Therapeutic sulfur ointment for acne is a complex preparation for topical use that has bactericidal, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties. Its course use helps not only to get rid of acne, but also to improve the overall condition of the skin, making it less susceptible to various diseases. This time-tested remedy differs from drugs with similar effects in its ease of use and low price.
Composition and release form
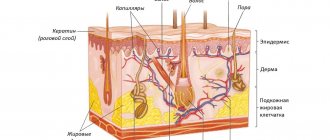
Cream with sulfur for the face is a thick mass of oily consistency, which has a rich yellow color and has a specific smell. The product is packaged in glass bottles and aluminum tubes. The active component is sulfur (ground, precipitated). Auxiliary components include:
- emulsifier;
- medical Vaseline;
- purified water.
The medicine may have a different composition. Instead of Vaseline, an ointment base made of paraffin and mineral oils is presented. Thanks to the emulsifier, sulfur penetrates better into inflamed tissues. Because of the Vaseline, the ointment has a greasy texture. The proportion of sulfur in the preparation is 10%, however, there is a release form containing 33% of this main component.
Disadvantages of ointment
The only noticeable drawback of the ointment is the pungent smell of alcohol that comes from it. This is due to the paraffin and emulsifier that are listed in the composition. It is for this reason that sulfur ointment is used after work, when there is no need to visit public places.
It should also be noted that the medicine cannot be used when there is at least some cosmetics on the face, since then the effect will be significantly reduced. Therefore, before applying the ointment, you must wash your face thoroughly.
There is a small part of the population that is against this ointment, which believes that it is useless and has no beneficial properties. There is a fair opinion that people who say this have either never used it or used it incorrectly.
Mechanism of action
Sulfur paste has pronounced antifungal, antiparasitic and keratolytic properties, which determine the medicinal qualities of the drug. Therefore, it is often used in cosmetology. When applied to the affected skin, the medication begins to interact with organic substances, forming sulfide compounds and pantothenic acid.
Thanks to the components of the product and accompanying derivatives, a targeted effect is exerted on the pathogenic microflora, preventing its vital activity. Sulfur quickly relieves inflammatory processes, prevents the development of acne, gets rid of blackheads and age spots, and helps with wrinkles. The ointment improves microcirculation and blood circulation.
The drug has an exfoliating effect, eliminating acne spots. It also eliminates swelling and removes pus from the pores. This product reduces the production of sebaceous secretions, which is the main cause of oily skin.
The ointment, which contains 33% sulfur, helps get rid of scars, scars, and subcutaneous acne. The components of the drug, together with sulfides, help activate the biochemical processes of restoration of the epidermis. The medication does not penetrate the systemic bloodstream, therefore it is considered a safe drug. However, it should only be used as prescribed by a doctor in recommended dosages.
This ointment has the following indications for use:
- acne;
- mycoses;
- seborrhea;
- psoriasis;
- demodicosis;
- lichen.
Indications for use
Sulfur ointment is a universal drug that is used to combat various skin lesions. Most often it is used in the treatment of such diseases and conditions:
- severe forms of acne, accompanied by enlarged pores, swelling, subcutaneous pimples, darkening and other complications;
- demodicosis, scabies and other skin diseases caused by parasites;
- psoriasis, accompanied by the appearance of papules and plaques on the skin, causing pain to the patient;
- dermatitis, except allergic;
- blackheads, pimples, blackheads and other rashes;
- lichens of bacterial and viral origin;
- dandruff;
- seborrheic skin lesions and other diseases arising from disturbances in the functioning of the sebaceous glands;
- mycoses - fungal diseases;
- post-acne, scars and scars left after acne removal;
- other skin diseases caused by pathogenic microorganisms.
Sulfur-based ointment is never used to treat irritations and rashes caused by allergic reactions. It is also ineffective in combating redness on the skin, the cause of which is damage to blood vessels or malfunctions of the circulatory system.
Contraindications
Contraindications include:
Before use, it is advisable to seek professional help from a dermatologist.
- pregnancy;
- lactation period;
- age up to 14 years;
- allergic reactions to the components of the product.
To find out if you are allergic to a medication, you need to test it. To do this, apply a small amount of the product to your wrist. If symptoms such as itching, burning, swelling, and redness do not occur within 24 hours, then the drug can be used for acne on the face.
Side effects
Sometimes the following side effects occur while taking ointment to treat acne:
- itching;
- swelling of the throat, tongue, face;
- redness of the skin.
In this case, you should stop using the ointment and choose another, more suitable remedy. If a woman has burned her face with sulfur paste, then it is necessary to remove the remnants of the drug with vegetable oil, wash with cool water and apply Dexpanthenol, Panthenol or Bepanten to the damaged areas of the skin.
The ointment is not recommended for use as compresses. It is forbidden to apply bandages to it, as this often leads to the development of an inflammatory process.
Methods of application
According to the instructions for use, the ointment should be used 2-3 times a day. The skin is pre-cleansed of cosmetics and various contaminants. It is advisable to treat it with antiseptic drugs - Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin. For this purpose, you can use alcohol-free tonics, infusions of calendula, string, and chamomile.
For effective treatment, the following recommendations must be followed:
- For small rashes the ointment should be applied in a thin layer, for large ones - in a thick layer;
- so that the product is well absorbed, it is left for 30 minutes;
- This drug is not recommended for use under airtight dressings.
The ointment is applied to the inflamed areas pointwise using cotton swabs. To wash off the residue, use vegetable or olive oil, soak a cotton swab with it and wipe the skin. If a woman smears this product on her face at night, and in the morning the skin becomes dry, then it is not suitable for long-term use.
The ointment is often used for subcutaneous acne, which causes severe discomfort. They mature over a long period of time and contain impurities of pus. If you press on such a pimple, severe pain occurs that does not go away for a long time. The presence of such acne on the face makes it lumpy.
After the sulfur ointment is applied, it is left for 1-2 hours. If the skin is oily or combination type, then the product is kept for 3-5 hours. Duration of treatment is 1–2 weeks. If it turns out to be ineffective, then therapy is extended for 5-7 days.
Sulfur ointment is used for acne spots. When the inflammatory process passes, the skin is enriched with useful substances. Metabolism and tissue regeneration are accelerated. After using the drug, the skin is completely restored: spots, scars, pits, and scars are eliminated. The medicine helps well against pigmentation. To do this, apply it to the stains, rub in with light movements and leave for 4–5 hours.
Sulfur ointment is used for scabies. The product is applied to the affected areas before bedtime, after taking a shower. It should remain on the skin for 24 hours, after which it is renewed. Wash off the drug on the fourth day. Use ointment to treat lichen. The skin is treated with an antiseptic and the mass is applied, gently rubbing it into the epithelial layer. The procedure is carried out 2 times a day. The duration of treatment is 10 days.
Remove the ointment from the surface of the skin using refined vegetable oil, which is pre-boiled in steam.
Long-term use of this remedy is contraindicated, since sulfur can accumulate in the blood and internal organs, leading to the development of various complications. During treatment, fried and spicy foods are excluded from the diet.
Theoretical and practical aspects of the use of sulfur preparations in dermatology
Basic sciences (pharmacology, biochemistry, physiology) include in their fundamentals the correction of vitamin and metal ligand homeostasis as a necessary background for conducting pharmacotherapy in a patient. Maintaining the balance of micro- and macroelements is, first of all, preserving the regenerative and reparative abilities of the body. Micro- and macroelements are contained in the human body in very small quantities, but the element can be part of an enzyme or coenzyme molecule, can simply activate a biological reaction, also form weak and super-weak biocoordination bonds or create an ionic environment. Of the 92 naturally occurring elements, 81 are found in the human body, among which sulfur is one of the important elements [1].
Research on sulfur content in the body and its metabolism continues, opening up new possibilities for its use in pharmacology. Currently, products containing sulfur have appeared on the Russian market, presented in the form of tablets for oral administration: dry purified yeast Evisent (dietary supplement) and specialized cosmetics for the care of problematic facial skin and scalp - Evisent based on brewer's yeast and sulfur. The Evisent drug complex is recommended for use in the treatment of onychodystrophies, trichodystrophies, acne, seborrheic dermatitis, rosacea and oral dermatitis. However, not only reliable information about drugs, but also its competent interpretation for subsequent justification of prescriptions is of particular importance. The success of therapy depends, among other things, on fundamental knowledge of the role of elements in the human body, which allows us to evaluate and rationally use drugs.
The macroelement sulfur is necessary for many vital functions in the human body and is an integral part of any living matter. The biological significance of sulfur is determined primarily by the fact that it is part of the amino acids methionine, glutathione and cysteine and, consequently, in the composition of proteins and peptides [1]. This macroelement plays its role through the formation of disulfide bonds and sulfhydryl groups.
Disulfide bonds or cysteine bridges (–S–S–) in polypeptide chains are involved in the formation of the spatial structure of proteins. Cysteine bridges link amino acids together to form a peptide, providing its unique structure, thus determining its basic physicochemical properties [2]. The cleavage of disulfide bonds leads to disruption of the native structure of proteins and their loss of biological activity [3]. It is thanks to disulfide compounds that the strength and elasticity of hair and tendons is maintained; without disulfide bridges, collagen formation is impossible.
Sulfhydryl groups or thiol compounds (–SH) play an important role in the active sites of enzymes. Possessing unique physicochemical properties and the highest reactivity, sulfhydryl groups easily enter into a reversible redox reaction under normal physiological conditions. Sulfur, as part of sulfhydryl groups, entering into alkylation, acylation, thiol-disulfide exchange reactions, forms mercaptides (when reacting with heavy metal ions), mercaptals, mercaptols (when reacting with aldehydes and ketones), thereby helping to neutralize toxic substances in the body. Sulfhydryl groups, being an integral part of coenzyme A and lipoic acid, are involved in enzymatic reactions of the formation and transfer of acyl residues associated with the metabolism of lipids and carbohydrates. It has been proven that blocking sulfhydryl groups using specific reagents causes partial or complete inhibition of the activity of many enzymes [3].
The scientific literature discusses the antioxidant properties of sulfur, which are manifested in the ability to attach an oxygen atom, thus, the oxidation of sulfur in the body reduces the free production of excess oxygen radicals. According to the authors, it is thanks to its antioxidant properties that sulfur slows down the aging process and increases life expectancy [4, 5]. Similarly, sulfur interacts with free radicals, neutralizing their damaging effects under conditions of oxidative stress [4–6].
According to the results of a scientific study conducted by V. A. Malozemova (2010), it was found that, with increasing age of the subjects, there is a tendency to increase the level of oxidized sulfur and to decrease the level of reduced sulfur, a decrease in its total amount and thiol-disulfide ratio with a significant change in indicators with every decade of life. This indicates the accumulation of oxidized products in the human body over the years of life and the intensification of free radical oxidation processes, which is confirmed by a significant decrease in the level of thiol-disulfide ratio and a decrease in SH groups with increasing age. In elderly patients, the greatest activity of sulfur oxidation and a decrease in its total amount were noted. These changes are associated with a decrease in the buffer capacity of the antioxidant system and can lead to pathological modification of the protein substrate, and also increase the risk of developing oxidative stress and associated morbidity [7].
Summarizing the above, we can say that sulfur ensures the stability of the structure of proteins, is part of the essential amino acids - methionine, cysteine, cystine and taurine, which are involved in the synthesis of proteins and enzymes, is an important catalyst for many biological processes and has antioxidant properties. It should be noted that the macroelement sulfur restores and maintains the elasticity and firmness of the skin, due to its participation in the synthesis of collagen, is part of the structure of hair and nails, normalizes the functioning of the sebaceous glands, and when applied topically has antiseptic, fungicidal and antiparasitic effects.
As is known, two groups of proteins are present in hair keratin: with a high sulfur content (16–24% cysteine) and ultra-high sulfur content (> 30% cysteine) [8]. According to numerous studies, trichodystrophy is based on defective synthesis of proteins with a high sulfur content. As a result, the macroelement is distributed unevenly along the entire length of the hair shaft, causing hair fragility [9–12]. When examined under a polarizing microscope, alternating dark and light zones are found in the hair [13], caused by defective synthesis of proteins with a high sulfur content.
However, according to observations conducted by British scientists, clinical signs of brittle hair in childhood are more common in sulfur deficiency conditions than in genetically determined trichodystrophies [14]. Taking all these observations into account, we can once again emphasize the important role of the macronutrient sulfur in the formation of a strong hair shaft structure.
Speaking about the therapeutic potential of sulfur preparations in the treatment of skin diseases, it is enough to recall the widespread use of precipitated sulfur (sulfur praecipitatum) in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis, eczema and allergic processes. However, when precipitated sulfur enters the body's intestines, sulfates are immediately formed. Sulfates are poorly absorbed from the intestines and are quickly excreted through the kidneys. It is well known that a dose of sulfates of 1.0–2.0, when taken orally, has a laxative effect on a person, leading to cleansing of the digestive canal. For example, magnesium sulfate, widely used in medicine, in concentrations above 100 mg/l acts on people as a laxative. Thus, the bioavailability of sulfur salts is very low. It follows from this that it is difficult to correct sulfur deficiency in a patient by consuming precipitated sulfur, since when it is taken orally, there is low absorption and assimilation, weak inclusion in metabolism and side effects, mainly from the gastrointestinal tract [15].
Currently, there is a modern solution to the problem using the second generation of organoelement preparations, in which macro- and microelements are contained in the form of organic salts or complexes with amino acids. Evisent dietary supplement - dry purified brewer's yeast contains a wide range of macro- and microelements: calcium, purified sulfur, vitamins (B1 (thiamine), B6 (pyridoxine), B2 (riboflavin) and other B vitamins). Brewer's yeast, which is part of the drug, contains vitamin PP (niacin), vitamin D (in the past, before obtaining a synthetic analogue, brewer's yeast was used as a raw material for the production of vitamin D); amino acids and orotic acid, which stimulates metabolic processes in the body.
However, the main advantage of Evisent is that vitamins and elements, including sulfur, are found in protein complexes, which determines the gradual nature of their entry into the human body and ensures easy digestibility of active substances. This property is achieved through a special technology for preparing the drug; incubation (growing) of yeast cultures occurs in special sulfur-enriched media. The technology ensures the absorption and preservation of micronutrients by the yeast cell. The unique low-temperature drying technology at the final stage of production guarantees an increased content of B vitamins in Evisent yeast.
It is important that in the production of the product an important point was taken into account - the synergism of vitamins, micro- and macroelements and amino acids. For example, vitamin B6, folic acid and magnesium, acting in synergy, suppress the active functioning of the sebaceous glands.
Brewer's yeast is also a source of other microelements - selenium and zinc. Selenium protects cells from ultraviolet damage, inhibits skin photoaging, and is also involved in the production of the sulfur-containing cellular antioxidant glutathione. Zinc has anti-inflammatory and sebum-regulating effects, is involved in the proliferation of skin cells, stabilizes cell membranes and regulates cellular immunity.
Don’t forget about the effectiveness of sulfur when applied topically to the skin. The keratolytic and antiseptic properties of sulfur are due to the reaction that occurs during direct interaction between sulfur and keratinocytes. Under the influence of sulfur, the cysteine present in the stratum corneum is converted into cystine, and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is released. As a result of this reaction, an antiseptic effect is achieved due to hydrogen sulfide and lysis of keratinocytes. In addition, the finer the sulfur when applied externally, the greater the degree of such interaction and, consequently, the therapeutic effect increases [16].
The effectiveness of external use of sulfur has been studied by many authors. A number of advantages in the use of sulfur preparations in anti-acne creams with simple manufacture, high stability and low cost have been demonstrated by JQ del Rosso (2009) and PY Chen et al. (2011). According to the authors, external therapy products containing 5% sulfur and widely used in the treatment of acne, rosacea, and seborrheic dermatitis from 1962 to the present are effective and non-addictive [17–20]. The continued relevance of using sulfur in external products is explained by its main advantage - the absence of the development of microflora resistance. Thus, the complex use of external cosmetics for problem skin “Evisent Yeast with Sulfur” (foam wash, lotion and spot cream) makes it possible to widely use the properties of sulfur in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis, oral dermatitis, rosacea, grade 1–2 acne and, as cosmetic care products for severe acne.
Evisent cleansing foam is created on the basis of a bioactive yeast complex, sulfur, which normalizes the drainage of sebum, zinc, which relieves inflammation and regulates the level of skin oiliness, and natural anti-inflammatory extracts - string and birch, allantoin with antioxidant and regenerating effects and inulin to increase local skin immunity. Thanks to its natural composition, Evisent cleansing foam thoroughly cleanses the skin, removes makeup residues, prevents the formation of comedones, narrows enlarged pores, regulates the functioning of the sebaceous glands, mattifies, eliminating oily skin, does not dry out, does not cause a feeling of tightness of the skin after use and is therefore ideal for deep cleansing of problem skin prone to acne.
Also an indispensable condition for proper daily care of problem skin is the use of a specialized lotion after washing Evisent. Evisent lotion, in addition to the bioactive yeast complex and sulfur, contains white willow bark extract, which is a natural source of salicylic acid with a pronounced antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect, and D-panthenol, which has a moisturizing and regenerating effect. Evisent lotion does not contain alcohol and has a neutral pH, so it is suitable for caring for any skin type.
Evisent spot-action cream based on yeast, sulfur and salicylic acid (source: white willow bark extract) is applied directly to the area of inflammation and the problem area, eliminates inflammation, has a keratolytic effect, and prevents the formation of “post-acne” type rashes. The patented component Sepitonic® M3 (zinc, copper, magnesium) normalizes the functioning of the sebaceous glands, stimulates cellular renewal, accelerates collagen production, stimulates skin regeneration and increases the energy potential of cells. Natural components - clover extract and rosewood oil - restore the skin, stimulate the synthesis of collagen and hyaluronic acid, have an antioxidant and soothing effect and eliminate swelling with a slight drainage effect.
The Evisent cosmetic line includes specialized cosmetics for problematic and thinning hair for basic care in the form of a soft shampoo without sulfates and Evisent balm based on a bioactive yeast complex, sulfur and garlic extract to improve microcirculation of the scalp and enhanced nutrition of the hair follicle. Evisent conditioner also contains dexpanthenol, which moisturizes and restores damaged hair structure.
Specialized cosmetics Evisent for problem skin and weakened, thinning hair and Evisent yeast, when used in combination, have a synergistic effect, potentiating each other’s action.
Thus, specialized cosmetics Evisent and Evisent yeast, containing the macroelement sulfur, vitamins, amino acids, can be considered as promising products in dermatology, the complex use of which can improve the treatment of acne, rosacea, seborrheic dermatitis, onychodystrophies, trichodystrophies, maintain the beauty and health of skin and hair and nails.
Literature
- Rebrov V. G., Gromova O. A. Vitamins, macro- and microelements. M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2008. 960 p.
- Byshevsky A. Sh., Odysseus A. T. Biochemistry for the doctor. Ekaterinburg, 1994. 384 p.
- Torchinsky Yu. M. Sulfhydryl and disulfide groups of proteins, M., 1971. 43 p.
- Nishida M., Kumagai Y., Ihara H., Fujii S., Motohashi H., Akaike T. Redox signaling is regulated by electrophiles and reactive sulfur species // J Clin Biochem Nutr. Mar 2020; 58 (2): 91–98.
- Spolitak T., Hollenberg PF, Ballou DP Oxidative hemoglobin reactions: Applications to drug metabolism // Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020 Jun 15; 600: 33–46.
- Wang MJ, Cai WJ, Zhu YC Hydrogen sulphide in the cardiovascular system: A cascade from interaction between sulfur atoms and signaling molecules // Life Sci. 2020, May 15; 153:188–197.
- Malozemova V. A. The role of sulfur in the pathogenesis of acute inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system and correction of its content in blood plasma. Author's abstract. diss. Ph.D. St. Petersburg, 2010. 30 p.
- Emonet N., Michaille JJ, Dhouailly D. Isolation and characterization of genomic clones of human sequences presumably coding for hair cysteine-rich proteins // J Dermatol Sci. Jan 1997; 14 (1): 1–11.
- Itin PH, Sarasin A., Pittelkow MR Trichothiodystrophy: update on the sulfur-deficient brittle hair syndromes // J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001 Jun; 44 (6): 891–920; quiz 921–924.
- Price VH, Odom RB, Ward WH, Jones FT Trichothiodystrophy: sulfur-deficient brittle hair as a marker for a neuroectodermal symptom complex // Arch Dermatol. 1980 Dec; 116(12):1375–1384.
- Khumalo NP, Dawber RP, Ferguson DJ Apparent fragility of African hair is unrelated to the cystine-rich protein distribution: a cytochemical electron microscopic study // Exp Dermatol. 2005 Apr; 14 (4): 311–314.
- Sass JO, Skladal D., Zelger B., Romani N., Utermann B. Trichothiodystrophy: quantification of cysteine in human hair and nails by application of sodium azide-dependent oxidation to cysteic acid // Arch Dermatol Res. 2004 Sep; 296(4):188–191.
- Elkin V.D., Mitryukovsky L.S. Selected dermatology. Rare dermatoses and dermatological syndromes. Handbook of diagnosis and treatment of dermatoses. Perm, 2000. 699 p.
- Cheng S., Stone J., de Berker D. Trichothiodystrophy and fragile hair: the distinction between diagnostic signs and diagnostic labels in childhood hair disease // Br J Dermatol. 2009 Dec; 161(6):1379–1383.
- Zupanets I. A., Naletov S. V., Viktorov A. P. Clinical pharmacology. In 2 volumes. Kharkov, 2005. 448 p.
- Fridman R. A. Cosmetics technology. 2nd ed., revised. and additional M.: Publishing house of food. prom-sti, 1984. 488 p.
- Del Rosso JQ The use of sodium sulfacetamide 10%-sulfur 5% emollient foam in the treatment of acne vulgaris // J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2009 Aug; 2 (8): 26–29.
- Draelos ZD The multifunctionality of 10% sodium sulfacetamide, 5% sulfur emollient foam in the treatment of inflammatory facial dermatoses // J Drugs Dermatol. Mar 2010; 9 (3): 234–236.
- Lin AN, Reimer RJ, Carter DM Sulfur revisited // J Am Acad Dermatol. Mar 1988; 18(3):553–558.
- Chen PY, Luo CH, Chen MC, Tsai FJ, Chang NF, Shih Y. Screen-printed carbon electrodes modified with cobalt phthalocyanine for selective sulfur detection in cosmetic products // Int J Mol Sci. 2011; 12(6):3810–3820.
Yu. A. Gallyamova, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor
FGOU DPO RMANPO Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Moscow
Contact Information
Reviews
Veronica, 33 years old, Moscow: “I have been suffering from acne on my face for a long time. To get rid of them, I tried many different drugs, many of which were expensive. But if they all helped, it was for a short period of time. A few months ago I met a friend at the pharmacy who recommended sulfur ointment. This product is inexpensive, so I decided to buy it. I treated my face with ointment once a day. This mass is too greasy, but the result pleased me: the acne has completely disappeared and has not appeared for six months.”
Margarita, 27 years old, Taganrog: “Recently large acne appeared on my chin, because of which I experienced psychological discomfort. To get rid of them, I tried several drugs, but they did not help. Mom recommended sulfur ointment. I applied it to my face as a mask, and after a while I felt it burning. This is how I developed an allergy to the drug. I quickly washed it off and won’t use it again.”
Olga, 20 years old, Samara: “I often use sulfur ointment for acne on my face, which has been bothering me since adolescence. I apply the product to the problem area, and after 5-7 days all acne disappears. This drug is affordable for everyone, so I recommend it.”
Cost in pharmacies
You can purchase this product at any pharmacy without a doctor's prescription. Sulfur ointment is an inexpensive and effective remedy for combating skin diseases.
| In Moscow and Moscow region | 35-50 rub. |
| In St. Petersburg | 22 -31 rub. |
| In Kazan | 28-38 rub. |
| In Novosibirsk | 25-28 rub. |
The price of sulfur ointment in all regions of Russia does not exceed 70 rubles. Despite the low price, the product is very effective and practically harmless.