- Properties and characteristics of erythromycin
- Erythromycin - acne tablets
- Erythromycin - acne ointment
- Contraindications to taking erythromycin
- Homemade masks with erythromycin
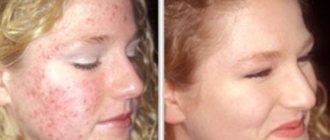
Chronic skin disease, expressed in the form of multiple acne, is not only a person’s physical illness, but also the cause of a lot of complexes and a feeling of constant dissatisfaction with oneself and one’s appearance. Antibiotics are used to solve most skin problems. Moreover, both for oral and external use. Erythromycin is a wonderful remedy that is available both in tablet form and as an ointment. The integrated use of these options will maximize the effect and speed up healing.
Erythromycin, acne tablets: application?
Erythromycin is a prescription drug that some doctors use to treat acne. It is known as a macrolide antibiotic, which means it falls under a different class of drugs than tetracycline antibiotics, which are also commonly used to treat acne.
Like other types of antibiotics, erythromycin is not specifically for acne. It is considered a narrow-spectrum antibiotic that is used to treat a variety of skin conditions, including acne.
Erythromycin is often combined with benzoyl peroxide in topical preparations (eg, benzamycin). Topical erythromycin is often combined with additional treatments (eg, oral antibiotics, retinoids, hormonal treatments, etc.) as part of a comprehensive acne treatment plan.
Erythromycin works similarly to penicillin, so doctors can prescribe it for almost any type of bacterial infection that needs treatment. As is often the case with antibiotics, erythromycin can be prescribed for both serious illnesses and less serious illnesses. One of the most common prescriptions is erythromycin for acne.
When the drug is not effective
The negative effect of Erythromycin can only be detected when taking tablets. Some body reactions to the drug are observed:
- the appearance of allergies;
- pain in the digestive system;
- symptoms of diarrhea, nausea;
- fungal infections of the mucous membranes;
- weakness, excess weight;
- decreased immunity;
- Due to the heavy load on the liver, the body begins to be poisoned with harmful substances.
When using the ointment, redness of the skin may occur, and in rare cases, peeling. If the drug causes headache, swelling of the respiratory organs, stomach upset, nausea and vomiting, then you should urgently consult a specialist.
Erythromycin ointment is allowed to be used in the treatment of children. It is prescribed to infants to treat skin rashes. It is also used in the treatment of infections that the baby contracted while passing through the birth canal.
Pregnant women very often experience rashes on their skin. This is due to an increase in androgen levels and increased secretion of the sebaceous glands. Such changes are observed throughout pregnancy and reach a peak in the third trimester.
Treating acne during this period is a difficult task, because many medications are contraindicated, but short-term use of Erythromycin is safe for both the woman and the fetus. It can be used for severe forms of acne.
Using Erythromycin Tablets for Acne
Poll: When did your acne appear? (Number of votes: 4295)
I've been suffering all my life
It's been a couple of years now
About a few months
Recently
To vote, click on the desired answer. results
Erythromycin kills and slows the growth of acne-causing bacteria Unlike many other antibiotics for acne, erythromycin can be provided in either oral (tablet) or topical (ointment or cream) form Both can be used in parallel or separately to reduce bacterial buildup for acne.
In 1987, researchers compared the difference between tetracycline (the most common type of antibiotic to treat acne) and erythromycin. They found that both people had similar effects on acne, with approximately 80 - 90% reporting a significant reduction in acne accumulation within the first 3 months of the study.
Most studies comparing these two treatment options reported that acne and erythromycin had about the same effect on tetracycline in almost every case. The differences were largely insignificant between the two drugs.
Similar benefits were found in the topical erythromycin group A study conducted on a group of 253 patients found that those using topical erythromycin found a significant reduction in the number of acne lesions compared to those using other acne clearing methods.
However, some researchers believe that the effect of topical erythromycin on acne is different from oral erythromycin. In one study, the researchers claim that this effect is more of an anti-inflammatory effect rather than leading to a reduction in bacteria. Essentially, erythromycin does not kill bacteria, but rather prevents the bacteria from creating skin lesions.
Despite this, research has been fairly consistent in showing that erythromycin is a good choice for clearing acne.
In what cases do antibiotics only worsen the condition of the skin and cause new acne to appear?
Description of the drug, its composition and release forms
Erythromycin is an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agent that is effective in destroying pathogens that cause infectious skin diseases.
On pharmacy shelves, Erythromycin for acne can be seen in such forms as:
- Ointment - available in aluminum tubes of 3, 7, 10 or 15 g. The consistency is dense and the color is white. Contains 10 thousand units of active substance per 1 g, in addition, it has auxiliary components in the form of petroleum jelly, lanolin and synthetic sodium derivatives;
- Round, biconvex tablets , enteric-coated - are available in the form of plates of 10 or 20 pieces, with a concentration of the active substance of 100, 200 or 500 mg per 1 tablet. White color. Auxiliary components include povidone and crospovidone, castor oil, titanium dioxide, calcium stearate, cellacephate, potato starch and talc;
- Powder for preparing a solution (lyophilisate) - presented in the form of a porous, hygroscopic, odorless white mass. Sold in bottles, V = 100 and 200 ml.
All forms of Erythromycin perfectly destroy:
- Propinobacteria that live in human skin. These microorganisms are the main culprits in the development of acne and the appearance of pimples, although in small quantities, on the contrary, they very actively fight various microbes;
- Gram-positive microorganisms - staphylococci and streptococci;
- Gram-negative pathogens - mycoplasmas, chlamydia, treponema.
They have pharmacokinetic properties such as:
- High level of absorption , independent of food consumption, therefore maximum accumulation in the blood is observed within 3 hours after consumption;
- To a greater extent (48%) Erythromycin is concentrated in organs such as the liver, spleen, kidneys , as well as in bile and urine. In addition, it can appear in the cerebrospinal fluid, placenta and fetal blood, and in inflammatory processes of the meninges - in brain tissue.
Erythromycin for acne should be taken strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
Resistant acne and erythromycin
One of the common problems encountered when using erythromycin for acne is bacterial resistance.
This problem is inherent in all types of antibiotics, and erythromycin is no exception. This is what causes concern when taking erythromycin for acne.
Bacteria Can Adapt When taking erythromycin, there is a high chance that drug-resistant bacteria will develop over time. Although this is not as dangerous, it does mean that at any point during your treatment, erythromycin may stop working and a new treatment will be required.
Additionally, in very rare cases, it can lead to more serious problems of drug-resistant bacteria for other conditions. Because of this, no antibiotic should be taken without a prescription, and it is best to make sure you have exhausted all non-drug options before trying any one. or an acne antibiotic, including erythromycin.
To reduce the likelihood of this resistance, it is extremely important to take the drug at the same time each day. Failure to take the drug as prescribed (for an extended period of time as required by the prescription) will increase the likelihood of developing resistance.
Additionally, there is some evidence that combining erythromycin with benzoyl peroxide will also reduce the risk of developing resistance. Research at the University of Leeds in the UK has shown that combining these two acne treatments may improve the ability to use erythromycin in the long term.
Antibiotic therapy
Anti-acne treatment, which includes external specialized drugs. All medications for external application that are prescribed to eliminate acne have an antimicrobial effect. They are designed to disinfect the surface of the skin; they contain salicylic acid.
Thanks to it, you can reduce the amount of rash, but you need to know that therapy takes a long time and is accompanied by side reactions depending on the individual characteristics of the patient. The situation is worsened by the fact that the composition of antiseptic preparations does not contain moisturizing substances.
On the topic: Hysterical personality type: causes, main features, behavioral characteristics
Side Effects of Erythromycin for Acne
Erythromycin, like most antibiotics, is subject to side effects. Compared to tetracycline antibiotics, these effects can be considered milder, but there are certainly risks associated with the use of an antibiotic, especially an oral one.
There are very few known side effects of topical erythromycin. Most side effects are superficial level on the skin where topical treatments were applied, including skin redness, burning, itching, and peeling. An allergic reaction is also possible, although these allergies usually tend to be less severe (a more severe allergic reaction possible, but less likely due to the absence of the drug in the skin).
The most common side effects of oral erythromycin were gastrointestinal disorders. These included side effects such as:
- Diarrhea;
- Abdominal pain;
- Nausea;
- Vomit.
Erythromycin affects a hormone known as motilin. This hormone is responsible for moving food through the intestines to make room for future meals. Erythromycin causes your body to produce more of this hormone, which in turn leads to faster bowel movements, which is normal (although and not always) is the reason that erythromycin causes the gastrointestinal disorders listed above.
An allergic reaction is a rare but possibly dangerous risk of erythromycin for acne, with reactions ranging from mild hives and rashes to seizures and jaundice. Erythromycin can also cause yeast infections, although this appears to be less common than with tetracycline antibiotics.
Severe adverse (non-allergic) reactions to this type of drug are extremely rare. While erythromycin has been associated with severe adverse drug reactions such as toxic epidermal necrolysis, the likelihood of contracting these diseases is extremely low. It has also been associated with psychological reactions (such as nightmares), but the mechanism that causes these reactions is less clear.
As with any prescription medication, tell your doctor if you are taking any other medications in addition to using erythromycin for acne. There are some medications that are not compatible with taking erythromycin.
Erythromycin may also interfere with the way some oral contraceptives work due to the way the drug affects the intestines. It can increase the rate at which oral contraceptives (as well as other medications) are metabolized, meaning these drugs may leave your body too early, resulting in a failure to prevent pregnancy.
Topical and oral forms of erythromycin have several side effects. Dermatologists report that side effects of the topical form of Erythromycin tablets include dryness, eye irritation, flaky skin, burning sensation, oiliness, and hives.
Side effects of erythromycin tablets include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, dizziness, stomach pain, fatigue, headache, skin rash, vaginal discharge and vaginal itching.
Reviews
Very often, erythromycin anti-acne tablets help in the fight against acne; reviews indicate their high effectiveness even with significant lesions.
Svetlana 22 years old:
To treat advanced purulent acne, I decided to try erythromycin. In my case, external treatment is not enough, so I purchased an oral product. At the pharmacy, the medicine was sold in tablets; instructions for acne were not included; I had to look it up on the Internet myself. I was accompanied by nausea throughout the entire course of therapy, but I did not interrupt the treatment. The skin really cleared up. Next time I want to choose an analogue so as not to suffer from side effects.
Irina 30 years old:
Despite the fact that the antibiotic erythromycin has a wide spectrum of action, the dermatologist prescribed it only after testing. Since this is a rather strong medicine, it has many contraindications and side effects. Therefore, you need to take it seriously, only with the permission of your doctor. To solve my problem, this drug turned out to be a godsend. It helps not only in the fight against acne, but also eliminates the manifestations of an allergic reaction.
Victoria 25 years old:
Erythromycin is the only antibiotic for me that does not disturb the intestinal microflora and does not cause problems with stool. Therefore, in the fight against ulcers, I only use it. What I like most is the quick effect; acne disappears in about five days. I have never encountered any unpleasant symptoms from such therapy.
Since erythromycin is considered a potent antibiotic, treatment with it requires special monitoring. During therapy, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the liver and kidneys, as well as focus on general well-being. If side effects occur, the course is interrupted, then it would be more rational to use analogue means.
Erythromycin dosage for acne
Like other antibiotics, erythromycin should be taken exactly as prescribed by your doctor to prevent bacterial resistance and increase effectiveness.
Always follow your doctor's instructions. He may recommend a dose that is different from what other people take when treated with erythromycin. The dosage of the drug is always based on your height, weight, age, previous diseases and medical history, type of acne, brand of drug, etc. .
Typically, erythromycin tablets are taken one hour before meals, although some doctors state that it is acceptable to take it with food. Dosage is usually 250 to 500 mg per day, given in 2 to 4 doses per day. Your doctor may also recommend a different type of topical treatment. to supplement oral erythromycin.
Topical erythromycin is usually used twice daily, although your doctor may prescribe something different.
Use only the dose of erythromycin that your doctor prescribes. The National Institutes of Health recommends taking this drug at least one hour before meals or two hours after.
Avoid taking erythromycin with carbonated drinks and fruit juices. If you miss your scheduled dose of an erythromycin tablet, take it as soon as you remember. Skip the missed dose if it is close to your scheduled next dose. Do not take two tablets at once to make up for the missed dose.
General Benefits of Erythromycin for Acne
Using erythromycin for acne may be extremely beneficial, at least compared to other antibiotics. While gastrointestinal side effects appear to be more common, the risk of a serious side effect is lower, and the drug appears to be well tolerated.
As usual, erythromycin may not clear up every type of acne or acne burst. It also does not clear up acne scars, so those with severe acne should expect some of their acne to remain. Plus, the risk of resistance is quite strong, so it's unlikely that you You will need to switch to a different type of antibiotic if the bacteria stop responding to erythromycin.
However, the use of erythromycin for acne has been a common practice for many years, and many doctors still recommend the antibiotic for those experiencing mild, moderate, or severe acne.
Acne occurs when dirt, oil, and bacteria clog pores in the skin. This causes whiteheads, pimples, or cysts to form. Some cases of acne require antibiotic treatment to kill bacteria and reduce the appearance of acne spots. Discuss the benefits and risks of taking erythromycin tablets with your doctor. determine whether it will improve your skin condition or whether its use on your face type and acne is not advisable.
Contraindications
In most cases, erythromycin acne tablets are well tolerated. Despite this, there are a number of restrictions on taking this medicine.
Instructions for use indicate the following contraindications:
- intolerance to the constituent components of the medication;
- progressive hearing problems;
- period of pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- disruptions in the functioning of the heart muscle;
- jaundice;
- age up to ten years;
- severe kidney and liver diseases.
Types of Erythromycin
Erythromycin has topical and oral forms to kill bacteria Applied directly to the skin, the topical version of the drug can be provided as a gel, solution, ointment, lotion, pads, and smears Oral erythromycin also comes in several forms, including tablets, long-acting tablets, capsules, capsules long-acting, liquid and chewable tablets.
Erythromycin ointment for acne, instructions and effect of use!
Your doctor will determine which combination will most effectively treat your acne. Some topical medications contain a combination of erythromycin and benzoyl peroxide, which prevents clogged pores by removing dead skin cells. Benzoyl peroxide also kills bacteria, preventing inflammation that leads to acne.
Possible analogues
Erythromycin has direct and indirect analogue drugs.
The first group includes drugs with erythromycin phosphate as an active component:
- Ilozon - country of origin - USA, cost from 100 rubles ;
- Altrocin is an Indian remedy that costs from 180 rubles .
Ilozon Altrocin
The second group includes drugs that exhibit similar effects to Erythromycin:
- Sumamed is the main component of azithromycin dihydrate, cost from 450 rubles ;
- Macropen - active substance midecamycin, cost from 200 rubles ;
- Clindovit is the main component of clindamycin phosphate, cost from 300 rubles .