not another type of tumor, will prescribe treatment or removal of the cyst.
If the tumor is on the head, then an ultrasound examination should exclude the possibility of a cerebral hernia, which usually occurs due to increased pressure inside the skull. With such a problem you need to contact a neurologist.
Diagnosis of atheroma in children
It is relatively easy to identify atheroma.
Even at the stage of the initial conversation with the patient or his parents, the surgeon assesses the general well-being of the child, collects anamnesis and analyzes complaints. When examining a neoplasm, the doctor pays attention to its size, location, pain, and the presence of redness. Before surgery, the surgeon prescribes a number of tests to comprehensively assess the child’s condition:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- blood test for infections (HIV, syphilis, viral hepatitis B, C);
- ECG, fluorography.
The child is also examined by an anesthesiologist and pediatrician before the operation. A mandatory diagnostic method is histological examination of tumor tissue after its removal. At this stage, it is possible to determine whether it was an atheroma or a lipoma (a tumor similar in appearance).
Atheroma on the stomach
All iLive content is reviewed by medical experts to ensure it is as accurate and factual as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable sites, academic research institutions and, where possible, proven medical studies. Please note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to such studies.
If you believe that any of our content is inaccurate, out of date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
In a morphological sense, the skin of the abdomen differs little from the skin of other areas. It also contains all the structural parts - the epidermis, the dermis itself, the subcutaneous tissue and the fat layer. However, there are also areas in which the sebaceous glands are more voluminous; in addition, their function can be influenced by the hormonal system. Similar specific areas include the abdominal area, which is considered estrogen-dependent, especially in female patients.
Atheroma on the abdomen is rarely congenital; more often it is defined as a retention cyst - a secondary atheroma. The development of such benign formations is due to the fact that in the abdominal area there are many cells - lipocytes, the receptors of which are extremely sensitive to changes in estrogen levels. In a cosmetic sense, such vulnerability manifests itself as the accumulation of lipid deposits, visually identified as cellulite. Lipid deposits provoke the formation of stretch marks (striae), hyperkeratosis, rosacea and, quite often, atheromatosis. In addition, the skin of the abdomen is prone to hypersecretion of sebaceous secretions (hyperfunction of the sebaceous glands), which in turn provokes the appearance of comedones, acne, and atheromatous cysts.
Atheroma on the abdomen requires careful differentiation, since fibromas, lipomas, and hernias often develop in this same area. Diagnosis involves examination of the abdominal area, palpation, and possibly a biopsy. If atheroma is confirmed, the choice of its treatment leans towards surgical removal, during which tissue sampling for histology is considered mandatory.
Treatment of atheroma in children
The optimal method of treating atheroma in children is its surgical removal.
However, the age of the patient decides a lot here. Thus, most pediatric surgeons, in the absence of severe clinical symptoms, recommend a wait-and-see approach. Sometimes the swelling may resolve on its own. This is especially true for newborns and infants. In such cases, the development of the neoplasm is observed until the age of three, and if it persists, only then is it removed. . Surgical intervention can be carried out traditionally using a scalpel or minimally invasively using a laser. In the first case, the surgeon excises the tumor with a capsule, which eliminates the risk of relapse. After this, cosmetic stitches are applied to the tissue to achieve the best aesthetic result. Laser removal in children is used for small tumors. Using this technique, it is possible to avoid incisions and the formation of postoperative scars. In both cases, a comprehensive examination of the child is first carried out with the selection of the optimal treatment option.
In the postoperative period, the child may be prescribed the following groups of medications:
- painkillers;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antibacterial.
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating discomfort and preventing infection of the postoperative wound.
Help from traditional medicine
Some parents, having noticed atheroma on a child’s leg or any other part of the body, do not rush to the doctor and try to eliminate the defect themselves. They resort to the help of recipes from traditional healers.
One of the most popular are compresses. For example, using leaves of coltsfoot, plantain and cabbage. They must be thoroughly washed under running water and lightly mashed so that the plants release their juice. Then any of the leaves should be applied to the affected area for several hours. This recipe is especially good for use on open areas of the body. For example, with atheroma on a child’s face.
It is important to understand that traditional medicine is a temporary treatment. It does not allow you to forget about a cosmetic defect forever.
Questions
- Which doctor treats atheroma in children?
A pediatric surgeon is involved in identifying and treating atheroma in children. - Is it possible to cure atheroma without surgery?
Sometimes in the early stages of the disease the surgeon chooses a wait-and-see approach. In 20-35% of cases, atheroma can resolve on its own. However, if the capsule is formed and the tumor is large, it will not be possible to do without surgical intervention. - How dangerous is atheroma in childhood?
Atheroma is a relatively safe tumor. It does not become malignant, rarely becomes complicated and is not accompanied by the development of permanent defects. However, this does not eliminate the need to consult a pediatric surgeon. Only a doctor can establish the correct diagnosis and select treatment. In addition, atheroma can sometimes become inflamed due to the addition of bacterial flora and cause a deterioration in the child’s well-being. - Is it possible to play sports after surgery?
After surgical removal of atheroma, it is recommended to refrain from active activities for 2-3 weeks. This will allow the tissues to fully heal and recover.
Clinical picture
At the beginning of its development, atheroma is a small nodule. It is located in the upper layers of the epidermis. The pathology is not accompanied by pain syndrome and does not pose a threat to life. In newborns, the cyst is usually localized on the cheek, groin or armpit.
After inflammation, the tubercle begins to turn red and becomes hot to the touch. The duct may ooze pus or even blood. When pressed, the atheroma causes pain. Shows sensitivity and the area around it. Over time, young patients develop fever, weakness, and loss of appetite.
In adolescents, this defect is most often found on the head, neck and face. However, it can also be localized on other parts of the body.
Is inflammation of atheroma so scary or a mere trifle?
There is no conservative treatment to get rid of atheroma; it will have to be removed . If you do this in a timely manner, you will be able to avoid complications such as inflammation of atheroma.
By its nature, atheroma is not an inflammatory formation in the sebaceous glands. It is also called a cyst.
Symptoms
This formation can appear anywhere, but most often in places where sebaceous glands accumulate:
The main symptoms of atheroma include:
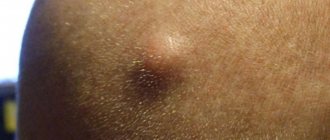
- a round or oval lump under the skin with a smooth surface;
- due to an increase in the excretory duct, swelling is observed in the center of the wen;
- The contents of the cyst are white and mushy.
Reference . It is worth remembering that the longer the atheroma is present on the human body, the larger it will be .
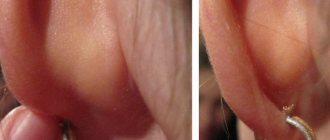
As a result of the inflammatory process the atheroma turns red and becomes painful. And after some time you can notice the presence of pus . In severe cases, a person's temperature may rise .
Causes
The inflammatory process begins in cases where the outflow of sebum is disrupted , or as a result of the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the wound. The following factors can provoke this condition:
- Heavy sweating.
- The presence of a disease such as seborrhea in oily form.
- Presence of acne.
- Congenital disorders in the structure of the sebaceous glands and ducts.
- Damage to the stratum corneum of the skin.
- Regular skin injuries.
- Hormonal imbalances in the body.
- Impact of hazardous production on humans.
- Lack of personal hygiene.
Reference. In addition, the likelihood of developing inflammation of atheroma increases due to poor environmental conditions, the use of low-quality cosmetics, unfavorable working conditions, and prolonged use of deodorant.
Photo
In the photo below, you can see what an inflamed atheroma looks like:
What to do and how to relieve inflammation?
If you notice redness on the atheroma , immediately begin taking steps to relieve inflammation. You can get rid of it at home. Here are the most popular recipes:
- Use Vishnevsky . It is applied to the wen and left for several hours. After this, the cyst bursts and its contents come out.
- Melt the lamb fat and rub into the inflamed formation.
- Mix garlic gruel with vegetable oil and apply to the area with inflammation; as a result of this treatment, the wen should break through.
- with aloe juice twice a day . The method is especially effective when a wen appears on or near the earlobe.
- Apply levomekol or ichthyol ointment .
- Baked onion applied to the atheroma and sealed with a band-aid on top helps Change the compress 2-3 times a day. The duration of treatment will depend on the degree of inflammation.
Attention! To prevent inflammation from developing, it is important to follow a diet. Eliminate fatty, spicy and salty foods from your menu.
It is also prohibited to heat or steam the wen in order to quickly “ripen” it. Water can spread germs further throughout the body, so it is not recommended to wet the inflamed wen .
After the wound heals, you can take a shower and wash with baby soap. Other cosmetic soaps with fragrances are prohibited until the wound has completely healed. This also applies to taking a bath.
Treatment
To get rid of atheroma forever, you will have to remove it . Other treatments are not effective . Radiosurgical devices are used more often. This method has a number of advantages over the traditional surgical method using a scalpel:
- Minimum damage to the skin.
- There is practically no blood loss observed.
- Doesn't hurt.
- The scars after the operation are faint.
- Wound healing is quick and painless.
If you remove atheroma using a laser method, local anesthesia is first applied and the procedure lasts an average of 30 minutes. If inflammation begins, the atheroma is not temporarily removed.
If pus accumulates, it must be opened and the contents cleared of liquid. After the pus is removed, the wen is treated with a local antiseptic and drainage is installed.
When the inflammation subsides, the capsule can be excised.
It happens that the cyst bursts on its own . You should not immediately run to the doctor with an open purulent wound.
First, use a sterile cotton swab to clean the contents of the capsule from pus, treat everything with an antiseptic and cover the atheroma with a band-aid.
After this, go to the doctor, since you will not be able to completely get rid of the pus on your own; only a specialist will clean out the cyst so that there are no complications in the form of an abscess.
Removal
Before proceeding with removal, the doctor, despite the fact that it is not difficult to make a diagnosis in this case, must still refer the patient for diagnostic tests. In controversial issues, an ultrasound examination is performed, and the patient is sent for a consultation with a dermatologist and oncologist.
Atheroma is often confused with lipoma. But its main difference is the presence of a capsule filled with liquid. Lipoma does not have such a capsule. If atheroma is detected in the stage of inflammation and suppuration, its removal is carried out within the walls of the hospital. The following methods are used:
- Radiosurgery . Radio waves burn out pathological tissue. The advantages of this method are described above.
- Surgical method , when the abscess is dissected and drained. It is also called the classical method. The advantages of this method are wide availability, low price, and when removing atheromas on the head, the swelling is not as pronounced as with other methods.
- Laser coagulation . The laser leads to the destruction of the cyst and its contents. Relapses with this method are extremely rare; it is a bloodless technique and there are no scars after surgery. But due to the high cost of the equipment, the method is not always available to everyone.
Is it possible to squeeze out?
It is not recommended to squeeze out a large wen on the body, especially if it is inflamed . You need to wait until it breaks through on its own, but it’s better to go to the doctor for a consultation.
Important! If you squeeze out the atheroma and inflammation begins, then immediately go to the doctor!
After the pus comes out, the capsule will clear, but after a certain time it will again be filled with purulent contents. Therefore, experts recommend removing the atheroma along with the sebaceous gland bursa.
After removal, a person usually should not be concerned about the deterioration of the condition. But if the temperature has risen, blood appears on the applied bandage, or there is purulent exudate, then this should be a reason to consult a doctor.
Source: https://kozh-med.com/novoobrazovaniya/ateroma/vospalenie.html
What does a cyst look like?
Typically, the neoplasm appears in areas with increased hair growth, but atheroma occurs on the finger, hands, face, neck, back, abdomen, and groin area.
The cyst looks like a bulge above the skin and has a clear outline. If you palpate it, you feel an elastic but dense structure. In the center you can see a black dot - a clogged duct of the sebaceous gland.
There is healthy skin above the tumor, sometimes it can take on a bluish tint.
With an inflamed cyst, the skin becomes redder, painful sensations appear, and nearby tissues swell greatly. At times, pus breaks out.
The atheroma cavity is filled with dead cells, gland secretion and pus. The contents are in a capsule formed by epithelial cells.