In the intimate area, men may experience a variety of changes. These include various types of formations, both on the surface of the skin and in deeper structures. Sometimes the cause of concern is a small ball in the testicle. Sometimes fears turn out to be unfounded, but in other cases such compactions do not pose a serious danger, although they require measures to eliminate them.
Have you had a full medical examination in the last 5 years?
Not really
Possible reasons for the formation of such phenomena include:
- cyst;
- cancer;
- orchitis, epididymitis;
- lymphadenitis;
- a consequence of the hernia process;
- hematocele;
- varicocele;
- hydrocele.
Despite the fact that in the vast majority of cases, lumps in the testicular area are benign, it is necessary to take timely measures to eliminate them. Moreover, any forms of self-medication are completely excluded in this case.
Spermatocele: definition
A spermatocele (seminal cyst) is a cavity filled with a clear or yellowish fluid. Most often, this pathology is detected in boys during the period of growing up and puberty, as well as in men over 40. In both cases, this is due to age-related changes occurring in the body. A congenital cyst may form. This is a minor malformation that can result from pregnancy complications in the mother.
Treatment
Treatment methods depend on the type of disease. First of all, inflammation needs to be cured. For this purpose, antibacterial, antiviral, and immunostimulating drugs are prescribed.
Another popular method for removing scrotal lumps is surgical resection. Varicose nodes and benign neoplasms are surgically removed, hernial loops are reduced, and fluid is pumped out for hydroceles.
If oncology is detected, the entire affected area with adjacent lymph nodes must be removed, the result is secured by undergoing chemotherapy. The prognosis for recovery when the disease is detected in the initial stage is close to 100%. In this case, most often the man retains the ability to conceive a child.
Treatment is accompanied by supportive and restorative procedures, which include physical therapy and compliance with doctor’s recommendations.
Treatment methods
In the early stages, doctors use a wait-and-see approach. It is possible that the pathology will disappear over time. This is especially true for congenital seminal cysts. If the ball in the scrotum enlarges, swelling forms on the testicle, pain or severe discomfort appears, then urgent treatment is indicated. Drug therapy or surgical removal of the cyst is possible.
Conservative therapy includes painkillers, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs. Often, the doctor recommends surgical removal of the cyst - this is the most effective method of treatment. In some cases, a microsurgical method is used, that is, scraping tissue from the cyst.
Diagnosis of seals in the scrotum
In practice, there are a number of conditions that can manifest as a lump or mass in the scrotum. To distinguish them and make a differential diagnosis, an examination by a qualified specialist is required. Many of them require emergency surgical treatment or consultation with a specialist of another specialization.
Conditions occurring under the guise of compaction in the scrotum:
- indirect inguinal hernia – formed when intestinal loops enter the inguinal canal
- epidermoid cyst
- spermatocele - a formation containing seminal fluid
- inflammatory process of the reproductive system organs
- Testicular torsion is an acute surgical pathology!
- testicular injury with hemorrhage.
When a patient comes in, the doctor examines the genitals. The next stage is palpation (feeling) or the so-called testicular examination. It allows the urologist to directly assess the size of the compaction, its consistency and displacement relative to adjacent tissues.
For further diagnosis, an ultrasound examination of the scrotum is performed with visualization of the testicles and their appendages. Additionally, the following may be assigned:
- urine test for infections
- sperm examination
- examination of prostate secretions
If the malignancy of the lump is suspected, a targeted biopsy is prescribed. The resulting punctate is sent to the laboratory for histological examination.
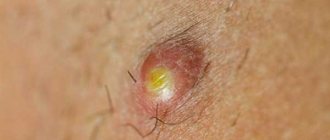
Wen: what is it?
A fatty tissue is a neoplasm that consists of adipose and connective tissue, can have different sizes and can be easily felt through the skin. A ball on the skin of the scrotum can be detected during the development of the inflammatory process. Then education becomes painful. When pressed, the fatty tissues roll freely under the skin. These are usually white balls that can reach a size of five to thirty millimeters. If there is no inflammation, then the biggest problem from wen is a cosmetic defect.
Why does a man feel itchy and dry?
The health of the male reproductive system depends on many factors, ranging from banal hygienic care to contact with all kinds of pathological microorganisms. The skin on the scrotum may become dry and itchy due to:
- Natural factors.
- A variety of diseases - parasitic, infectious, dermatological, etc.
It is quite difficult to independently determine which factor led to the occurrence of unpleasant symptoms in the scrotum area. An experienced urologist or dermatologist can handle this task.
Natural causes of itching in and under the testicles
As a rule, the occurrence of itching in the scrotum area is associated with completely natural factors that can be easily corrected at home. Such a disturbance in well-being can occur when:
- Not wearing the right size underwear or trousers.
- Using underwear made of synthetic fabric.
- Poor-quality underwear, for example, made of rough fabric or with protruding threads, etc.
- Prolonged friction, for example, during certain types of physical activity - running, cycling, etc. Severe abrasions can appear as a red rash and even blisters, involving the skin under and on the scrotum.
- Insufficient or irregular hygiene of the external genitalia. Men need to shower at least once a day, and even more often in hot weather.
- Hair growth after shaving or during adolescence.
- Inaccurate use of the razor, when the blades injure delicate skin.
Sometimes violations of the integrity of the epidermis on the scrotum, caused by natural factors, provoke the occurrence of serious diseases, for example, lead to the development of infection. Therefore, such causes of itching need to be promptly identified and eliminated.
What diseases do they cause?
Itching on or under the scrotum may occur due to:
- Development of various fungal diseases.
- The occurrence of allergic reactions.
- Development of a viral disease - human papillomavirus.
- Development of parasitic infections, in particular, pediculosis or scabies.
- The occurrence of chronic dermatological disease - psoriasis.
- Ingrown hairs.
- Development of cancer.
The list of factors that can provoke itchy skin on the scrotum is quite long. A doctor can make a correct diagnosis based on a number of studies.
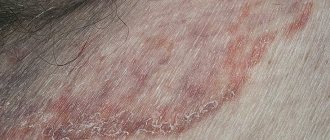
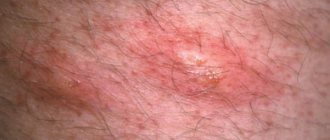
Redness and severe itching due to fungus
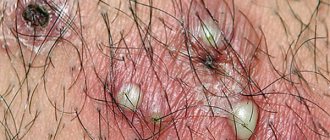
The delicate skin of the scrotum and groin often becomes a target for pathogenic fungi. Some of them are constantly present on the human body and begin to actively reproduce due to decreased immunity, insufficient hygiene, excessive sweating and other factors. It is quite possible to become infected with other fungi through contact with other unhealthy people or even animals. In this case, doctors can talk about the occurrence of lichen. Possible signs of fungal diseases include:
- The appearance in the fold under the scrotum of a small scaly red spot (one or several), no more than 0.5 mm in size. Over time, the spot increases in size and bubbles and crusts form on it. The skin swells and itches, and it seems as if the blood is not draining from it at all. A ridge is visible along the edges of the lesion. The spots may spread to the skin of the groin.
- The appearance of dry, scaly areas that are round in shape and itchy a lot.
- The appearance of red unformed spots with a white coating. This is how thrush can manifest itself - candidiasis. But with this disease, the lesion is first observed on the penis and only later, in the absence of adequate therapy, does it spread to the scrotum.
Unobtrusive itching in the scrotum area may be the first manifestation of a fungus. In the absence of timely diagnosis, the disease spreads and causes more obvious health problems.
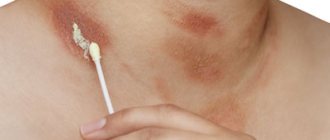
Allergic reactions in the intimate area
As a rule, allergies in the intimate area manifest themselves primarily on the glans penis, which is particularly sensitive to a variety of external influences. But sometimes the scrotum can also suffer from such a problem. Allergies can manifest themselves:
- The appearance of itchy red spots.
- Increased dryness and flaking of the skin. Sometimes the epidermis cracks and even peels off.
- The appearance of a small red rash that itches noticeably.
- Crusts and weeping in the folds under the scrotum.
Allergies in the scrotum area are most often of a contact nature and can occur due to the body’s sensitivity to detergents (soap, shower gel, washing powder, etc.) or locally used medications (in the presence of concomitant diseases). It is extremely rare that other types of allergies appear in the scrotum area - to food, systemic medications, etc. In such a situation, the patient is usually bothered by dermatitis in other parts of the body.
Distinguishing allergies from infections and other health problems is quite difficult. This may require skin scrapings, blood tests, and other tests.
Severe itching due to pediculosis
Even in the modern world, doctors quite often have to deal with phthiriasis - pubic lice or pubic lice. You can catch such parasites in a bathhouse or swimming pool, as well as during sexual intercourse, on the beach or on a train. You can suspect the presence of pubic lice by:
- Severe itching.
- The appearance of bluish or dark spots up to 1 cm in diameter on the affected skin, which quickly disappear. This is what hemorrhages or sites of injection of secretion from the salivary glands of parasites look like.
- Dark spots on underwear are waste products of parasites.
- Blisters - red bumps, blisters and eczema. Such skin manifestations occur on the skin due to constant scratching.
It is almost impossible to see pubic lice with the naked eye. But the doctor will cope with this task very simply.
Genital warts in humans
The appearance of genital warts on the body is associated with infection with the human papillomavirus. It can be picked up during sexual contact, including protected sex - by simply touching the infected skin of a partner. Sometimes such contacts do not lead to the appearance of growths on the intimate organs, but with a decrease in immunity, condylomas - flesh-colored or dark-colored growths - may appear on the skin of the groin and scrotum, as well as on the penis and near the anus. At the very beginning of their appearance, they may itch noticeably, but over time this discomfort disappears.
Growths on the body are dangerous in terms of cancer development and potential danger to other people - they are contagious. The only method of getting rid of them is removal using different methods.
Causes of progressive hardness and itching
The appearance of a dense nodule or subcutaneous formation on the scrotum, which itches noticeably, can be associated with both completely harmless conditions and life-threatening diseases. This symptom may be explained by:
- A banal ingrown hair. Sometimes the hairs cannot break through the skin and begin to grow under it, twisting into a spiral. This problem most often occurs when wearing tight underwear and tight, tight trousers. An ingrown hair does not always hurt, but it feels like a subcutaneous lump and itches. It can become inflamed, and in such a situation cause more obvious discomfort.
- Benign tumors. Often, such neoplasms do not itch and do not manifest themselves in any way, but itching can appear as a result of their constant compression or injury.
- Cancerous tumors. Unexplained lumps on the scrotum that cause discomfort may be a sign of cancer. Of course, this situation occurs very rarely, but it is better not to leave tumors without medical supervision.
You should not scratch the itchy areas on the scrotum, this can lead to the development of an inflammatory process. It is better to provide the problem area with maximum rest before visiting the doctor.
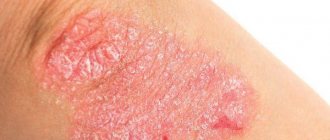
Peeling with genital psoriasis
Psoriasis is considered a chronic dermatological disease; it can be localized in different parts of the body, including the external genitalia. You can suspect the development of the disease by:
- The appearance of a small reddish-pink rash.
- Peeling, itching and a visible white or silvery coating.
- The formation of psoriatic plaques - spots protruding above the skin, covered with many white scales. Sometimes the rash remains demarcated and does not merge into spots. If you pick off the scales, you will see inflamed skin underneath, which cracks and bleeds.
Psoriasis can be accompanied by very severe itching, but many men mistake its primary symptoms for sexually transmitted diseases and self-medicate instead of consulting a doctor in a timely manner. In this case, the disease can develop into a widespread advanced form.
Red and itchy due to scabies
Scabies is a parasitic infection caused by the scabies mite. Most often, the first signs of the disease appear on the hands, and in men the parasite can easily get on the penis, as well as on the scrotum, which is accompanied by:
- Severe itching, which intensifies at night and disrupts night rest.
- The appearance of scabies on the skin, similar to lines up to 5 mm in length. Pinkish stripes - scratches - may also be detected.
- Pimples-nodules.
- Redness.
- Scratching, secondary pustular rashes, crusts.
Scabies is often complicated by a bacterial infection, which in turn can cause other serious complications. Fortunately, this disease can be successfully treated if you seek medical help in a timely manner.
Causes of pathology
A ball on the skin of the scrotum can form due to active secretion of the sebaceous glands and metabolic disorders. Sometimes such neoplasms develop as a result of slag deposits due to pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract or endocrine system. Equally important are various hormonal imbalances or excessive sweating. Fatty skin can occur after injury, mechanical damage to the skin, as a consequence of acne, with a sedentary lifestyle or poor diet.
External manifestation
It is not difficult to notice a wen on the scrotum. Such neoplasms are easily palpable and diagnosed during a standard examination. A characteristic sign of the accumulation of sebaceous gland secretions under the skin is the appearance of a wen, resembling a small pea that easily rolls under the skin. Wen are rarely painful, but if an inflammatory or purulent process occurs, they begin to cause discomfort. Sometimes discomfort can occur due to friction with clothing or as a result of injury.
If a ball is found in the scrotum, you should consult a specialist to determine that the neoplasm is truly a safe wen. Alarming symptoms are pain, rapid increase in the size of the formation, sudden disturbances in the genital area or difficulty urinating, discomfort when walking due to friction with clothing. Any of these signs should alert a man.
Varicose veins, dropsy and cyst
Very often, men confuse varicose veins of the spermatic cord with a hard seal.
In this case, a swelling appears in the upper left part of the testicle, which causes high pressure, which in turn provokes dilation of the vein. Usually this swelling decreases sharply or completely disappears when taking a horizontal position. Balls in the scrotum also appear due to the accumulation of fluid in it - these solid formations are considered harmless, but they must be shown to a doctor, since a tumor may be hidden under them. Diagnosis of testicular hydrocele occurs by pumping out fluid from the formed ball, which is sent for examination.
Also, ball-shaped formations in the scrotum can be caused by a cyst of the spermatic cord, which is smaller in size than dropsy (less than 11-12 mm in diameter) and easily displaces when pressed. Treatment of such a cyst is not mandatory, but if the patient wishes, the doctor can shrink the formation by aspirating the fluid that contains dead sperm.
Treatment of wen
You can get rid of the tumor surgically. Today, this is the most effective treatment method that helps quickly eliminate cosmetic defects. The doctor may suggest several methods of performing the operation: traditional excision or liposuction.
Liposuction involves preliminary suction of the contents of the wen with a special instrument. The use of this method does not guarantee that over time a new formation will not appear in the same place. During liposuction, only the fat filling is removed, while the capsule itself remains. Practice shows that after such a procedure the relapse rate is very high.
Traditional surgical removal of the wen involves removing both the contents and the capsule completely. The procedure is painful and is therefore performed under local anesthesia. Today, this is the most effective technique that helps get rid of wen without relapse. After the operation, the contents of the formation are necessarily sent for histology to exclude malignancy.
Treatment for itchy scrotum
If we talk about such a symptom as itching of the scrotum rationally, then it can be reduced or completely eliminated.
For example, to reduce itching, you can wash the scrotum yourself with antiseptic solutions.
Every home has them (hydrogen peroxide, furatsilin tablets or solution, miramistin, chlorhexidine).
After washing, you can use Sinaflan ointment.
It is best to rinse before going to bed.
If we talk about folk methods, then various baths made from infusions of chamomile, oregano, and sweet clover have worked well.
If you nevertheless visit a doctor, then know that he will definitely prescribe hydrocortisone ointment.
This is the most famous and proven remedy for the treatment of itching of the scrotum.
Sometimes the doctor may also prescribe antihistamines to reduce itching and pain in the testicles.
Such drugs as triderm, panthenol, nezulin, gistane very well reduce itching in the scrotum.
Such ointments and tablets made on the basis of menthol cannot be used when the patient has deeply scratched the skin and there are ulcers and bloody cobwebs.
But basically, treatment will be effective only if the diagnosis is correctly determined.
With timely administration of appropriate medications and in order to avoid various complications.
But remember, every drug has side effects.
Therefore, before taking any medications, it is necessary to consult a specialist (urologist, infectious disease specialist).
Traditional methods
In some cases, the formation of a wen is associated with the formation of atypical fat cells. In this case, treatment can be carried out using traditional methods, and surgical intervention is usually not required. Before starting treatment at home, consultation with a specialist is mandatory.
You can remove the wen using a fresh Kalanchoe leaf. You need to cut the plant and apply it to the damaged area, securing it with a bandage. The bandage needs to be changed approximately once a day. The course of treatment is usually not too long. It takes about one to two weeks for the fat to disappear on its own.
You can use coltsfoot dressings for ten days. The sheet should be applied to the sore spot and changed as needed. Lamb fat is quite effective. A tablespoon of the product is melted in a water bath and then cooled to room temperature. Then a small amount of fat is applied to the wen area and massaged a little. After just a couple of procedures, you can notice that the tumor becomes smaller.
Judging by the reviews, cosmetic red clay, which is mixed with sour milk and salt to enhance the effect, helps a lot. The mixture is applied to the wen, after which you need to protect the damaged area with a piece of polyethylene. The procedures must be repeated until the wen completely disappears.
You can take burdock root internally. First you need to pass the plant through a meat grinder (500 g is enough) to get a paste. Next, the slurry is poured with 700 ml of vodka, and then left to infuse for about a month. When the infusion is ready, you need to take one tablespoon twice a day.
Treatment of testicular lumps
Your treatment plan will vary depending on the cause of the lump in the testicles.
Varicocele
Pain from varicoceles usually goes away without treatment. However, your doctor may prescribe pain medication or recommend over-the-counter pain medications. In cases of recurring episodes of discomfort, you may need surgery to relieve congestion in your veins. Surgery may involve tying off the affected veins or diverting blood to those veins using other methods. This will force blood to bypass these veins, which will eliminate the swelling.
Hydrocele of the testicle
Treatment for coma hydrocele may also include surgery, but most often resolves on its own by age 2. The operation involves making a small incision in the scrotum to drain excess fluid.
Epididymal cyst
An epididymal cyst does not require treatment unless it causes pain or discomfort. You may need surgery. During this procedure, your surgeon will remove the cyst and seal your scrotum with stitches, which usually dissolve within 10 days.
Testicular torsion
Testicular torsion requires immediate surgery to untwist the testicle and restore blood flow. Your testicle may die if you don't get treatment for torsion within six hours, warns the American Cancer Society. If your testicle dies, your doctor will have to surgically remove it.
Epididymitis and orchitis
Your doctor can treat infections in your epididymis or testicles with antibiotics if bacteria are the cause. If you have an STD, your partner may also need treatment.
Hernia
A hernia is often treated with surgery. Your doctor may refer you to a hernia specialist for treatment.
Testicular cancer
Testicular cancer is treated with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation and other methods. Your specific course of treatment will depend on how early the cancer is found and other factors. Surgical removal of the testicle may help prevent the cancer from spreading to other parts of your body.