A lump on the elbow can be a manifestation of bursitis, epicondylitis, tendovaginitis, deforming osteoarthritis, tumor and some other unpleasant conditions. You can learn about why bumps appear on the elbows of the hands from the proposed material. The article describes in detail all the common causes. Methods of safe and effective treatment without surgery are described.
If a lump appears on the elbow, you should not engage in self-diagnosis - the patient is unlikely to be able to make a correct diagnosis for himself, since his assessment will be subjective. It is best to consult an experienced specialist in the field of orthopedics or traumatology (if the appearance of the tumor was preceded by traumatic exposure).
If you have a lump on your elbow and you are located in Moscow, you can sign up for a free initial consultation at our manual therapy clinic. We employ experienced orthopedists. Doctors will be able to make an accurate diagnosis, give recommendations for additional examination (if necessary), and prescribe effective and safe treatment.
Which doctor will help if a lump has grown on the elbow?
You need to know which doctor is needed when a lump appears on the elbow, and which specialist you should make an appointment with at a city clinic or in a private clinic. The answer to the question of which doctor will help with a lump on the elbow depends on the reason for which the tumor grew.
Pay attention to the principle of choosing a doctor:
- if the cause of this pathology is an injury, even one that occurred several days ago, then you should contact a traumatologist for an appointment;
- if the appearance of a tumor was preceded by redness of the elbow, pain, then it is best to visit an orthopedist;
- if you work as a painter or perform other types of professional duties associated with increased stress on the elbow, then you need the help of a chiropractor or osteopath;
- if the lump is painful, dense and adherent to the surrounding tissues, you need to contact an oncologist surgeon.
In this case, if a lump grows on the elbow several weeks after the injury, the help of a professional rehabilitation doctor may be required. This specialist helps conduct rehabilitation courses in order to restore the physiological state of damaged bone, cartilage, ligamentous and muscle tissues of the musculoskeletal system. For these purposes, massage and osteopathy, therapeutic exercises and kinesiotherapy, laser therapy and much more are used.
Methods of treating diseases
Which methods will be used depends on the reason why the lump has formed on the elbow joint.
Treatment of bursitis
If the form of the pathology is acute, a tight bandage is applied to the elbow, and the doctor also prescribes anti-inflammatory medications (Ibuprofen, Meloxicam, Diclofenac) to take. Sometimes a therapeutic puncture of the synovial bursa is performed.
If acute bursitis is accompanied by the formation of a purulent infiltrate, then anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed in combination with painkillers (Bupivacaine, Trimecaine). Punctures are also performed.
Sometimes they are not enough, and then surgical methods are used: the synovial bursa is opened and drained (pus is removed from the joint using a tube).
In the chronic form, only excision (removal of the affected tissue with a scalpel) of the synovial bursa is effective, since punctures do not give results - some time after removing the infiltrate, it forms again and the joint swells.
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and the nodules that form due to it
As a local treatment, ointments and creams with glucocorticosteroids (drugs based on adrenal hormones: Hydrocortisone, Betamethasone) are used. They allow you to relieve the inflammatory process in the nodules themselves and reduce them.
It is also necessary to treat rheumatoid arthritis itself, which consists of taking:
- anti-inflammatory drugs (non-steroidal or glucocorticosteroid);
- antirheumatic medications (Methotrexate, Sulfasalazine);
- immunosuppressants (Remicade, Enbrel, Orencia).
Treatment of gout
You can get rid of a tumor on the elbow, which is caused by gout, by relieving the exacerbation.
| To do this, the doctor will recommend taking one of the anti-inflammatory drugs | To prevent relapses it is prescribed |
| Colchicine | Low Doses Colchicine |
| Indomethacin | Medicines that interfere with the production of uric acid (for example, Allopurinol) |
| Naproxen | Medicines that accelerate the excretion of uric acid (Sulfinpyrazone, Azapropazone) |
| Phenylbutazone |
Treatment of a malignant tumor of the elbow
Depending on the stage, choose one of the following tactics:
- At the initial stage of disease development, radiation therapy (targeted exposure to high doses of radiation to destroy tumor cells). It is also used as preoperative preparation at later stages.
- At a more severe stage - removal of the cancerous tumor.
- In very advanced cases – amputation of a limb.
Anticancer drug therapy is also used to prevent metastases (the appearance of tumor cells outside the primary focus) in the lymph nodes.
Lump on the arm under the elbow, below the bend
A lump that appears on the arm under the elbow may be a consequence of vascular pathology or the appearance of hygroma. Often this localization is chosen by the so-called “fat” - lipomas. These two types of tumors are benign. They are elastic, move easily under the skin and are not fused to surrounding tissues. There are no unpleasant sensations during palpation.
Vascular pathology leads to the fact that a lump on the arm below the elbow occurs as a result of compression of the blood vessel that drains venous blood from the tissues of the hand and forearm. It often accompanies tunnel syndromes, in which the conductivity of blood and lymphatic vessels is disrupted due to deformation of the tissue and cartilage tissue. In this case, the vein expands at the site of local compression. It swells in the form of a soft and elastic lump, rising above the skin.
Another type of tumor is osteosarcoma. It is also often localized on the radius or ulna below the fold. A distinctive feature of the cone is its immobility. This indicates that the tumor is growing into the bone structure. The condition is accompanied by severe pain, loss of appetite and deterioration in general well-being. If such signs are present, you should immediately contact an oncologist.
Symptoms of occurrence
Swelling of the upper extremities indicates the progression of internal disease. Almost all of them cause severe health problems. Therefore, it is necessary to look closely at yourself in order to recognize the symptoms of hand swelling in time.
See a tumor ( a pathological process represented by newly formed tissue, in which changes in the genetic apparatus of cells lead to disruption of the regulation of their growth and differentiation
) on the hand is not difficult, because it clearly appears under the skin. If a limb is swollen after sleep, normally everything goes away a few hours after waking up. If the swelling does not go away by the evening, then this indicates the development of pathology. Patients notice that their hands are swollen and painful. Swelling can appear at any time of the day.
If the fingers are the first to swell, then the swelling evenly covers the entire upper limb. From time to time a person notices that his hands, which are swollen, also itch. When you press on the skin at the site of swelling of the hands, a depression remains on it, which does not go away for a long time. People ( a social being with reason and consciousness, as well as a subject of socio-historical activity and culture
) who wear rings on their fingers notice that they cannot take them off. The presence of such symptoms indicates a large overload on the body, as a result of which all internal organs suffer. Failure to heal the pathology can be a prerequisite for huge health problems.
Lump on the inside of the elbow
Any internal lump on the elbow requires a careful approach to differential diagnosis. This is usually how venous pathology manifests itself. In particular, a lump on the inside of the elbow may appear as a result of an unsuccessful intravenous injection. Thrombosis forms stagnation of blood and provokes dilation of a large vessel. In such situations, emergency assistance from a vascular surgeon or phlebologist is required.
But most often, a lump on the arm on the inside of the elbow is a symptom of epicondylitis. This disease mainly affects people engaged in manual labor. These are painters, builders, finishers, hairdressers, loaders, packers, etc. medial epicondylitis provokes numerous scar changes in the tissues of tendons and ligaments. In the absence of timely treatment, complete loss of professional ability to work is possible.
A painful lump on the inside of the elbow can accompany various types of tendonitis and tendovaginitis. These pathologies develop after traumatic exposure. Sharp swinging of the arms, lifting unusual weights and prolonged static load, all this can provoke the appearance of microscopic cracks in the tendon and ligament tissue. In these places, an inflammatory process forms, exudate accumulates and a small dense lump is formed. It resolves on its own after adequate treatment of the underlying disease begins.
Benign tumors of the upper extremities
- Cysts. This neoplasm affects the finger and is localized in the phalanx area. Causes pain, joint mobility is limited.
- Chondromas and endrochondromas. They are localized in the area of the phalanges, formed from cartilaginous cells, can be located inside or outside the bone, be single or multiple. If the tumors are multiple, there is a risk of malignant degeneration.
Benign tumors of soft tissues.
- Cysts. Epidermoid and implantation. They appear when the surface epithelium penetrates into the deepest layers of the skin. Prerequisites for occurrence: trauma, amputation.
- Xanthomas. They appear near the fingers on the side of the palm and cause pathological division of epithelial cells of tendon sheaths, sweat and sebaceous glands, blood vessels and lymphatic ducts.
- Fibromas are pronounced skin changes. Placed on the inside of the fingers and palms, they can cause acute pain when pressed.
- Pigmented. They rise above the skin and may have hair. There is a possibility of degeneration into melosarcoma.
- Tendon ganglia are one of the most common formations on the hand, appearing after an injury or with constant physical overload. They are localized above the projection of the tendons and have an elongated shape.
- Warts. Appear when the epithelium is infected with the papilloma virus. Can be solitary or growing. There is a risk of malignant degeneration.
- Lipomas are tumors of fatty tissue. They can grow through the bones and turn the hand into a kind of pad. Localized at the initial step on the palms.
- Hygromas are formed from the joint capsule. At the initial stage, when pressure is applied, the neoplasm goes into the articular cavity.
- Glomus tumor is a neoplasm of the circulatory system. Localized in the wrist and forearm, it is very painful. Nerve sectors and arterial anastomosis are involved in its formation. There is a risk of progression to cancer.
- Hemangiomas - vascular tumors - have a congenital nature. In 80% of the variants it is a doughy mixture, but from time to time it is also solid. More often they are localized at the base of the huge toe. There is severe pain when pressed.
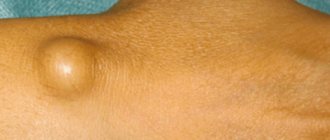
A lump has formed under the skin on the elbow - what is it?
Many patients are interested in information about why a lump appears on the elbow under the skin, what kind of pathology it is and how treatment can be carried out at home. We hasten to disappoint you - except for an experienced doctor who has an entire arsenal of modern diagnostic tools, no one can give you an accurate diagnosis. You should not look for fragmentary information and take it into account. Self-diagnosis always leads to very disastrous consequences. if you treat a completely different disease, you will not only not get improvement, but will also provoke an acceleration of the process of tissue destruction.
If a lump forms on your elbow, it could be:
- rheumatoid arthritis (only special tests can confirm it);
- deforming osteoarthritis (diagnosis requires an x-ray);
- gout, systemic lupus erythematosus and even psoriasis (only a doctor can recognize it using special blood tests);
- cicatricial deformities of soft tissues (diagnosis can be established using ultrasound and MRI);
- dilation of blood vessels in the form of an aneurysm (Doppler scanning is necessary for confirmation);
- bursitis, tendovaginitis, synovitis, epicondylitis, etc.
And this is only a small part of the probable pathologies in which a lump on the elbow can develop. Needless to say, you are unlikely to be able to diagnose it yourself. But you can get reliable information from an experienced doctor at any time convenient for you. To do this, you need to make an appointment for a free appointment with an orthopedist at our manual therapy clinic.
Diagnostics
To identify the cause, the doctor will interview and examine the patient.
The purpose of examination procedures depends on what disease is suspected:
- For possible rheumatoid arthritis: a complete blood count (one of the confirmations of the disease is an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate), a blood test for antibodies to cyclic citrulline-containing peptide (substances found in the blood of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis), for rheumatoid factor, as well as an x-ray for evaluation swollen joint condition.
- If gout is suspected: examination of the synovial fluid for the presence of uric acid crystals, sometimes an additional x-ray is prescribed to determine how much the joints are affected by gout.
- To confirm the diagnosis of bursitis, as well as determine its type, a puncture is taken from the synovial bursa and then the infiltrate (accumulation of cellular elements mixed with blood and lymph) is examined in the tissues. If the picture does not become clear, an MRI of the joint is prescribed.
- If a malignant neoplasm is suspected in the elbow joint, a biopsy (tissue sampling) of the tumor is performed.
1 – laboratory blood test; 2 – X-ray diagnostics; 3 – puncture of the elbow joint
A hard lump appeared on the bend of the elbow
Any bump on the bend of the elbow prevents movements in their full physiological range. Therefore, the longer a hard lump remains on the elbow, the higher the likelihood of contracture formation.
This is a condition in which deformation of tendon and muscle tissue occurs. The smaller the range of motion, the shorter the ligaments become. Therefore, after removal of the lump, the amplitude of mobility may remain limited. It is very important to start treatment in a timely manner.
If a hard lump appears on the elbow, then pathologies such as:
- deforming osteoarthritis of the elbow joint;
- chondromalacia and chondropathy;
- bursitis and tendonitis;
- scar changes in muscle and tendon tissue;
- lateral epicondylitis;
- bone cyst;
- development of osteosarcoma.
If the appearance of a hard lump was preceded by a fall on the arm, a sudden movement, dislocation or other types of traumatic effects, then consultation with a traumatologist is required. In this situation, the head of the bone, its tip or hematoma, formed as a result of internal bleeding, can be determined in the form of a hard lump.
Traditional methods
If, during a visit to a doctor, a benign neoplasm was diagnosed and appropriate therapy was prescribed, you can additionally engage in self-medication. In this case, proven folk methods will help:
- Propolis tincture: pour 20 g of the substance with alcohol (120 ml) and leave for 5 days in the dark. Apply lotions to the bump until it completely disappears.
- Cut the potatoes into thin slices and place on your elbow. Then wrap with film and warm cloth. Do the procedure at night and leave until the morning. When wrapping, you can also use raw beets and cabbage leaves.
- Take a pine bath: take 10 liters of water for 2 kg of pine needles, boil and leave for 12 hours. The procedures last 20 minutes.
- Infuse horse chestnut and aloe. For half a bottle of raw material, take 500 ml of alcohol. Leave for 2 weeks. Moisten a cotton napkin and apply it to the cone, additionally wrap it in a woolen cloth and hold for 3 hours.
You can also make infusions using pine cones, chamomile, St. John's wort, and plantain. These plants have anti-inflammatory and absorbent properties. You need to make a decoction of them and use them as lotions at night. To avoid pain in the joint, you can apply heated salt or sand to it. To improve immunity, it is useful to drink rosehip infusion instead of tea.
Before using traditional methods, you should consult your doctor. You should not completely trust self-medication methods. Sometimes this can negatively affect the body and lead to accelerated growth of the tumor.
Source